Urine is an important waste product of human life, which is excreted by the kidneys. Thanks to urine, toxic substances, waste, salts and excess water are removed from the body. Disruption of the urinary process and changes in urine parameters indicate the onset of pathological changes in the body.
Normally, the temperature of a person's urine should correspond to body temperature. In a healthy state, the temperature of biological fluid is approximately 36.9 degrees .
The perception of temperature is considered a conventional concept. Receptors sensitive to cold are not fixatives, therefore the calculation of temperature indicators of urine occurs depending on the internal temperature of the body.
What's normal?
Urine is typically the same temperature as the body, averaging 98.6°F.
This means that when urine leaves the urinary tract, called the urethra, it may feel warm on the skin it touches, including the genitals, arms or legs. At low temperatures, a person may observe steam escaping from urine.
Noticing that your urine feels warm or hot is completely normal. Urine may be especially warm if the person's body or hands are cold.
However, if a person notices that their urine is warmer than usual or hot as it comes out of the urethra, this may indicate that there is an infection or injury. A hot, burning or painful sensation when urinating is called dysuria.
Symptoms
The hot sensation when urinating can be painful and can even cause a person to retain urine. Parents of young children who are reluctant to urinate should consider the possibility of burns during urination.
Most people who experience a hot sensation when urinating also notice other symptoms. This may include:
- a tumor in the genitals or urethra.
- discharge from the vagina or penis.
- fever
- bad smelling urine
- dark urine
- cloudy urine
- increased need to urinate
- difficulty urinating
- nausea and vomiting
- pain in the back or stomach
Signs
A hot feeling during emptying the bladder causes significant discomfort and even pain. This may cause a person to be afraid of urinating and try his best to delay it until a later date.
If a small child does not want to urinate, parents should take into account that the reason for this may be a burning sensation during the process of emptying the bladder.
However, in most cases, the symptoms are not limited to burning sensation alone. Quite often, patents also complain about the following symptoms:
- swelling of the external reproductive organs and urethra;
- pathological discharge from the genitals;
- fever;
- unpleasant smell of urine;
- darkening of urine;
- turbidity of biological fluid;
- increased urge to empty the bladder;
- difficulty urinating;
- pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen and/or back;
- nausea (in especially severe cases it can result in vomiting).
Causes of hot urine in both sexes
If a person's core body temperature rises—for example, if they have a fever caused by an infection or if they've just done intense exercise—the urine may be warmer than normal.
Below is a list of causes of hot urine or hot urination.
Urinary tract infection (STI)
Urinary tract infections are one of the most common reasons why urinating outside feels hot or burning. UTI occurs when harmful bacteria, often E. coli, enters the urinary tract.
UTI most often affects the bladder. People with UTI may experience the following symptoms:
- burning pain when they urinate.
- frequent need to urinate
- strong urge to urinate even immediately after a trip
- bad smelling urine
- blood in urine
In most cases, antibiotic treatment will quickly cure UTI. If left untreated, the infection may spread to the kidneys or other areas of the body. STIs can affect both sexes but are more common in women than men.
Other infection
One of the ways the body fights infection is heat. This is why people often develop a fever when they are sick. When urine warms up above normal temperature, it may mean a person has a fever.
Fever can be caused by an infection anywhere in the body, so it is important to monitor symptoms and see a doctor if they do not improve.
When urine feels physically warm and burns when urinating, it could mean someone has a UTI or infection in their kidneys.
Injuries around the urethra.
Urine is acidic. This means that when coming into contact with an injury, even a small one, a person may experience the sensation of a hot, hot burn. An injury in or around the urethra may cause the urine to feel hot and hot.
People who shave their genitals may have tiny cuts near the urethra. Friction caused by sexual contact, tiny pimples, cuts and scrapes can all cause urine to become warmer.
Minor injuries usually go away on their own. In case of pain in the urethra, fever or severe wound, the patient should consult a doctor.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Sexually transmitted infections can cause urinary tract problems. They can also damage the genitals or the area around the urethra, causing pain during urination.
Anyone who is or is sexually active can become infected with an STI, even if they have previously tested negative. Some STIs do not have symptoms for a long time, so a long period of time without symptoms does not necessarily mean that a person does not have an STI.
Chlamydia is an STI that often causes a burning sensation when urinating. It can also lead to vaginal or penile discharge and, in men, swelling or pain in the testicles.
Intertitial cystitis
Intertitial cystitis is a poorly understood chronic disease that causes symptoms of IUP even when IUP is absent.
This disease is more common in women than in men.
Researchers don't fully understand what causes this, but one possible cause is damage to bladder tissue. People with interstitial cystitis may experience a burning sensation when urinating or other unusual sensations, such as the urine feeling too hot.
Doctor Komarovsky about small urination in a child
Symptoms of oliguria in children can occur for the same reasons as in adult patients.
A well-known specialist believes that the first reason for the development of this pathology is E. coli. For this reason, he considers mainly girls to be at risk. The structural features of the ureteric system allow bacteria to quickly penetrate the canals, ureter and kidneys.
Komarovsky believes that such a problem is very dangerous for infants; it should be treated at any time in order to prevent it from becoming chronic.
The doctor claims that it is necessary to treat with antibiotics, since the intestinal microflora is restored much faster than the kidneys themselves. The therapy takes about two weeks, but within three days the child’s condition improves significantly.
Komarovsky recommends that parents do not use self-treatment methods; at the slightest suspicion, immediately contact an experienced specialist.
Reasons for women
Causes specific to women include:
Postpartum pain
After giving birth, many women develop tears in the area between the vagina and anus, called perineal lacerations. Tears may appear near the urethra or inside the vagina.
If urine comes into contact with these lesions, it can cause burns for several weeks after birth.
Spraying a warm perineal irrigation bottle during urination may reduce pain.
vaginal infection
A vaginal infection can irritate the tissues of the vagina and vulva. If irritated tissue comes into contact with urine, a burn and a feeling of high temperature may occur.
Diagnosing a vaginal infection based solely on burns is not possible, so it is important to see a doctor for urinary burns. The symptom may be caused by infections such as
Postmenopausal vaginal changes
After menopause, the body produces less estrogen. This can change the vaginal tissue, causing it to tighten and loosen. The vagina may also feel dry, which can make the skin and other tissues feel tender and sore.
When urine comes into contact with the vagina or urethra, it may feel hotter than before due to these changes.
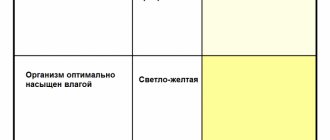
Reference values depend on:
- large intake of water and other liquids;
- use of osmotic diuretics;
- diabetes insipidus;
- various kidney diseases (renal failure, chronic pyelonephritis, polycystic kidney disease, etc.);
- sarcoidosis, hypoaldosteronism, myeloma.
The daily volume of urine with polyuria is ¾ of the liquid drunk. With polyuria, more than 2000 ml is excreted per day, the reasons are due to:
- chronic renal failure;
- pyelonephritis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- heart failure;
- prostate disease;
- cancerous tumor in the pelvic area
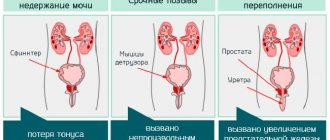
With oliguria, less than 400 ml is excreted per day. The decrease in volume may be due to:
- ultra-low intake of water and other liquids;
- swelling of any origin, arising from cardiac or renal failure;
- high fluid loss (with vomiting, diarrhea, heavy sweating).
With anuria, the volume of daily urine is reduced to 200 ml or completely absent, the reasons are due to:
- violation of secretory function;
- cessation of glomerular filtration due to large blood loss, shock, uremia;
- urinary dysfunction;
- bladder damage;
- excretory anuria.
Reasons in men
Causes specific to men include:
prostatitis
Prostatitis is swelling, pain and inflammation in the prostate, often caused by a bacterial infection. Men with prostatitis may experience pain or a burning sensation when urinating, as well as changes in the flow of urine.
They may also have nausea and vomiting, or pain during ejaculation. It is important to diagnose the cause of prostatitis, so men who suspect they have a prostate problem should see a doctor.
epididymitis
Epididymis is a tube containing sperm on the testicles. Infection or inflammation in this tube can cause painful burns when urinating. Men with epididymitis may also experience swelling around the testicles, pain in the penis or testicles, and fever.
This painful condition is usually caused by a bacterial infection or surgery and responds well to antibiotics and rest.
Treatment
Treatment for hot urine depends on the cause. Because urine can feel hot for many reasons, and because many diagnoses have similar symptoms, it is important to see a doctor before attempting home treatment.
Many causes of painful or hot urination can be easily treated with antibiotics.
Drinking plenty of water can also help flush bacteria from the urinary system and make urination a little less acidic.
Perspective
Urine is naturally hot, but cools quickly after leaving the body. People who accidentally put their hand in a stream of urine may be surprised by how hot urine feels.
Most causes of hot urine are easy to treat, and symptoms usually improve within a few days. However, prostatitis can be difficult to treat, and interstitial cystitis is a chronic pain syndrome.
It is important to see a doctor who specializes in treating urinary tract disorders to reduce the severity of symptoms and decide on appropriate treatment.
In most cases everything is fine. However, when the urine becomes hot or painful, it is time to see a doctor. Most urinary problems are common and easily treatable, so there is no need to worry or feel ashamed. In many cases, only a urine test and a medical record are required to make a diagnosis.
Features in pregnant women
During such a period, rare emission of urine may be due to the pressure of the uterus on the ureteric passages, due to which the kidneys cannot cope with the drainage of fluid. The second reason may be associated with increased hydrophilicity of tissues, which is accompanied by swelling of an internal or external nature or dropsy.
Pregnant women must be monitored by a doctor. If characteristic signs are identified, the specialist will prescribe the necessary treatment, establish fasting days, create a drinking regimen, and dietary nutrition.