Diagnostics
To identify the disease, the ophthalmologist performs a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- study of the fundus;
- measurement of IOP (intraocular pressure);
- ultrasonography;
- pachymetry (diagnostic method in which the thickness of the cornea is measured);
- visometry;
- biomicroscopy.
How is biomicroscopy performed?
This disease is characterized by an increase in the horizontal size of the cornea. If a patient’s cornea size is 2 mm larger than normal (which is determined depending on the patient’s age), then he is given an appropriate diagnosis. For example, for newborns the norm is a cornea of 9 mm, therefore, if the baby has a cornea larger than 11 mm, then he will be diagnosed with megalocornea.
Large cornea in a child
The cornea
is one of the most important optical structures of the eye. She is very vulnerable due to almost continuous contact with the environment while awake.
Since the cornea is located in the area of the open palpebral fissure, it is most exposed to light, heat, microorganisms, and foreign bodies, so various morphophysiological and functional disorders can occur in it.
Post-traumatic and inflammatory pathology of the cornea is especially unfavorable, since it is often not strictly isolated due to the common blood supply and innervation of the cornea and other parts of the eye (conjunctiva, sclera, choroid, etc.).
Corneal pathology occurs in the form of congenital anomalies, tumors, dystrophies, inflammation and damage.
Corneal abnormalities
Corneal anomalies are often characterized by changes in its size, radius of curvature, and transparency.
Microcornea
Microcornea, or small cornea
, a condition of the cornea in which its diameter is reduced. When measuring the cornea, it is revealed that it is reduced in comparison with the age norm by more than 1-2 mm, i.e. the diameter of the cornea of a newborn may be not 9, but 6-7 mm, and of a 7-year-old child - not 10.5, but 8-9 mm, etc.
Macrocornea
Macrocornea, or megalocornea
, - a large cornea, i.e. its dimensions are increased compared to the age norm by more than 1 mm.
Depending on the magnitude of deviations from the age norm, they can affect clinical refraction and visual functions to varying degrees, since this changes the radius of curvature of the cornea, and sometimes its transparency.
In addition, it should be borne in mind that conditions such as micro- or macrocornea may be accompanied by increased intraocular pressure.
Therefore, it is necessary to examine the intraocular pressure in every child with both a small and a large cornea.
Such conditions are usually not treated. There may only be a need for spectacle or contact correction of ametropia of various types and sizes.
Keratoconus
Keratoconus
- a condition of the cornea in which its shape and curvature are significantly changed (Fig. 89). In this case, predominantly its central part protrudes cone-shaped. The presence of such an anomaly should be assumed in cases where a decrease in visual acuity is detected in children with transparent refractive optical media and a normal fundus.
Rice. 89. Keratoconus
In such cases, it is necessary to determine the shape, curvature and refraction of the cornea (keratometry, ophthalmometry, refractometry). In this case, pronounced astigmatism is always detected, often irregular. Keratoconus often has a malignant course, i.e. its degree increases, and most importantly, clouding of the cornea occurs and progresses, and at the same time vision decreases sharply.
Biomicroscopic examination reveals ruptures of the basement membrane of the epithelium, thickening, fibrillary degeneration and cracks of the anterior limiting plate (Bowman's membrane), folds and bends of the posterior limiting plate (Descemet's membrane).
The process occurs more often at the age of 8-9 years and older, develops slowly, usually without inflammatory phenomena. As a rule, both eyes are affected, but not always at the same time and to varying degrees. In the initial stage of the disease, a protrusion (cone) appears, the degree of which and the direction of the axes periodically change. Gradually the top of the cone becomes cloudy.
Sometimes corneal hyperesthesia occurs, accompanied by pain and photophobia. The apex of the cone may re-ulcerate and even perforate. Sometimes a condition called acute keratoconus occurs: the posterior limiting plate ruptures, allowing chamber humor to penetrate the cornea and cause edematous stromal opacification.
Posterior keratoconus is extremely rare.
. The cornea has a normal structure, but its posterior surface is thinned, which is more curved than usual.
Keratoglobus
Keratoglobus
characterized by the fact that the surface of the cornea has a convex shape not only in the center, as with keratoconus, but throughout its entire length.
Ophthalmometry reveals an altered radius of curvature of the cornea in different meridians, which is accompanied by astigmatism.
Vision with keratoglobus is often reduced according to the degree of change in corneal curvature, i.e., the amount and type of ametropia.
Source: https://mir-ua.ru/bolshaja-rogovica-u-rebenka/
Possible complications
As a rule, this disease is characterized only by an increase in the horizontal size of the cornea (there are no other pathological changes).
However, due to the increased size of the cornea, an increase in the amount of interchamber fluid is possible, which can lead to disruption of the lens and retina. As a result, the following complications may occur:
- displacement or dislocation of the lens, phacodonesis (tremor of the lens), iridodonesis (tremor of the iris);
- development of cataracts;
- pigmentary glaucoma;
- possibility of retinal detachment;
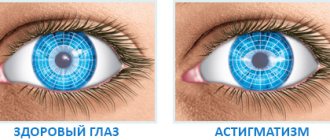
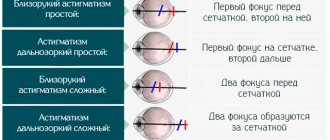
- the appearance of astigmatism or myopia (this is in cases where there is also curvature of the cornea);
- embryotoxon development is an abnormal clouding of the cornea in a circle;
- the development of miosis (constriction of the pupil) is possible.
Treatment
The disease we are considering does not require special treatment if there are no other pathological changes (for example, there is no impairment of visual acuity, intraocular pressure remains unchanged).
However, despite the absence of a threat, it is necessary to regularly visit an ophthalmologist.
If megalocornea accompanies other visual impairments (astigmatism, myopia, etc.), then correction with glasses and contact lenses is necessary.
At the same time, it is quite difficult to perform eye surgery in this case, since there is a high risk of complications (such as lens dislocation, rupture of the posterior capsule, displacement of the artificial lens, and so on).
Preventive measures
Today, unfortunately, no effective prevention methods have been developed that can prevent congenital changes in the cornea.
However, due to the fact that this disease is often diagnosed in newborns, doctors give some recommendations specifically to pregnant women:
- During this period, you should pay special attention to your diet. It must contain all the necessary substances, vitamins and minerals. A pregnant woman must include fresh fruits and vegetables in her diet.
- Experts recommend spending more time outdoors.
- Don’t forget about your daily routine: you need to combine rest, work and sleep.
- It is necessary to avoid stressful situations, as well as other negative emotional experiences.
- You should not neglect routine examinations by specialists and follow the necessary doctor’s recommendations.
- It is also recommended to protect yourself from colds and viral diseases.
If you follow the recommendations of specialists, the risk of developing the disease in a newborn baby will be minimal.
Megalocornea in children - causes, symptoms and treatment
Megalocornea is a fairly serious eye disease when the total diameter of the cornea exceeds the normal dimensions corresponding to the standard by more than two millimeters. For example, when a newborn baby has a total diameter of one or two corneas exceeding 11 millimeters, and the norm is 9+1 millimeters, in such cases a diagnosis of megalocornea disease is made.
Development of the disease
If, with the development of this pathology, a violation of the normal transparency of the cornea does not occur, the anterior chamber takes on a more enlarged and deeper state, in contrast to the norm. At the same time, the condition of the eyeball will be in a normal state, and no congestion will be observed. The state of palpation and ophthalmotonus also remains within normal limits.
When this disease has been discovered, it is imperative to consider the possibility that obtaining an enlarged cornea may be a very basic sign of the presence of congenital glaucoma (this disease is also called hydrophthalmos). In this case, a note is placed in the completed baby’s chart indicating that the patient was found to have an anomaly in the development of the cornea of the eye. There are suspicions of congenital glaucoma.
Megalocornea differs from hydrophthalmos mainly in that it does not tend to progress, which is why the cornea can remain transparent for a long time. Development of the disease:
- does not cause thinning and serious expansion of the limbus;
- does not cause any ruptures in Descemet's membrane;
- glaucomatous excavation and functional disorders are not observed;
- intraocular pressure is normal.
In the absence of the listed symptoms and signs, a final diagnosis can be made during the examination of the patient.
Possible complications
With the initial development of megalocornea disease, a serious deviation from the normal radius of curvature of the cornea of the eye may be observed (the deviation usually increases), as a result, the cornea acquires the lowest optical power.
The patient's anterior chamber becomes much deeper, and there is also a likelihood of developing ametropia. If the patient has a unilateral symptom, there may be a risk of developing the disease anisometropia. As a result, this may lead to accelerated progression of amblyopia.
The worst thing is that strabismus may develop. In this case, the child must definitely visit an ophthalmologist. The specialist will be able to conduct a thorough check of your visual acuity and assess the condition of the entire fundus, ophthalmotonus and refraction.
It may also be that a small patient will be prescribed the necessary preventive measures to prevent strabismus and amblyopia. When an accurate diagnosis of congenital glaucoma is made, the patient is prescribed urgent treatment, because only in this case is it possible to prevent the development of complications.
In exceptional cases, the patient experiences embryotoxon, ectopic pupils, and miosis, which may result from dilator atrophy. In addition, pigment deposition on the back surface of the cornea, displacement of the lens and other processes may occur.
Symptoms of the disease
This serious disease is considered a certain defect in successful development that is congenital in nature. Very often, such a disease can be in the nature of family-hereditary anomalies. It is important to consider that megalocornea is in many cases a sign of hydrophthalmos.
Sometimes sick patients may experience embryotoxon and mycosis, as well as ectopic pupils. This leads to unwanted dilator atrophy. In addition to all of the above, lens displacement, pigment deposition and other serious associated anomalies are possible on the back surface of the cornea of the eye.
To diagnose this disease, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the patient and establish an accurate diagnosis. This can only be carried out by an experienced, highly qualified ophthalmologist; usually the pathology is noticed during a routine examination of infants.
For vision, the prognosis is most often favorable, because menalocornea is not capable of having a bad effect on the level of your visual acuity; you can find out about this from the specialists who will examine you. Remember that the diagnosis of megalocornea can only be established by a professional specialist who has extensive experience of successful work in this industry.
Prevention
Unfortunately, today there are no sufficiently effective methods for prevention. Therefore, it is impossible to completely prevent the development of such an unpleasant eye disease as megalocornea, because it is congenital.
Because, in most cases, this disease is detected in newborns and during pregnancy, a woman should be especially attentive to her health. Prevention of the disease includes following the recommendations of a specialist and following all his indications. In this case, the consequences may be completely harmless to the patient.
The patient’s diet must be balanced and complete, and must also contain a sufficient amount of beneficial vitamins and minerals, which are required for the proper formation of a healthy fetus.
It is also important to walk in the fresh air as much as possible, undergo regular scheduled examinations with a doctor, and also consult trusted specialists about the exact reasons that caused the onset of the development of this eye disease.
In this case, when during pregnancy a woman strictly follows all of the above recommendations, the likelihood of complications developing can be reduced to a very minimum.
Treatment
Megalocornea currently requires absolutely no treatment, because it is not capable of having a possible negative effect on the general condition of vision. It does not matter when the patient was diagnosed with the disease; at any age, there are no unpleasant prognoses associated with vision loss for the patient.
The stage of the disease and the age of the patient do not affect its course and the occurrence of possible complications. To avoid possible worries for parents when a child is diagnosed with a disease, they should be advised to regularly undergo a full examination by an ophthalmologist.
Source: https://o-glazah.ru/drugie/megalokornea.html