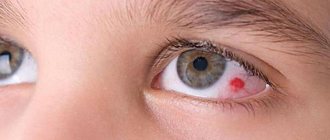
Causes of red whites of the eyes in a newborn
Immediately after birth
Redness that occurs immediately after the birth of a child can be caused by conjunctivitis, which the baby contracted in the womb from the mother. Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane. The infectious form of the disease manifests itself immediately after birth, since the immune system is imperfect.
Dacryocystitis is another cause of red eyes immediately after childbirth. Inflammation of the lacrimal organs is considered a borderline condition between a congenital anomaly and an acquired disease. The congenital disease manifests itself only as hyperemia of the mucous membrane; other symptoms appear 2–3 days after the birth of the baby.
Other diseases that can develop in the womb and lead to hyperemia immediately after birth:
- Blepharitis - the causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. The cause is infectious or allergic diseases during pregnancy in the mother. The development of blepharitis in a child is caused by a lack of vitamins, anemia, dry keratoconjunctivitis in a pregnant woman, which are not treated in a timely manner.
- Uveitis is an inflammatory process of the uveal tract. Its development in a newborn is provoked by the herpes virus, mycobacteria, Koch's bacillus or toxoplasmosis, which were discovered in the mother during pregnancy. The baby's optic tract becomes infected, and hyperemia appears at birth.
Conjunctivitis manifests itself in a newborn as a viscous, opaque or yellowish discharge from the eyes. The baby's body temperature rises.
If the birth was difficult and long, the baby could develop oxygen starvation. It appears as a result of prolonged presence of the head in the birth canal and compression. Due to the increase in blood pressure, the baby’s blood pressure rises, the vessels cannot withstand it and burst. The result is reddened whites of the eyes.
Sometimes oxygen starvation manifests itself as one small spot. This redness is considered physiological and does not entail complications or threaten the life of the newborn. The redness goes away within 2–3 days, even before the baby is discharged from the maternity hospital. Hyperemia may be a consequence of severe hemorrhage in the fetus or the result of passage through the birth canal. The integrity of the blood vessel of the eyeball is possible for the following reasons:
- Using medical forceps during the birth of a baby. They are designed to extract the fetus by the head in strict accordance with the natural biomechanism of childbirth. They are used for weak labor, acute intrauterine fetal hypoxia, and prolapse of umbilical cord loops. The fetus may experience more than just reddening of the whites, complications such as compression of the brain and hemorrhage into the cranial cavity are possible; in the latter case, the eye is very red and filled with blood.
- The use of labor stimulants - Dinoprostone and Oxytocin. Medicines affect the fetus, one of the side effects is eye hyperemia.
- Improper breathing of a woman during labor.
Sharp redness
Unexpected hyperemia can frighten the parents of a newborn. However, there is not always a reason to panic. The cause of redness may be prolonged crying of the child or ordinary fatigue. It is difficult for some infants to put them to bed on time; long games lead to overexertion and fatigue, hence the redness of the eyes.
Not a terrible reason - irritation of the mucous membrane from sunlight or wind. The child’s visual organ is very vulnerable; it reacts to ARVI, crying, bright light, rain, wind and sun rays. Therefore, it is recommended to protect the baby in every possible way from prolonged exposure to weather conditions that can cause such signs and discomfort.
Sharp redness appears when foreign bodies enter the eye. The eyeball is scratched, immediately there is a burning sensation, lacrimation and hyperemia.
The next reason is a consequence of an allergic reaction. Redness appears when you are allergic to external or internal irritants. For example, for pollen or food. Symptoms disappear when the provocateur is eliminated, sometimes treatment is required.
Diagnostic methods
To determine the causes of red eyes in newborns, it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist with your child.
To determine the diagnosis, the doctor will perform an ophthalmoscopy of the baby’s eyes.
The doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease. The main thing in determining the diagnosis is an ophthalmological examination of the condition of the eye area. The eyes of an infant are examined in the following main ways:
- Ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus and the condition of blood vessels.
- Biomicroscopy is a detailed examination under a microscope.
- Tonometry is the measurement of eye pressure.
Parents' actions
If a symptom has not gone away by the evening or morning of the next day, you should not ignore it. Even if there is a physiological problem, you should consult an ophthalmologist or pediatrician to prevent complications.
The child should be seen by a doctor as soon as possible. Before visiting the doctor, you can take the following measures to alleviate the baby’s condition:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene of the child;
- change bed linen (boil dirty ones);
- disinfect toys so that the child does not introduce infection into an already inflamed eye;
- ventilate the room more often, humidify the air in the baby’s room so that the eyes do not dry out;
- walk at least 2 hours a day;
- cut your nails and keep them clean;
- do not allow rubbing of eyes;
- do not allow watching cartoons for a long time, this will worsen the redness;
- make the light in the room less bright.
Before visiting a doctor, it is recommended to rinse your eyes with boiled, cooled water at least 2 times a day. Each visual organ is treated with a separate cotton pad. You should rinse from the outer corner to the inner one, this will prevent the development of an infectious process if the baby has conjunctivitis, blepharitis or uveitis.
If you have a runny nose, sneezing, lacrimation and hyperemia, this is an allergic reaction. Write down on paper all the foods your child ate that day. This will help the doctor identify the allergen. If an allergic reaction occurs, protect the child from flowers and pets, monitor the condition before visiting a doctor and write everything down in a notebook.
Causes and symptoms
There are many reasons for redness, in some cases everything goes away quickly without medical intervention, in others you need to seek help from a doctor.
- V.Rohto eye drops will help restore vision after intense or prolonged work in front of the computer;
- Eliminate itchy eyes and restore clarity of vision;
- Relieve signs of fatigue;
- Moisturize your eyes if they are excessively dry, including those caused by wearing contact lenses.
Possible factors influencing the condition of a newborn's eyes are fatigue and eye strain when the child has been awake for too long. In such cases, the redness is slight, the eyes itch, the child behaves restlessly, and there is no discharge.
It is possible for a foreign body or speck to get into the eye. The baby will rub his eyes with his fists, further irritating his red, watery eyes. Injuries to the mucous membrane of the eye and infections can also cause redness of the mucous membrane.
Blockage of the tear duct, or dacryocystitis, very often occurs in newborns in the first months of life. This is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac as a result of obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, when the thin septum covering the opening of the lacrimal duct did not break through at birth. Symptoms in this case will be redness, swelling of the inner corner of the eye, mucous or purulent discharge, especially when pressed.
Conjunctivitis due to allergies is a fairly common occurrence. Sometimes babies are allergic to dust, pollen or other allergens. Symptoms: red eyes, tear discharge, itching.
Ophthalmic diseases (uveitis, blepharitis, glaucoma) often provoke inflammation.
Uveitis is an inflammation of one of the three parts of the uveal tract: the iris, the cirial body, or the choroid. The cause may be infection, fungus, parasites or injury. In addition to redness, uveitis is accompanied by pain, photophobia, and blurred vision.
Blepharitis or “stye” is swelling and red edges of the eyelids, which are necessarily accompanied by purulent sputum. It is observed when the eyelids are affected by demodex mites or as a manifestation of allergies. This type of disease can become chronic and difficult to treat.
Glaucoma is increased pressure inside the eye, a dangerous and serious disease.
What not to do
If redness is detected, you should not begin self-treatment. Put eye drops, ointments and other medications aside. Do not allow other family members to treat the child themselves.
You cannot do the following:
- apply compresses - moisture will aggravate the situation;
- do not use home remedies (even washing with furatsilin or chamomile decoctions);
- do not touch the baby’s eyes unnecessarily - this creates additional conditions for injury to blood vessels;
- Don’t try to get the speck out if you can’t wash it off with water.
Why do my legs swell after childbirth?
Sometimes after childbirth a woman experiences severe swelling of the lower extremities. This is how inflammation of the veins (phlebitis) makes itself felt.
Usually, after a couple of weeks, swelling disappears on its own, but if it is accompanied by severe pain, be sure to tell your doctor; you may need to prescribe medications or use special ointments.
To reduce swelling, place your legs on an elevated platform more often, or take a knee-elbow position. This way, the pressure on the veins of the lower extremities is reduced, and the blood flow in the pelvic vessels and kidney function are normalized.
Women prone to varicose veins should be especially careful about the issue of edema.
Treatment by a doctor
The cause of redness is determined by your family doctor or ophthalmologist. It is better to contact a specialist in a narrow field. Drops and ointments and other therapeutic and preventive measures are used.
Hyperemia caused by the allergen is eliminated with antihistamines. The most common method of treatment is taking second-generation antihistamines - Claritin, Kestin, Zyrtec. Immunostimulating medications are prescribed.
Dacryocystitis is treated by massaging the lacrimal sac, washing the eyes with Furacilin solution and Levomycetin eye drops. Treatment lasts 2 weeks. The regimen for using medications and rinses varies depending on the severity of the condition. If conservative therapy does not help, the doctor prescribes lavage of the lacrimal ducts.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia; a probe is inserted into the lacrimal canaliculus and passed through the lacrimal ducts.
For ophthalmological pathologies of an infectious nature, treatment is long-term. Blepharitis in a newborn is treated with lotions of medicinal plants, eye washes and treatment of the eyelids with special gels.
For conjunctivitis, rinsing with a solution of potassium permanganate or furatsilin is prescribed. Both products have antibacterial and antiseptic properties. Next, antibacterial eye drops are used. In severe cases, medications are given by injection.
Uveitis is treated with anesthetics, glucocorticosteroids, antiviral and antimicrobial medications. Medicines are selected exclusively by the attending physician. The type of drugs chosen depends on the origin of the inflammatory disease.
Drug therapy for red mesh in the eyes of a child
If it is necessary to treat red eyes, medications for young children are prescribed based on the cause that provoked the release of blood vessels in the proteins. The main means are ointments and drops; in more acute situations, antibiotics will also be required.
- For newborn children with blocked tear ducts, disinfecting drops Okomistin are prescribed. You need to put 1-2 drops into your eyes two or three times a day. Tetracycline ointment is also prescribed for infants; it helps the pustules on the eyelids and eyelashes come off. It is possible to use a folk remedy: tea leaves. It is prepared like this: take 1 tbsp. l. loose tea leaves and pour 50-75 ml of boiling water. Cool the composition, then moisten a cotton swab generously and apply it to the baby’s eyes. For complex treatment, acupressure of the lacrimal sacs is required. See video.
The manifestation of blepharitis is treated by washing with tar soap, tansy oil lotions, as well as using ointment and a drop of Tobrex or Tobradex in an age-appropriate dosage. If the form of the disease is acute, additional treatment of children's eyes with Amitrazine is possible.
- For uveitis, glucocorticoid drugs with prednisolone are prescribed for infants. As complementary therapy, hemosorption (a procedure by which toxic substances are removed from the blood) and plasmapheresis (blood purification in the laboratory and returned to the bloodstream) are prescribed.
- Cases of glaucoma in infants are treated with the use of Betoxalol and Pilocarpine. With a strong increase in intracranial pressure, surgical intervention is indicated.
Red eyes in infants may be a sign of an allergic reaction