The vessels of the fundus of the eye are a reflection of vascular pathologies occurring in the human body. These are the only blood vessels of the internal organs of the human body that can be seen using non-invasive research methods - various types of ophthalmoscopy.
Vasoconstriction (angiopathy) of the retina is not an independent disease, but almost always indicates the presence of a general somatic pathology in the patient.
I recently read an article that talks about the drug Choledol for cleaning blood vessels and getting rid of CHOLESTEROL. This drug improves the general condition of the body, normalizes the tone of the veins, prevents the deposition of cholesterol plaques, cleanses the blood and lymph, and also protects against hypertension, strokes and heart attacks.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered a package. I noticed changes within a week: the constant pain in my heart, heaviness, and pressure surges that had tormented me before receded, and after 2 weeks they disappeared completely. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
Drug therapy
The basis of treatment is the elimination of the underlying disease. With the active development of vascular disorders, ophthalmic therapy is additionally prescribed. Eye drops are required for angiopathy, which help normalize blood circulation in the vessels. In particular, such products as “Vazonit”, “Trental”, “Emoxipin”, “Arbiflex” are used. These medications are contraindicated during pregnancy and for the treatment of children (they can be prescribed in the most extreme cases). Eye drops for retinal angiopathy help normalize vision and eliminate existing symptoms.
Also required are drugs that prevent thrombus formation, such as Lospirin, Trombonet, Aspirin. It is imperative to carry out a course of vitamin therapy, and also require drugs that strengthen and tonic the walls of blood vessels, for example, Calcium Dobesilate, Parmidine.
The duration of therapy, treatment regimen, as well as the drugs used are selected individually for each patient. All therapeutic measures are determined by the attending physician. During pregnancy, there is a risk of rupture or dangerous damage to retinal blood vessels during labor and childbirth. Therefore, angiopathy becomes an indication for cesarean section.
Risk group
The category of people most prone to disorders:
Non-surgical eye treatment in 1 month.
- pregnant women;
- diabetics;
- patients with moderate and complex myopia.
The disorder occurs more often in hypertensive patients. Retinal angiopathy develops as a result of circulatory disorders.
- hypertensive;
- diabetic;
- youthful;
- traumatic.
The hypertensive form is accompanied by dilation of blood vessels and an increase in branches. Often people have a feeling of pulsation, the fundus of the eye is covered with dilated vessels. Cloudiness occurs in several places if the pathology becomes more complex.
Macroangiopathy or microangiopathy develops in diabetics. The walls of small or large vessels are affected.
Causes of angiopathy
The retina is the most important structure of the eye; it responds quickly to the smallest disturbances in the blood supply system. Angiopathy, not being an independent disease, is often included in the symptoms of certain diseases, signaling the reaction of the eye vessels. In this case, the pathology affects the walls of blood vessels and also modifies their structure. Most often, angiopathy is provoked by the following reasons:
- Hypertension. Increased pressure, as a rule, has a detrimental effect on the walls of blood vessels, disrupting the structure of their inner layer. Wall compaction is observed, accompanied by fibrosis. The result is a narrowing of blood vessels, leading to difficulty in blood circulation, increasing the risk of blood clots or hemorrhage. Prolonged high blood pressure can result in bursting of some blood vessels. This angiopathy has a characteristic manifestation - narrowed vessels of the fundus, having a tortuous shape. At the same time, characteristic symptoms are noticeable in a third of patients suffering from the first stage of hypertension, and in the third stage of the disease, modifications of blood vessels are detected in almost all patients. Timely treatment can prevent or stop the development of angiopathy.
- Diabetes. The consequences of the disease, among other things, are damage to the vascular walls throughout the body. An increased glucose content provokes the development of occlusions, thickening of capillary walls, vasoconstriction, gradual leakage of blood into the retina and a progressive decline in blood microcirculation in the eyes. As a result, vision loss may occur.
- Head and spine injuries. In some cases, intracranial pressure may increase, vascular walls may burst, and blood may enter the retina.
Angiopathy can also develop due to some other factors. The presence of bad habits increases the risk of narrowing of the vessels of the fundus. Sometimes symptoms of angiopathy can be observed as a consequence of poisoning. Well, age-related changes in the human body quite often lead to angiopathy.
Why does it appear
The causes of narrowing of the vessels of the fundus include the following physiological and pathological conditions:
- arterial hypertension;
- atherosclerotic lesions (characterized by the formation of plaques blocking the lumens of large and small vessels);
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- spinal and head injuries;
- diabetes;
- elderly and senile age;
- genetic predisposition;
- abnormalities in the structure of the fundus vessels (excessive tortuosity or bends);
- arterial hypotension (persistent decrease in pressure);
- degenerative-destructive changes in the cervical spine (osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis);
- chronic intoxication of the body;
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- poor nutrition;
- being overweight;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- exhaustion of the body;
- physical and psycho-emotional overload;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- consequences of prolonged work at the computer;
- oncological diseases of the hematopoietic system (leukemia);
- autoimmune pathologies (systemic vasculitis, periarteritis nodosa);
- infectious lesions of the central nervous system.
There are the following types of narrowing of the retinal arteries:
- Renal angiopathy. Develops against the background of a long course of glomerulonephritis and renal failure. A typical sign of this form of pathology is darkening of the eyes. When examining the fundus, vascular tortuosity and the presence of foci of ischemia are revealed.
- Hypertensive retinopathy. When blood pressure changes, the vessels in the retina narrow and dilate. A specific protein (hyalin) is released, which penetrates the endothelium of the artery, causing sclerotic changes. Gradually, all vessels of the fundus are involved in the pathological process. An ophthalmological examination reveals streak-like hemorrhages.
- Diabetic retinopathy. When the level of glucose in the blood increases, the nutrition of all tissues is disrupted. Changes in the condition of the retina are caused by an increase in the permeability of the vascular walls. Examination helps to identify swelling of the fundus and pronounced narrowing of the arteries. No spots or stars are found on the surface of the retina. Due to diabetic retinopathy, peripheral vision is impaired.
- Retinal degeneration. This disease is widespread among elderly patients. Degeneration is caused by age-related changes in the body. It has a progressive course and leads to vision loss.
- Pigmentary degeneration. The first symptom of the pathology is night blindness. When examining the fundus, bone bodies are detected. Increasing ischemia is accompanied by narrowing of the capillaries and atrophy of the optic nerve. The pathological process is bilateral.
What happens with angiopathy?
If a patient has angiopathy, the tone of the blood capillaries, as well as the outflow of blood, is disrupted. Constriction of the fundus vessels does not occur on its own, but is a harbinger of other diseases.
It signals the occurrence of various pathological processes that lead to eye damage
Doctors pay great attention to the treatment of angiopathy, as it can cause complete loss of vision
Narrowing of the fundus vessels occurs in both adults and children. However, it is more often observed after 30 years. In children, the severity of angiopathy depends on the position of their body (standing or sitting). And in adults, the disease makes itself felt against the background of increased intracranial pressure. If angiopathy is not treated, cerebral microangiopathy may appear, which often leads to irreversible processes.
Why does it appear?
The reasons why vasoconstriction of the fundus occurs can be different. As noted above, angiopathy is not an independent disease, but signals another, more serious eye disease.
The following causes of angiopathy are distinguished:
- Hypertension. Constant high intracranial pressure negatively affects the wall of the blood vessels of the eyes, as a result of which its inner layer is damaged. In addition, capillaries burst due to pressure. If you start hypertension to the third stage, then the probability that a narrowing of the vessels of the fundus will occur is 100%.
- Diabetes. With this disease, the vascular wall of not only the eyes, but also the entire body is damaged. This is caused by an increase in blood glucose levels. As a result of this pathology, the diameter of the vessel decreases, and therefore blood circulation in the eye worsens. If treatment is not started in time, the consequences of such a cause can be fatal - complete loss of vision.
- Injuries to the eyes, spine or head. This leads to a rapid increase in intracranial pressure, rupture of fundus vessels and hemorrhage.
- Hypotension. This disease leads to noticeable pulsation in the eye area and causes the formation of blood clots in them.
The reasons for the development of angiopathy lie not only in the above diseases.
A number of other factors can lead to its appearance:
I recently read an article that talks about the natural cream “Bee Spas Kashtan” for treating varicose veins and cleaning blood vessels from blood clots. With this cream you can cure VARICOSIS FOREVER, eliminate pain, improve blood circulation, increase the tone of veins, quickly restore the walls of blood vessels, clean and restore varicose veins at home.
I’m not used to trusting any information, but I decided to check and ordered one package. I noticed changes within a week: the pain went away, my legs stopped “humming” and swelling, and after 2 weeks the venous lumps began to decrease. Try it too, and if anyone is interested, below is the link to the article.
- smoking or alcohol abuse;
- osteochondrosis;
- food or chemical poisoning;
- age over 30 years (but the disease also occurs in children);
- congenital defects of the blood vessels of the eyes.
The causes of angiopathy almost completely coincide with its types. This is how they distinguish:
Hypertensive. If angiopathy of this type is started, changes in the retinal tissue may occur. At the initial stage of hypertension, the symptoms of angiopathy can be eliminated.
Inflammation of the retinal venous vessels occurs. Connective tissue may form inside the eye. Some complications are also possible (cataracts, glaucoma).
Symptoms
Narrowing of the blood vessels in the eyes manifests itself in a number of symptoms. The patient begins to gradually lose vision: at first the image becomes cloudy, and then the patient cannot distinguish objects. Lightning appears in the eyes.
For the treatment of VARICOSE and cleaning blood vessels from THROMBUS, Elena Malysheva recommends a new method based on the Cream of Varicose Veins. It contains 8 useful medicinal plants that are extremely effective in the treatment of VARICOSE. Only natural ingredients are used, no chemicals or hormones!
Yellow spots, pinpoint hemorrhages are observed on the surface of the eyeball, and small vessels are clearly visible.
Many of our readers actively use a well-known method based on natural ingredients, discovered by Elena Malysheva, to treat VARICOSE. We recommend that you check it out.
Clinical signs of pathology
Clinically, there are three degrees of retinal angiopathy - first, second (moderate) and third.
The degree of narrowing of the vessels of the fundus can only be determined during ophthalmoscopy.
In the initial stages of retinal vascular narrowing, the patient usually does not have complaints or has complaints that are general.
With slight narrowing of the retinal vessels (first degree angiopathy), patients may complain of:
- headache;
- discomfort in the eyeballs;
- visual disturbances (floaters, fog or spots before the eyes, slight decrease in visual acuity).
Changes in the fundus vessels in the first degree of angiopathy are reversible, as they are functional. Provided that effective treatment of the disease that caused angiopathy is prescribed in a timely manner, these changes can be easily regressed.
As angiopathy progresses, more specific signs appear, by which the clinician may suspect pathology of the fundus vessels:
But given the fact that the narrowing of retinal vessels is not an isolated pathology, the symptoms characteristic of the underlying disease, which caused the onset of angiopathy, come to the fore in the symptoms.
Ophthalmoscopy in the second degree of angiopathy reveals organic vascular lesions that are difficult to regress:
To clean VESSELS, prevent blood clots and get rid of CHOLESTEROL, our readers use a new natural drug recommended by Elena Malysheva. The preparation contains blueberry juice, clover flowers, native garlic concentrate, rock oil, and wild garlic juice.
Enlarged veins of the eye: causes, symptoms, treatment
The eyes contain a powerful system of veins, consisting of many branches, the main of which are considered to be the upper and lower. They have no valves and connect directly to the vessels of the face. The main task of this system is to drain blood from all components of the eye - muscles, lacrimal glands, the eyeball itself, etc.
Enlarged veins in the eyes can occur due to increased blood pressure in them. In this case, the disease manifests itself in the form of thinning of the vascular walls, as a result of which they become more permeable and less elastic. This manifests itself in the form of swollen areas under the eyes of a dark color (bags), in which interweaving of blood vessels can be distinguished.
Symptoms of ocular varicose veins are expressed as follows:
- decreased visual acuity;
- pulsation of the ophthalmic vein noticeable to the naked eye;
- the appearance of a “haze” or “film” before the eyes;
- headache;
- tachycardia or bradycardia;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- noticeable bulging of veins.
Diagnostic signs include swelling of the optic nerve with a noticeable enlargement of its head; it is difficult to distinguish individual branches in the mass of blood vessels. The main branches are noticeably expanded and have a tortuous shape; in some places the doctor can see hemorrhages.
Reasons for appearance
Before you begin treatment for varicose veins, you need to understand why this disease occurred. This will help prevent relapses in the future. In most cases, pathology occurs as a complication of other ophthalmological diseases.
In some cases, ocular varicose veins are a consequence of congenital abnormalities of blood vessels, for example, their weakening or thinning. Also, the cause of the pathology may be a hereditary predisposition to varicose veins.
Another cause may be exophthalmos, a disease in which protrusion of the eyeballs occurs at their normal size.
The provoking factor may be a disease of another system or organ, for example, diabetes, hypertension or atherosclerosis.
Treatment of pathology
If you notice alarming symptoms in the eye area, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, since the sooner treatment begins, the lower the risk of complications.
Since the observed manifestations of the disease are similar to other eye pathologies, self-diagnosis is not possible.
For this reason, you first need to contact an ophthalmologist, and after a series of examinations, he will give a referral to a phlebologist - a doctor who deals with vein diseases.
Although modern medicine has made great strides even compared to the last century, eye treatment is always difficult.
Surgeries to remove varicose veins of the ophthalmic vein are performed extremely rarely, since few doctors have the necessary skills and experience in this field, and it is difficult to predict the outcome of the intervention in advance.
Most often, conservative therapy is prescribed to eliminate the pathology if the patient’s condition is not regarded as advanced.
The effectiveness of treatment is highest in the first days of development of varicose veins, so the patient is hospitalized for constant monitoring. From the first days of treatment, droppers with Eufilin solution are placed, and intramuscular injections of magnesium sulfate solution are also given.
In some clinics, the patient may be offered unconventional treatment methods, for example, placing leeches on the temples.
After several days of such treatment, angioprotectors are additionally prescribed, for example, Ascorbic acid or Rutin. These drugs help reduce the permeability of vascular walls, normalize metabolic processes and improve blood circulation.
Gradually, treatment with Heparin is replaced by taking anticoagulants - drugs that help thin the blood, resolve clots and prevent blood clots. Iodine preparations, which can be used as intravenous injections or as an adjunct to electrophoresis, can complement therapy. It is advisable to take vitamin-mineral complexes.
Such a treatment course can last several months, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient. After recovery, you will need to be regularly monitored by a phlebologist and ophthalmologist and carry out preventive treatment several times a year. This will prevent the recurrence of ocular varicose veins.
Symptoms
- scotomas form in the field of view;
- a veil appears before the eyes;
- visual acuity decreases;
- horizons narrow;
- throbbing pain occurs;
- hemorrhage occurs;
- migraine;
- dizzy;
- blood clots form more often.
The disease, which is inherited, manifests itself in early childhood. Narrowed and excessively tortuous vessels are detected after ophthalmoscopy. The doctor identifies areas of expansion and areas of the macula that are filled with blood.
The structure of the fundus and why its diseases can help in diagnosis
By the term “fundus”, doctors mean the inner part of the eyeball, which can be seen during ophthalmoscopy (this is a non-invasive examination, it is carried out by eye doctors using an ophthalmoscope in a dark room). During ophthalmoscopy, without interfering with our body, we can see eye diseases, as well as the first symptoms of many systemic diseases. So, with the help of an ophthalmoscope, the doctor sees:
- The structure of the vessels of the eye, veins and arteries, their filling, possible narrowing or, conversely, expansion, the presence of hemorrhages.
- Optic nerve and macula, their defects.
- Retina, its thinning (dystrophy), detachments, ruptures.
We ourselves will not be able to see the fundus of the eye, but the doctor will tell a lot about the state of our health simply by looking at the fundus of the eye through an ophthalmoscope.
Fundus pathology is always secondary. Therefore, it is imperative to look for the underlying disease.
Any disturbance of blood circulation in the eyeball immediately leads to disruption of its function, therefore the eye has a rich network of blood vessels that provide nutrition and function to all its tissues.
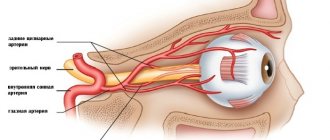
Blood flows to the eyeball from the main branch of the internal carotid artery - the ophthalmic artery, which supplies not only the eye, but also its auxiliary apparatus. Direct tissue nutrition is provided by a network of capillary vessels.
Harmful metabolic products entering the bloodstream from cells are removed through the veins.
The venous network of the eye follows the structure of the arteries. A feature of the veins of the eye is the absence of valves in them that limit the reverse flow of blood, as well as the connection of the venous network of the face with the veins of the orbit, and then the brain. At the same time, purulent processes on the face through the venous blood flow can spread towards the brain, which is potentially life-threatening.
Why does the fundus of the eye hurt?
The reasons for changes in the fundus picture may relate to the position and shape of the optic disc, vascular pathology, and inflammatory diseases of the retina.
Vascular diseases
The fundus of the eye most often suffers from hypertension or eclampsia during pregnancy. Retinopathy in this case is a consequence of arterial hypertension and systemic changes in arterioles. The pathological process occurs in the form of myeloelastofibrosis, less commonly hyalinosis. The degree of their severity depends on the severity and duration of the disease.
The result of an intraocular examination can establish the stage of hypertensive retinopathy.
First: slight stenosis of arterioles, the beginning of sclerotic changes. There is no hypertension yet.
Second: the severity of stenosis increases, arteriovenous crossovers appear (the thickened artery puts pressure on the underlying vein). Hypertension is noted, but the condition of the body as a whole is normal, the heart and kidneys are not yet affected.
Third: constant vasospasm. In the retina there is effusion in the form of “lumps of cotton wool”, small hemorrhages, swelling; pale arterioles have a “silver wire” appearance. Hypertension levels are high, the functionality of the heart and kidneys is impaired.
The fourth stage is characterized by the fact that the optic nerve swells and the blood vessels undergo critical spasm.
Arterial hypertension can be an indirect cause of thrombosis or spasm of the retinal veins and central retinal artery, ischemia and tissue hypoxia.
Examination of the fundus for vascular changes is also required in case of systemic disturbances in glucose metabolism, which leads to the development of diabetic retinopathy. Excess sugar in the blood is detected, osmotic pressure increases, intracellular edema develops, the walls of the capillaries thicken and their lumen decreases, which causes retinal ischemia. In addition, microthrombi form in the capillaries around the foveola, and this leads to the development of exudative maculopathy.
Diagnostics
Places of development of ischemia and hemorrhage are identified during examination.
Ultrasound diagnostics reveals blood clots and areas of vascular blockage.
- Indirect is carried out using a magnifying glass and a mirror device. The fundus is examined through magnified reflection.
- Direct examination is performed using an electric ophthalmoscope. This analysis provides more useful information.
- Ophthalmochromoscopy is carried out using equipment with replaceable filters. Colored lenses in different combinations reveal changes in the arteries at an early stage, which are difficult to detect with natural color.
- Polarization allows you to diagnose retinal edema at the first stage.
The results of ophthalmoscopy are clarified by additional examinations:
- Biomicroscopy is performed using a slit lamp and a fundus lens. A device with 3 mirrors is installed on the cornea for a detailed examination of the retina.
- An ultrasound machine is applied to the closed eyelid if the patient has no contraindications to such a procedure. The condition of the retinal vessels is studied and the speed of blood flow is measured. Ultrasound allows you to determine minimal vasoconstriction.
- Laser ophthalmoscopy, in which the retina is illuminated with optical rays, the refractive characteristics of which are displayed on the monitor. The technique allows you to study the condition of the fundus of the eye when the lens is clouded.
- Rheoophthalmography is a contact method for examining the blood supply system, in which pulse waves of the arteries are detected. A lens with electrodes is placed on the cornea to sense impulses.
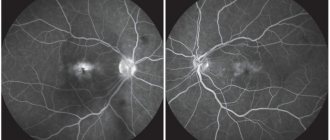
- Fluorescein angiography is based on photographing blood vessels after administration of a contrast agent. Diagnosis is carried out using a slit lamp with fundus lenses.
- Densitometry is photography performed after the administration of a contrast agent.
These diagnostic methods complement information about the patient’s condition, but do not replace each other. The ophthalmologist independently chooses examination methods, taking into account the possibilities of the examination.
Physiotherapy methods to eliminate spasms:
- acupuncture;
- use of laser equipment;
- magnetic therapy;
- neck massage.
- microcirculation correctors are used to normalize blood supply;
- angioprotectors restore the permeability of vascular walls;
- antiplatelet agents are used for high blood clotting;
- antihypertensive and hypoglycemic drugs are used to treat the underlying disease;
- eye drops help improve the quality of vision.
Hawthorn, chamomile and lemon balm extract help in the treatment of retinopathy. Surgical intervention is performed when conservative treatment methods are insufficiently effective. Laser coagulation is performed and the vitreous body is removed.
How to detect pathology?
It is impossible to detect retinal angiopathy with the naked eye. This requires special equipment - ophthalmoscopes, slit lamps, ultrasound machines.
Ophthalmoscopy
An ophthalmoscopy allows the ophthalmologist to examine the arteries and veins of the fundus through the pupil. The most common methods of examining the retina include:
- Indirect ophthalmoscopy (mirror). This procedure is performed using a mirror ophthalmoscope and a magnifying glass. The fundus image is presented as a mirror image and provides only an overview.
- Direct ophthalmoscopy. Examination of the fundus is carried out using an electric ophthalmoscope. This procedure is more informative compared to the mirror procedure.
- Ophthalmochromoscopy. Examination of the fundus with an ophthalmoscope with replaceable filters. The use of colored glasses (red, green and blue) in different combinations during the procedure makes it possible to identify initial changes in the retinal vessels that remain invisible in white.
- Polarizing ophthalmoscopy. Examination of the fundus in polarized light makes it possible to detect retinal edema in the initial stage.
Clarifying research methods
In modern medicine, many other methods of studying retinal vessels are used to clarify the results of ophthalmoscopy:
- Biomicroscopy of the fundus using a slit lamp with fundus lenses. This is a contact method for examining the fundus, in which a three-mirror lens is placed on the cornea, allowing a detailed examination of the entire surface of the retina.
- Doppler ultrasound examination of the eyes. It is carried out through a closed eyelid and has no contraindications. Allows you to study the vessels of the retina and evaluate the speed of blood flow through them. Determines the narrowing of the fundus vessels in the initial stages.
- Laser ophthalmoscopy. With this research method, the retina is illuminated with a laser, and an image of the retina is displayed on a monitor. The advantage of this method is the ability to examine the fundus of the eye while reducing the transparency of the lens and vitreous body.
- Rheoophthalmography. This is a contact method for studying the blood supply to the retina, based on recording pulse waves from the vessels of the fundus. To capture impulses from them, electrode lenses are applied to the cornea.
- Fluorescein angiography of the fundus. This is a highly informative method based on photographing contrasted vessels of the fundus. The contrast agent is administered intravenously. The procedure is performed using a slit lamp with fundus lenses.
- Densitometry. The procedure is performed similarly to fluorescein angiography, but photographs of the retina are taken, which allows one to evaluate the blood flow in it over time.
These methods do not replace each other, but complement each other perfectly. The choice of diagnostic procedure in most cases depends on the doctor’s preferences, territorial and financial accessibility of the diagnostic method, and the transparency of the eye structures.
The preservation of the functions of such an important human sensory organ as the eye depends on this. Do you still think that it is completely impossible to RESTORE blood vessels and the BODY!?
Do you still think that it is completely impossible to RESTORE blood vessels and the BODY!?
Have you ever tried to restore the functioning of your heart, brain or other organs after suffering pathologies and injuries? Judging by the fact that you are reading this article, you know firsthand what it is:
- Do you often experience unpleasant sensations in the head area (pain, dizziness)?
- You may suddenly feel weak and tired...
- I constantly feel high blood pressure...
- there is nothing to say about shortness of breath after the slightest physical exertion...
Did you know that all these symptoms indicate INCREASED CHOLESTEROL levels in your body? And all that is necessary is to bring cholesterol back to normal. Now answer the question: are you satisfied with this? Can ALL THESE SYMPTOMS be tolerated? How much time have you already wasted on ineffective treatment? After all, sooner or later the SITUATION WILL GET WORSE.
That's right - it's time to start putting an end to this problem! Do you agree? That is why we decided to publish an exclusive interview with the head of the Institute of Cardiology of the Ministry of Health of Russia, Renat Suleymanovich Akchurin, in which he revealed the secret of TREATING high cholesterol. Read the interview...
The most effective means
Pharmaceutical preparations (drops) and folk remedies are the most effective in terms of treatment.
Pharmacy
A burst vessel is treated with drugs such as Taufon, Emoxipin, Aisotin, Quinax, etc. And now more about each of them.
Visine
The drops help eliminate swelling and last for 8 hours. Visine is also recommended for conjunctivitis, allergies and frequent use of contact lenses. The product must be instilled 1-2 drops several times a day (until the redness is completely eliminated). Side effects may include burning, itching, tearing, and blurred vision. However, side effects do not last long (on average 1–2 minutes).
Emoxipin
The drug helps strengthen blood vessels through angioprotective action, making capillaries thicker and stronger. The product is used 2 drops 2 times a day. The course of treatment is determined individually. It should be remembered that Emoxipin drops are not recommended to be combined with similar drugs.
Taufon
The drug is prescribed for conjunctivitis, retinal dystrophy, damage to the cornea and rupture of blood vessels. Taufon normalizes blood circulation and stabilizes intraocular pressure. It is recommended to use the product 2 drops 4-5 times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician.
Aisotin
The drug contains a complex of Ayurvedic herbs, due to which it has a positive effect on ruptured blood vessels, cataracts, amblyopia, glaucoma, color blindness, etc. It is recommended to use the product 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day (until symptoms disappear).
Hyphenleuse
The drug has a protective effect on the cornea, protecting it from the irritating effects of negative environmental factors. Hyphenate restores and stabilizes the optical characteristics of the tear film, simultaneously improving the condition of blood vessels. The product is used 1-2 drops 4-6 times a day for a total course of 1-2 weeks.
Quinax
Used to treat broken blood vessels and cataracts of the eye. The drug is instilled 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye 3-5 times a day. The course of treatment is determined individually. But a long course of therapy is usually required.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can be used as an addition to the main treatment. Here are some effective recipes:
- Apply a cold compress to the eye. To do this, you need to moisten the gauze in cold water, squeeze out the water and place it on the closed upper eyelid. Water will moisturize the mucous membrane, and cold will prevent re-bleeding. It is recommended to repeat the procedure several times a day.
- Lotions made from linden or chamomile. Method of preparation: 1 tbsp. l. dry herbs, pour a glass of boiling water and let it brew for 30–40 minutes. Strain the finished infusion and use as a lotion (moisten a cotton or gauze swab and apply to the eye for 10–15 minutes). Frequency of use: 3-4 times a day (until symptoms are completely eliminated).
- Using fresh vegetables. Apply slices of fresh cucumber or peeled potato slices to the upper eyelid of the diseased eye. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. Frequency of use: several times a day (until symptoms disappear).
- Fresh cabbage juice. Using a blender or juicer, squeeze the juice from fresh cabbage and use for instillation (2 drops 4-5 times a day). The course of treatment is 5–6 days.
Note! If, when using folk remedies, allergic reactions occur or the patient’s condition worsens (pain and pain in the eye, lacrimation, etc.), therapy must be suspended and another remedy must be selected.
About related faults
A lighting device for any purpose that refuses to perform its function can signal to the owner of the Lada Largus that the fuse is faulty. If it is discovered that the jumper in the fuse link has burned out, then such an element requires unconditional replacement, which also means replacing the marker light bulb. This is quite easy to do. The mounting block is located on the left edge of the interior panel in close proximity to the unit for switching the modes of lighting devices. Here are the inserts numbered F1 - F39. Fuses numbered 9 and 10 are responsible for ensuring the operation of the low and high beam, respectively for the left and right headlights of the Lada Largus car.
Insufficient contact at the terminals in the fuse block can also cause problems with the normal functioning of the head optic components.
There may be cases of premature burnout of the contact inside the lamp itself or banal oxidation of contacts with the ground. The last option can be easily eliminated. To do this, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the contacting surfaces of the cable lugs. A wire brush will do. If these methods do not give the desired result and the functionality of the Lada Largus lighting devices is not restored, then you will need to contact professionals for a more thorough diagnosis of the causes of the malfunctions and their subsequent elimination.
How it manifests itself
Deteriorating vision combined with other serious illnesses should be a cause for concern
Destructive vascular changes do not occur immediately, and this is important to prevent irreversible death of eye tissue. It was revealed that with trauma, unilateral defects develop (only 1 eye is affected), systemic disorders radically change vision
The onset of the disease sometimes occurs without pronounced symptoms. The patient notes the following signs:
- recurrent headaches;
- dark spots or spots, red veil;
- recurring throbbing pain in the eye;
- increased sensitivity to light, burning and dryness;
- the appearance of spots and hemorrhages on the mucous membrane;
- blurred vision.
If treatment is not started, the destructive processes will continue: narrowing of the retinal vessels can cause hemorrhage in the eyeball and swelling of the optic nerve.
The longer a patient suffers from hypertension, the more pronounced the structural changes in the eye will be. The danger is that a person gets used to high blood pressure, stops feeling it and feels good (hypertension is detected by narrowed irises in the eyes). In this case, the walls of the blood vessels lose their elasticity, blood plasma penetrates into the retina, and swelling of the optic nerve reduces its conductivity.
Increased intracranial pressure poses the risk of not only vascular rupture, but also the formation of blood clots. They can block the entire lumen of the vessel, cause tissue necrosis and cause death.
Causes
Factors influencing vasoconstriction:
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- genetic structural abnormalities;
- lowering blood pressure;
- toxins in the body;
- elderly age;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- poor quality of sleep, fatigue;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- insufficiently active lifestyle.
Vasoconstriction occurs as a result of the development of the disease. The blood stagnates, many blood clots appear, and retinal tissue ischemia develops. At the same time, the veins dilate, the tissues of the eye swell due to the large accumulation of blood. The tone of blood vessels deteriorates due to frequent changes in pressure, they burst, hemorrhage occurs, and the quality of vision deteriorates.