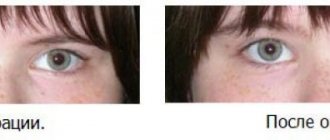
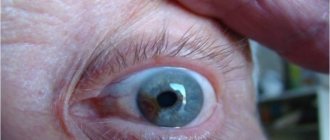
Prevention
To prevent the formation of various types of dermatitis on the eyelids, you need to follow the recommendations:
- you need to carefully choose personal hygiene products and decorative cosmetics; low-quality cosmetology products can cause allergic dermatitis;
- Observe strict hygiene rules daily using soap with an antibacterial effect;
- if you are prone to hay fever during the period of large-scale flowering of plants, you need to do wet cleaning of the premises daily;
- If you have poor vision, change contact lenses every day or wipe your optical glasses several times a day with special wipes. Even if the lens manufacturer claims that daily changing is not necessary;
- in case of secondary infection, it is worth treating the surface with an antibacterial agent;
- personal cosmetics - mascara, eye shadow and pencils should be for individual use.
Dermatitis around the eyes: division into types and symptoms
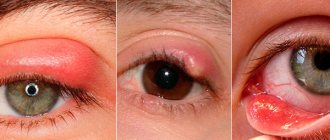
- Sharp form. It is distinguished by the speed of formation and intensity of symptoms. There is severe hyperemia of the skin on the eyelids and around the eyelids, a feeling of itching, and dryness of the skin. Coarsening of the skin is also noted. Areas of weeping are less likely to form. Swelling of the eyelids occurs, which in severe cases leads to complete closure of the eyelids. The skin may become covered with rashes or blisters. Pain and tearing are also noted. The disease can also affect general well-being: headaches, dizziness, chills and weakness are observed.
- Chronic form. It has a long course and affects two eyes at the same time. In the initial stages, there is pain in the eyes, itching and burning sensations. Next, thickening and roughening of the skin occurs, dryness and flaking are noted. Mild redness and slight swelling are also noted. This form of dermatitis is accompanied by small rashes or conjunctivitis.
- The atopic form of dermatitis is classified as a chronic recurrent pathology. External causes of its formation are allergic reactions (to food, medications, cosmetics, household chemicals, pollen) or infections against the background of a violation of the integrity of the epithelial layer. Atopic dermatitis also occurs against the background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, helminthic infestations and metabolic disorders. This type of dermatitis manifests itself as redness of the skin layer, constant debilitating itching and burning. Manifestations of dermatitis can affect both eyes, or one eye, or even one eyelid (upper or lower) or part of it. The epithelium is covered with small blisters filled with clear liquid. After the blisters rupture, areas of weeping and open wound surfaces appear. Over time, the wounds dry out, become crusty and crack. Open wounds increase the likelihood of secondary infection and the addition of suppuration.
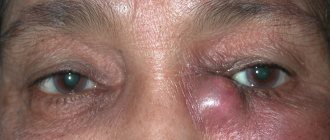
- Allergic dermatitis of the eyelids. The formation of contact or allergic dermatitis occurs after the interaction of thin and delicate tissues on the eyelid with an allergen. Allergens can include: decorative cosmetics (mascara, eye shadow, foundation), medications (ointments or potassium for the eyes), household chemicals (soap, laundry detergent, fabric softener, face wash), plant pollen , household dust, animal hair, insect bites. During allergic dermatitis of the eyelids, severe hyperemia and swelling of the tissues are observed, the intensification of which is caused by mechanical scratching. The pathology is accompanied by intense itching and burning, tearing, the formation of a rash and blisters filled with clear liquid. Often accompanied by other allergic symptoms, allergic rhinitis or allergic conjunctivitis.
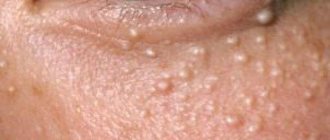
- The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are similar to those of blepharitis. The ciliary edge of the eyelids is covered with multiple yellow crusts and white scales. The skin becomes red and very itchy, covered with small rashes in the form of pimples. There is a feeling of dryness of the eyes and a feeling of “sand” in the eye, a feeling of stinging. Eyelashes fall out and grow incorrectly. In severe cases of seborrheic dermatitis of the eyelids, vision deterioration and an inflammatory process in the cornea of the eye occur.
- Drug-induced or drug-induced dermatitis on the eyelid is formed due to the use of eye medications in the form of drops or ointments, as well as after administration of the drug into the conjunctival sacs. The symptoms of the pathology are acute. The use of eye drops leads to intensification of inflammatory processes in the area of the inner corner of the eye. The use of ointment leads to inflammation of the conjunctiva, upper and lower eyelids.
- The eczematous type of eyelid dermatitis is a fairly rare pathology. Its appearance is facilitated by the use of eye ointments with an antibiotic or sulfanilamide, antiviral agents or electrophoresis over a long period of time. The causes of its occurrence can also be disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract and helminth infestations. Hyperemia and swelling occur on the skin, rashes and small blisters appear. The epithelium becomes painful, very itchy and itchy.
What forms are there?
It is customary to divide eyelid dermatitis into acute and chronic.
Acute form of pathology
Symptoms directly depend on the body's sensitivity to the allergen. If an allergy has already manifested itself to a substance, in the future the symptoms will be more obvious, and damage to the eyelids will occur faster. The pathology will affect not only the area in contact with the substance, but a much larger area.
The manifestation of acute dermatitis after contact is as follows:
- in redness of the skin, which intensifies;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- dry and rough skin of the eyelids;
- an increase in skin temperature due to inflammation.
In severe forms of the disease, the following are added to the main manifestations:
- complete closure of the palpebral fissure;
- wet areas;
- pain;
- severe tearing;
- the appearance of transparent bubbles.
The acute form of eyelid dermatitis is characterized by the rapid development of pathology and severe symptoms.
The patient may also complain of:
- chills;
- migraine;
- itching;
- weakness.
Chronic form of eyelid dermatitis
The clinical picture of the disease is sluggish and can drag on for several years with periodic relapses. Symptoms appear gradually and intensify over time.
Characteristic symptoms:
- puffiness/swelling of the eyelids;
- slight redness of the skin around the contact area;
- gradual thickening of the eyelids;
- gradual hardening of the eyelids;
- dry skin;
- peeling;
- the possibility of developing conjunctivitis.
In the chronic form of eyelid dermatitis, bilateral symmetrical damage to the eyes occurs.
Chronic dermatitis affects both eyes.
Treatment methods for eyelid dermatitis
In order for the treatment to have the maximum effect, refuse any skincare or decorative cosmetics, and exclude foods that can cause allergies from your daily diet. Dermatitis on the eyelids is treated with medications and folk remedies. Also used to improve the patient’s condition:
- Physiotherapy (massage, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, reflexology, phonophoresis, ultraviolet irradiation of the affected areas, applications with ozokerite).
- Homeopathic medicines (Aconitum, Arsenicum album, Acedum S).
Drug treatment
Drug therapy is prescribed after diagnosis and identification of the irritating factor. During treatment, you should not use cosmetic cleansers. Foci of inflammation can only be washed with running water. If the use of cosmetics after recovery causes allergic reactions, you need to switch to hypoallergenic cosmetics. Most often, doctors prescribe the following medications:
- zinc ointment (for treating affected areas);
- hormonal, anti-inflammatory eye drops;
- antihistamines;
- probiotics.
For the treatment of all types of dermatitis, local medications must be used. In most cases, creams and ointments are prescribed:
- Triderm. It is a universal medicine. It simultaneously contains hormones, an antibiotic, and an antimycotic agent.
- Pimafukort. Prescribed for seborrheic dermatitis. Consists of antibiotic, synthetic hormones.
- Clotrimazole. It is mainly used in the treatment of fungal diseases, but doctors also advise treating inflamed areas with seborrheic dermatitis.
- Skin cap. The cream has a wide spectrum of action. Its active ingredient is zinc, the distinctive property of which is to dry out weeping spots, pimples, and blisters.
In addition to treatment with these drugs, a specialist may prescribe additional drug treatment, taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body:
- With reduced T-cell immunity, immunomodulators (Tactivin, Levamisole) are prescribed.
- Various energy sorbents (Polysorb) are used to cleanse the body.
- To normalize the functioning of the autonomic and central nervous systems, the doctor prescribes sedatives based on motherwort and valerian. If the case is more severe, drugs such as Diazepam, Oxazepam are used.
- If dermatitis is accompanied by intestinal dysbiosis, the patient needs to take probiotics (Lactobacterin, Sporobacterin).
- If the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, the patient is prescribed Biofestal, Enzistal, Pepsidil or others.
- A hypoallergenic diet is required.
Traditional medicine recipes
Combinations of folk remedies and medications will help improve the general condition of the patient and significantly speed up recovery. Here are the most popular ones:
- Pumpkin juice lotions. Make juice from pumpkin pulp, soak a cotton pad in it, and apply to the area of inflammation. You can also apply pumpkin seeds and pieces of pulp to the wound for 5-10 minutes.
- Decoction of birch buds. Pour 4 tablespoons of birch buds into 1 liter of boiling water, leave to steep for 5-9 hours. Wipe the inflamed areas with the tincture or add the decoction to the bath before bathing.
- Aloe mask. Pour one tablespoon of eucalyptus oil and aloe juice into the bowl. Mix well. Apply the resulting mixture to the lower and upper eyelids. After 20 minutes, wipe the skin around your eyes with a cotton swab or paper towel.
- Chamomile decoction. Chamomile is famous as a healing plant and a natural antidepressant. It neutralizes signs of allergies, relieves itching and inflammation. Pour boiling water over the flowers and leave to steep for 10-12 hours. After this time, decant the broth. Add it to your bath and wash your wounds.
- Oatmeal baths. Boil the oats until they become a pulp; after cooking, squeeze out the mucus. Add the resulting mixture to the bath before bathing. This remedy reduces rashes, relieves itching and burning.
Traditional methods of treating dermatitis on the eyes
Traditional recipes have never been and will never be an independent method of treatment. They are effective only as an adjunct to drug therapy and other types of professional intervention and only with the permission of a doctor.
The most popular are various herbal decoctions and infusions that quickly and carefully relieve the symptoms of inflammation. Sequence, chamomile, calendula and hops are well suited for compresses.
Compresses from the string are excellent for treating eyelid dermatitis
A mask of aloe juice and eucalyptus oil heals wounds and soothes irritated skin in 20 minutes. You can also prepare a product based on aloe leaves. Its disadvantage is that it takes quite a long time to prepare (2 weeks).
The leaves are chopped into small pieces and placed in a cool, dark place. After 2 weeks, you can add castor oil and dry red wine to the aloe and use it as a lotion.
A decoction of parsley and cucumber helps get rid of irritation, itching and inflammation. A decoction is made from parsley, a cotton swab is dipped in it and applied to the eyes for a few minutes. After this, thin slices of cucumber are placed on the damaged areas.
How does herpes appear on the eyelids?
Regardless of the location, on the upper or lower eyelid, the first symptoms of herpes will be the same:
- swelling and inflammation of the skin and mucous membranes of the eye and eyelid;
- copious secretion of tear fluid;
- pain or burning sensation;
- discomfort in the eye.
The main symptom of herpes is blistering rashes that tend to merge. They are accompanied by itching and have transparent contents. The wounds do not heal for a long time after opening the vesicles .
If the herpes virus affects the retina of the eye, the following symptoms are observed:
- distortion of the visual image (cloudness, fog, bending of lines);
- flashes, sparks before the eyes;
- double vision;
- eyelid spasms.
Types and their symptoms
There are several types of ocular dermatitis.
Chronic
This species is characterized by a slow development of the inflammatory process. If, in the case of an acute lesion, only one eye is exposed to suffering, then here the location of the lesion falls on both visual organs.
There is redness of the eyelids, peeling of the skin and severe itching. This form is also accompanied by swelling and rashes.
Eczematous
It is extremely rare. It may occur due to the use of ointments containing sulfonamide components. It can also be caused by taking certain antibiotics. The main symptoms are itching, redness, and pain in the eyes.
Seborrheic
This type is characterized by signs such as redness of the skin, decreased vision, itching, a feeling of sand in the eyes, and loss of eyelashes. Only this type of disease is distinguished by the formation of a yellow crust on the eyes that has scales.
Spicy
Its difference lies in the abrupt onset of the course, which is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and rapid swelling of the eyelids. In some cases, dizziness and chills may occur.
Whatever the form of inflammation, you must immediately seek help from a specialist.
Atopy
This is a chronic disease, the predisposition to which is usually transmitted genetically. External factors or general diseases can provoke an exacerbation of atypical inflammation of the skin on the eyelids. External factors:
- mechanical injuries;
- allergies associated with the use of any foods or medications.
Internal factors causing atopic dermatitis on the eyelids are as follows:
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- liver disease, intestinal disease;
- worm infection.
Characteristic signs of atopic lesions of the eyelids:
- constant itching;
- redness;
- formation of vesicles and weeping surfaces;
- formation of crusts on the inflamed surface.
Allergy
The development of allergic inflammation is provoked by skin contact with an allergenic substance. It could be:
- decorative cosmetics (eye shadows, glue for artificial eyelashes);
- cosmetic eye creams;
- flower pollen;
- bites of blood-sucking insects.
The main symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- formation of erythema, swelling; in severe cases, the eyelids may swell so much that it is impossible to open the eye;
- lacrimation;
- Sometimes there is the formation of vesicles and weeping surfaces.
In addition, allergic inflammation of the skin of the eyelids can be triggered by infectious conjunctivitis.
Seborrhea
With this type of disease, the symptoms resemble those of blepharitis. Dermatitis around the eyes is manifested by the following symptoms:
- peeling is observed along the eyelash growth line;
- there is severe itching on the eyelid;
- the eyelids turn red and become covered with small blisters;
- there is a feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the eye;
- There is abnormal growth of eyelashes or their complete loss;
- inflammation can spread to the cornea, which can negatively affect vision.
Herpes
Many people believe that herpes is manifested by the formation of a rash on the lips. But in some cases, rashes may appear on the eyelids. Herpetic dermatitis of the eyelids manifests itself as follows:
- skin redness;
- the formation of small bubbles filled with transparent contents, which become cloudy over time;
- in place of the bubbles, open erosions form, which become covered with crusts;
- With herpetic infection, general symptoms are often observed - chills, fever, headaches.
Medication type
Drug-induced dermatitis under the eyes is caused by the use of eye drops or ointments. The dosage form manifests itself as acute ocular dermatitis, and:
- if the process is provoked by eye drops, then pronounced symptoms are noted on the skin closer to the bridge of the nose;
- if the development of the disease was a side effect of lubricating the skin with ointment, then an inflammatory reaction is observed over the lower and upper eyelids. In addition, inflammation can be visible in the eye itself, that is, on the conjunctiva.
It is one of the less common types and has other names - contact, periorbital. The cause of the disease is contact with inappropriate substances or other allergens, for example, pollen. Other causes may be mosquito bites or the development of conjunctivitis.
Allergic dermatitis of the eyelids is characterized by the following symptoms:
- redness of the eyelids and skin around the eyes;
- the reddened areas are very itchy;
- pimples with clear liquid may appear;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- Severe lacrimation may occur.
Despite the fact that dermatitis is an allergic reaction, the allergic type of pathology is not so common.
This pathology is chronic in nature with frequent exacerbations.
External causes:
- allergies to food, pollen, cosmetics, household products, medications or chemicals;
- violation of the integrity of the conjunctival sac;
- violation of the integrity of the skin of the eyelids.
Internal causes:
- helminthic infestations;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- metabolic disorder.
Atopic dermatitis of the eyelids can appear on the upper or lower eyelid, or on both eyelids of the same eye.
Symptoms:
- severe itching;
- formation of small bubbles;
- weeping areas that appear after the opening of small pimples;
- cracks and crusts after drying out wet areas;
- purulent inflammation caused by infection when scratching.
Atopic dermatitis usually affects 1 eye.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can be confused with seborrheic blepharitis because:
- epithelial scales appear on the edges of the eyelids in places where eyelashes grow;
- the affected areas are itchy;
- the affected areas turn red;
- small pimples appear on hyperemic areas;
- dry eyes are noted;
- there is a feeling of a foreign body in the eyes;
- complete or partial loss of eyelashes or their abnormal growth;
- in severe forms of the disease, vision deteriorates or the pathological process spreads to the cornea of the eye.
The symptoms are similar to those of acute dermatitis, but there are also features:
- if the allergen is eye drops, then the most intense damage to the eyelids is observed in the inner corners of the eyes;
- if the allergen is ointment, the pathological process spreads to the lower and upper eyelids and conjunctiva.
Drug-induced dermatitis of the eyelids can cause allergic conjunctivitis, which makes treatment of the disease more difficult.
Carefully! Drug dermatitis can cause allergic conjunctivitis. Rarely found
The reasons for the appearance may be long-term use:
Rarely found. The reasons for the appearance may be long-term use:
- ointments with antibiotic and sulfonamide components;
- antiviral drugs;
- electrophoresis sessions.
The nature of eyelid eczema can be exogenous or endogenous, but with the presence of an allergic component.
Symptoms:
- damage to the upper/lower eyelid, but sometimes both eyelids are affected;
- reddening of areas;
- swelling;
- rash;
- the appearance of bubbles;
- soreness;
- severe itching.
Eczematous dermatitis on the skin of the eyelids is rare due to excessive use of topical medications and electrophoresis.
Shapes:
- Herpes simplex is known to many by a rash on the lips called a “cold”. However, it also appears on the eyelids. Symptoms:
- redness of the affected areas;
- the appearance of watery small bubbles. As the pathology develops, their contents become cloudy. After which they dry out and crusts form. Within 1-2 weeks they go away on their own;
- possible increase in temperature;
- Chills and headache may occur.
- Shingles. With this disease, the trigeminal nerve (in Latin sounds like nervus trigeminus), the ciliary ganglion or gasserian ganglion is affected. There are three options for the development of pathology: 1 - damage to the 1st branch of the trigeminal nerve, when the upper eyelid is affected; 2 - lesion of the 2nd branch, affecting the lower eyelid; 3 – damage to both branches. The pathological process is always one-sided. Symptoms:
- formation of transparent blisters on the skin;
- drying of bubbles and formation of crusts;
- before the formation of bubbles, severe pain of a neuralgic nature may appear in the area of the trigeminal nerve;
- scarring of the skin after the ulcers have passed;
- If the nasociliary nerve is damaged, corneal pathology may develop.
The herpetic type of eyelid dermatitis has 2 forms.
There are different types of eyelid dermatitis, which may differ in their symptoms. They can be expressed to varying degrees.
Spicy
Symptoms of acute dermatitis depend on whether the patient has previously encountered the allergen. If there has already been contact, the reaction occurs faster and is more pronounced.
There are several types of eyelid dermatitis, each of which is characterized by different causes and symptoms:
- Contact (also called allergic) type. It occurs as a result of contact of the skin of the eyelids with an allergen (cosmetics, plant pollen, fur of cats, dogs, other animals) or as a result of an infectious disease. The same type of dermatitis also develops after insect bites. In addition to general symptoms, lacrimation and the appearance of bubbles with clear liquid are possible.
- Atopic. It occurs in a chronic form with frequent relapses of exacerbations. Affects one or both eyes. The causes are both external (injury to the skin or conjunctival sac, allergies) and internal (pathologies of the esophagus, metabolic disorders) factors. Small bubbles appear on the eyelids, which burst and form weeping areas, and then cracks and crusts. Wet areas are very dangerous because bacteria can enter through them, which causes suppuration.
- Medicinal (medicinal). Develops after local use of medications (ointments, drops), electrophoresis. It has an acute flow. After applying the drug, the skin temperature rises, the eyelids become inflamed, and rashes appear. If the cause of the allergy is drops, then the inner corners of the eyes are more affected.
- Eczematous. The rarest type of allergic dermatitis. Most often it develops in children due to the use of antibacterial ointments, antiviral drugs, electrophoresis, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, and helminths. Accompanied by redness, pain, itching, swelling, rash, weeping burst vesicles. Affects one or both eyelids.
- Herpetic. The causative agents of this type of dermatitis are herpes simplex and the Zoster virus (shingles). In the first case, the skin turns red, blisters appear on it, which dry out on their own over time and form crusts. With shingles, before the blisters appear, a person feels pain and itching, and after the crusts heal and disappear, scars remain in their place.
- Seborrheic. Occurs under the influence of a fungus due to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. Symptoms include peeling, redness of the eyelids, swelling, loss of eyelashes, a burning sensation in the eyes, and the appearance of a small rash. Due to increased dryness of the skin, the bubbles burst, and many scales form in their place.
Causes of the disease
Dermatological disease of the eyelids can be found in adults and children. Children suffer it in an acute form, adults - in a chronic form. Characterized by redness of the skin around the eyes, causing discomfort. Patients note the appearance of capsules with watery contents, which completely disappear after 10–14 days. There is pain, swelling, and wrinkles.
The main factors provoking the development of dermatitis on the eyelids:
- allergic reactions;
- viral infections;
- problems of the digestive system;
- disruption of the sebaceous glands;
- decreased immunity.
Treatment methods depend on the characteristics of the patient (age, weight), concomitant ailments (causes, area of damage, symptoms).
When dermatitis on the eyelids becomes chronic, complications are possible with a further impact on visual acuity.
The non-infectious species in the international classification of diseases has the ICD-10 code: H01.1.
During illness, external factors appear that affect a person’s attractiveness and cause discomfort. There are a number of reasons for the formation of pathology that can provoke the appearance of other reactions.
The skin may peel and lose turgor, which leads to the early appearance of wrinkles.
The use of cosmetics during treatment for dermatitis is strictly prohibited. May cause skin irritation.
Possible complications and consequences of untimely treatment will lead to the risk of:
- the formation of infectious foci on the eyelids - if hygiene is not observed and the area is frequently scratched, the likelihood of infection and subsequent scar formation increases;
- spread to the mucous membrane of the eye, cornea with further effects on vision. There is a danger of developing chronic diseases.
As an auxiliary treatment method for dermatitis, it is possible to use folk remedies in home therapy: treat the skin of the eyelids with tea tree oil, chamomile, string, celandine tincture.
External and internal factors lead to the formation of the disease. Therefore, doctors are not always able to detect the true cause of the disease. As a rule, in children the inflammatory process is provoked by atopic reactions. The disease can manifest itself as a result of herpetic infection, measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever.
Dermatitis of the eyelid can also develop as a response to antigens. An allergic reaction occurs to pharmaceuticals, certain foods, pollen, animal dander and other allergens. In addition, pathological effects of physical and chemical factors, as well as dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, lead to the disease.
General approaches to treatment were given above, but there are many specific ones. The medications prescribed by the doctor are aimed primarily at eliminating the root cause of the problem. For example, if an allergy is to blame, then you first need to get rid of it, and after that the dermatitis of the eyelids will gradually go away.
Here's how each specific type of eyelid dermatitis is treated:
- Enterosgel Allergic. A combination of antihistamines, such as Boromenthol ointment, hormonal medications to relieve itching, such as Prednisolone, and scratch treatments, such as Actovegin, are used.
- Atopic. An individual approach is required, but usually it all starts with antihistamines, like Suprastin or the more effective Cetirizine or Loratidine. Next, corticosteroids, for example, Hydrocortoisone, as well as non-hormonal immunomodulators, can be given.
- Herpetic. In this case, the most important thing is to fight the herpes virus. Antiviral medications such as Vectavir or Gerpevir help for this. To dry the affected areas, use a regular solution of brilliant green.
- Medication. The main thing to do in case of this type of pathology is to stop using medications and ointments that could provoke the problem. You also need to cancel physical procedures, such as electrophoresis.
- Eczematous. If the pathology is poorly developed, it may be sufficient to moisturize the skin with fat-based ointments. If the case is more severe, then external agents such as Dexamethasone or Prednisolone are used, and in especially severe cases, Dermovate or Galcinonide.
Prednisolone
Inflammation of the skin of the eyelids and periorbital area is a pathological reaction that occurs in response to the influence of many exogenous and endogenous factors. It is not always possible to establish the etiology. In childhood, the leading role is given to atopic reactions. The main reasons for the development of pathology:
- Infectious diseases. Most often, the appearance of symptoms of dermatitis is associated with infection with the herpes simplex or herpes zoster virus. Secondary inflammation of the skin is detected in patients with measles, chicken pox, and scarlet fever.
- Allergic reactions. Allergens include medications, food, pollen, animal hair, etc. Inflammatory manifestations are also found in other parts of the body. Local damage to the eyelids is typical for allergies to cosmetics.
- Impact of physical factors. The disease may be a consequence of excessive sun exposure or a reaction to cold. Cases of radiation injury caused by ionizing radiation have also been described.
- The influence of chemicals. Pathological changes develop when household chemicals accidentally come into contact with the skin or due to prolonged contact of the skin of the eyelids with chemicals in a production environment when safety precautions are not followed.
- Dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. Increased production of sebum by the sebaceous glands creates favorable conditions for the occurrence of seborrheic dermatitis.
The response of the immune system is triggered by substances that come from outside and are perceived by it as foreign. The body begins to actively defend itself, producing specific compounds - histamine and immunoglobulin E. The permeability of small vessels increases. As a result, you can observe typical manifestations of an allergic reaction - itching, hives, swelling, etc. Since the skin of the eyelids is thin, delicate, capillaries are located close to the surface, the negative symptoms are more acute.
Irritants can be:
- Decorative cosmetics (mascara, eye shadow, eyeliner), eye and face creams, lotions, masks, tonics, etc. Often such products contain fragrances, preservatives, formaldehydes and other harmful substances. Moreover, according to statistics, allergies are more often caused by products for the face, hair, and nails, and not by those produced specifically for the skin of the eyelids. High-quality cosmetics intended for eye care always undergo thorough ophthalmological control.
- Hair dyes (contain the strong allergen paraphenylenediamine).
- Shampoos (cocomidopropyl betaine).
- Nail coatings (formaldehyde).
- Applicators and accessories for eyelash care (they often contain rubber and nickel).
- Ophthalmic solutions (antibiotics, preservatives).
- Household chemicals.
- Dust.
- Plant pollen.
- Medicines (most often antibiotics).
- Some foods (nuts, fish, cow's milk, citrus fruits, chocolate, etc.).
- Insect poison.
- Saliva, fur, epidermis of domestic animals.
Additional factors that can provoke the development of dermatitis:
- impaired metabolism;
- pathologies of the digestive tract;
- reduced immunity due to chronic diseases;
- viral and fungal diseases;
- infection of the body by parasites.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Effective treatment of candidiasis in women with drugs, choosing the best
Kinds
Seborrheic dermatitis of the eyelids
It is characterized by unpleasant sensations in the eyes in the form of itching and burning, a decrease in the level of visual acuity, increased redness of the surface, and the formation of dry crusts on the eyelids of a yellowish color.
Atopic dermatitis
This type is manifested by peeling and thickening of the surface of the affected eyelid; in addition, if left untreated, the skin begins to crack, scales form between the eyelashes, which causes pain.
Allergic dermatitis
The allergic form makes itself felt within 30 minutes after contact with the allergen. Manifested by redness of the eyelid and itching. After eliminating contact with the allergen, the discomfort goes away within 2-3 hours. Does not require treatment as such.
Drug or drug-induced dermatitis
Develops due to long-term use of strong medications. The disease occurs after several courses of electrophoresis. Also, some medicinal ophthalmic drops can cause similar irritation in the eyes, but the damage is observed only on the inner corners of the eyes.
Eczematous dermatitis
This type of pathology is extremely rare. It manifests itself against the background of the use of local products, which are based on antibacterial components and sulfonamides. The disease is accompanied by severe pain in the eyes.
Herpetic dermatitis
Many people believe that the herpes virus forms only on the lips, but it also occurs on the mucous membranes and surface of the skin of the eyelids.
The disease is characterized by the development of small blisters on the eyelids with purulent or watery contents. With treatment, after 2 days the dropsy dries out, resulting in the formation of crusts that cannot be touched, they must fall off on their own, otherwise there is a risk of relapse within 5 days after the initial infection.
Causes of herpetic lesions of the eyelids
The body produces antibodies that protect against viruses and other foreign agents. A decrease in the production of immune bodies in the body can occur due to a number of reasons:
- weakened immunity due to stress, acute colds, vitamin deficiency;
- trauma to the eyelid and eye area;
- period of bearing a child;
- immunosuppression - treatment with drugs that suppress the immune system (cytostatics, glucocorticoids).
Routes of infection:
- close contact with an infected person;
- use of common household items.
Ways of spread of herpetic rashes:
- Endogenous - when it first enters the body, the virus enters the bloodstream, settles in the nerve ganglia, where it can remain for years, waiting for a breakdown in the immune system.
- The exogenous route is the spread of the virus with the contents of blisters on the skin. For example, children can scratch the rash, spreading the infection to other areas of the face, including the eyes .
Diagnosis and treatment of eyelid dermatitis
Zinc ointment is used in the treatment of eczematous dermatitis
For any inflammation of the skin of the eyelids, you should consult an ophthalmologist. After listening to the patient’s complaints and external examination, the attending physician will prescribe an examination. It consists of blood tests and an allergen test. Then treatment will be prescribed. In this case, you should refrain from using decorative cosmetics, at least for the duration of treatment.
The use of corticosteroid ointments is the most common prescribed treatment measure. You can also apply ointments that do not contain antibiotics. This is done twice a day for a week. Sometimes treatment lasts two weeks.
Sometimes drops are prescribed, such as a solution of prednisolone or adrenaline hydrochloride.
Along with local treatment, general restoratives are prescribed. For example, calcium chloride. It is administered intravenously.
Eczematous dermatitis must be treated with a special method. First, zinc ointment is used. Then, when the skin of the eyelids begins to dry out, it is necessary to lubricate the eyelids with hydrocortisone ointment. No bandages are used. Tea lotions for the eyes help a lot. It is good to simultaneously cleanse the intestines during treatment.
In general, any allergy occurs due to slagging in the body, self-poisoning with decay products. That is why you need to monitor your diet and natural functions.
What type of eyelid inflammation is determined by an eye specialist. He examines the patient and records the picture of symptoms. The ophthalmologist must know the suspected allergens that the patient comes into contact with. Its task is to exclude infectious eye diseases.
The first step in treating allergic dermatitis of the eyelids is to avoid those products that could potentially cause the disease.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=zMf4COzzR8s
These are cosmetics, various powders and cleaning gels. Dermatitis can occur from contact with pets. Therefore, for a while they need to be placed in good hands.
Then the ophthalmologist prescribes a course of basic treatment:
- Use of corticosteroid ointments. Antibiotics are excluded from their composition. If they do not help, then stronger means are used. But their use is justified if an emergency situation develops;
- The patient should begin taking desensitizing medications;
- You can use herbal compresses, provided that these types of plants do not cause allergies;
- Take allergy medications.
To get rid of inflammation of the eyelids, you need to follow these instructions:
- Treat reddened areas of skin with zinc ointment;
- If the bubbles have burst and formed weeping islands, then herbal lotions will help. You can use used tea bags;
- Hydrocortisone ointment can be applied to clean skin;
- Additionally, cleanse the body, remove toxins, and take anti-allergy medications.
If the patient has not encountered allergy tests before, the doctor, in addition to a detailed blood test, prescribes an allergen test.
Diagnosis of pathology is usually carried out in several stages:
- First, the specialist examines the problem area visually. Often this is enough to determine the type of pathology, to suggest which allergens were the root cause of the problem, this can even be determined from the patient’s photo. Taking an anamnesis allows you to find out whether the patient has a genetic predisposition to the disease, as well as draw conclusions about the frequency of relapses.
- Next, you may need to donate blood to conduct a general analysis and an analysis for eosinophils.
- After this, other dermatological and ophthalmological diseases are excluded. The set of analyzes will be individual in each case.
- Laboratory skin tests may be performed to determine which allergens are present in the body.
Provoking factors
Depending on the time of occurrence, herpes can be congenital or acquired. Herpes over the eye can be caused by the following pathogens:
- herpes simplex;
- chickenpox virus;
- genital herpes;
- cytomegalovirus.
In a healthy person with a strong immune system, the eyes are well protected from pathogenic microflora. Tears contain immunoglobulins, which prevent the spread of viral infection.
Herpes on the eye is a highly contagious disease, meaning it is very easy to become infected with herpes viruses. Let us highlight the main routes of transmission of infection:
- airborne;
- contact;
- sexual;
- domestic;
- transplacental;
- ascending.
Primary infection usually occurs through contact with an infected person or through the use of shared objects.
Let's consider the provoking factors leading to the appearance of herpes near the eye:
- stressful situations:
- hypothermia;
- weakened immune system;
- infectious diseases;
- eye injury;
- pregnancy;
- taking cytostatics or immunosuppressants;
- prolonged stay in conditions of abnormally low or, conversely, high temperatures;
- long-term antibacterial therapy;
- monotonous food.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Diagnosis of pathology is usually carried out in several stages:
- First, the specialist examines the problem area visually. Often this is enough to determine the type of pathology, to suggest which allergens were the root cause of the problem, this can even be determined from the patient’s photo. Taking an anamnesis allows you to find out whether the patient has a genetic predisposition to the disease, as well as draw conclusions about the frequency of relapses.
- Next, you may need to donate blood to conduct a general analysis and an analysis for eosinophils.
- After this, other dermatological and ophthalmological diseases are excluded. The set of analyzes will be individual in each case.
- Laboratory skin tests may be performed to determine which allergens are present in the body.