Diagnosis in children
Difficulties in the perception of nearby objects are divided into degrees, which allows you to understand whether such vision is normal for a child at a certain age or not:
- weak degree - normal for preschoolers. By the time you enter school, the eye will have “ripened” and the problem will resolve itself;
- moderate degree - deviation from optimal vision ranges from 2 to 5 diopters. This is normal for preschoolers and first-graders (since they are not yet accustomed to school loads). But already in second-graders such a deviation is a signal to contact an ophthalmologist;
- high degree (highest degree) – abnormal for any age, deviation from normal vision > 5 diopters. If such vision is detected in a one-year-old baby, he should be regularly examined by an ophthalmologist to avoid progression. This condition requires correction with glasses or lenses; without them, a person sees quite poorly both near and far.
How is it determined whether there is a violation? Young patients undergo diagnostic vision tests annually. Babies first undergo an ophthalmological examination at the age of 3 months, and after that at one year. In this case, medications are used that dilate the pupil, for example, atropine or mesaton. The ligamentous apparatus relaxes, and the doctor sees the real picture of refraction.
The following diagnostic methods are also used:
- fundus examination (ophthalmoscopy);
- examination of the retina and blood vessels (retinoscopy);
- examination through a slit lamp (biomicroscopy).
In addition to an ophthalmological examination, if diseases that contribute to the development of decreased visibility are suspected, instrumental studies such as MRI or ultrasound are prescribed.
Definition of disease
Hypermetropia has a more common name - farsightedness. With this disease, the image of objects located in the distance is reflected at a certain point on the retina, and in the area behind it. It is characterized by weak refraction, when there is a strong load on accommodation to display distant objects.
Farsightedness and hypermetropia are common among newborns due to the specific structure of the organ of vision. The size of the organ itself is still significantly small for the refractive power of the lens, so the image is distorted towards a hypermetropic deviation. As a rule, before 6 years of age, the eye is fully formed and the disease goes away on its own. Doctors do not prescribe any correction, because... this can harm natural development. If the child has not “outgrown” farsightedness, then treatment is selected.
In addition to the congenital nature of the disease, there is also a natural change in the organ of vision due to age. This farsightedness is called presbyopia and is caused by a change in focal accommodation. The lens becomes less elastic with age, causing it to lose its ability to change curvature when viewing smaller objects.
Like any other disease associated with impaired visual function (astigmatism, farsightedness), hyperopia has its own degrees:
- Weak - up to 3.0 D - is characterized by a slight deviation when viewing objects at a distance, but the perception of objects close up changes significantly. Another concomitant symptom is eye fatigue (asthenopia).
- Average – from 3.25 to 5.0 D – visual function is significantly reduced when examining small objects (reading, working with fine motor skills), distance vision remains good.
- High – from 5.25 and above – vision is impaired when viewing objects at a distance and near.
Diagnostics at six months and a year
After three months, the baby’s vision becomes better, he can already keep his eyes on the toy and pick it up. Parents should be wary of the following points:
- frequent redness of the eyeballs;
- discharge;
- persistent strabismus;
- rhythmic vibrations of the eyes.
If one of these symptoms appears, you should not wait for a scheduled check-up; show your baby to an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Checking the visual acuity of a six-month-old child is performed in the same sequence as for a three-month-old child. The degree of farsightedness may decrease slightly or remain at the same level. The research results must be compared with previous ones. There should be no squint at this age. The retina becomes pink, and the optic disc becomes pale pink and has precise contours.
At one year of age, a child with normal visual acuity can distinguish objects well and perceive the facial expressions of others, but it is worth considering that vision during this period is still different from that of an adult. At an appointment with an ophthalmologist, viziometry, skiascopy or autorefractometry is performed, which allows you to clarify the degree of refraction.
Farsightedness should decrease compared to the values obtained at six months and range from +2.5 to +3.0 diopters. A child’s visual acuity is then checked when he or she reaches the age of two, when registering for a preschool (mostly 3 years old), at 4 years old, and also before entering school. Normally, there should be no visual disturbances during this period. During study, examinations are performed annually.
What is myopia in childhood
Myopia in children is a visual impairment in which the image of distant objects is not focused on the retina and therefore appears blurry. This can be caused either by an irregular shape of the eyeball - more elongated, or by too much refraction of the rays in the eye.
Most newborns who are born at term have a so-called reserve of farsightedness - vision of +3...+3.5 diopters. This is due to the fact that the eyes of newborn babies are still very small. In order for the eye to have normal optical power when it grows, it exhausts this reserve of hypermetropia as it grows, and by the time the eye’s formation is complete, vision becomes normal. If this reserve is initially not there or is insufficient, then the baby at a certain age becomes myopic.
Features of preschoolers
If the baby cannot speak yet, it is not easy to notice his vision problems
Therefore, it is important not to neglect preventive appointments with an ophthalmologist, even if parents see no reason to worry. They are carried out in the maternity hospital, then at 3 months, at six months, at a year, and at such an examination the doctor will be able to determine whether the child has myopia
In children under one year of age, myopia is rare; this is due to the natural reserve of farsightedness. At this age, myopia can be congenital; this happens in premature babies. Such babies should be constantly monitored by an ophthalmologist. One of the signs of myopia in a baby may be divergent strabismus.
In young children 3-6 years old, it is easier to notice visual impairment: they can speak and can report that they have difficulty seeing. In addition to this, there are other obvious signs: the baby comes close to objects to see them, and begins to instinctively squint, looking into the distance.
Features of schoolchildren and teenagers
Myopia in school-aged children is much more common. It is the primary and secondary school age that is most rich in the onset of myopia. At the age of seven, a child begins schooling, which means that the load on his eyes increases significantly, while the eyeball continues to grow in length. A few hours at school, then homework, and in between - a mobile phone, TV or tablet. The eyes work constantly, and this leads to the fact that myopia in school-age children can begin to develop quite quickly.
Whether myopia can be cured at school age depends on the type. We can definitely say that false myopia is curable - a disorder of distance vision caused by a spasm of the eye muscle. This condition can develop at the age of 7, 10, and 17. After the spasm is relieved, vision is restored.
Treatment
For timely diagnosis, it is recommended to conduct a preventive vision examination at least once a year. It should be borne in mind that a routine examination will not reveal hypermetropia in a child. Detection requires special studies, since a weak degree of farsightedness can be compensated by the accommodative apparatus of the eye.
Subsequently, such hidden farsightedness necessarily progresses and makes itself felt by headaches and rapid eye fatigue. In the later stages of the disease, the only method of correction is surgery.
Drug therapy
The main treatment method in the early stages of detecting pathology is wearing glasses and contact lenses. Up to 3 years of age, as a rule, such correction is not prescribed, since the child’s visual apparatus is still in the formative stage.
Glasses are prescribed to younger children, and contact lenses - in adolescence, when the child already understands all the responsibility when using this product. And most importantly, he can independently fulfill all sanitary and hygienic requirements associated with the use of lenses.
To relieve spasm and train all oculomotor structures, hardware and physiotherapeutic treatment can be used.
These methods include:
- Transcutaneous electrical stimulation, which improves the quality of blood supply to the ocular structures;
- Electrical stimulation with a low-intensity laser, which also has a positive effect on increasing blood supply and circulation of intraocular fluid;
- Color pulse stimulation;
- Exposure to ultrasound;
- Vacuum massage;
- Electrocoagulation.
In addition to the above remedies, the doctor can prescribe the necessary medications in accordance with individual indications for each child. These will most likely be drops to improve vision.
The duration of wearing glasses and lenses depends entirely on the degree of hypermetropia and the stage at which treatment began:
- With a low degree of farsightedness, which does not go beyond age norms, the correction will be temporary, and the need for it will completely disappear when the formation of the eye structures is finally completed;
- With a high degree of hypermetropia, which does not go away with age even after correction, wearing glasses is mandatory on a regular basis;
- For moderate farsightedness in children 7 years of age and older, glasses correction or wearing lenses (as prescribed by a doctor) can only be used for near work.
Surgically
If there is no effect from conservative treatment methods, when the child reaches 18 years of age, surgical correction of vision is possible in order to get rid of farsightedness.
Surgical methods can be carried out in the following way:
- Scalpel operation;
- Laser correction.
To restore normal visual perception, the refractive power of the lens or cornea is corrected in the direction of strengthening it. In this way, the image entering the eye is focused on the central organ of perception - the macula (macula).
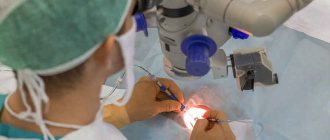
Carrying out laser correction
Depending on the patient’s condition, the operation can be performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital, and its average duration is 15-20 minutes. Today this is one of the most effective methods of vision correction. The only negative point is the presence of several contraindications.
Characteristics of the treatment process
To eliminate farsightedness, you need to regularly train the organs of vision, while the load on the eyes alternates.
The following methods are effective:
- You need to alternate between drawing and reading.
- Doctors insist that children move actively. When the blood is well saturated with oxygen, all organs develop normally, in particular the eyes.
- You should additionally take medications that accelerate metabolic processes in tissues. But since such remedies, in most cases, are not a cure, you should not hope that only they can cure farsightedness.
- Microsurgical intervention is not performed for children under 3 years of age. This is due to the active development of the ocular apparatus.
- Laser surgery is only used when the patient is over 18.
- Vacuum massage and electrical stimulation would be appropriate.
- Auto-training is often used.
As already mentioned, hypermetropia is normal before the age of 3, and is usually not corrected. It is dangerous for a child to use glasses or contact lenses. Doctors advise not to worry too much if there is a mild degree of the disease. It will most likely go away on its own. Of course, there are exceptions, and even young patients are diagnosed with a high stage of pathology.
Older children are prescribed glasses if the doctor decides that they really cannot be avoided. Contact lenses can be used during adolescence.
Most often, the child is recommended to wear glasses. True, this is not always comfortable, because they can slip, fall off, that is, it is difficult to actively move with them. As for the lenses, it takes time to get used to them. For some, lenses are contraindicated.
Vitamin therapy occupies a special place. If hypermetropia is detected, vitamins should be supplied to the body. It is desirable that they have a natural shape.
That is, we are talking about the use of:
- peaches, bananas;
- prunes, apricots;
- walnuts, dried apricots, raisins;
- carrots, tomatoes, cabbage, peas.
The named products contain potassium. In order to have enough vitamin C and A, it is recommended to include rose hips, zucchini, and citrus fruits in the menu.
Treatment of farsightedness in children will be effective if they are given wild blueberries to eat, which perfectly improve visual functions and help get rid of fatigue.
Correction and treatment
Hypermetropia can be treated in different ways. Depending on the degree of visual impairment, conservative, laser and surgical treatment may be offered.
Conservative treatment is limited to vision correction with glasses or lenses. Here, each person decides for himself what he likes best. A person feels more confident wearing lenses, but such optics are not suitable for excessive eye sensitivity
Glasses require less financial investment, but you should be careful when wearing them
Conservative treatment necessarily includes hardware procedures and taking various vitamin preparations. Optics are effective only at the initial stage of the disease, when vision is not yet severely impaired.
Laser correction is suitable if vision is no more than +5 diopters. In most cases, this treatment is recommended for patients aged 18–45 years. Using a laser, the doctor removes part of the eye tissue, correcting the curvature. This method of treatment is the most preferable. Laser correction is performed on an outpatient basis, it is painless and recovery is quick.
Surgery is indicated only in severe cases. Lens replacement or phakic lens implantation may be recommended. In some cases, plastic surgery of the corneal layer is indicated.
Symptoms
Symptoms of hyperopia may vary depending on the degree of hyperopia:
- With weak farsightedness in a child, usually, determination of visual acuity shows high results, both at long and near distances, but at the same time he may complain of fatigue, dizziness and headache.
- If a child has an average degree of hypermetropia, he can distinguish objects well at long distances, but visual acuity at close distances is quite reduced.
- With high degrees of farsightedness, vision is quite difficult both at close and long distances. This is caused by the eye's inability to focus the image on the retina.
Symptoms of the disease
Farsightedness in young children is often a physiological norm and is asymptomatic. Often, the first signs of hypermetropia appear only at the age of 5-7 years. The main manifestation of the disease is unclear visibility of objects placed at a distance of less than half a meter from the organs of vision.
At the initial stage of the pathology, the following signs may be observed indicating the presence of hypermetropia:
- rapid eye fatigue;
- frequent migraines;
- dizziness;
- tearfulness;
- irritability;
- insomnia.
If the degree of refractive error exceeds 3 diopters, then the child becomes capricious and withdrawn, cannot perform the same work for a long time, or concentrate vision on one object for a long time. In the initial stages of development of the pathology, only near objects are unclearly visible, and in advanced forms of hypermetropia, distance vision also deteriorates. Various inflammatory processes in the organs of vision, burning and sensation of a foreign object in the eyeball often occur.
If farsightedness treatment is not started in a timely manner, there is a high risk of developing the following complications:
- Strabismus. When trying to see an object, the child begins to squint and tilt his head, which can lead to the development of strabismus - a deviation of the central axis of vision from the norm.
- Amblyopia. With an advanced form of farsightedness, the baby often strains the healthy eye, and the second organ of vision remains unused. This leads to the fact that the eye ceases to participate in the visual process and loses its functionality.
- Spasm of accommodation. The brain tries to compensate for the lack of an adequate level of vision, as a result of which its functionality is significantly reduced, and prolonged static tension of the eye muscle is observed.
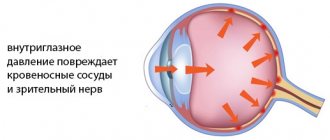
- Glaucoma. Progressive hypermetropia can disrupt the outflow of intraocular fluid, which will provoke an increase in ophthalmotonus and the development of glaucoma.
Farsightedness in children is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms that can lead to the development of various unpleasant consequences.
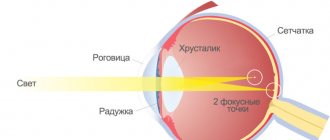
What it is
What is farsightedness?
Hypermetropia is a vision pathology characterized by the fact that the light refraction of the eye changes, and as a result, the image is focused behind the retina, and not on it, as it should be normally. Thus, with farsightedness, a person clearly sees objects that are far from the eyes.
People with hypermetropia may have a shortened ocular axis, or the cornea may have weak refractive power.
Farsightedness is due to the fact that the refractive power of light rays is not great, so the rays that come from distant objects and pass in parallel through the eyes converge not on the retina, but behind it. Doctors suggest that hypermetropia is a congenital vision pathology, but it can occur after removal of the lens or as a result of diabetes.
The causes of cataracts, symptoms, treatment and prevention are described here.
This kind of farsightedness is difficult to diagnose, so over time the disease progresses, leading to serious problems.
What other exercises exist to restore vision can be found in the article.
Children may not notice deterioration in vision for a very long time, but they may experience some discomfort, headaches and irritability.
General information
Congenital hyperopia (farsightedness) is a change in refraction. That is, light rays hitting the pupil of the eye begin to refract and focus behind the retina, and not on it, as it should be in a healthy person. As a result, a person begins to see nearby objects poorly, but he sees images located in the distance clearly. The reason for this is the shortening of the eyeball.
Newborn babies have exactly this structure of their visual organs, and this is considered the norm.
In an adult, fully formed person, the length of the eyeball is from 2 to 4 centimeters, while in infants this figure is equal to 1.8 centimeters.
As children develop, the shape of their eyes begins to change, and they begin to see all objects clearly. Unfortunately, in 25% of cases of farsightedness, a child at the age of seven continues to see objects blurry. Such children need consultation with a professional ophthalmologist and immediate vision correction, otherwise it will be too late and hypermetropia cannot be corrected. How mild hypermetropia manifests itself is described in this material.
Treatment of farsightedness in children
There are conservative and surgical methods for treating farsightedness in children.
The main non-operative method is the selection of spectacle or contact correction.
It must be remembered that the effect of the drug is temporary, and non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations leads to the fact that due to a certain discomfort that occurs when wearing without achieving persistent cycloplegia, the child will take off his glasses. In this case, farsightedness will either progress, or vision will be significantly reduced, which can lead to amblyopia - “lazy eye” syndrome.
If spectacle vision correction is adequately selected and the child is old enough to wear lenses, contact vision correction can be used. In the case of hypermetropic astigmatism, it is possible to select lenses with an astigmatic component.
To avoid unwanted diseases, you should follow the rules for wearing and caring for lenses, which will be explained in detail by your ophthalmologist.
Surgical treatment can only be performed on those over 18 years of age. It consists of one type of laser vision correction, implantation of special phakic lenses, or planned removal of the lens with implantation of an intraocular lens. This age was not chosen by chance, since it is believed that it is before this age that the anatomical and functional development of the organ of vision occurs. For patients with astigmatism, there are toric lenses that take into account the astigmatic component.
Surgical treatment is selected taking into account all the individual characteristics of the patient. It is possible to carry out combined surgical interventions in order to obtain the highest visual acuity.
Symptoms of childhood farsightedness
The main manifestation of childhood farsightedness is the inability to clearly see objects located nearby. To do this, he strains his eyesight.
With mild farsightedness (up to 2 diopters), the activity of the eye muscles is compensated by good contractility and elasticity of the eye lens. Provided that the ciliary muscle contracts, the eye lens has a convex shape, and the center of refraction is fixed on the retina. Thus, the child sees well at different distances. Prolonged eye strain leads to pain in the head, fatigue, eye fatigue, and nervousness. Such children often fall behind in their studies.
When the degree of refraction is from 2 to 5 diopters, the doctor detects an average degree of defect in the child. These children have excellent distance vision, but the ability to clearly distinguish objects located in the distance is gradually lost.
With moderately developed hypermetropia, children are not able to concentrate on one task for a long time. The older ones (after 9 years) note that they had “sand poured into their eyes.”
With severe farsightedness (more than 5 diopters), patients have difficulty seeing far and near. The visual part of the brain is damaged because normal images are not received here and the cells cannot develop properly. This leads to amblyopia (“lazy eye syndrome”). If a child has farsightedness, complete vision correction is impossible (its acuity does not reach 100 percent with glasses). Long-term development of severe hypermetropia leads to the formation of strabismus.
Causes
Explicit and latent forms of farsightedness in children can develop due to the following reasons:
- Loss of transparency and cloudiness, irregular curvature of the cornea;
- Slow and abnormal development of the eyeballs and the visual apparatus as a whole;
- Pathologies and developmental disorders of the lens (or lack thereof);
- Traumatic injuries.
You should also pay attention to congenital factors that lead to improper formation and further development of the visual organs:
- Mother's stress during pregnancy;
- Bad ecology;
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy, non-compliance with the regime.
Is it possible to warn?
Are there methods to prevent the disease? In order to prevent the occurrence of farsightedness or detect the disease in time and begin treatment, it is necessary:
- Regularly visit an ophthalmologist for preventive examinations.
- Monitor the variety of your child’s diet (include foods rich in vitamins and microelements).
- Properly organize the place where the child will study (maintain the correct height of the chair and desk, monitor the lighting).
- Limit your child's time at the computer or TV.
- Take your baby for walks in the fresh air more often.
Farsightedness that appears at a young age (up to a year), as a rule, does not cause serious discomfort to the child, and by the age of 4 it can go away on its own .
Things are worse if the child has already started school, and signs of the disease are still making themselves felt.
In this case, treatment is necessary; the choice of one or another method is made by the doctor after diagnosis.
An ophthalmologist talks about farsightedness in children in this video:
Causes
Farsightedness in older people is a natural phenomenon due to age-related changes in a person. This is due to the loss of elasticity of the lens and due to weakening of the muscles that hold it. Against the background of these changes, a person’s visual acuity decreases.
In addition, the occurrence of this problem is often associated with the following factors:
- flat cornea shape
- short length of the eyeball;
- decreased accommodative abilities of the lens.
The appearance of these eye defects can be caused by a number of reasons:
Hereditary factor. If one of the parents has been diagnosed with farsightedness, the child must be regularly shown to an ophthalmologist. The presence of various pathologies. The trigger for the occurrence can be other human diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, myopia and astigmatism. Congenital form. The baby’s vision function is formed at the initial stage of development, immediately after conception.
Therefore, during this period it is especially important to monitor a woman’s health, avoid stressful situations, and eliminate bad habits. A mother's healthy lifestyle is a prerequisite for giving birth to a healthy baby.
In children, the presence of this disease is common, especially at an early age, which is associated with an anomaly in the anatomical structure of the visual organ. Since a baby of this age has an eyeball that is smaller in size than necessary. However, with further growth it increases, and the problem goes away on its own. The appearance of this pathology in children is associated with a congenital defect, which is expressed by weak refractive power of the lens or cornea.
Causes
Children's farsightedness can occur for the following reasons:
- Violation of the anatomical structure of the eye, for example, deepening of the lens, its irregular shape, short ocular axis or insufficient curvature of the cornea. This type of pathology is called congenital farsightedness.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Increased intraocular pressure (glaucoma).
- Poor nutrition of a pregnant woman, bad habits of the mother during pregnancy.
At one year of age, an ophthalmologist must examine the child’s eyes using special instruments.
Congenital farsightedness in children can go away 3 months after birth, since the eye organs of a child up to one year old are rapidly developing. But if the pathology remains, then constant medical monitoring is needed. Usually we are talking about high degree hypermetropia.
Farsightedness in children under one year of age is also called physiological. It is normal and is caused by a shortened size of the eyeball. This feature of the eye structure is inherent in all newborns under the age of 2 months. The pathology goes away on its own and does not require treatment.
Visual gymnastics for hypermetropia
You can cope with farsightedness in a child with the help of visual gymnastics. A properly selected set of exercises helps improve blood supply, strengthen the eye muscles, and enhance the accommodative ability of the lens. You can correct farsightedness and restore your vision by regularly performing the following exercises:
- Close your eyes and relax your eyelids. From above, additionally cover your eyes with your palms, creating darkness. In this position, move your eyeballs sideways for 1-2 minutes.
- With your eyes open, move left and right and up and down.
- Draw an imaginary figure eight and other numbers and shapes with your eyes.
- Standing in front of the clock, alternately look from 12 to 3, and then to 6 and 9. Repeat the exercise 3 times and then do it in the opposite direction.
- Standing at the window, you need to carefully look at the palm of your hand for a few seconds, then move your gaze to the window frame and then examine the objects located on the street.
- Slowly move your gaze from nearby objects to those that are much further away and vice versa.
When working with a child suffering from congenital farsightedness, it is necessary to ensure that he does not get tired and is interested in the exercises, otherwise he will quickly get bored with it and there will be no positive result. You can cure hypermetropia in a baby only with a good amount of patience. In addition to performing visual gymnastics, it is recommended to read small inscriptions located at a distance of 25 cm from the eyes. To restore vision, you should also alternate visual loads on the organs of vision, alternately closing one or the other eye while reading, drawing or watching TV.
Symptoms to suspect farsightedness
Childhood farsightedness has a number of indirect symptoms that allow attentive parents to suspect this refractive error and promptly consult an ophthalmologist:
low visual acuity or its decrease. A 2-3 year old child examines fairly large objects at close or very far distances. Carefully watch the child to see if he always does this or is just playing. If your baby has a sufficient vocabulary, you can try to test his visual acuity by placing his toys at different distances. And ask to show where which one is
For a 4-5 year old child, you can try showing pictures, circles, letters at a distance;
It is difficult for a child to concentrate his attention on activities that involve the development of fine motor skills and books. In this case, try to determine whether the baby likes what he is doing.
Perhaps he is simply tired of fixing his gaze up close, or he does not like this activity; after creative reading activities, the child complains of a headache; the appearance of progressive strabismus. Children under 1.5 years old may squint their eyes in an attempt to look at an object. This is explained by the imperfection of gaze fixation mechanisms. If strabismus does not decrease, but intensifies, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment of farsightedness in children
Farsightedness in children up to 3 diopters is normal and does not require treatment. But if by the age of three the number of diopters does not decrease or the baby was born with a high degree of hypermetropia, then vision correction is necessary. To select a treatment method, you should contact a pediatric ophthalmologist.
An ophthalmologist's diagnosis is made based on the results of the following diagnostic studies:
- medicated pupil dilation;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- visometry;
- tonometry;
- biomicroscopy;
- Ultrasound of the eyes.
Additional diagnostic methods may be prescribed to assess the condition of the visual organs and select the correct treatment. Physiological farsightedness in a child does not need correction. The pathological form of hypermetropia can be treated with the following methods:
- Spectacle correction. Prescribed in the absence of improvement no earlier than 3 years. Glasses are selected individually and are intended for constant wear. The period of spectacle correction depends on the stage of the disease.
- Lens correction. For older school-age children, soft contact lenses may be prescribed. Most often, the lens correction method is necessary for children who simultaneously suffer from amblyopia. Lenses are more convenient to use than glasses, but can cause an allergic reaction.
- Hardware treatment. It is used both for the treatment and for the prevention of childhood farsightedness. Hardware therapy for hypermetropia may include the following techniques: electrical stimulation, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, vacuum massage, stimulation with light pulses, the use of massage glasses, electrocoagulation. To achieve a positive effect, eye physiotherapy must be performed at least 3 times a year. All of them are absolutely painless, effective and interesting for children. Various computer programs are also prescribed for the treatment of farsightedness.
- Laser surgery. Prescribed for advanced forms of farsightedness in children over 16 years of age. Promotes complete restoration of visual functions.
In addition to the above methods of treatment for farsightedness in children, visual gymnastics, vitamin therapy, and massage of the collar area are prescribed.
How do physiological farsightedness differ from congenital farsightedness?
So, the norm for farsightedness in children under 5-6 years of age is no more than +4 diopters. After 6 years it decreases noticeably. Between the ages of 8 and 10 years, eyeball growth is at its fastest. During this time, vision usually returns to normal, although in some cases the eyes may change their shape as a result of body growth up to 18-20 years.
Farsightedness is observed in all children under 6 years of age. It can be distinguished from congenital hypermetropia, which already has a pathological basis, during a routine examination by an ophthalmologist.
Most often it is detected during an examination, which is carried out at school in the first grade. Children of preschool age are not always examined annually, so congenital farsightedness can progress, thus “hiding behind” the physiological form of this refractive defect. Parents who themselves suffer from it should check their child’s vision more often in order to notice the development of the disease in time.
Treatment Options
If a child’s farsightedness progresses, there is no need to panic under any circumstances. Modern medicine has achieved such development that many problems in the functioning of the visual apparatus can be completely eliminated without harm to the future health of the baby.
How to restore vision with farsightedness? Treatment methods most often used in this case:
- Prescribing glasses that can not only correct hypermetropia, but also eliminate strabismus.
- Prescribing eye gymnastics, which helps improve muscle function and reduce the development of the problem.
- Hardware therapy is used, with the help of which in just 5-7 sessions it is possible to significantly reduce the degree of development of farsightedness.
An effective remedy for combating pain and swelling is the instructions for Diclof eye drops.
It is important not to create problems from the necessary vision correction
If deviations from the above standards do not exceed 2.5 diopters, treatment is usually not carried out. It is believed that this problem will disappear on its own with age. However, doctors recommend being examined as often as possible in order to notice deviations in time.
Dr. Komarovsky also speaks about this. The famous doctor notes that childhood farsightedness and astigmatism are extremely common problems, and in no case should they be ignored. It is recommended to regularly engage in eye exercises with children, wear special glasses with blinders for astigmatism, and have their vision checked by a doctor.
Dr. Komarovsky recommends using glasses until the doctor notes progress in treatment.
Breastfeeding is the basis for the formation of healthy organs (including visual ones)
Possible methods of treating age-related farsightedness are described in the article.
How to recognize the disease
Problems with seeing objects are easy to recognize if parents are attentive to their growing children. Babies blink frequently and then open their eyes wide. School-age children can already tell themselves that they see poorly - reading and writing are difficult for them, since they require looking at elements up close. Previously favorite pastimes may not please you - construction sets, puzzles, drawing, etc. Even computer games may not be attractive because they cause discomfort in the eyes and headaches.
Diagnosis of eye hypermetropia in children of weak, moderate or high degree is performed by an ophthalmologist. There are special tables for this, as well as hardware research methods.
CHOOSE A CONVENIENT CLINIC. CHECK YOUR VISION →
Our website contains clinics and ophthalmological medical centers from all over the country - and this list is constantly expanded and updated.
Prevention measures
The main preventive measure is timely examination by a specialist. Therefore, in no case should you neglect regular checks with an ophthalmologist.
Pediatrician Komarovsky’s opinion on the prevention of children’s vision problems:
You can also prevent the progression of childhood farsightedness in the following ways:
- Reasonable planning of work and rest.
- Use of natural and artificial lighting sources when organizing a workplace at home.
- Limit exposure to television or computer by time and distance.
- Preventive exercises for the eyes, carried out during the period of rest from reading or watching TV / working with a computer.
In addition to the above, it is important to prevent the occurrence of possible disorders even at the stage of pregnancy planning:
- eliminate the influence of harmful factors, such as smoking, alcoholism, drugs and, if possible, the impact of negative production factors;
- minimize stress factors;
- normalize the expectant mother’s diet by eliminating unhealthy foods and diversifying the diet with healthy foods;
- rationalize the work and rest regime;
- Maximize periods of exposure to fresh air.
The use of these measures will help prevent rapid progression of vision loss if it already exists. This will also prevent it from appearing in the near future.
It is important to remember that it is imperative to regularly take your child for a medical examination so as not to miss possible violations.
Farsightedness in childhood is not a rare phenomenon. In very young patients this is a variant of the norm, and in newborns it is a completely natural condition, indicating the normal development of the visual apparatus. Over time, the anterior-posterior size of the eyeball will increase, and vision will correct itself. However, you should be wary if your baby shows signs of anxiety, increased fatigue and irritability. This means that the eye grows at a slower pace.
Causes of farsightedness in children - what causes the pathology?
In adulthood, hypermetropia can occur after eye injury, due to complications caused by operations on the organs of vision. Sometimes farsightedness is caused by eye diseases of an infectious nature, as well as tumors in the eye and orbital areas. These factors can cause farsightedness in children, but this happens rarely. Hypermetropia in childhood is mainly due to a genetic factor.
Actually, there are two main causes of farsightedness in childhood: improper eye shape and damage to the eyeball system, which is responsible for refracting light rays. Sometimes the occurrence of hypermetropia is a consequence of both of these reasons.
Physiotherapy
For farsightedness, hardware treatment helps well, thanks to which spasm is eliminated and the eye muscles are trained. This is a secondary prevention of visual impairment.
For mild hypermetropia, especially in childhood, the following techniques help well:
- Visual color stimulation. Exposure of the eyes to light and color pulses. As a result, the functioning of the iris, retina, and lens is restored.
- Software and computer techniques. Synaptophore, amblyocor.
- Laser stimulation. Low-intensity infrared radiation is used. Its effect relieves inflammation, accelerates the outflow of intraocular fluid, and restores blood flow in the vessels of the eye.
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. With its help, the trophism of the retina and ciliary muscle improves
Vacuum massage, magnetic therapy, electrical coagulation, and massage glasses are used for hypermetropia. Physiotherapy helps well with mild farsightedness, especially in combination with optical correction.
As additional remedies, you can drink infusions of blueberry and cherry leaves, eyebright. Lotions made from potato pulp or cherry fruits, which are applied twice a day for 5-6 minutes, help.
These techniques are quite sufficient to correct low degrees of farsightedness. Surgical intervention is performed only for moderate and high degrees of the disease; weak degrees can be easily corrected without surgery.