Constriction of fundus vessels
Diseases of the circulatory system are displayed on the vessels of the fundus.
Diagnostic methods allow for visual examination of veins and arteries and a detailed assessment of the patient’s condition.
Constriction of the fundus vessels does not occur independently. The disorder always occurs with the development of general somatic pathologies.
Causes
Factors influencing vasoconstriction:
- hypertension;
- diabetes;
- genetic structural abnormalities;
- lowering blood pressure;
- toxins in the body;
- elderly age;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- poor quality of sleep, fatigue;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- insufficiently active lifestyle.
Vasoconstriction occurs as a result of the development of the disease. The blood stagnates, many blood clots appear, and retinal tissue ischemia develops. At the same time, the veins dilate, the tissues of the eye swell due to the large accumulation of blood. The tone of blood vessels deteriorates due to frequent changes in pressure, they burst, hemorrhage occurs, and the quality of vision deteriorates.
Risk group
The category of people most prone to disorders:
Protection against coronavirus
How to boost immunity and protect loved ones
>
- pregnant women;
- diabetics;
- patients with moderate and complex myopia.
The disorder occurs more often in hypertensive patients. Retinal angiopathy develops as a result of circulatory disorders.
Types of angiopathy:
- hypertensive;
- diabetic;
- youthful;
- traumatic.
The hypertensive form is accompanied by dilation of blood vessels and an increase in branches. Often people have a feeling of pulsation, the fundus of the eye is covered with dilated vessels. Cloudiness occurs in several places if the pathology becomes more complex.
Macroangiopathy or microangiopathy develops in diabetics. The walls of small or large vessels are affected.
Juvenile angiopathy is expressed by inflammation of the veins, hemorrhage occurs in the retina or vitreous body. Sometimes detachment occurs or glaucoma develops.
Traumatic angiopathy appears after severe compression of the chest. The pressure in the blood vessels increases, and hemorrhages appear in the area of the retina and nerve tissue.
Symptoms
Clinical signs:
- scotomas form in the field of view;
- a veil appears before the eyes;
- visual acuity decreases;
- horizons narrow;
- throbbing pain occurs;
- hemorrhage occurs;
- migraine;
- dizzy;
- blood clots form more often.
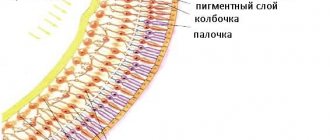
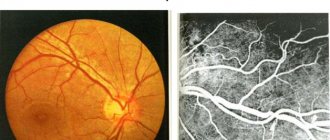
The disease, which is inherited, manifests itself in early childhood. Narrowed and excessively tortuous vessels are detected after ophthalmoscopy. The doctor identifies areas of expansion and areas of the macula that are filled with blood.
Diagnostics
Places of development of ischemia and hemorrhage are identified during examination.
Procedures:
- blood analysis;
- MRI;
- angiography.
Ultrasound diagnostics reveals blood clots and areas of vascular blockage.
Types of ophthalmoscopy:
- Indirect is carried out using a magnifying glass and a mirror device. The fundus is examined through magnified reflection.
- Direct examination is performed using an electric ophthalmoscope. This analysis provides more useful information.
- Ophthalmochromoscopy is carried out using equipment with replaceable filters. Colored lenses in different combinations reveal changes in the arteries at an early stage, which are difficult to detect with natural color.
- Polarization allows you to diagnose retinal edema at the first stage.
The results of ophthalmoscopy are clarified by additional examinations:
- Biomicroscopy is performed using a slit lamp and a fundus lens. A device with 3 mirrors is installed on the cornea for a detailed examination of the retina.
- An ultrasound machine is applied to the closed eyelid if the patient has no contraindications to such a procedure. The condition of the retinal vessels is studied and the speed of blood flow is measured. Ultrasound allows you to determine minimal vasoconstriction.
- Laser ophthalmoscopy, in which the retina is illuminated with optical rays, the refractive characteristics of which are displayed on the monitor. The technique allows you to study the condition of the fundus of the eye when the lens is clouded.
- Rheoophthalmography is a contact method for examining the blood supply system, in which pulse waves of the arteries are detected. A lens with electrodes is placed on the cornea to sense impulses.
- Fluorescein angiography is based on photographing blood vessels after administration of a contrast agent. Diagnosis is carried out using a slit lamp with fundus lenses.
- Densitometry is photography performed after the administration of a contrast agent.
These diagnostic methods complement information about the patient’s condition, but do not replace each other. The ophthalmologist independently chooses examination methods, taking into account the possibilities of the examination.
Treatment
Physiotherapy methods to eliminate spasms:
- acupuncture;
- use of laser equipment;
- magnetic therapy;
- neck massage.
Drug treatment:
- microcirculation correctors are used to normalize blood supply;
- angioprotectors restore the permeability of vascular walls;
- antiplatelet agents are used for high blood clotting;
- antihypertensive and hypoglycemic drugs are used to treat the underlying disease;
- eye drops help improve the quality of vision.
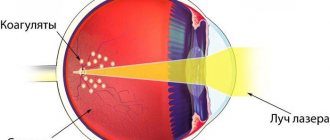
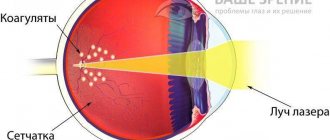
Hawthorn, chamomile and lemon balm extract help in the treatment of retinopathy. Surgical intervention is performed when conservative treatment methods are insufficiently effective. Laser coagulation is performed and the vitreous body is removed.
Complications and consequences
Violation of doctor's recommendations leads to the following consequences:
It is necessary to consult a doctor and carry out therapy immediately if the veins are dilated and the arteries are narrowed. The delay affects the effectiveness of therapy. It is important to begin procedures at the stage of functional impairment, before detachment or necrosis occurs.
Prevention
Sugar levels in the body are controlled to prevent vascular problems. Proper nutrition, a healthy lifestyle and regular exercise prevent the narrowing of blood vessels in the fundus.
More useful information about vasoconstriction of the fundus can be obtained by watching the video.
Was the article helpful?
Source: https://proglazki.ru/bolezni/suzhenie-sosudov-glaznogo-dna/
Diagnostics
During the examination, the patient's eye pressure must be measured.
- viziometry (visual acuity test);
- tonometry (measurement of intraocular pressure);
- ophthalmoscopy;
- angiography;
- computed and magnetic resonance imaging;
- Dopplerography.
During the examination, the patient's eye pressure must be measured.
The condition of the vessels of the visual organs can be checked during the ultrasound procedure.
It is impossible to determine the disease on your own. It is easily confused with other eye pathologies. An ophthalmologist and a phlebologist - a doctor who treats venous disorders - will help to correctly diagnose varicose veins. It is possible to recognize varicose veins primarily due to external signs. After a detailed history collection, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostic measures - ultrasound scanning. It is necessary in order to determine the state of the venous system of the eye. After the diagnosis is made, the necessary medications and procedures are prescribed to eliminate the pathology.
Narrowing of the fundus vessels - causes, symptoms and treatment
In medicine, narrowing of the fundus vessels is called angiopathy. Usually the pathology does not have an independent character, but becomes a symptom of another disease. To cope with the disorder, you need to consult an ophthalmologist in time.
Otherwise, the anomaly will lead to poor vision and headaches.
Hypertensive angiopathy
A chronic increase in pressure destroys the walls of blood vessels, leading to damage to their inner layer - the endothelium. As a result, compaction of these areas is observed. After some time, they undergo fibrotic processes.
In the area where the vessels intersect, compression of the veins is observed, which leads to impaired blood flow. As a result, conditions are created for the formation of blood clots and hemorrhages.
A person has high blood pressure, rupture of individual vessels. As a result, angiopathy transforms into retinopathy.
A typical symptom of hypertension is vascular tortuosity. According to statistics, at the early stage of hypertension this symptom is diagnosed in 25-30% of people, while at the third stage all people experience abnormal processes.
In difficult situations, hemorrhages occur, the retina becomes cloudy, and destructive processes are observed in its tissues.
Diabetic angiopathy
When diabetes appears in a patient, the structure of the small vessels of the retina and larger vessels of the internal organs is disrupted. As a result of these processes, the patient becomes disabled.
A complex consequence of disorders is retinopathy. It occurs in 90% of people with diabetes. This deviation can be detected already in the initial stages of the disease. This is carried out during an ophthalmological examination, when there are still no symptoms from the organ of vision.
Deterioration of vision is a late sign that indicates the irreversibility of changes. With prolonged diabetes, vision is impaired so severely that the person becomes unable to work.
Complete blindness with this disorder is 25 times more common in patients with diabetes than in those who do not have this disease.
Traumatic angiopathy
This form of pathology is caused by compression of the skull, chest, and abdominal cavity. It can also be a consequence of a neck injury. Damage to the blood vessels of the organ of vision is caused by a sharp increase in pressure and compression of the blood vessels in the neck area.
Characteristic symptoms of such an anomaly include severe vasoconstriction and hemorrhage in the retina. This process is characterized by a sudden deterioration in vision. Moreover, it is not always possible to normalize it.
Hypotonic angiopathy
Weakening of vascular tone and a decrease in the rate of blood flow during hypotension form the prerequisites for the appearance of blood clots.
This type of illness is accompanied by a noticeable expansion and branching of the arteries, a sensation of pulsation in the veins, which a person can feel. Many people also experience headaches and dizziness.
Patients often experience weather dependence.
Juvenile angiopathy
The second name for this little-studied anomaly is “Eales disease.” This condition is extremely rare. It manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the retinal vessels, which has an unclear etiology.
With this disease, hemorrhages occur. They can be localized in the area of the retina or vitreous body. There is also a risk of connective tissue overgrowth. This leads to dangerous consequences such as retinal detachment or the development of cataracts.
In addition, the anomaly can cause glaucoma.
Medications
Vascular damage requires the use of a whole range of medications:
- Drugs to normalize blood flow. These include Trental, Actovegin. It is worth considering that this category of products should not be used by women during pregnancy and lactation. They are also contraindicated for children. If it is necessary to treat these categories of patients, the decision on the appropriateness of a particular drug must be made by the doctor.
- Means for reducing the permeability of vascular walls. This group includes calcium dobesilate and parmidine.
- Substances to reduce platelet aggregation. These include dipyridamole and ticlodipine.
- Vitamins. It is important to take vitamins B, C, P, E.
Courses of therapy usually last 2-3 weeks. They must be repeated 2 times a year. All substances can be used only after consulting a doctor.
If you have diabetes, it is important to use medications to lower your blood sugar and stick to your prescribed insulin dosage. In case of atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension, means are needed to normalize blood pressure parameters and cholesterol levels.
In addition to systemic medications, the ophthalmologist may prescribe eye drops. The most effective means include the following:
- Vitaminized substances - these include lutein complex and anthocyanin forte;
- Vascular agents – emoxipin, taufon.
Medicines ensure normal blood flow in the eyes. Thanks to this, the patient's condition improves significantly.
Physiotherapy methods
For treatment to be effective, it must be comprehensive. Most often, the following methods are used to treat angiopathy:
- Magnetic influence;
- Acupuncture;
- Laser exposure.
Folk remedies
In addition to standard therapy, you can use home recipes:
- Mix 100 g of chamomile, immortelle, St. John's wort. Take the same volume of birch and yarrow buds. Add 500 ml of boiling water to 1 large spoon of the mixture and leave for 20 minutes. Bring the strained product to the original amount. Take 1 glass in the morning and before bed. In the evening after using the product, it is forbidden to drink or eat.
- Take 1 small spoon of mistletoe powder, add 1 cup of boiling water and leave to steep overnight. Take 2 large spoons twice a day. Treatment should last 3-4 months.
- Mix 15 g of lemon balm and valerian rhizomes, add 50 g of yarrow. Mix 2 small spoons of the mixture with a glass of water and leave for 3 hours. Infuse the composition in a cool place. Place in a steam bath for a quarter of an hour, cool and strain. Add water to make 250 ml. Take throughout the day in small portions. This treatment should be continued for 3 weeks.
Narrowing of the eye vessels indicates various pathologies and can provoke negative health consequences. To minimize the likelihood of illness, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner and strictly follow his instructions.
Source: https://zrenie.guru/suzhenie-sosudov-glaznogo-dna
Treatment, causes and manifestations of dilated fundus veins
Negative changes in the condition of the eyes, which were not identified in a timely manner and caused deterioration of vision, are often associated with pathologies of the veins located in the fundus. It is in this part of the eye that changes in the veins can be observed, which provoke circulatory disorders of the tissues in this area.
The cause of such pathological changes in the veins of the fundus, such as their expansion, can be an increase in blood pressure caused by hypertension, metabolic disorders (diabetes), kidney damage and hormonal changes, which most often occur during pregnancy.
When the arteries are narrowed and the veins are dilated, the fundus of the eye does not receive the required amount of blood and nutrients, which requires prompt medical correction.
Enlarged veins in the fundus of the eye - causes of pathology
The eyes are a particularly sensitive organ to many pathologies that occur in the body. Their health can be affected by factors such as surges in blood pressure, significant fluctuations in body weight, and a decrease in the degree and quality of the immune system.
The reasons why veins in the fundus may be dilated are as follows:
- hypertension, in which there is a sharp increase in blood pressure, which negatively affects the condition of the veins and blood vessels in the fundus of the eye;
- damage to the kidneys and urinary system, which also increases fluid pressure in the skull and in the veins of the eye fundus;
- deterioration of the condition of the veins, the appearance of cholesterol deposits in them - vascular atherosclerosis causes an increase in blood pressure in the brain and worsens the process of blood movement in the veins of the fundus;
- during pregnancy, especially in the last quarter.
Impaired blood supply to the eyes, hormonal changes, metabolic disorders (primarily diabetes mellitus), and retinal thrombosis can also cause dilation of the veins located in the fundus of the eye. The reason for this negative manifestation lies in changes in the blood supply to the eye tissues and increased pressure. Microcirculation disorders are also often observed.
This lesion is accompanied by a gradual deterioration of vision, the appearance of fog before the eyes, and the causes that occur in adults and children are basically similar.
And if adults are characterized by acquired diseases (hormonal imbalances, age-related changes, atherosclerosis of blood vessels and veins), then children are more characterized by congenital anomalies: insufficiency of microcirculation in the tissues of the eye, increased blood pressure due to pathologies of the brain.
Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
When the veins of the fundus of the eye are dilated, a number of characteristic symptoms appear, allowing one to identify the initial stage of the pathology, which is more amenable to treatment.
Pathological narrowing of blood vessels may indicate a violation of blood circulation and microcirculation in the tissues of the fundus, and the development of various diseases may be noted.
For example, atherosclerosis of blood vessels and veins, accompanied by the formation of cholesterol deposits, interferes with the normal movement of blood through them, which causes increased pressure when the veins of the fundus of the eye expand.
Hypertensive angiosclerosis, which causes disturbances in the condition of the fundus veins, causes the following characteristic symptoms:
- swelling of the eyes, which occurs in more advanced stages of the disease;
- feeling of a constant veil before the eyes;
- deterioration in the quality of vision both at close and far distances;
- changes in the tissues of the retina, which is accompanied by a violation of blood microcirculation in it;
- the field of view may decrease, some parts of it seem to fall out of view.
Patients may also complain of headaches that arise due to excessive eye strain; the clinical picture reveals swelling of the optic nerve, an increase in the size of the disc, blood vessels “drown” in the swollen mass, and the veins are excessively tortuous, which impairs blood circulation in them. If the therapeutic effect on the affected part of the fundus is insufficient, the symptoms worsen, which provokes the development of retinal thrombosis.
Treatment of retinopathy and angiopathy
Dilated veins, localized in the tissues of the fundus of the eye, require therapeutic intervention, since if treatment is insufficient, there is a high probability of aggravation of symptoms.
In subsequent stages of the disease, more active treatment is required, with the use of medications to restore the elasticity and normal functioning of the veins.
Treatment of the underlying disease is based on the impact of the root cause of the pathology of the veins of the fundus, therefore you should promptly pay attention to even minor changes in the quality of vision.
The main direction of treatment is the use of absorbable agents, and their use is carried out in combination with drugs that relieve swelling. Thanks to them, it becomes possible to prevent the possibility of hemorrhage in the tissues of the fundus, which can lead to complete loss of vision.
Thrombosis
Signs of cholesterol deposits forming on the walls of the veins, which can cause the formation of blood clots that interfere with blood circulation, must be promptly eliminated. The transition of the disease to the next stage is fraught with a significant deterioration in the quality of vision, therefore diagnosis of the pathology should be carried out at the first manifestations of changes in vision.
Thrombosis of the central retinal artery is extremely susceptible to disturbances in the blood circulation; its aggravation can be prevented by the combined use of drug decongestant therapy with physical procedures: magnetic therapy, acupuncture.
Inflammation
In some cases, an inflammatory process may occur, and deterioration of vision is accompanied by the possibility of bleeding in the fundus tissues. The therapeutic method is selected depending on the condition of the eye and the presence of edema.
Optic atrophy
Enlarged optic discs, which can cause inflammation of the fundus tissues, can cause gradual atrophy. The following characteristic symptoms are noted:
- blurred vision;
- loss of image clarity;
- flashing "fly" before the eyes.
In difficult cases, in the absence of the necessary therapeutic intervention, retinal detachment is likely to occur, which can lead to complete loss of vision, which cannot be cured in the future.
Delaminations
Manifesting itself in the vascular tract of the eye, detachment is accompanied by the destruction of blood vessels, which provokes changes in the flow of blood into the veins.
When the retinal layer is destroyed, there is a threat of vision loss, and the treatment method differs in that agents must be used that ensure the germination of blood vessels that ensure normal blood supply to the fundus tissues.
Any damage to the cornea is accompanied by a deterioration in the quality of vision, but it is detachment that is the most serious problem among other eye pathologies.
Retinal tumors
Cancerous lesions can also affect such a delicate and sensitive organ of the human body as the eye. In advanced stages of the pathological process, treatment becomes increasingly difficult; foci of exudation can be localized in different parts of the eye.
The therapeutic method for diagnosing tumor processes is most often based on surgical removal of pathological cells and preventing the worsening of the disease.
Dystrophy
Lesions of the veins of the eye can be accompanied by symptoms of dystrophy, manifested in deterioration of vision, loss of clarity of the picture, and flickering of “spots” before the eyes. Dystrophy may require the use of medication in combination with surgical correction of the retina.
Fundus vascular diseases in children
In childhood, as in adults, symptoms of significant visual impairment, damage to the retina and fundus tissues may occur.
For children, the most typical manifestation is congenital anomalies in the development of the eyes, in particular the fundus.
Since eye lesions in childhood are likely to progress rapidly, an ophthalmological examination of the child should be carried out regularly in order to promptly identify the onset of fundus vein disease.
The blood vessels of a child's eyes are more susceptible to negative effects, especially with a hereditary predisposition. It is the genetic factor that plays a special role in the occurrence and development of any pathology of the fundus veins.
As Dr. Malysheva advises in her program about health, children need to undergo a doctor’s examination even at an early age, since childhood eye diseases at an earlier stage of development are more amenable to treatment.
Possible complications
In the absence of the necessary treatment, there is a high probability of developing complications that negatively affect vision. The most common complications include:
- deterioration of vision, which with further inattention to the condition of the eyes can develop into complete blindness;
- hemorrhages in the retina - this consequence can occur with improperly selected treatment, significant strain on the eyes, as well as with the development of hypertension, which is expressed in increased blood pressure;
- damage to the cornea, which can provoke the formation of cataracts. These conditions, in turn, can lead to gradual loss of vision and headaches, which significantly reduce the patient’s quality of life.
Retinopathy develops in later stages of the disease, which is likely due to insufficient therapeutic intervention or too late diagnosis of the disease. Therefore, to prevent possible complications and maintain visual acuity, it is recommended to pay attention to any changes in the condition of the eyes in a timely manner.
Disease Prevention
To prevent possible consequences, loss of vision and deterioration of well-being, you should make some changes in your own life. The following points of a preventive approach to problems with fundus veins should be considered important:
- Introducing healthier lifestyle habits: quitting smoking, alcohol.
- Sufficient physical activity to activate blood circulation in the tissues of the brain and fundus of the eye.
- Regular preventive examinations with a doctor, in particular an ophthalmologist.
- Nutritional control - lowering cholesterol levels, introducing more fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs into the daily diet, preventing digestive disorders.
The recommendations listed are easy to apply and will help preserve the vision and health of every person.
Source: https://venaz.ru/simptomy/arterii-suzheny-veny-rashirny-glaznoe-dno
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms of progressive varicose veins of the eyes include:
- visible pulsation of the vein near the eye;
- development of vision problems;
- headache;
- blood pressure problems;
- puffiness under the eyes;
- convexity of blood vessels.
Having discovered a problem, immediately contact a phlebologist and, having agreed on the prospects with him, take the measures that the doctor advises. In addition to surgery, there are many other methods to correct the situation, hide a cosmetic defect and improve blood flow.
Even with modern methods of treating the disease known to medicine, it is difficult to remove blood vessels in the eye area. Such operations are risky, and it is quite difficult to predict the result.
But the disease cannot be started, so if possible, take preventive measures against varicose veins of the eyes to prevent the appearance of the first symptoms.
The main sign of venous enlargement of the eyes is easy to determine. This is the occurrence of telangiectasia - “spider veins” that appear around the eyes and on the eyelids. They look like a venous network of bluish, red and purple colors, 3-5 mm in size. In addition to the appearance of “spider veins”, swelling occurs; the so-called pouches, blood vessels become convex, and the pulsation of the vein is easily noticeable. In addition to external factors, symptoms of ocular varicose veins include:
- headache;
- blood pressure surges;
- blurred vision;
- the appearance of a “veil” before the eyes;
- pain.
Arteries are narrowed, veins are dilated, the fundus of the eye is dilated
Retinopathy is a pathological change in the structure and function of the retina of the eye, and one of its signs can be considered a narrowing of the vessels of the fundus.
In addition to capillary sclerosis, other disorders can be noticed, for example, congestion of the optic nerve head, unevenness of the vascular network, hemorrhages, and more. Among the complaints of patients suffering from retinopathy of any origin, the most common are decreased visual acuity and foci of darkening in the field of vision (scotomas).
Based on the origin of retinopathy, they are classified into:
- renal;
- diabetic;
- hypertensive;
- rheumatic;
- leukemic and others.
Each of them has a characteristic clinical picture, and with the help of ophthalmoscopy, ophthalmochromoscopy, fluorescein angiography and other ophthalmological techniques, the cause of retinopathy can be determined with high accuracy. Each of them should be discussed in more detail.
Renal retinopathy
This disease can be caused by prolonged glomerulonephritis and renal failure due to a “wrinkled kidney”. Patients complain of decreased vision and darkening of the eyes, which is limited to spots or spreads to the entire field of vision.
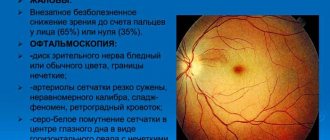
When examining the fundus, congestive optic discs can be noted, and against the background of tortuous and narrowed retinal vessels, whitish foci of ischemia are located, which, merging in the area of the retinal spot, form a figure resembling a star. The process will almost always be two-way.
Hypertensive retinopathy
By assessing the vessels of the fundus of the eye, with hypertension of various origins, one can judge the characteristics of the course of the disease in a particular case and its stage. Depending on the intensity of changes in the fundus, it is customary to distinguish between angiopathy, angiosclerosis, angioretinopathy and angioneuroretinopathy.
The first of them is inherent in the first stage of hypertension and is reversible. At this stage, functional disorders and an unstable increase in blood pressure are observed.
Against the background of these jumps, the vessels experience successive narrowing and expansion of the walls. Because of this, their shape changes, they become more convoluted (especially the veins) and tend to intersect each other (the Salus phenomenon).
At the same time, the veins lying under the arteries are constantly in a state of compression and gradually undergo thinning.
Retinal degeneration is a common disease among the elderly population; in extremely rare cases, it can occur in children and adolescents. Most often, vascular dystrophy is of a hereditary nature or is associated with the aging process. This disease always has a progressive course and leads to a gradual decrease in vision, up to blindness.
Degenerative processes have various features of the clinical picture, based on this, their main types can be distinguished:
- pigmentary degeneration;
- spot white degeneration;
- central dystrophy (with the most common age-related macular degeneration).
Senile macular degeneration
It affects mainly older people, can be one-sided and tends to progress fairly quickly. Sometimes patients can even note the time of onset of blindness. For some time, partial vision correction with glasses is possible. Fundus damage begins from the periphery and spreads to the central fovea of the macula.
Causes of vasoconstriction in the fundus
Changes in the caliber of retinal vessels are a fairly common phenomenon. In the development of this pathology, two pathogenetic mechanisms play the greatest role: spasm and sclerosis.
None of them is realized against the background of absolute health, therefore the reason for the change in the diameter of the feeding arteries of the retina should generally be sought in other organs.
The condition of the fundus capillaries may be affected by:
- local injuries;
- inflammatory processes (it is worth highlighting tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, rheumatism);
- neuroendocrine diseases;
- increased intracranial, intraocular/blood pressure.
Features of the visual picture, during an ophthalmological examination, together with the analysis of the patient’s complaints, can most often lead to a diagnostic search to the correct diagnosis.
The retina is the most important structure of the eye; it responds quickly to the smallest disturbances in the blood supply system. Angiopathy, not being an independent disease, is often included in the symptoms of certain diseases, signaling the reaction of the eye vessels. In this case, the pathology affects the walls of blood vessels and also modifies their structure.
Other types of pathology
It should be remembered that angiopathy can also develop for reasons independent of disease. These types of pathologies include:
- Juvenile angiopathy. The cause of the development of the inflammatory process of retinal vessels is unknown. Symptoms of this pathology are manifested in microscopic hemorrhages observed in the vitreous and retina. The most severe course of the pathology can lead to retinal detachment, provoke the development of glaucoma or cataracts, and in the worst case, result in the child’s blindness.
- Angiopathy of newborns. A rather rare pathology, the main provoking factor of which is birth complications or trauma. Symptoms of the disease are determined by proliferative changes in blood vessels with obvious narrowing and restriction of blood flow. Most often found in premature babies.
- Angiopathy in pregnant women. The development of pathology usually occurs after the first half of pregnancy against the background of certain diseases (for example, hypertension) characterized by weakening of the vascular walls. The early stages of the pathology are without dangerous consequences, but if treatment is not carried out, irreversible changes and dangerous complications are possible.
Clinical signs of pathology
Clinically, there are three degrees of retinal angiopathy - first, second (moderate) and third.
The degree of narrowing of the vessels of the fundus can only be determined during ophthalmoscopy.
Source: https://BoliGolovnie.ru/varikoz/arterii-suzheny-veny-rashirny-glaznoe-dno.html
Congested veins, retinal vascular angiopathy in newborns, increased intracranial pressure
Full-blooded and tortuous retinal veins are what parents often read in reports and what is presented to them as some kind of retinal vascular angiopathy.
What is angiopathy? Literally translated, the term “angiopathy” itself means that there is a pathology “pathy” of the vessels “angio”, but what kind of pathology this term does not indicate.
This term is used in modern ophthalmology, but with clarifications. Example: diabetic retinopathy (Diabetic Angiopathy). However, in the cases that we discuss, the word “angiopathy” is used in isolation.
In addition, this diagnosis is made very often and on the basis of it the neurologist draws some conclusions - usually nootropics are prescribed (which in fact never makes sense).
The term: “Retinal angiopathy” simply does not carry any meaning without specification and is often used by pediatric ophthalmologists in relation to children who, in their opinion, have blood vessels that are somehow different from the norm. How they differ is also an uncertain question. No criteria other than personal impression are used.
And most importantly, these “changes” do not reflect any pathological process. In fact, such a diagnosis is made only in our country and the countries of the former USSR; it does not carry any specifics and usually children who receive such a diagnosis are absolutely healthy. Unfortunately, this “diagnosis” still occurs quite often.
Unfortunately, neurologists also take this “diagnosis” into account. I even know one doctor who was reprimanded for not diagnosing “retinal angiopathy” during consultations with a large number of children. Needless to say, nothing serious was missed and this was an argument against which it is difficult to find objections.
Although, in my opinion, research should be the argument for a doctor.
How it all started:
Diagnosis of increased intracranial pressure is in particular based on the condition of the fundus. In the fundus of the eye, the ophthalmologist sees part of the optic nerve - the nerve that carries information about what a person sees in the brain. Essentially this is the part of the brain that is accessible to inspection. The ophthalmologist sees, as it were, a section of this nerve and it appears to him in the form of a circle or oval.
From the center of this circle, artery and vein blood vessels emerge onto the surface of the retina, which take part in the blood supply to the periphery of the retina. With intracranial hypertension, swelling of the optic nerve is possible, which leads to changes in the shape of the visible disc and its edges.
The disc becomes uneven, part of it protrudes anteriorly.
Arteries and veins are compressed; Accordingly, arterial blood enters in less quantity and the arteries become narrow, and venous blood cannot flow out in full and the veins become plethoric (thick) and tortuous.
Those. there is some kind of sequence: changes in the optic nerve - narrowing of the arteries - dilation of the veins.
This condition is called: “Congested optic disc”. With a stagnant disc, the venous congestion is pronounced and there is a narrowing of the arteries. Such changes are secondary to papilledema and this is a very serious symptom, and children with such a symptom should be urgently hospitalized.
Fortunately, increased intracranial pressure is not common, but many parents are faced with the fact that the ophthalmologist refers the child to a neurologist because of plethora of veins. This is explained by the fact that over time, the plethora of the veins itself began to introduce oculists into sacred awe. Those. plethora without changes in the optic nerve head and narrowing of the arteries.
Congestion of the retinal veins is a very subjective sign. This sign may be assessed differently by different doctors. The plethora of the veins can change depending on the child’s position (standing, lying), physical activity, and other things. A lot depends on the subjective assessment by the doctor.
It is impossible to talk about the caliber of the retinal veins as something constant and diagnostically significant.
Unfortunately, in Russia, medical knowledge is transmitted by so-called regional schools and it is passed on by word of mouth. For a long time, ideas about a particular diagnostic sign may not change and even become overgrown with fiction.
In Moscow, you can still find ophthalmologists who suggest checking with gastroenterologists for inflammatory eye diseases or “getting rid of worms.”
An approach from the position of evidence-based medicine is extremely rare and often leads to irrational waste of energy for the patient and doctors.
Diagnosis: Retinal vein angiopathy – does not exist.
UPD -Dear friends, I have to note that the diagnosis “Retinal Angiopathy” does not exist and it does not make sense.
It is very difficult for me to discuss with you the information that your child was diagnosed with this in a very respected clinic by your respected doctor. This doesn't change anything.
I hope for understanding, I can only discuss this from the position that this diagnosis is absurd, there is nothing more to add.
Good luck to all.
Frequent blinking in children
SPECIALIST CONSULTATION IS REQUIRED ONLINE CONSULTATIONS ARE NOT CONDUCTED. ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS ARE NOT GUARANTEED.
Any use of site materials is permitted. Links are welcome.
Veins dilated arteries narrowed fundus
Negative changes in the condition of the eyes, which were not identified in a timely manner and caused deterioration of vision, are often associated with pathologies of the veins located in the fundus. It is in this part of the eye that changes in the veins can be observed, which provoke circulatory disorders of the tissues in this area.
The cause of such pathological changes in the veins of the fundus, such as their expansion, can be an increase in blood pressure caused by hypertension, metabolic disorders (diabetes), kidney damage and hormonal changes, which most often occur during pregnancy.
When the arteries are narrowed and the veins are dilated, the fundus of the eye does not receive the required amount of blood and nutrients, which requires prompt medical correction.
Vasoconstriction and the development of various diseases
Have you been struggling with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
Vasoconstriction is an important mechanism in the development of many diseases. The normal state of the vascular bed presupposes a sufficient supply of organs and tissues with blood, and due to the blood supply - with nutrients, components for energy production, and oxygen. Both arteries and veins are important.
Undoubtedly, the influence on vascular tone of impulses from the brain and hormonal balance. Many factors can lead to vasoconstriction.
Our readers successfully use ReCardio to treat hypertension. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention. Read more here...
Conditions for the occurrence of narrowing of veins and arteries
The causes of vasoconstriction are very diverse. They depend on the type of vessel, external and internal factors, and the duration of their exposure.
External reasons
Arteries have a pronounced muscular layer, so they more often react with spasm to unfavorable factors. During spasm, small arteries narrow temporarily, but frequent repetition can lead to loss of the ability to relax and become stable.
Contributing factors are:
- smoking,
- stressful situations,
- alcohol consumption,
- hypothermia.
A similar external effect on the arteries is observed:
- with the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- in the initial stages of hypertension and ischemic disease;
- with frostbite of the extremities;
- with Raynaud's syndrome.
Longer-term narrowing of arterial vessels from external factors is observed with mechanical compression:
- during severe injuries (long-term compartment syndrome);
- tumor growth near blood vessels;
- the pressing action of the bone tissue of the spinous processes of the spine;
- prolonged incorrect use of a tourniquet to stop bleeding (this is why first aid requires placing a note indicating the time of application).
Internal reasons
Internal causes of vasoconstriction include:
- atherosclerotic damage to the wall - between the middle and inner membranes of arteries of the muscular-elastic type, a low-density fraction of lipoproteins is deposited with the formation of plaques, over time they are supplemented with calcium salts, the lumen of the vessel loses its diameter;
- inflammatory changes (vasculitis, arteritis) - swelling of the walls reduces blood permeability;
- endarteritis - an unclear allergic reaction from the intima of the arteries of the legs and arms, leading to complete obliteration of the vessel;
- congenital pathology (aortic stenosis);
- thrombosis and embolism - play an important role in the development of pathology of the brain and heart;
- metabolic disorders in diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, obesity.
Source: https://zdorov108.ru/simptomy/veny-rashirny-arterii-suzheny-glaznoe-dno