Why do my eyes itch?
Reasons why a child scratches his eyes include:
- teething,
- foreign body entering the eye,
- dacryocystitis,
- conjunctivitis,
- demodicosis
The baby may rub his eyes when moving from a dark room into a brightly lit room.
Sometimes a child rubs his eyes due to a bad habit. Such children need to be weaned off it by transferring their attention to another activity, otherwise they can get an infection in the eye.
Itching may be caused by the use of certain medications (in this case, you should consult your pediatrician - they may have to be discontinued).
Precautionary measures
Remember your child's hand hygiene
There are certain steps that parents can follow to minimize the risk of itchy eyes in their child.
- It is important that the child maintains hand hygiene. You need to understand that children who are actively exploring the world around them constantly touch various objects and can even pick something up from the floor, including on the street. Therefore, it is extremely important to prevent the child from rubbing his eyes with dirty hands. Make sure he washes his hands. And if your little one touches something outside, immediately wipe his hands with antibacterial wipes.
- It is important to control how much time your child spends in front of a TV or computer screen. It is worth remembering that there are certain age restrictions regarding being in front of a blue screen. You also need to take into account the fact that children who study at school spend a lot of time doing homework, including in class, and their eyes are already overstrained.
- Try to strengthen your child's immunity. Equally important in this matter is having a daily routine, proper nutrition, and healthy sleep.
- It is important to understand that when the first manifestations of a disease occur, you should immediately consult a doctor, do not delay, and do not risk the development of complications.
Now you know why a child’s eyes may itch. It is important to understand that the culprit may be either ordinary fatigue or the presence of allergies or a pathological process in the organ of vision. Therefore, if you have any doubts, it is better not to delay and visit a doctor.
Foreign body in the eye
Accompanied by redness. You can try to get the mote yourself:
- 1. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- 2. Examine the conjunctiva of the lower eyelid. To make the child look up, his attention is attracted by a rattle, and at this time the eyelid is gently pulled down.
- 3. Remove a speck or eyelash using a dry cotton swab or a cotton swab moistened with a solution of strong tea. If this happens during a walk, you can use the corner of a clean handkerchief.
- 4. Repeat the procedure with the upper eyelid.
- 5. After removing the foreign body, wash the eyes with plenty of clean water or a solution of strong tea.
To prevent infection, it is recommended to use drops - a solution of chloramphenicol or Albucid. If the parents were unable to get the foreign body, then you need to contact an ophthalmologist.
Dacryocystitis
Represents inflammation of the lacrimal sac caused by narrowing or blockage of the lacrimal duct. Usually it is accompanied not only by itching, but also pain.
For treatment, newborns are given a special light massage to eliminate blockage of the duct. Use antibacterial drops and ointments as prescribed by a doctor.
Dr. E. O. Komarovsky believes that it is impossible to cure the disease with drops alone, and recommends regular massage. The technique proposed by the specialist is as follows:
- 1. Wash your hands, trim your nails if necessary.
- 2. Lubricate your finger with baby cream.
- 3. Clean the child’s eyes with a cotton pad soaked in a furatsilin solution.
- 4. Place the baby on a flat surface.
- 5. Use your finger to feel the dense lacrimal sac located between the corner of the eye and the eyebrow.
- 6. Apply light pressure from the eye to the nose (5-10 repetitions). This will clear the blockage and cause the membrane to rupture.
- 7. Apply drops to your eyes (as prescribed by your doctor).
Treatment of pathology
Therapeutic measures depend on the identified pathological process. The specialist, based on the individual characteristics of the patient (weight, age) and the severity of the disease, can prescribe the following medications:
Antiallergic drugs
The following drugs are used:
- Visine (cost 370 rubles);
- Allergodil (costs 450 rubles)
- Ketotifen (cost from 80 rubles).
Visin Allergodil Ketotifen
In advanced cases, drugs containing hormones are prescribed:
- Dexapos (cost 70 rubles);
- Dexamethasone (costs 120 rubles);
- Maxitrol (price 560 rubles).
Antiviral drugs
They strengthen the immune system, eliminate infection, reduce the risk of complications and exacerbations, relieve pain, and speed up the healing process:
- Oftalmoferon (cost 270 rubles);
- Oftan Idu (cost from 90 rubles);
- Poludan (costs from 95 rubles);
- Aktipol (costs from 270 rubles);
- Adgelon (cost from 650 rubles);
- Tobradex (price 446 rubles);
- Futsitalmic (costs 266 rubles);
- Okomistin (cost 170 rubles).
Oftalmoferon Oftan Poludan Actipol Adgelon Torbadex Fucithalmic Okomistin
Antimicrobials
For infectious diseases, the use of antibacterial eye drops is indicated, among which the following are considered the most popular and effective:
- Tobrex (cost from 170 rubles);
- Tsifran (costs 187 rubles);
- Gentamicin (costs 95 rubles);
- Levomycetin . Can relieve red eyes in infants and adults. Inexpensive, accessible drug. Costs 60 rubles.
Torbex Cifran Gentamicin Levomycetin
Remedies against demodicosis
Dermatologists prescribe antibiotics for dermodicosis:
- Trichopolum (cost 83 rubles);
- Ornidazole (cost 94 rubles);
- Metronidazole (costs 160 rubles).
Ornidazole Trichopolum Metronidazole
Additionally, immunomodulators and sedatives are used.
Treatment for eye irritation
Treatment for redness caused by eye irritation is based on:
- using cold compresses and tea bags. They remove swelling, redness, and discomfort;
- washing eyes with rose water. 5 drops of the product are dissolved in a glass of warm water and the procedure is carried out in the morning and evening hours. Rinsing is done by instilling the prepared solution with a pipette, 3-5 drops each;
- using herbal infusions as compresses. They help remove dryness and redness if you steam a large spoonful of herbal raw materials in a glass of boiling water, leave for half an hour, strain, soak pieces of cloth in the prepared solution and apply to the eyelids for 5-7 minutes.
Conjunctivitis
If the eyes are red and the baby constantly scratches them, conjunctivitis is possible - inflammation of the mucous membrane. Can be viral, bacterial, allergic.
In a baby
Many people believe that the disease does not occur in infants, but often it develops in newborns with a reduced level of immunity.
Premature babies are at risk. The reasons for the development of conjunctivitis are very diverse. Depending on them, gonococcal, chlamydial and viral forms of the disease are distinguished. The bacterial staphylococcal form is rare in newborns.
Gonococcal
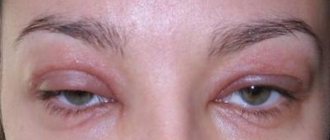
Non-compliance with the hygienic regime in the obstetric hospital cannot be excluded as a reason. Babies develop gonoblenorrhea or gonococcal conjunctivitis, which appears on the 2-3rd day after birth, since infection occurs during childbirth. This is a very dangerous form of the disease that leads to loss of vision. In addition to itching, the situation is accompanied by severe swelling and redness of the eyelids.
The form is treated with sulfonamides and broad-spectrum antibiotics. In maternity hospitals, it is mandatory to prevent the disease by washing the eyes with furatsilin and instilling a solution of sodium sulfacyl.
Sulfacyl sodium itself can cause itching and conjunctivitis.
Chlamydial
Infants can develop chlamydial conjunctivitis when pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted from the mother during childbirth. Usually occurs on the 14th day from birth, less often – a month later. Films form on the lower eyelid, which can be easily removed. The disease is manifested not only by itching. Sometimes it causes complications in the ears in the form of otitis media, and other inflammatory processes develop. Signs of general intoxication are also possible - fever, headaches. This infection is treated with antibiotics.
Viral
Viral conjunctivitis is often caused by the herpes simplex virus. This form usually affects one eye and lasts a long time, but is sluggish. The eyes itch and blisters appear on the eyelids. Adenoviral infection is less common in infants, but it also leads to conjunctivitis. Then other signs of ARVI appear.
The child has a fever and a stuffy nose. In such cases, antiviral drugs are prescribed, for example Viferon. The eyes are washed with antiseptic solutions, sage infusion (1 tablespoon per glass of boiling water, be sure to strain before use).
In preschoolers
Bacterial and allergic forms of pathology are common in preschool children.
Bacterial
The bacterial form of conjunctivitis is typical for children aged 2-7 years. The incubation period of the disease is 1-3 days. The main causative agent of the bacterial form is Staphylococcus aureus. Both eyes are involved in the inflammatory process - the baby constantly rubs them. They turn red, purulent discharge and crusts appear in the inner corners.
In such cases, the doctor prescribes rinsing with an antiseptic solution, drops based on broad-spectrum antibiotics, for example, furatsilin.
Antibiotics are selected depending on the age of the child. Tobrex drops or preparations based on chloramphenicol solution are effective. At first, the frequency of instillation will be maximum, 6-8 times a day, then it decreases. Treatment usually takes 2 weeks.
Allergic
Allergic conjunctivitis in preschool children is caused by contact with pet hair or pollen, or a reaction to food. A distinctive feature is that the baby sneezes often. In order to get rid of the problem, you need to eliminate the allergen. Therefore, treatment involves following a hypoallergenic diet, when chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs, cow's milk, and seafood are removed from the diet.
The child is prescribed age-appropriate antihistamines. Fenistil drops can be given as early as two months of age. As for itching, it is eliminated with the help of drops based on sodium cromoglycate.
Other reasons
Itching, redness and peeling of the skin around the eyes can be caused by somatic diseases, both congenital and acquired. The main reason for their occurrence is nervous shock, against which serious illnesses develop, for example, glaucoma, cataracts, diabetes, hormonal imbalance, and pathologies affecting internal organs.
Genetic individual trait
Congenital skin pathologies (for example, pigment spots) can be localized in close proximity to the organs of vision, causing the visual sensation that the eyelids are red and constantly swollen.
Worm infections
Redness and peeling of the skin around the eyes provoke helminthic infestations. They suppress the body's immune system, which leads to inflammation of the skin of the eyelids and the development of blepharitis.
Age characteristics of children 1-3 years old
Redness and swelling around the eyes in newborns and children under 3 years of age indicates that an inflammatory process of an infectious nature is developing in the body. It may be accompanied by intoxication of internal organs and systems.
In addition, redness can be caused by:
- changes in the circulatory and lymphatic system;
- tendency to colds;
- illnesses and teething;
- genetic predisposition;
- ailments affecting the liver, kidneys, heart;
- anemia.
Since the cause of alarming symptoms can be hidden in any factor, only a doctor can tell you what to do to eliminate it.