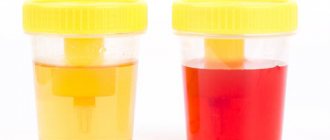
Cloudy, cloudy urine, sediment, and small flakes may indicate a health problem.
But cloudy urine can also be due to certain foods you've recently eaten. How to interpret this symptom? In general, if this is a one-time event, there is no need to worry, but if cloudy urine is produced consistently, it can be caused by a variety of different conditions, ranging from relatively mild to severe. These conditions may include dehydration, urinary tract inflammation, sexually transmitted infections, kidney stones, diabetes and other problems.
Sometimes cloudiness and discoloration indicate increased protein, crystalline substances, blood, pus, or irritating chemicals in the urine. Health care providers use other terms to describe cloudy urine. They may use words such as milky, foamy, or cloudy white urine, or the term albinuria (protein in the urine). Dehydration: Particularly Risky in the Young and Old Many people know that dark-colored urine is a sign of dehydration, but cloudy urine can also indicate that you're not getting enough clean water. It is especially dangerous for young children and older adults to become dehydrated during hot weather or when sick. People are also at increased risk of dehydration if they have recently had intense exercise, vomiting, diarrhea, or fever. In addition to cloudy urine, other signs of dehydration may include:
- dark urine;
- very infrequent urination;
- fatigue;
- feeling of intense thirst;
- confusion;
- dizziness or disorientation in space.
If a person experiences severe diarrhea, confusion, vomiting, or bloody or black stools, an ambulance should be called immediately. Delay is dangerous! Mild to moderate dehydration is treated with plenty of fluids, such as clean, still bottled water. But severe dehydration may require treatment in which intravenous fluids are given in a doctor's office or emergency room in addition to oral rehydration.
1.General information
It has been known in medicine since time immemorial: everything that circulates in the body or leaves it can sometimes tell much more and better about the patient’s condition than the patient himself. All that remained was to learn to understand this “language” - the language of biological fluids, mucus and other substances.
Modern medical science is armed with powerful optical and electron microscopes, centrifuges, filters, spectrum analyzers; developed methodology for laboratory biochemical, bacteriological, virological research, computer databases and other technologies that could not even be imagined a hundred or two hundred years ago. However, some diagnostic criteria and principles do not change: physical characteristics such as color, consistency, smell, volume, and frequency still matter to the doctor.
A change in the color of urine (in particular, darkening), especially if it is accompanied by any discomfort or pain, cannot but alert you. Urine is one of the most important biological fluids, and, being a residual waste product of blood filtration in the kidneys, it serves as an informative indicator of the general condition of the body and the processes occurring in it.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Cloudy urine not associated with pathological processes
If the urine is not clear, it is called cloudy or foamy. This phenomenon does not necessarily have to be a consequence of illness. Urine often becomes cloudy due to a lack of fluid entering the body. In the absence of other symptoms, this is considered normal. More often, this phenomenon occurs during prolonged exposure to the sun, after visiting a sauna, steam bath, or physical activity. The body loses a lot of water through vomiting, diarrhea, and high fever.
Often cloudy urine is observed in women in the morning. This may be a sign of a high content of mineral salts. Due to dehydration, diuresis decreases, which also causes clouding. The balance of the amount of liquid and salts changes, the urine in this case is defined as slightly cloudy.
If you consume less than 2 liters of liquid per day, the intercellular matrix thickens. As a percentage, the amount of salt residue increases and the amount of water decreases. Urine becomes cloudy and dark yellow in color. Salts gradually form sand and stones, disrupt urinary flow, which creates the preconditions for stagnation and the development of inflammation.
Another reason for cloudy urine may be an incorrectly collected test. If urine is exposed to air for a long time, it crystallizes. Under the influence of oxygen and low temperatures, mineral salts precipitate. Therefore, a urine test is taken in the morning; urine can be stored for no more than 2 hours after collection.
Cloudy urine may occur when taking certain medications. Therefore, during the examination you need to notify the attending physician about this. The clarity of urine is affected by a woman's diet. Beets, blueberries, and other coloring foods can change the natural color of your urine.
Learn about the symptoms of bladder tumors in women and how to treat the disease.
Effective methods for removing ureteral stones in men are described in this article.
2. Reasons
It is important to understand that no processes or changes in the body occur without reason, and urine does not change color according to a random principle. The question is whether these causes are natural, normal and transient (passing without any consequences), or whether this is the tip of a formidable pathological “iceberg”, one of the manifestations of a latently developing disease.
It has long been known that the basic composition of urine is quite complex and includes, in addition to water, many organic and inorganic components: acids, proteins, salts, ions, etc.
The natural color of urine, varying within the yellow range, is due to the presence of urochrome, a pigment substance formed as a result of the biochemical transformation of bile and hemoglobin. The concentration of urochrome is usually higher in the morning, but, in addition, it can increase significantly (and the urine, accordingly, change color to a darker and more saturated color) due to situational dehydration, increased sweating during prolonged exercise and/or in a hot climate, consumption of a number of foods, mainly of plant origin (carrots, beets, blackberries, etc.). When the daily dose of fluid consumed is normalized, or after the complete removal of natural dyes, the color of urine is restored.
Often, urine darkens in pregnant women - due to increased load on the kidneys and liver, dehydration due to toxicosis and vomiting.
One of the most common causes of dark urine in the modern world is taking medications. Many antibiotics, vitamins B and C, laxatives, nitrofuran derivatives and a number of other drugs, the final compounds of which are metabolized through the kidneys, can significantly change the color of urine, as the information insert necessarily warns about.
If the effect of such factors is monitored and controlled by a person, and does not last too long, it can be considered relatively harmless or at least reversible. However, there is a huge, without exaggeration, number of reasons for darkening of urine, which are clearly pathological and indicate serious problems in one or another system of the body. It is not possible to list all these diseases; Below we are talking specifically about groups of diseases, each of which may have its own specificity in changes in the physical and biochemical properties of urine:
- damage to the urinary tract (urolithiasis, pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis, polycystic kidney disease, difficulty passing urine due to strictures in various areas, etc.);
- damage to the liver and biliary system (cirrhosis, hepatitis of any etiology, cholelithiasis, etc.);
- infectious and inflammatory processes in the urogenital area, incl. including sexually transmitted diseases (urethritis, cystitis, prostatitis, adnexitis, orchiepididymitis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and many others);
- injuries;
- cancer in any of the above systems, as well as in the pancreas and other related organs;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- some types of helminthiasis primarily affecting the urogenital system;
- vascular inflammation (vasculitis);
- chemical intoxication.
Visit our Gynecology page
Preventive measures
The risk group includes those patients who at different times suffered from diffuse connective tissue pathologies (or currently have disorders).
It is important to know! If specific pathogens (such as streptococcus) have previously penetrated the urinary system, there is a high probability that under the slightest unfavorable circumstances the disease may occur again or manifest itself in the form of another pathology.
In this regard, doctors advise adhering to the following recommendations regarding the prevention of the disease:
- promptly identify and treat infections;
- avoid hypothermia;
- eat wisely;
- do not abuse alcohol;
- do not experiment with pharmacological products.
Glomerulonephritis and other inflammatory processes localized in the renal structures can cause the development of all kinds of complications: renal failure (acute or chronic form), hypertension, liver pathologies, heart failure. Preventing a disease is much easier than dealing with its negative consequences.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
Having noticed intense darkening of urine, you should first of all inspect your own well-being and analyze what situational factors this phenomenon may be associated with. If such factors are found and there are no other disturbances, it is usually enough to restore the water balance and/or normalize the diet so that the urine acquires a natural color within one to two days.
If dark urine is accompanied by disturbances in well-being or signs of any dysfunction, you should consult a doctor immediately: wait-and-see tactics in such cases can pose a very real risk to health and life. At an appointment with a urologist, gynecologist, andrologist, nephrologist (depending on which specialist intuitively seems most logical in a particular situation), you will need to answer a number of questions, and you need to be prepared for this: the urine has just darkened or become cloudy; the shade changed to brown, red, dark orange; whether there is an unusual smell; are there any impurities of blood, pus, mucus, and if so, how much and what kind (flakes, threads, foam, clots, etc.); whether the frequency and volume of urination has changed; what is the nature and localization of painful sensations; what is the chronology and dynamics of the development of disorders, etc.
Based on the results of a clinical interview, external examination and palpation examination, laboratory tests will be prescribed (needless to say, the first on the list will be a urine test) and instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound, CT, MRI, urocystoscopy, one or another radiographic technique).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
General rules for taking the test
Improper urine collection often leads to distorted results and is often the cause of cloudy urine. Because of this, a woman has to retake the test, wasting her time and energy. To prevent this from happening, you need to know the general rules for taking a urine test:
- before you start collecting urine, you need to wash yourself with clean warm water without using soap;
- the container for collecting material must be sterile;
- collect an average portion of urine. To do this, you need to flush the first stream into the toilet, then fill the jar and complete the urination process;
- before collecting urine, it is not recommended to consume foods that can change the color of urine, and you should also avoid diuretics;
- The jar must be taken for analysis within 2 hours after collecting the material.
Urine must be collected correctly. If it is not possible to take the jar right away, then it can be placed in the refrigerator, but for no more than a day. Based on the results of the study, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
4.Treatment
Not so frequent cases of conditionally normal darkening of urine under the influence of controlled situational factors (and restoration of color in a natural way) are discussed above. As for pathological causes, then, of course, therapeutic prescriptions will be determined by the entire complex of diagnostic data and individual anamnestic information. It is unrealistic to identify all possible schemes or at least directions of treatment in this case.
However, again and again we draw attention to the fact that the timeliness of seeing a doctor is not just important - this factor can have a critical, life-saving significance.
Urinary tract diseases
Urinary tract diseases are the main reason why women's urine becomes cloudy. Thus, the pathological causes of cloudiness can be the appearance in the urine of:
- erythrocytes (red blood cells);
- leukocytes;
- bacteria;
- fat;
- lymph.
Why does cloudy urine appear in men?
Hematuria
The appearance of bloody urine (hematuria) is the most common symptom of kidney or urinary tract pathology. When examining a urine sample under a microscope, detection of more than 2 units (red blood cells) may indicate the likelihood of developing the following diseases:
- glomerulonephritis;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- pyelonephritis;
- Urolithiasis
A characteristic phenomenon with hematuria, in addition to changes in color and loss of transparency, can be considered the appearance of blood clots in the urine. Moreover, it is the shape of the clots that is of great importance in diagnosing pathology. Thus, shapeless clots, as a rule, indicate bleeding of the bladder mucosa, and elongated “worm-shaped” clots indicate renal bleeding.
Hematuria in urolithiasis usually appears after renal colic (a painful symptom that appears as a result of the displacement of a stone and damage to the blood vessels of the kidneys).
Microscopic examination of red blood cells can determine the source of bleeding, since blood cells that enter the urine from the kidneys are smaller than red blood cells that come from the urethra or bladder.
With hematuria, urine may vary in color from cloudy pink to brownish brown or the color of cherry jam.
Bacteriuria and leukocyturia
Bacteria, regardless of their number, are not capable of causing cloudy urine. However, the body’s natural reaction to the penetration of infection into tissues is the production of leukocytes. Leukocyturia with an antibody concentration of more than 50 units in the field of view causes not only cloudiness of the urine, but also a change in its color from white to pale green.
As a rule, leukocyturia of bacterial origin does not cause difficulties in choosing therapeutic tactics, and its treatment comes down to the competent selection of antibacterial drugs or antibiotics.
In addition to the bacterial nature of development, the following types of leukocyturia are distinguished:
- Mononuclear. As a rule, it appears in diseases associated with impaired renal function (interstitial nephritis, thunderonephritis).
- Lymphocytic. Develops in response to systemic connective tissue lesions of immune origin (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus).
- Allergic. Leukocyturia, in this case, is a reaction of the body with increased sensitivity of the immune system to the influence of any irritant (allergen).
The number of leukocytes exceeding 200 units in the field of view of the microscope is called pyuria
Lipuria
With lipuria, the urine is very light and cloudy due to the presence of microscopic fat droplets in it. In the urine of a healthy woman, fat is determined only by residual traces. Excessive lipid concentrations may be due to a number of reasons:
- excessive consumption of fatty foods;
- overweight;
- diabetes mellitus;
- yellow fever.
It can also occur due to the penetration of lipids into the renal tubules after surgery in patients who are obese or after multiple fractures of long bones.
From a diagnostic point of view, lipuria is not a sign of pathologies of the urinary tract, and therefore, it is only important when diagnosing metabolic disorders.
Hiluria
A predominantly parasitic disease caused by small worms less than 1 millimeter in length. During their life, parasites block the lymphatic vessels, promoting stagnation of lymph and its subsequent penetration into the urine.
There is also a non-parasitic nature of the development of the condition when lymph enters the urine due to the formation of small fistulas in the lymphatic tract. The mechanism of the disease is not fully understood, therefore, in treatment, generally restorative drugs are used. In most cases, the disease goes away on its own.
Thus, the appearance of cloudy urine in a woman can be caused by a variety of reasons. To eliminate some of them, you only need to be attentive to your own body (drink enough fluid, adjust your diet, maintain hygiene); others may require laboratory testing, followed by a course of therapy in accordance with the diagnosis.
How to determine turbidity in the laboratory
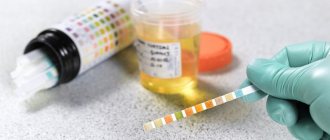
A general urine test (UCA) is one of the most informative diagnostic methods that evaluates the physical characteristics of the fluid. The main purpose of the examination is to identify urological diseases and abnormalities in kidney function. Cloudiness in urine is determined by the naked eye.
To clarify the composition of the sediment, microscopic and biochemical analysis is used. Sometimes chemical methods for identifying suspended matter are used:
- cloudy urine with urates becomes transparent when alkali is added and heated;
- if the suspension contains oxalates, they disappear with the introduction of hydrochloric acid;
- dissolution of the sediment after the introduction of ethanol indicates the accumulation of fat molecules in the liquid.
If the urine is light but cloudy, this does not always indicate a urological disease. The transparency of the liquid depends on various factors:
- region of residence;
- nutritional characteristics;
- physical activity.
When the kidneys and urinary tract function normally, the urine is clear. Slight turbidity is acceptable due to impurities of urates, epithelial cells and mucus. Transparency is affected by the quality of genital hygiene. In 15% of cases, cloudy urine is the result of non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules.
If your urine is cloudy, smells bad, or takes on a reddish tint, you should consult a urologist.
Forecast
The prognosis of pathologies characterized by discoloration of urine depends on the type and severity of the disease. For type 1 diabetes mellitus, the prognosis can be called conditionally favorable. Such a person can live for a long time, but only if the therapy is effective. Such a diagnosis implies the assignment of a disability group.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are considered incurable diseases. With type 2 diabetes mellitus, a disability can also be assigned, which is associated with severe complications of this pathology.
With timely treatment, urolithiasis has a fairly favorable prognosis, but this pathology is prone to relapses and the development of inflammatory processes, which, in the absence of proper therapy, eventually lead to renal failure. The latter pathology can boast a favorable prognosis only if kidney function is fully compensated.
In the absence of pathologies, the problem of light-colored urine is solved by reducing the amount of liquid drunk, and the color of urine is stabilized after the removal of foods and medications that tint it.
What responsibility lies with urine?
For the most part, the kidneys are responsible for clearing protein from the body. If there is a lot of this element in the analyzes, then this indicates violations in their work.
Urine is divided into primary and secondary . The first is formed in the kidneys after filtering the blood. She is not like the one we are used to seeing. In its composition it can be compared to blood plasma.
Further, passing through a complex filtration system, the secondary one collects all the harmful components from the body, after which they are removed outside of it.
Is light urine in a child good or bad?
Compared to children's secretions, the urine of an adult always has a more pronounced color. The child’s biological fluid acquires a light yellow hue as it grows older.
That is why, if clear urine is excreted in infants, then this phenomenon is considered normal. This color of urine is explained by the baby’s diet, because children during the first 6 months of life consume only breast milk or special adapted formulas. At this time, the child’s urinary tract is not yet mature enough, so the number of urinations reaches 20-24 per day.
When the baby turns 3 months old, the first complementary foods begin to be introduced. During this period, the discharge may change its character - become a little richer. Subsequently, the color of the urine gradually becomes yellowish.
If colorless urine continues to be excreted in a child after 6-8 months of life, parents have a reason to visit a pediatric urologist. In such a situation, it is important to promptly exclude the possibility of developing the following disorders:
- pyelonephritis;
- failure of metabolic processes in the body;
- kidney failure;
- nephritis of various etiologies;
- congenital anomalies of the urinary organs.
Typology of precipitation
- Crystal. Most often, it indicates an excess of salts. With the appearance of crystalline sediment, acidity may also increase. The study may show the presence of different salts - or phosphates.
- Flaky. With such sediment, a person appears, and a person’s urination is accompanied by painful sensations or itching in the urethral area. observed in patients with diseases of the bladder or gastrointestinal tract.
- Organic. In this case, a white sediment appears in the urine, indicating an increase in the level of leukocytes and the proliferation of protein molecules that appear from the epithelial cells of the human genitourinary organs.
Pus, which is accompanied by thread-like formations, appears in connection with inflammation of the renal and urinary systems, as well as with the appearance of a sexually transmitted infection or prostatitis.
If there is a change in color, odor, or the appearance of pain, not only a general urine test should be performed, but also microscopy of the urine sediment. The latter analysis helps to conduct a more detailed microscopic examination and identify the content of squamous epithelium, which in a healthy person should be found only in isolated cases.
Diagnostic measures
Since a large number of red blood cells can cause the intense color of urine, the shade of “meat slop” can be determined purely visually. Against the background of unfavorable color changes, other urine indicators may also suffer. In this regard, the patient is prescribed the following types of studies:
- general urine analysis;
- analysis according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko;
- blood test;
- bacterial sowing;
- blood immunology;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- CT and MRI of the kidneys;
- cystoscopy;
- urography.