Fluorescein angiography of the retina (FAG) is a method for studying the vessels and capillaries of the retina and choroid, contrasting them with a special contrast dye (fluoroscein). During the examination, the ophthalmologist observes how the contrast agent passes through the vessels of the eye in dynamics, takes a series of photographs, and then draws up a conclusion about the state of the vascular system of the eye. The method has been used in ophthalmology since 1961.
A distinctive feature of FA is its high sensitivity and specificity, which allows for a thorough analysis of the condition of the fundus vessels.
What diseases can be detected using FA
In skillful hands, this research method can provide the doctor with a lot of valuable information about the state of the vascular system of the eye, including microscopic changes that cannot be seen with a standard ophthalmological examination.
Using FA, you can evaluate the structure of the vessel wall, their geometry and patency, as well as detect changes such as neovascularization (formation of functionally defective vessels), hemangiomas or aneurysms, and in some cases it is possible to diagnose tumors of the choroid.
Despite the fact that during the study, the device creates a detailed image of the vessels of the fundus, the results obtained must be deciphered by a highly qualified diagnostician with relevant experience in diagnosing retinal pathologies.
Video procedure
Doctors at the Retina Center have extensive experience in diagnosing and treating patients with various eye diseases. We carry out eye diagnostics using the most modern equipment, quickly, efficiently and at affordable prices.
The method of fluorescein angiography of the retina helps:
- Conduct differential diagnosis in patients with pathological changes in the fundus or clarify the existing diagnosis
- Determine the localization and extent of the pathological process
- Identify changes that require laser coagulation of the retina
- Monitor the course of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of prescribed treatment
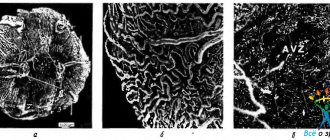
Research results
Normal picture
The drug, injected into the patient’s vein, reaches the retina of the eyeball in a matter of seconds. After individual segments of the vascular system are filled with the drug, the retina takes on the desired appearance. In the next phase, the substance enters the artery. Having filled it, it begins to circulate in the venous system. After one hour after administration of the drug, it leaves the retina. In a normal study, no leakage of dyes from the vascular system occurs.
Deviations from the norm
Retinal angiography is a highly complex procedure that must be performed by an experienced specialist. Only an ophthalmologist with a wealth of knowledge is able to identify deviations and the development of pathologies at the earliest stages. Already at the initial stage of the study, various diseases of the visual organs can be identified. The circulation of the dye through the arteries, venous and vascular systems should occur evenly. Slowing down the process or stopping it may indicate the presence of a serious illness.
In the case when a patient is diagnosed with hypertensive retinopathy, FA of the retina of the eyeball will help identify areas that have changed their structure and localize areas with pathological changes. In the presence of tumors and neoplasms, the picture is ambiguous and its completeness depends on many factors.
There is a fairly wide range of contraindications to fluorescein angiography.
How the research is carried out
The entire procedure usually lasts about 30 minutes, and the patient may be asked to sign an informed consent before starting. A preliminary consultation with a doctor will also be required to exclude possible contraindications, as well as an allergic intradermal test with fluoroscein.
After instilling drops to dilate the pupil, the patient places his head on a special stand and must look forward in front of him, without moving and maintaining calm breathing throughout the entire examination. After intravenous administration of a contrast agent, the doctor takes a series of 25 to 30 photographs of the fundus.
In most cases, patients tolerate contrast administration well, but if a metallic taste in the mouth, severe nausea and vomiting, allergic rash, dizziness, or loss of consciousness occurs, the study should be stopped and resuscitation measures initiated.
Within two days after the FA procedure, residual contrast circulating in the body may change the color of the skin or urine; this condition is reversible. To speed up the removal of the contrast agent, you will need to drink more fluid. In some patients, dilation of the pupils after instillation of mydriatics can cause blurred near vision for 10-12 hours, which goes away on its own the next morning. For the period until the pupils fully restore their size, it is recommended to limit visual stress and avoid direct sunlight.
How is fluorescein angiography of the retina performed?
The patient is asked to take a comfortable position, placing his head on a special stand and touching the crossbar with his forehead. The nurse injects fluorescein into the vessel, and for some time the patient is supposed to sit motionless in a fixed position without changing the breathing rhythm. From the moment the contrast agent is administered, the actual examination can begin, taking pictures at a frequency of one per second for about half a minute. If it is necessary to fix the gaze in the directions of interest to the doctor, the patient will receive instructions regarding this.
The nurse then removes the needle from the vein and applies a bandage to the injection site. The following photographs showing the dynamics of drug removal should be taken within twenty minutes of the start of dye administration.
Throughout the procedure, the medical staff closely monitors the patient’s well-being, ready to provide assistance if there are signs of an allergic reaction.
Fluorescein angiography of the fundus is interpreted by a specialist who can make a reliable conclusion about its results. Normally, fluorescein should not be visualized outside the vascular bed. The appearance of contrast in the retina always indicates its pathology.
If you want to entrust fluorescein angiography of the retina to qualified doctors at an affordable price, contact the multidisciplinary medical center named after.
S. Fedorov. Doctors and nursing staff who have been working using this method for many years will ensure fast and qualified fluorescein angiography of the eye at a price that pleases the eye. Fedorov Medical Center is always on guard of your health! Making an appointment Today: 24 registered
In what cases should FA not be performed?
Fluorescein angiography of the retina is not used in patients suffering from glaucoma, as well as in pseudophakia, since in these diseases the pupil cannot be dilated, and this is a prerequisite for performing the study. It is impossible to perform FA when the internal media of the eyeball is clouded.
Fluorescein angiography is contraindicated in cases of bronchial asthma, severe kidney disease accompanied by impaired excretory function, thrombophlebitis, as well as in the case of an allergy to radiocontrast agents or a history of mydriatics.
It is not recommended to perform FA for certain groups of patients, these include:
- Patients under 14 and over 65 years of age
- Persons who suffer or have ever suffered from epileptic seizures, mental illness, or have suffered an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke
If indicated, fluorescent fluorography can be performed during pregnancy or lactation, but in the latter case, after the study, you will need to stop feeding for 2 days.
Advantages of the FAGD method
Essentially, the fluorescein angiography method is unique, and in combination with computer processing of the data obtained, it is unlikely that anything similar in efficiency will appear in the coming decades. It is only possible to chemically improve the properties of the contrast fluorescent injected into the vein, which will make it safer and more accessible for patients with allergies today.
The very technique of illuminating the vascular network with fluorescent down to the smallest branches of the capillaries and making them clearly visible in the images allows for a detailed analysis of the condition and diagnostics that does not allow any double interpretations of what is seen.
Possible side effects
FAHD is, in most cases, a safe way to examine the retina for the patient. All possible side problems can be divided into
- Mild ones, like nausea or less frequent vomiting.
- Moderate, such as vegetative symptoms, possible to the extent of loss of consciousness, rash on the limbs and body, itchy skin.
- Heavy. These include anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema, which can lead to death. Such cases are described in the medical literature. They are extremely rare, but their possible manifestations should not be discounted.
Manifestations of severe cases should be considered categorical contraindications to the use of fluorescein disodium.
Side effects of the procedure
The FA study can cause a number of side effects, including mild dizziness or weakness, nausea (up to 5% of cases), allergic rashes and itchy skin, sneezing, numbness of the tongue, vomiting (no more than 1% of cases). All of these side effects are reversible and, as a rule, do not require medical attention.
In very rare cases, the procedure may be accompanied by more serious complications (anaphylactic shock, respiratory arrest, disruption of the cardiovascular system, etc.), requiring emergency resuscitation measures. That is why the diagnostician and the nurse who administers the contrast must be trained to recognize dangerous symptoms of complications in a timely manner and must be able to carry out the necessary resuscitation measures.
How is fluorescein angiography performed?
The duration of the study is about half an hour. Before starting fluorescein angiography, you must sign a written consent, find out the presence of contraindications and talk about possible side effects.
The patient sits facing the camera, after which a mydriatic solution is placed into the conjunctival cavity. The subject's chin is firmly fixed in a special stand so that the forehead touches the crossbar. During angiography, your gaze should be directed forward, your breathing should be kept even and try not to blink.
First, the doctor takes several control photographs, after which an intravenous injection of dye is performed. During imaging of the peripheral retina, the patient is asked to look away in the appropriate direction.
During fluorescein angiography, patients often experience nausea and fever. This is not a reason to stop the study. In this case, a metallic taste in the mouth, severe dizziness, vomiting, loss of consciousness, and urticaria are alarming symptoms that characterize fluorescein intolerance. Sometimes this requires resuscitation measures.
After intravenous injection of the dye, the doctor takes a series of pictures (25-30 pieces with a frequency of 1 frame per second). If you need to repeat the study with contrast, this can be done after 20 minutes, when the dye is still present in the vascular bed. An hour after administration, it will completely leave the retinal vessels.
Within two days after fluorescein angiography is performed, the patient’s urine, skin, and other biological fluids may change color. To speed up the removal of fluorescein from the body, you need to drink as much water as possible. Within 12 hours after angiography, patients note a decrease in visual acuity, so it is better to observe a protective regime for the eyes. It is also important to avoid direct sunlight, including due to pupil dilation.
The quality of images during angiography can be negatively affected by low permeability of optical media to light (destruction of the vitreous, cataracts, partial hemophthalmos, corneal opacity), and insufficient dilation of the pupillary opening.
Carrying out
FAG of the eye is performed in a specialized clinic. Before the procedure, the doctor prescribes allergy tests; a fluorescent substance can cause a reaction. The patient must provide information to the doctor about previous eye surgeries and known diseases. It is also important to indicate whether prescription lenses are used and what medications the patient is taking. The eyes should rest 4 hours before the procedure. Therefore, it is recommended to remove lenses or glasses and not subject the organ to stress.
During the procedure, the doctor observes the bloodstream of the eye.
Fluorescein angiography is performed over 30 minutes. First, the doctor uses drops to dilate the pupils. Then the component is injected into the cubital vein, after 10 seconds it reaches the vessels of the eyes and retinal FA can begin. A special camera takes pictures, recording the condition of the blood vessels throughout the entire organ area. The doctor receives an image every second. Then a break of 15-20 minutes is prescribed and the examination is repeated. It is necessary to analyze the reaction of the retina to the injected substance and to protect against bleeding. If examination of a second organ is necessary, it is carried out no earlier than 30 minutes later.
Contraindications
Diagnosis is not carried out if the transparency of the eye structures is impaired.
The injected dye can cause a number of side effects, which is why it is not always advisable to carry out this diagnostic method. To determine the patient's readiness for the administration of a contrast agent, an additional examination is carried out in advance. Eye angiography is not prescribed if the patient has the following conditions:
- glaucoma of all stages of development;
- impaired transparency of eye structures due to pathological degenerative or metabolic processes;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- neurological diseases;
- rehabilitation period after cardiac and neurological illnesses;
- renal failure;
- allergy to the proposed drug;
- regular use of antidepressants.
Relative contraindications include the patient's age under 16 years. It is not recommended to perform FA in elderly people with chronic processes. For pregnant women, the procedure is prescribed only if a tumor is suspected. During lactation, the use of a contrast agent is allowed, but it is necessary to interrupt feeding for 4 days after its administration.
Indications
Fluorescein angiography of the retina is considered a highly informative examination method. It is used to determine disorders in the microvascular circuit of the visual organ. Using a high-frequency camera allows you to examine all components of the eye and obtain information from hard-to-reach places. An ophthalmologist prescribes FAGD when diagnosing the following conditions:
This examination may be necessary for retinal hemorrhage.
- macular degeneration due to age-related changes;
- retinopathy in the form of complications of diabetes mellitus;
- neoplasms in the visual organs;
- traces of hemorrhage in the retina;
- thrombosis of local veins;
- serous type choriopathy;
- optic nerve pathologies;
- inflammatory process in the posterior chambers of the eyeball.
These examinations make it possible to calculate not only the presence, but also the nature, exact localization and stage of the pathological process.