Deterioration of vision is a problem that many people face with age or after heavy strain on the eyes. This should serve as a serious signal to take care of your eye health. Because the sooner treatment is started, the higher the chance of a successful outcome. If left untreated, the problem can lead to surgery and even blindness.
However, in the vast majority of cases there is no need to be afraid, since this phenomenon can be corrected quite well. What to do when vision deteriorates? In this article we will provide answers to these questions. You will also learn the possible causes of vision impairment and what to do about it.
Decreased visual acuity
The norm of visual acuity in children after five years of age, in adults should be 1.0. This indicator indicates that the human eye clearly distinguishes objects.
Vision does not always drop sharply - just from year to year a person notices that he cannot distinguish the number of an approaching tram, and a year later he finds it difficult to get a thread into the eye of a needle, and later realizes that newspaper font is now inaccessible without a magnifying glass.
A person sees thanks to the inner shell of the eyeball - the retina, which receives and reproduces light. If the retina is destroyed, the person goes blind. For normal vision, the retina must collect all the rays of light, and for the picture to be clear, the lens provides precise focusing. It is in perfect condition.
If the eye muscles are tense, the lens becomes more convex when an object approaches. Trying to see something in the distance relaxes the muscles and straightens the lens. Optical axis impairment progresses over the years, making some people nearsighted and others farsighted, depending on the initial condition.
It is believed that young people have better vision than old people, however, in fact, many people already after 25 experience a decline in vision. And how many children are forced to wear glasses already from school. Let's figure out why vision declines. Having found out the reasons, we may be able to take measures to solve this problem.
Types of visual impairment
- Refractive error, i.e., deterioration in the ability of the eye to clearly distinguish objects located at a certain distance from the eye.
- Violation of accommodation - for example, presbyopia, deterioration in clarity when looking at objects at different distances.
- Impaired peripheral vision - deterioration in the ability to see objects located to the side of the eyes, objects in motion.
- Adaptation disorder - this visual impairment is characterized by a deterioration in the adaptation of the eye in conditions with rapidly changing lighting. For example, with this type of visual impairment, the eye takes a long time to adapt to darkness, or cannot adapt at all.
- Hemeralopia - impaired ability to navigate at dusk or in a dark room (nyctalopsia - night blindness).
All types of visual impairment can be divided into two groups - organic and functional types of visual impairment.
Organic types of visual impairment
Organic types of visual impairment include ophthalmological pathologies that develop accompanied by structural changes - these are atrophic lesions of the visual nerve, and, as well as some others. These visual impairments can affect the incorrect path of light rays in the organ of vision.
Functional types of visual impairment
Functional types of visual impairment can also develop accompanied by structural changes. But the deterioration of visual function in this case is due to a completely different reason - changes in the path of light rays, which, penetrating into the organ of vision, form an image of the object. These types of visual impairments are related to refractive pathologies.
Options for visual impairment
Double vision
This condition is called diplopia. With it, a visible object can double horizontally, vertically, diagonally, or two images are rotated relative to each other. The oculomotor muscles are to blame for everything, the work of which is not synchronized and which do not allow the eyes to concentrate on an object at the same time.
Often, damage to the muscles themselves or the nerves that supply them in systemic diseases begins with diplopia.
The classic cause of double vision is strabismus: convergent or divergent. At the same time, a person cannot manage to direct both central foveae of the retina strictly along the course.
The second typical picture is alcohol poisoning. Ethanol causes a disorder in the coordinated movements of the muscles of the visual organ.
Temporary double vision has been played out many times in movies and cartoons: when a hero is hit on the head, not only sparks often fly out of his eyes, but the picture in front of his eyes moves apart.
These are all examples of binocular diplopia.
Double vision in one eye can develop when the cornea is too convex, the lens is subluxated, when the calcarine groove of the occipital region of the cerebral cortex is affected.
Lack of binocular vision
The ability to see with two eyes allows a person to expand the field of vision, improve its clarity by 40%, see the volume of an object, estimate its approximate size and shape. This is stereoscopic vision. Another important purpose is distance estimation. If one eye does not see or the difference in the eyes leaves several diopters, the weaker one, which can cause diplopia, begins to be forcibly switched off by the cerebral cortex from the vision process.
First, binocular vision disappears, and then the weak eye may go completely blind. In addition to myopia and farsightedness with a large difference between the eyes, uncorrected astigmatism leads to a similar phenomenon. It is the inability to judge distance without glasses that forces many to use glasses or contact lenses while driving.
More often, binocular vision is absent with strabismus. To be honest, almost no one has an ideal balance between the position of the eyes, but since even with deviations in muscle tone, binocular vision is preserved, this does not require correction. If convergent, divergent or vertical strabismus deprives a person of vision with both eyes, it is necessary to perform surgical correction or use glasses.
Visual field pathologies
The part of the surrounding reality visible to the fixed eye is the field of vision. In spatial terms, this is not a field at all, but rather a 3D hill, on the top of which the visual acuity is the highest. Worsening towards the base, more along the slope near the nose and less along the temporal. The fields are limited by the anatomical protrusions of the facial skull, and at the optical level by the capabilities of the retina.
For white color, the normal field of vision is: to the inside - 55 degrees, to the top - 50, to the bottom - 65, to the outside - 90 degrees.
For one eye, the field is divided into two vertical and two horizontal halves.
The fields can change in the form of scotomas (dark spots), in the form of concentric or local narrowings (hemianopsia).
Color vision disorders
Color blindness is a congenital defect in distinguishing between red and green that is not recognized by the patient. More often detected in men.
Temporary shifts in the perception of white develop as a result of surgery to remove the lens affected by cataracts. Shifts towards blue, yellow, red colors may develop, that is, white will be bluish, yellowish, reddish.
After cataract removal, the brightness of colors may also change: blue becomes more saturated, and yellow and red fade and become pale.
A shift in perception towards long waves (yellowing, redness of objects) may indicate retinal or optic nerve dystrophy.
Objects become discolored due to old degeneration of the macular region, which is no longer progressing.
Most often, color disturbance occurs in the central part of the field (within 10 degrees).
Blindness
Amorosis is atrophy of the optic nerve, complete retinal detachment, acquired or congenital absence of the eyeball.
Amblyopia is the suppression of the previously seen eye by the cerebral cortex against the background of ophthalmoplegia, with severe drooping of the eyelid, Benche and Kaufman syndromes, opacities of the ocular media, the presence of a large difference in diopters, strabismus.
Definition of vision
Man is endowed by nature with five senses that allow him to perceive the world around him.
Vision is a person’s ability to perceive information by converting the energy of electromagnetic radiation in the light range.
In order for us to see, our visual apparatus does a very complex job. The eye picks up optical stimuli, processes them into nerve impulses that are transmitted to the cerebral cortex, to the area responsible for processing them and forming a certain image. This complex process involves the extraocular muscles, the optical system of the eye, the structure of which includes the cornea, lens, iris and vitreous body, optic nerve and visual centers of the brain. If a functional failure occurs in any of these elements, it causes vision impairment. Damage to different structures manifests itself in different disorders.
A person receives more than 80% of information through vision. Visual impairment partially or completely deprives him of this opportunity. Visually impaired people are not uncommon these days.
Why does vision weaken?
The eye is one of the main organs for perceiving the world around us. If vision falls or deteriorates, it prevents a person from enjoying life and brings discomfort to it. This may be due to various factors - overwork, decreased immunity, lifestyle, serious diseases of the eye or nervous system.
Let's find out the reasons for visual impairment. If the causes are known, then the treatment will be as effective as possible. Note. If you have a sharp deterioration in your vision, then only a doctor can tell you the reasons and what needs to be done. Be sure to consult a specialist.
Causes of visual impairment
There are many reasons why people experience certain vision problems, and each case is individual. The most significant among them are:
- genetic characteristics,
- increased load on the visual organs,
- gross violation of hygiene rules,
- past infectious diseases,
- endocrine diseases,
- circulatory disorders,
- pathologies of spinal development,
- eye injuries,
- chemical or radiation exposure,
- age-related diseases.
The causes of decreased vision are also:
- deviations in the cortical region;
- damage to the optic nerve;
- deviations in the retinal area;
- muscle pathologies;
- changes in the transparency of the lens, cornea, and vitreous body.
In a normal state, the transparent media of the eyeball are capable of refracting and transmitting light rays according to the principle of lenses. In the presence of pathological, dystrophic, autoimmune, infectious and inflammatory processes, the degree of transparency of the lenses is lost, and accordingly an obstacle appears in the path of light rays.
Also, in addition to the main reasons for the decline in vision, there are additional accompanying factors that stimulate this process. Among them, doctors name a decrease in human immunity, lack of vitamins in the body, lack of sleep, stress, fatigue, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
A wide range of factors influencing the acuity of vision suggests that, to one degree or another, every person is at risk of partial or complete loss of vision. In order to avoid such an outcome, it is very important to carry out comprehensive prevention of eye diseases.
According to the degree of violations
The degree of visual impairment is determined by the level of decrease in visual acuity - the ability of the eye to see 2 luminous points with a minimum distance between them. Normal visual acuity, equal to one - 1.0, is taken to be a person’s ability to distinguish letters or signs of the tenth line of a special table at a distance of 5 meters. The difference in the ability to distinguish characters between the next and the previous lines means a difference in visual acuity of 0.1.
There are several groups of people with visual impairments:
- Blind people are people with a complete absence of visual sensations or with residual vision, as well as retaining the ability to perceive light.
- Totally blind are persons with a complete absence of visual sensations.
- Partially blind people are people who have only light perception.
- Visually impaired - persons with visual acuity from 0.05 to 0.2. Their difference from the blind is that with a pronounced decrease in the acuity of perception, the visual analyzer remains the main source of perception of information about the surrounding world and can be used as a leader in the educational process, including reading and writing.
Depending on the time of appearance of the defect, there are 2 categories of blind people:
- Born blind are people with congenital total blindness or who became blind before the age of 3 years. They have no visual ideas, and the entire process of mental development is carried out in conditions of complete loss of the visual system.
- Blind people are people who lost their sight in preschool age and later.
Eye diseases leading to vision loss
Various ophthalmological diseases can cause vision impairment.
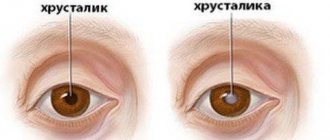
Cataract
One of the most dangerous diseases, which without adequate treatment leads to blindness. It is an irreversible clouding of the lens that often occurs in older people.
The danger of the disease is that early symptoms may not be noticeable, because the clouding begins from the peripheral areas of the lens and does not affect the optical zone for some time. However, the disease is constantly progressing, and without treatment, clairvoyance will inevitably deteriorate.
Retinal detachment
An equally serious disease that can lead to complete loss of visual function. If vision has deteriorated in only one eye, flashes or sparks flash in front of it, or a veil effect has appeared, these may be symptoms of retinal detachment.
Diabetic retinopathy
In diabetes mellitus, the functioning of the eye is disrupted and so-called diabetic retinopathy occurs - the capillaries of the retina are affected, and the eye tissues do not receive the necessary blood supply.
A sharp drop in acuity or complete loss of vision in one eye indicates irreversible changes in the functioning of the visual system.
Keratitis
Inflammatory disease of the cornea leads to clouding and can result in loss of the eye if not treated appropriately. With keratitis, vision deteriorates as a result of decreased transparency of the cornea. With early diagnosis, keratitis can be effectively treated, and visual function will be completely restored. If therapy is not started in a timely manner, a thorn may remain.
Glaucoma
A most dangerous disease that leads to destruction of the optic nerve, resulting in blindness. Significant symptoms of progressive glaucoma are decreased peripheral vision, gradual expansion of the affected area and limited visibility.
Glaucoma is the second most common cause of blindness in the world, so if you notice deterioration in peripheral clairvoyance or other symptoms, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
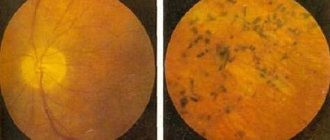
Macular degeneration
Age-related macular degeneration of the retina is a lesion of the macula - the central zone of the retina, which leads to gradual loss of vision. With this pathology, a person’s perception of the shape, size, and color of surrounding objects is impaired. Also, macular degeneration is characterized by the perception of objects in a reduced form; flashing dots or luminous lines may appear before the eyes.
This is not a complete list of dangerous eye diseases that affect the ability to see. However, diagnosing yourself without medical education is dangerous. Only an experienced ophthalmologist can accurately answer the question of why your vision has become worse.
One eye sees poorly
If vision in one eye has deteriorated sharply, the patient may have retinal detachment. This disease is also characterized by a feeling of a veil. Patients often confuse the onset of retinal detachment with an inflammatory process on the surface of the eyeball. To eliminate it, they prescribe washing themselves with water and tea, which, of course, does not bring the desired result. Diabetic retinopathy in the initial stages of development does not cause complications on the visual organs. Although the damage to small fiber vessels is already progressing. Then the patient may stop seeing in one eye, and after some time - in the second. Arterial capillaries are affected by atherosclerosis. Blood stagnates in the venous vessels and they expand significantly.
Cataract is a pathology that leads to partial and even complete blindness. The intensity and degree of vision impairment depend on the area in which the cataract is located. Localized in the center, it leads to a serious condition.
Diseases of the body are closely related to our eyes
A sharp deterioration in vision can be a consequence of not only eye diseases. Often its causes are various ailments of internal organs. Among them:
- Toxic neuropathy. In case of intoxication of the body with alcohol substitutes or products resulting from the breakdown of methyl alcohol, sometimes partial loss of vision occurs.
- Intervertebral hernias and osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. With the development of degenerative disorders in the area of the spinal canal, compression of the vessels occurs. This causes disruption of the blood supply to the eyeballs.
- Pituitary tumor. With neoplasms, the site of which is this endocrine gland, compression of the optic nerves occurs and the quality of visual perception decreases.
- Diabetes. With this endocrine disease, metabolic disorders occur and the preconditions for diabetic retinopathy arise with the formation of a large number of capillaries in the retina.
- Hypertension. This disease negatively affects the capillary network and disrupts the transport of oxygen to the retina.
- Traumatic brain injury. In cases where a fracture or injury occurred in an area located at the base of the skull, or in the visual center, the person’s visual ability will be immediately impaired.
- Retrobulbar neuritis. This disease accompanies an inflammatory process occurring in the nerve endings. Among the main symptoms of the disease are decreased visual perception, flashing “sparks” and “flies”, pain and burning. The disease affects either one eye or both at the same time.
The acuity of visual perception can be greatly influenced by a decrease in the overall level of immunity: due to prolonged stress or poor ecology, bad habits, lack of sleep, sludge in the body, poor nutrition, infectious diseases.
If the diseases listed above are diagnosed, the doctor will prescribe their treatment, which will eliminate the symptoms of the pathology, including decreased vision.
Children with visual impairments
The first years of a child’s life are a time of intensive vision development. It is during this period that vision is formed, which means that in the period from 3 to 7 years the best effect is achieved in the treatment of timely identified problems. Therefore, ophthalmologists say that the main thing that parents should know about their child’s vision is that all major vision problems in children appear before the age of 7. After 7 years, the child’s visual system begins to experience increased stress associated with school and “comes to light” everything that was not noticed earlier and that could have been prevented: myopia, astigmatism, amblyopia.
At the same time, it is already more difficult to fight the disease, since precious time is lost, and therefore much more effort will be expended to obtain a good result. Unfortunately, in kindergartens, vision examinations are carried out nominally, and it is very difficult to independently determine whether a child has problems. After all, if a child does not experience severe pain, he often simply does not understand that he sees poorly.
And after 12 years of age, problems with visual impairment in children, as a rule, cannot be treated, and all that remains is to wait until childhood is over to begin to deal with the problem as an adult, that is, to do laser vision correction and other surgeries that could have been avoided. It is clear that all this also leaves a certain imprint on the psychology of these people. In addition, such people are exposed to all sorts of dangers due to poor eyesight. These include falls, collisions on the streets, and traffic accidents.
Children with visual impairments: classification
The level of impairment is determined by the degree of decrease in visual acuity. It depends on whether the eye is able to see two bright points located at a minimum distance to it. In the case when children’s eyes are able to distinguish letters or signs located on the tenth line of the ophthalmological table (the distance from the child to the table is 5 meters), their vision is considered normal and corresponds to a value of 1.0. A deviation down or up from line 10 corresponds to a change in sharpness by a value of 0.1.
Classification of children with visual impairments involves division into several groups:
- Visually impaired children - impaired development of visual acuity corresponds to values of 0.05-0.2. But even with a significant deviation from the norm, children absorb information through visual images. When attending kindergarten and school, a child can fully comprehend educational material, including no restrictions on writing or reading.
- Blind children are diagnosed with a complete arrest of vision development, there is no figurative perception of information. Residual vision may be present, corresponding to a value of 0.04 in the best-seeing eye with the use of vision correction devices, sometimes the ability to distinguish light is preserved. As prescribed by a doctor, home schooling or kindergarten and compensatory school are recommended.
- Partially blind children - the ability to distinguish light and form images is retained, the degree of development of visual acuity corresponds to a value of 0.005-0.4 Completely blind children (total blindness) - there are no visual images. Children are not recommended to attend the kindergarten; individual training and education is required.
The classification also includes a temporary division of the manifestation of visual development disorders:
- Children blind from birth have total blindness, which was diagnosed immediately at birth or occurred during the first three years of life.
- Children who became blind gradually - from birth the development of vision function occurred, but at the age of 6 years and after - it stopped.
Types of visual impairment in children
Visual impairment in children is a problem that is present at birth or as a result of injury. Poor vision in children is a serious cause for concern for parents. The child has certain difficulties in studying the world around him; such children are significantly limited in social contacts, including when they enter kindergarten or school. The most common types of visual impairment in children:
- Myopia is a disease that can be either congenital or acquired. The mechanism of development of the disorder is the elongation of the eyeballs. If a myopic child goes to kindergarten, you need to check the conditions in which classes are held (the room should be well lit).
- False myopia - pathology is characterized by constant tension of the eye muscle, that is, its relaxation does not occur at those moments when the eyes are at rest. Children with this disorder have difficulty seeing objects located far from them. Associated symptoms are headaches in the frontal area, eye fatigue. A child suffering from false myopia should sit at the first desk. Special treatment is also necessary, otherwise the disease will develop into true myopia.
- Farsightedness is a pathology characterized by a violation of the anatomical structure of the eyes. A violation can be detected by the following signs: while reading, the child moves the book far away from him. In the process of visual stress, pain appears, the eyes turn red, and rapid fatigue develops.
- Strabismus - can be transmitted at the genetic level if someone in the family had similar problems, but most often it indicates the presence of other diseases. With strabismus, the eyeball deviates from the central axis to the left or right, less often in the vertical direction.
- Astigmatism is a congenital disease caused by the irregular shape (curvature) of the cornea of the eye. With this disorder, the child has difficulty distinguishing objects both close and far from him, there is rapid fatigue, and his eyes begin to hurt when reading or being at the computer. Children with such a disorder should attend a compensatory kindergarten.
- Amblyopia, or “lazy eye” - a feature of this disease is the difference in the images obtained from the right and left eyes, which does not allow connecting all the elements together. Gradually, the child begins to see with only one eye, and the second one stops performing its functions. Associated symptoms are: headaches, discomfort in the eyes, rapid fatigue. Correction of this pathology should begin at an early age.
Causes of visual impairment in a child
When parents wonder why a child’s vision is falling, it is necessary to look for the answer to the primary reasons. They can be congenital or acquired.
Congenital causes
- visual impairment as a result of the negative effects of bacterial and viral microorganisms, for example, previous influenza or the effect of parasites on the child’s nervous system;
- metabolic dysfunction during pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition;
- benign congenital brain tumors.
Acquired reasons
- trauma (head injury in early childhood or trauma received during childbirth);
- hemorrhage, both intraocular and intracranial;
- increased eye pressure;
- consequences of the disease;
- premature birth (so-called retinopathy of prematurity may develop).
Prevention and treatment of visual impairment in children
In order to avoid a decrease in visual acuity in a child, it is important to ensure that a sufficient amount of certain vitamins and biologically active substances enters his body. Specially developed for eye health, the food supplement “LUTEIN-COMPLEX® for Children” is a multicomponent product that contains substances necessary for the normal functioning of the visual organs of a schoolchild from 7 years of age:
- lutein;
- zeaxanthin;
- lycopene;
- blueberry extract;
- taurine;
- vitamins A, C, E and zinc.
A combination of biologically active components, carefully selected taking into account the needs of the visual organs, protects the child’s eyes, which is especially important to do starting from the age of 7, when the first serious visual stress begins in primary school, and reduces the risk of eye diseases.
Features of development of children with visual impairments
A person with disabilities experiences difficulties every day. This is the result not only of his limited capabilities, but also of the characteristics of his mental development. Children with visual impairments differ from their peers from childhood and require a special approach, both in communication and in learning. To do this, parents must understand the need and timeliness of treatment and education.
Mental development
From an early age, children with visual impairments face difficulties in doing basic things. Against this background, they experience a change in mental development. Thus, when communicating with peers who do not have vision problems, the child feels insecure, as he feels difficulties in play and communication. Such uncertainty can contribute to the fact that the child will sooner or later withdraw into himself. Growing up, the child will feel great uncertainty, which may be caused by poor coordination of movements and orientation in space. The child will begin to feel deprived, which will lead to an aggravation of his mental state.
A child who feels misunderstood by others withdraws into himself and does not want to let anyone into his world. Often, as a result of worsening mental development, a child may show aggression towards others. Aggression is a kind of defensive reaction. In addition, the peculiarities of the mental development of a child with visual impairment are his excessive emotionality, the child becomes nervous, irritable, and is stressed all the time. If you do not provide proper attention to such a child, then the peculiarities of mental development, in particular, being in constant tension, can negatively affect the cerebral cortex. In this case, disruptions in the balance of excitation and inhibition processes are possible.
Causes of decreased vision in a child
Parents often worry that their child’s ability to see has sharply decreased. Let's consider the reasons for this phenomenon. In childhood, a real scourge is a spasm of accommodation. This is the so-called false myopia, which is provoked by overwork of the muscle that serves as a regulator of the curvature of the lens.
At an early age, the development of congenital myopia, or true myopia, often occurs. This usually happens at school due to a sharp increase in visual load. However, it is always worth remembering that the human body is a rather complex, interconnected system.
That is why vision loss may not always be associated with the eyes. And if there was no load on the organ, it is worth going to a consultation with a doctor to check your general condition.
Vision problems in children
Good vision is an indispensable condition for the health and full development of a child. It is through vision that a child acquires basic communication skills, forms an idea of the world around him and his own vision. This is where the development of the child’s personality begins.
If a child's visual acuity is reduced, the baby's development can be significantly hampered, so questions about children's vision are extremely important. Vision problems in a child primarily affect parents, because they are responsible for the health of their child. Under no circumstances should these problems be allowed to arise.
Causes
It is impossible to treat visual impairment in children if you do not know their causes. So, the main factors of visual impairment in children are:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Stress;
- Reduced hemoglobin level;
- Poor visual hygiene (reading in low light conditions, reading or playing on a mobile phone while lying down, working on a computer, etc.);
- Failure to comply with visual safety rules: manipulation with sharp objects, addiction to looking at bright light without glasses.
The most common vision disorder in children is myopia. This is due to the fact that the age from 7 to 15 years is combined with increased visual stress (reading, writing, school lessons). Failure to follow the rules of watching TV and working with a computer, genetic predisposition, nutritional deficiencies and other negative factors can lead to the development of strabismus, myopia, amblyopia and other vision problems in children.
Any visual impairment or eye disease in a child requires immediate medical attention. Remember: the earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of a full recovery and no problems in the future, regardless of the cause of visual impairment in children. Preserving children's vision is an important responsibility of parents.
Features of psycho-emotional development
Deficiencies in visual perception lead to the formation of fuzzy, unclear images and ideas in the child, and negatively affect the development of mental operations (synthesis, analysis, comparison, generalization, etc.), which leads to difficulties when studying at school and mastering educational material. In addition, visual impairment significantly narrows the scope of sensory cognition, thereby affecting the general qualities of emotions and feelings, their significance for life, and therefore the formation of a person’s personal qualities. Children often feel doomed and useless, and this depressed state leads to slower intellectual growth.
Psychologists note that children with visual impairments have the following specific features:
- They have an increased personal level of anxiety;
- Children have a poorly developed emotional-volitional sphere;
- Poor correlation of emotion with facial expression;
- Insufficiently competent in expressing emotions;
- Poorly understand the facial expressions of other people's emotions.
Features of physical development
Visual impairment in children complicates spatial orientation, delays the formation of motor skills, and leads to a decrease in motor and cognitive activity. Some children experience a significant delay in physical development: the correct posture when walking, running, natural movements, and outdoor games is impaired, coordination and accuracy of movements are impaired.
Visual impairment leads to secondary deviations in the physical development of children. Many children with visual impairments have a low level of development of tactile sensitivity and motor skills of the hands and fingers.
Due to the absence or sharp decrease in vision, children cannot spontaneously, by imitation of others, master various objective and practical actions, as happens in children with normal vision. Because of this, the arm muscles become sluggish or, conversely, too tense. All this leads to a low level of development of tactile sensitivity and hand motor skills and negatively affects the formation of subject-related practical activity.
Visual impairment: symptoms
In most cases, vision does not disappear immediately, but deteriorates gradually. Therefore, it is important to notice the first signs of such deterioration in order to make a diagnosis in time and, if necessary, begin treatment.
There are many warning signs of decreased acuity that should prompt a person to visit an ophthalmologist:
- Deterioration of vision in one eye with its preservation in the second;
- Sensation of a veil before the eyes;
- Spots before the eyes that cover certain fields;
- Lack of peripheral vision;
- Unpleasant sensations when rotating the pupils;
- Pain in the eyes accompanied by headache;
- Blurred direct vision;
- Reducing the brightness and contrast of the image;
- Feeling of “sand in the eyes”;
- Double image;
- Floating spots, stripes.
In rare cases, vision declines rapidly. Usually this process is gradual, but most patients prefer not to think about this problem, to drive it away. You shouldn't make such a mistake. It is in your interests to contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible so that he can conduct the necessary examinations and prescribe treatment.
Symptom Definition
Currently, visual impairment can be understood as the following problems:
- Reduced severity;
- Impaired perception of colors and shades;
- Visual field disorders;
- Ghosting;
- Binocular vision problems;
- Blindness.
Moreover, these options for deterioration of the visual apparatus can be both temporary and permanent. Often, abnormalities can progress as the disease progresses and lead to complete loss of vision.
If vision has deteriorated, classical eye gymnastics will help reduce the risk of further development.
What to do if your vision decreases
The doctor chooses the treatment method based on the diagnosis, concomitant ailments, and the general condition of the patient. Therapy includes taking medications of various effects, using external agents in the form of drops, ointments, and physiotherapeutic treatment.
The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory compounds. For significant pain, short-term use of corticosteroids is recommended. Hormonal drugs give a quick effect, but are characterized by the presence of numerous side reactions, so they cannot be taken for a long time.
Long-term use of vitamin-mineral complexes designed specifically to improve the functioning of the visual organs gives good results. The restoration process is controlled by specialists. To improve visual ability, glasses and contact lenses are prescribed.
In some cases, only surgical intervention can solve the problem, completely or partially restore visibility. Laser correction technologies are widespread in ophthalmology today. They are minimally invasive, do not require serious preliminary preparation, and have no contraindications. Ophthalmological centers perform lens, retinal or corneal transplantation operations.
If you take timely measures, it is quite possible that you will be able to identify certain complex ailments in the early stages and cure them in time, thus avoiding the loss of clairvoyance.
What is the difference between myopia, farsightedness and old age vision?
Briefly, the difference between myopia and farsightedness can be explained as follows: with the first defect, a person sees poorly in the distance, and with the second, in front of him. That is, if you are diagnosed with myopia, the problem may arise while watching a movie in the cinema, and if you are farsighted, the problem may arise while reading a book.
How poorly or well a person diagnosed with one of these defects will see will depend on the extent of the defect. It is measured in a special unit called diopter.
With myopia we are talking about minus indicators (hence the colloquial expression “I have a minus”), and with farsightedness we are talking about positive indicators. There are three main stages of defect severity:
- weak: up to ±3 diopters;
- average: from ±3.25 to ±6 diopters;
- high: over ±6 diopters.
However, six diopters is far from the limit. In particularly serious cases, values can reach -30 diopters. How does a vision problem with myopia differ from farsightedness at different stages, if explained briefly?
At a weak stage, a person no longer sees as clearly as before, and may begin to wear glasses or contacts - constantly or put them on when necessary.
In the middle stage, a person may be unable to read text in front of him even if he squints (farsightedness) or has difficulty navigating the street without glasses or contacts (myopia).
At a high stage, wearing glasses or contacts becomes mandatory. A person diagnosed with farsightedness has poor vision not only near, but also in the distance.
As for presbyopia, it is an age-related type of farsightedness that begins to form after 35 years.
We think that now you will no longer be confused about definitions.
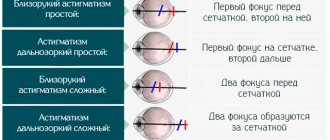
Difference in Image Formation
When a person suffers from myopia, the image of the object is formed in front of the retina, and in case of farsightedness - outside the retina.
Causes
Myopia occurs when the eyeball is very long (stretched out), causing the focal length of the eye's lens to decrease, so incoming light is diverted from focusing directly on the retina.
Farsightedness occurs when the eyeball is very short (flattened), causing the focal length of the eye's lens to increase, so incoming light is diverted from focusing directly on the retina.
Presbyopia occurs because the lens of the eye hardens, causing the eye to focus light behind rather than on the retina when looking at close objects.
Symptoms
Symptoms of myopia include:
- fatigue and eye strain;
- headache;
- blurred vision.
Symptoms of farsightedness include:
- the need to squint to see better;
- blurred vision;
- headache;
- “lazy” and tense eyes.
As you can see, the symptoms of both defects are very similar.
Risk factors
Risk factors for myopia are:
- genetics;
- environmental influences such as sunlight.
For farsightedness:
- short eyeball;
- high blood sugar;
- poor functioning of the ciliary muscles;
- problems with blood vessels in the retina.
For presbyopia:
- elderly age;
- eye injury;
- poor blood circulation in the eye;
- hypermetropia;
- diabetes;
- multiple sclerosis.
Diagnostics
Myopia is diagnosed by performing tests such as visual acuity, biometry, examination of the eyeballs, eyelids and cornea, extra eye muscle movement, slit lamp examination and fundoscopy.
The diagnosis of hypermetropia is almost the same as myopia as it is based on observed symptoms and clinical signs. Presbyopia is diagnosed during routine, comprehensive eye exams that test the ability to see both near and distant objects.
Treatment
Myopia can be corrected with glasses with concave lenses, and farsightedness with convex lenses. In addition, soft contact lenses can be used to correct vision.
Both defects can be eliminated with the help of refractive eye surgery, however, if the patient has indications for such an operation.
Complications
Myopia increases the risk of developing cataracts and glaucoma, gradual loss of vision and retinal detachment.
But farsightedness rarely has complications, but vision problems such as amblyopia and strabismus may occur. Strabismus is a condition that affects the coordination of the eyes and makes it difficult to focus on an object, while amblyopia is a childhood condition that affects vision in only one eye.
Presbyopia can have complications such as astigmatism, which is an imperfection in the curvature of the cornea that causes blurred vision. Other complications may include anisometropia and corneal ectasia.
- Author: Maria Minaeva
Vision is decreasing, what should I do? Is it necessary to wear glasses?
Ophthalmologists answer this question unequivocally in the affirmative in cases of myopia and farsightedness. Correction with glasses not only provides maximum comfort and the ability to clearly see the world around you. The main task is to prevent the progression of the disease. Indeed, increasing myopia is fraught with stretching of the membrane of the eye, rupture and detachment of the retina.
If a person is uncomfortable, he begins to strain his eyes, squint - an additional load arises, which leads to greater loss of vision. It is important to contact a good specialist and choose the right glasses. Wearing them will not interfere with the comprehensive treatment of the disease.
Diagnostic methods
In rare cases, only an initial examination is sufficient to determine the cause of loss of vision quality. Studying the patient's medical history, as well as the results of his survey, play an important role. But the most important thing here is the hardware examination, which includes:
In some cases, the ophthalmologist is forced to take a smear and samples of secreted fluid for analysis. With their help, the doctor determines the presence and type of bacteria, viruses and fungi, if any.
In order for the doctor to receive the most complete and clear picture of the disease, it is necessary to remember the approximate time of the onset of vision loss and all observations regarding the symptoms.
Vision is decreasing, what should I do? Gymnastics for the eyes
Various techniques necessarily include special exercises. Both opponents and supporters of correction with glasses recognize the effectiveness of training the eye muscles. It is advisable to repeat the set of exercises twice during the day, at the same time.
During gymnastics, the head should remain motionless and the facial muscles should be relaxed. The starting position is to look straight. Each exercise should be performed 8-10 times in each direction.
- Direct your gaze up, then down.
- Move your eyes as far as possible to the left, then to the right.
- Visualize a dial in your mind. Move your eyes in a circle, clockwise, without cutting corners. Repeat in the opposite direction.
- Raise your head, look upward. Repeat the movements of the previous exercise.
- Do exercises 1-4 with your eyes closed.
- Imagine a bow tie. Describe this outline with your eyes. Perform movements: diagonally from bottom to top, then down, again diagonally from bottom to top and down.
- Describe the figure eight with your eyes. After completing the complex, you need to relax your eyes, blink easily, without tension.
The exercises are aimed at solving various problems of the visual organ and allow you to: improve blood circulation; train accommodation; relax the eye muscles. Within a month, if you perform the exercises correctly, you can get the first result.
Prevention of visual impairment
Maintaining good vision, the prevention of diseases of which is sometimes given insufficient attention, is a rather difficult task. In addition to regularly visiting an ophthalmologist, the following methods are recommended.
Sport
Exercising will help strengthen vision and restore its sharpness in the initial stages of the disease. Ideally, you should give preference to this type of training where constant focusing of the eyes is necessary, for example, badminton, tennis, basketball, football.
Water treatments
Contrast water procedures help improve blood circulation in the retina. In the morning, rinse your eyes alternately with warm and cold clean water about 20 times. An alternative is hot and cold compresses, which must be applied alternately to the eyelids.
Read correctly
In a sitting position, holding the book at a sufficient distance. The child can use a special stand that provides optimal tilting of the book. Reading lying down is unacceptable - in this position of the body, the vessels of the neck, which supply blood to the brain, are compressed. And if you lie on your side, one edge of the book is closer than the other, and therefore the necessary alignment of the eyes on the line is constantly changing. Reading on public transport is also undesirable. Due to the chaotic movements of a car or bus, your eyes are forced to constantly re-focus on the letters, which increases the load on your visual organs.
Vitamin diet
To preserve vision, a diet rich in carotenoids and, in particular, lutein and zeaxanthin is recommended. These substances can accumulate in the retina of the eyes, increasing its protection from harmful external influences. In addition to carotenoids, antioxidants such as beta carotene, vitamin C, vitamin E, as well as zinc and omega-3 fatty acids have a positive effect on vision. These nutrients are rich in oranges, carrots, kiwi, green leafy vegetables (Brussels sprouts, spinach), bell peppers, as well as nuts, legumes, dairy products and eggs.
Exercises to prevent visual impairment
Special exercises for vision have a good effect on increasing blood supply to the eye tissues, increasing the tone, elasticity and strength of the eye muscles, strengthening the muscles of the eyelids, and relieving fatigue. There are a lot of techniques for doing eye exercises. We offer one of the simplest. It can be used by both children and adults during a break from work or study. Close your eyes and look first to the right, then to the left. Repeat 10 times. Without opening your eyes, make circular movements with your eyes clockwise and in the opposite direction (also 10 times). Open your eyes, bring your pupils to the bridge of your nose (10 times). Select near and distant objects in front of you. Move your gaze from one to another, focusing your vision on each. Finally, close your eyes again and begin to describe letters, numbers or shapes in the air with the tip of your nose.
Exercises for vision correction
To treat myopia, the American ophthalmologist W. Bates offers the following exercises, which he developed after familiarizing himself with the Indians’ methods of improving vigilance. He determined that the phenomenal vigilance of North American Indians is not a genetic trait, but is developed in early childhood through exercise. Here are some of them.
- The head is fixed so that only the eyes can move. In an outstretched hand is a pencil. Over a wide amplitude, it moves repeatedly to the right, left, and down. You have to keep your eyes on him.
- Stand against the wall of a large room and, without turning your head, quickly move your gaze from the upper right corner of the room to the lower left, from the upper left to the lower right. Repeat at least 50 times.
- Feet shoulder-width apart, hands on the belt. Sharp turns of the head to the right and left. The gaze is directed in the direction of movement. Perform 40 turns.
- Look at the bright light for 3 seconds, then close your eyes with your hand and give them rest. Repeat 15 times.
- Open your eyes wide, squint hard, close your eyes. Repeat 40 times.
- Look out the window at a very distant object and gaze at it for 10 seconds. Look at your wristwatch. Repeat 15 times.
It is recommended to perform these exercises 2 times a day. After a month, take a break for 2-3 weeks, and then start all over again. This mode of eye work strengthens the eye muscles, trains and massages the lenses, improves blood circulation and nutrition of the eyes.
Special exercises for the extraocular muscles
Exercises for the eyes (turns, circular movements, etc.) were part of ancient gymnastic systems. Undoubtedly, they are useful, as they train the muscles that control eye movements, activate blood circulation in this area, and relieve mental fatigue well. After them, people feel much more energetic. In addition, such exercises help get rid of the so-called bags in the area of the lower and upper eyelids (as a rule, this is a sign of aging skin and loss of elasticity). The positive effect is based on certain functional connections between the oculomotor nerve and the nerve cells of the brain vessels.
Here are a few exercises that will help strengthen the extraocular muscles, maintain the elasticity of the skin of the eyelids, and delay its aging (Fig. 2.3). They should be performed for approximately 10 minutes.
- Close your eyes tightly and open wide. Repeat the exercise 5-6 times with an interval of 30 seconds.
- Look up, down, right, left without turning your head.
- Rotate your eyes: down, right, up, left and in the opposite direction.
It is recommended to do the second and third exercises not only with open, but also with closed eyes. They must be performed while sitting, repeating each exercise 3-4 times with an interval of 1-2 minutes.
Exercises to relieve eye fatigue
- Performed while standing. Look straight ahead for 2-3 seconds. Then place your finger at a distance of 25-30 cm from your eyes, look at the tip of your finger and look at it for 3-5 seconds. Lower your hand. Repeat 10-12 times. The exercise relieves eye fatigue and facilitates visual work at close range. Those who use glasses must perform the exercises without taking them off.
- Performed while sitting. With three fingers of each hand, lightly press on the upper eyelid, and after 1-2 seconds, remove your fingers. Repeat 3-4 times. Exercise improves the circulation of intraocular fluids.
Vision is decreasing, what should I do? Folk remedies
Almost all folk methods of combating vision pathologies are aimed, first of all, at restoring natural metabolic processes by saturating the body with additional vitamins and minerals.
- At home, when vision decreases, take freshly squeezed juice from: carrots, chicory, parsley and celery. These components must be taken in equal quantities.
- A tincture of calendula and calamus has a beneficial effect. The grass is taken in equal proportions and poured with half a liter of vodka. Store in a dark place for at least 12 days. Take one teaspoon before meals.
- Young nettle is used in juices, decoctions, and salads.
- Blueberries are also good for the eyes in any form: dried, fresh, frozen.
- Sprouted wheat sprouts have a well-known positive effect.
- People over 40 years old should pay special attention to nutrition. For eye health, you need to eat more cholesterol-lowering foods.
- Carotenoids: lutein and zeaxanthin protect the retina from age-related degeneration. They are found in kiwi, sweet pepper, carrots, lettuce, spinach, and greens.
- Very useful for vision loss are: sweet potatoes, flaxseeds, sea fish, eggs, nuts.
- Massage relieves tension and fatigue. You can learn simple techniques on your own. The main thing is to avoid discomfort and pain. Using the middle and index fingers, you can easily massage: the point between the eyebrows, the line of the eyebrows, points under the eyes, on the temple and earlobes. These movements improve blood circulation.
Solving the problem must be approached comprehensively. A preliminary consultation with a doctor is required. Gymnastics, proper nutrition, adherence to a regimen, and gentle exercise will certainly have a beneficial effect on the body as a whole and on visual acuity.
Causes
Good vision depends not only on the eye, but also on its interaction with the brain. The causes of visual impairment are divided into 3 groups:
- Damage to parts of the eye or structural abnormalities.
- Refractive error occurs when the eye is unable to focus an image on the retina.
- Damage to the part of the brain that is responsible for interacting with the eye.
Factors that can cause visual impairment:
- Active mental activity leading to overstrain of the eye muscles and nerves. It is known that in the absence of the required amount of rest, all these systems begin to work worse and vision decreases.
- Long work at the computer. In this case, the person blinks less often, so the eyes do not receive the necessary moisture. It is also worth remembering about the blue light that comes from the monitor. A number of studies have confirmed that it can have a negative effect on the retina.
- Poor or very bright indoor lighting. Lack of light, as well as its excess, have a negative effect on vision.
- The bright sun can damage the retina, and the absence of light can cause great eye strain and provoke the development of myopia.
- Drinking alcohol and smoking. Toxins contained in alcoholic beverages and nicotine negatively affect the health of the entire body. In particular, they impede blood circulation in the vessels of the eye, which leads to insufficient oxygen supply to the tissues and impaired vision.
- Poor nutrition. A diet high in fat and fast carbohydrates, and almost devoid of the vitamins found in fresh fruits and vegetables, deprives our eyes of the nutrients necessary for normal vision.
Features of psycho-emotional development
The psyche of blind and visually impaired people does not differ significantly from the psyche of normally sighted people, but it has some peculiarities due to the enormous role that vision plays in the processes of reflection and control of activity.
Visual impairment and its extreme form - blindness - significantly narrows the scope of sensory cognition and can affect the degree of manifestation of certain emotions, their external expression and the level of development of certain types of feelings. Many researchers note that blindness entails changes in the nature of emotional states towards the predominance of asthenic moods of sadness, melancholy, or increased irritability and affectivity that suppress the individual’s activity. Such conclusions were made in the course of studies of late-blind people who are seriously experiencing the loss of vision, as well as people born blind and early blind.
Features of physical development
Loss or profound impairment of vision function primarily affects the fundamental property of human reflective activity - activity. Visual impairments especially significantly complicate orienting and search activities. This phenomenon is explained by the fact that the development of activity depends not only on the ability to satisfy the need to know everything around, but also on external influences that contribute to the emergence of a motive for orienting activity. The number of such impacts on visually impaired and especially blind people is sharply reduced due to impaired visual functions and the resulting limited ability to move in space.
Prevention
Both in medical and folk practice there are a lot of effective recipes that can save a person from vision problems. And, unfortunately, no one is safe from them. There are effective methods, although not preventing, but slowing down the process of vision deterioration. This includes eye exercises, vitamin eye drops, and traditional medicine.
All methods are quite effective in each specific case, therefore they should in no case be ignored or considered primitive, outdated. By using them regularly, you will be able to avoid serious illnesses and even improve your current level of acuity.
All that is needed to cure an illness is to pay attention to the problem in a timely manner and begin its effective treatment. In this case, you will definitely achieve positive results.