Development of myopia - causes
contact lenses, because if vision correction is insufficient, the eyes will be subjected to severe stress, which will lead to various complications.
But even if all doctors’ recommendations are followed, vision deterioration due to myopia is not uncommon. Unfortunately, with myopia, the shape of a person's eyes undergoes changes. What does this mean? The eyeball lengthens, the blood supply to the retina is disrupted and this can lead to dangerous hemorrhages. When the retina is stretched or thinned, there is always a risk of its rupture. What else can cause vision impairment in myopia? Visual acuity may decrease due to developing cataracts, which are more common in older people, although recently the number of cases of ophthalmologists registering this disease in young patients has increased. Cataracts are one of the main causes of complete loss of vision, so routine examinations of people at risk are mandatory. It must also be remembered that in case of cataracts, patients who have myopia do not undergo laser surgery to correct vision. In this case, you can get rid of myopia by replacing the lens with an intraocular lens with diopters.
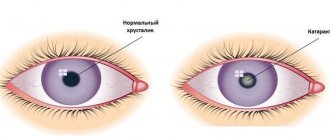
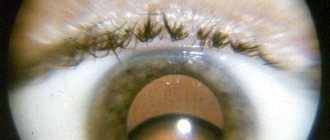
What is a cataract?
drops that slow down the development of the disease.
The processes that occur with cataracts are associated with the natural aging of the human body. What causes this pathology in infants and young people? Newborns born with a vision pathology such as cataracts are diagnosed with “congenital cataracts.” The development of the disease in this case is associated with the impact of various infections on the child’s mother’s body: measles, chickenpox, rubella, influenza, as well as parasitic diseases such as toxoplasmosis. The appearance of pathology can also be affected by the incompatibility of the Rh factor of the mother and child.
Causes of cataract development
Modern science knows that clouding of the lens can be caused not only by aging, but also by injuries, as well as the negative influence of toxic compounds accumulated by the body. Such toxins are formed as a result of complex biochemical reactions that occur under the influence of sunlight. With a decrease in the body's protective functions, weakened immunity, against the background of ongoing infections, diabetes, vitamin deficiency, nutrition and blood supply to the visual organs are disrupted, creating the prerequisites for the development of myopia and the appearance of cataracts.
Risk factors for developing cataracts in myopia:
- being in areas with increased radiation, places with unacceptable doses of radiation and ultraviolet exposure;
- work in highly toxic industries (interaction with mercury components, paraffin, etc.), thermal effects on the eyes in thermal shops;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, anemia, metabolic disorders in the body;
- high degree of myopia, retinal dystrophy, glaucoma, chorioretinitis.
Myopic people are at risk, since with severe myopia the possibility of developing various complications increases several times. Therefore, at the first signs of deterioration in visual acuity due to myopia, they need to urgently contact specialists to look for the causes of possible complications.
Lens replacement for high myopia
The key reason why it is necessary to replace the lens (the biconvex natural lens in the visual system) is a high degree of myopia with an indicator of 20 diopters. But ophthalmologists warn that this is one of the extreme measures; the need for such surgical intervention occurs if there is:
- congenital eye diseases;
- contraindications for laser vision correction;
- curvature or clouding of the transparent body.
Not all people with a large degree of deviation are indicated for implantation of an artificial lens, or, as experts say, an intraocular lens. Thus, the operation cannot be performed on patients who have not reached the age of 18, since their visual system is still at the stage of formation, so myopia indicators can change both for the better (even without the help of a doctor) and for the worse.
In addition, removal of the natural lens is contraindicated for people with a progressive anomaly. This is due to the presence of a huge number of factors that can influence significant vision deterioration. Therefore, professionals are obliged to find out the exact cause of the development of myopia and eliminate it, only after which they can proceed with the operation.
The optimal age, according to ophthalmologists, for lens replacement for high myopia is 40 years and above. It is during this period that a person loses his accommodative ability, the natural biconvex lens loses its elasticity, and the first symptoms of cataracts may appear.
Symptoms of cataracts
An early sign of myopia with developing cataracts is optical distortion in the form of double vision. When one eye is closed, this double vision disappears. This important symptom should not be ignored, because at the initial stage of the disease, special drops are quite effective in preventing the rapid progression of the disease. By using such drugs, you can somewhat slow down the development of cataracts.
Important symptoms during the development of cataracts:
- familiar images seem fuzzy and blurry - existing distortions cannot be corrected by glasses or contact lenses;
- the appearance of flashes and glare in the daytime and evening, which cause severe discomfort;
- increased light sensitivity, the appearance of halos around light sources;
- deterioration of twilight and night vision;
- violation of color perception.
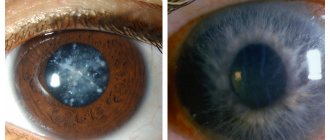
With complete or partial clouding of the lens, a person experiences a significant deterioration in visual acuity, which is accompanied by the presence of optical distortions: flashes, lightning, stripes, balls and floaters before the eyes. Developing cataracts reduce the quality of life, since vision is affected not only by myopia, but also by the symptoms of the new disease. Human activity becomes less productive: reading, writing, working with small details are very difficult.
Clinical picture
The person loses the ability to see clearly. He complains of a yellowish tint to some objects, diplopia, poor night vision, decreased clarity and color vision, and the appearance of a “luminous halo.”
There is periodic dizziness, photophobia, difficulty reading and working with small parts. He does not recognize his relatives and acquaintances on the street, and professional and social disadaptation occurs.
The patient's vision becomes blurred, as if he is looking at the world around him through a white veil or curtain. Some people first try to overcome the difficulties they have encountered on their own and use glasses. The ophthalmologist is able to detect the problem with slit lamp biomicroscopy after dilation of the pupil. In this way, the location and degree of opacity and its relationship to the optical axis can be accurately determined.
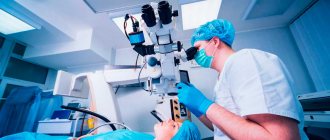
Surgical treatment
Drug therapy is prescribed only in the early stages; its purpose is to prevent the progression of the pathology. However, there are no medications yet that can restore translucency.
If the disease becomes visually significant, surgery will be the only effective treatment. The definition of “visually significant” has evolved, its current value being visual acuity of 20/40 or worse.
When cataract surgery was in its infancy, the term was used to describe the already mature stage. Thanks to advances in ophthalmic surgery and innovative technologies, the lens of the eye can be removed even if small whitish inclusions appear.
The main signal for intervention will be a significant increase in visual dysfunction, which greatly limits work activity and causes discomfort in everyday life. Before the manipulation, the specialist must select an intraocular lens in advance.
| The technique itself is painless and is performed on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. To do this, special drops are instilled within 1-2 hours. The lens is removed in 20-30 minutes. In the evening, the operated patient goes home. A follow-up examination is scheduled for the next day. |
Indications:
- Overripe form;
- Swelling form;
- Dislocation and subluxation;
- Abnormal types of opacity;
- Secondary glaucoma.
It is not uncommon for people whose professional activities involve high demands on eye health (for example, drivers, pilots, operators) to turn to doctors.
Contraindications:
- Infectious diseases;
- Exacerbation of a chronic illness;
- Uveitis;
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- History of recent heart attack or stroke;
- Oncology;
- Mental disorders.
Age under 18 years is considered a relative contraindication to manipulation. The doctor must make an individual decision for each patient.
It is very dangerous to remove the lens for cataracts in a decompensated form of glaucoma, since hemorrhage can be provoked, which will lead to complete blindness. Therefore, the best option would be a preoperative decrease in intraocular pressure.
If during the examination of the patient it was revealed that he has lost light perception, then the intervention does not make sense, since irreversible transformations have begun in the retina.
Preoperative diagnostics must be performed. Endoscopy is indicated to exclude other ocular diseases. The refractive power of the cornea, the depth and length of the anterior chamber must be measured. This is necessary to calculate the dioptric power of the IOL.
Some people are also diagnosed with age-related macular degeneration or diabetic retinopathy. In these situations, the procedure does not lead to noticeable improvement.
The ophthalmologist is obliged to inform the person in advance about the advantages and disadvantages of all types of therapy.
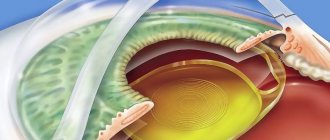
Operation technology
| Initially, a tunnel micro-incision is made in the eye wall, the size of which is 1.8-3.2 mm. A special diamond knife is used for this; | |
| The anterior lens capsule is removed using tweezers; | |
| Fragmentation of the native lens occurs through the use of an ultrasonic needle, after which each individual fragment is modified into an emulsion, which is removed (aspirated) with special instruments; | |
| Next, it is necessary to implant an intraocular lens. | |
Diagnosis of cataracts in severe myopia
Diagnosis of cataracts is complicated by the fact that in the presence of severe lens opacities, it is quite difficult to examine the vitreous body and retina using standard methods. For people who have cataracts and myopia, surgery is recommended in most cases, so such patients are sent for a detailed examination to clinics equipped with modern diagnostic equipment.
Examination for the development of cataracts:
- biomicroscopy - a study using a slit lamp, allows you to examine the optical section of the lens, study the structure of its elements, the degree of their displacement, localization, etc.;
- entoptic tests - necessary to obtain complete information about the functionality of the retina;
- electrophysiological tests - study the lability of the optic nerve, check electrical sensitivity;
- visometry - the method determines visual acuity;
- ophthalmoscopy - examination of the condition of the fundus;
- Ultrasound scanning according to indications - ultrasound is prescribed in the presence of severe opacities.
The risk of developing cataracts increases after age 60. The task of the specialist performing the examination is to determine not only the cataract itself, but also the nature of the clouding of the lens, the location and stage of the disease. Cataracts can be anterior, with clear boundaries, central (the distortion is located in the center), posterior, fusiform, etc. Cataracts are divided into types and can be initial, swelling, mature, or overripe. At the stage of mature cataract, the lens completely closes, and the person can only see the light. In 20% of patients, the disease develops rapidly, passing through all stages in 4-5 years. To avoid complete blindness from cataracts, a person will need surgery. The sooner it is completed, the sooner a person’s life will become more comfortable.
Types of artificial lenses
Before replacing a lens with a high degree of myopia, the ophthalmologist needs to select a suitable implant for the patient. At the same time, it will rely on the state of the person’s visual system, his type of activity and age. The most common types of artificial lenses used in ophthalmic practice:
- Multifocal - the special design of these optical products, in addition to providing the functions of a natural biconvex lens, increases visual acuity at long and near distances, eliminating the need for the user to wear glasses, and compensates for the previously lost ability of accommodation. Designed for people who need visual adaptation at various distances.
- With the application of a special yellow filter - such a filter is an analogue of the filter of the natural lens of the eye; it is necessary to protect the retina from the negative effects of ultraviolet rays and reduce the risk of developing various diseases of the retina.
- Aspherical - have an aspherical shape and are equipped with a yellow filter. Their special design provides contrast vision in low light conditions. These lenses are great for people whose work activities mostly take place in the dark.
Is it possible to get rid of myopia after cataract surgery?
It is impossible to solve the problem of lens clouding without surgery, since irreversible changes have already occurred in the structure of the eye. A person's vision with a progressive disease becomes worse, so only surgery can help avoid complete blindness. Indications for surgery for myopia and developing cataracts:
- disease progression;
- significant visual impairment;
- the presence of other complications such as high myopia, etc.
Patients who, in addition to cataracts, also have myopia, are interested: is it possible to permanently get rid of these two ailments at the same time? Yes, you can. Moreover, the results of such operations are impressive. New types of artificial lenses provide good vision at different distances and also protect the retina from exposure to ultraviolet radiation. Many people, after cataract surgery, see the world without glasses for the first time in their lives.
For people diagnosed with developing cataracts, surgery is recommended. The sooner the operation is performed, the better for the patient, because cataracts can develop for years, and all this time the person will have to live in constant discomfort. The risks are minimal, and the effectiveness of such intervention is high. You will be able to enjoy high visual acuity for many years, because replacing the lens will eliminate both cataracts and myopia.
Contraindications
In case of myopia, the condition of the retina may be a contraindication to its implementation. For example, its severe dystrophy increases the risk of detachment. In addition, if there are serious degenerative changes in the central zone of the retina - the macula, which provides high visual acuity, lens replacement surgery will not significantly improve vision.
Problems with intraocular lens implantation can arise with extremely high degrees of hypermetropia, micro- or nanophthalmos, and if the size of the anteroposterior axis of the eye does not reach 19 mm. And this also becomes a contraindication to performing the operation.
The higher the optical power of the artificial lens, the thicker it must be, and this causes a serious discrepancy between the sizes of the eyeball and the intraocular lens. In addition, such a lens is difficult to bend (if it is soft). Sometimes a similar problem can be solved by implanting two thinner lenses instead of one, whose total optical power completely compensates for farsightedness. The use of the method of replacing a transparent lens in case of farsightedness must take into account another point - how well the patient sees in his best glasses. If there is no significant improvement in vision from strong glasses, then you can’t count on it after surgery either. These and other issues must be resolved by the refractive surgeon before surgery.
Technically, the operation to replace a clear lens differs very little from the surgical treatment of cataracts. The difference here is only in the goals pursued. It is known that cataracts are accompanied by clouding of the lens, which interferes with good quality of vision. During the operation, the cloudy lens is replaced with a completely transparent artificial lens, which compensates for its optical power. In myopia and hypermetropia, the lens remains transparent, but has too much or too little optical power to provide good vision. Replacing it with a transparent intraocular lens of appropriate strength will bring the desired effect. In addition, the person who has performed such an operation will never encounter the problem of cataracts, since artificial lenses are not subject to age-related clouding, unlike natural ones.
Is surgery for cataracts and myopia safe?
multifocal lens.
Surgery for cataracts and myopia - features:
- cataract extraction technologies are constantly being improved and are therefore absolutely safe;
- The cost of cataract surgery depends on the type of lens being implanted;
- the most suitable type of lens can be selected for the patient depending on the indications;
- high visual performance after surgery - the latest types of lenses are used for implantation, providing high visual acuity;
- intraocular lenses are made from biocompatible materials, so they do not interact with surrounding tissues, are completely safe, and do not cause allergic reactions;
For myopia and cataracts, surgery is necessary, as it reduces the risk of developing glaucoma, which often occurs against the background of increased intraocular pressure. How is glaucoma different from cataracts? Glaucoma can significantly reduce vision, as can cataracts, up to complete blindness. The difference is that in glaucoma the disturbances affect the fibers of the optic nerve, while in cataracts the lens undergoes changes. Lenses implanted into the eyes are much thinner than the natural lens, so the outflow of intraocular fluid will not be impeded, which means there will be fewer reasons for increased pressure.