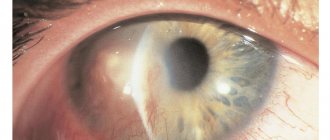
Maculopathy is a complex ophthalmological disease, the main cause of which is diabetes mellitus. To prevent fatal complications caused by the progression of maculopathy, the patient needs timely and adequate medical care:
- clear interaction between specialists caring for a patient with diabetes mellitus (endocrinologist, angiosurgeon, neurologist, ophthalmologist);
- detailed consultation with an ophthalmologist and a full diagnostic examination;
- assessing the level of risk when identifying retinal damage leading to progressive deterioration of vision;
- timely prescription of adequate treatment.
Causes
Diabetic maculopathy occurs due to the development of generalized microangiopathy - vascular damage caused by fluctuations in blood sugar levels during diabetes. Factors that aggravate the negative impact of high sugar levels on retinal vessels in diabetics are:
- arterial hypertension, persistent increase in blood pressure;
- lipid metabolism disorder;
- nephropathy – kidney damage.
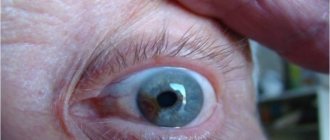
Diabetic maculopathy is characterized by damage to blood vessels in the macula. It is caused by an uncontrolled rise in blood sugar levels due to diabetes. Symptoms of the disease can have different degrees of severity, regardless of the stage of the disease.
This condition requires prompt assessment and follow-up by specialists, as there is a high risk of sudden deterioration in visual function.
To manage patients with edematous maculopathy, it is necessary to clearly determine the topography of the macular area involved in the pathological process.
The macular area is a differentiated zone of the retina, with a size of 3500 - 5000 microns. It is localized in the temporal side of the retina with a deviation of 1500-2000 µm from the edge of the optic nerve head.
Retinal maculopathy
People who suffer from diabetes are always at risk of encountering complications from this disease.
They can affect the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Diabetic maculopathy occurs as a result of the progression of pathology in the retina. With ophthalmoscopy, this area is visualized as a yellow spot. Treatment focuses on the underlying disease and then on eliminating its consequences.
Causes
Basically, this pathology affects both eyes. A single lesion is very rare. The main reasons for the development of this pathology:
- neuropathy - the gradual destruction of nerve endings in the retina due to the influence of high amounts of sugar (it is worth noting that this affects not only the eyes, but the nervous system as a whole);
- microangiopathy – accompanied by impaired microcirculation in the eye;
- Chronic increase in blood sugar leads to chorioretinal dystrophy.
The etiology of pathological processes is determined by the doctor after a full examination. It is impossible to independently determine this disease and the cause of its development. If unpleasant symptoms develop, you should consult a doctor.
Risk group
People who suffer from any type of diabetes are at risk. They must constantly monitor their condition and monitor their blood sugar levels. Patients should regularly visit an ophthalmologist to monitor their eye conditions.
Classification
Eye maculopathy has the following main types: edematous, ischemic, exudative. Each of these forms is accompanied by certain symptoms:
Protection against coronavirus
How to boost immunity and protect loved ones
>
- The diffuse form is accompanied by thickening of the retina. Upon examination, the doctor may notice cystic changes. Swelling occurs. Macular edema has a cystic form.
- Edema form. It is distinguished by large edema. In the initial stage of development, you can get rid of the pathology using laser coagulation. In most cases, this will help normalize the condition of the retina. This form of the disease is often encountered by older people who depend on insulin.
Any form of maculopathy requires elimination of retinal damage factors. It is very important to monitor the concentration of glucose in the blood and, if necessary, normalize it. It is worth noting that this must be done quickly, since irreversible processes may occur in the retinal blood vessels. To prevent such processes, antiorogectors are needed.
Symptoms
The signs of this pathology are complex. Manifest in the form of such violations:
- macular edema, which the doctor determines by ophthalmoscopy;
- decreased visual acuity;
- the development of dry macular degeneration is accompanied by the absence of exudative manifestations;
- wet macular degeneration - has a favorable prognosis, but can be accompanied by a serious complication - retinal detachment;
- increased intraocular pressure is accompanied by severe symptoms and requires emergency medical attention;
- pain (may intensify when focusing your gaze), feeling of sand.
If any suspicious symptoms develop, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
Initially, the doctor must conduct a visual examination and listen to the patient’s complaints. After this, study your medical history to rule out the presence of chronic diseases.
Additional research:
After a complete diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the necessary treatment. It is forbidden to self-medicate or ignore such manifestations. This can cause severe complications and negative consequences.
Treatment
Treatment of maculopathy will not be effective unless the main cause of its development is eliminated. Therefore, the doctor should focus therapy on eliminating diabetes mellitus. Treatment can be carried out at home or in a hospital. It depends on how the patient feels and the development of symptoms. Therapy is mainly aimed at taking medications that lower blood sugar levels.
Patients who suffer from this disease must constantly monitor their blood glucose levels. To do this, they must take fast-acting and long-acting medications. Regular use of medications stabilizes glycemic levels and prevents the development of ophthalmic complications.
In severe cases, you will need to administer insulin before meals. With the development of maculopathy, the patient should take vitamin complexes and minerals. In severe cases, glucocorticosteroids are used.
Complications
The development of complications occurs due to improper treatment or its absence. If measures are not taken in time, a person may lose his vision. Diabetes mellitus requires regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. Otherwise, the person may fall into a diabetic coma. Such patients should be under constant medical supervision.
Forecast
In most cases, the prognosis for maculopathy is favorable. Especially if you stabilize your blood sugar levels in time. Diabetes is an incurable disease. Therefore, in order to prevent the development of complications, you should constantly be under the supervision of a doctor. It is also necessary to visit an ophthalmologist several times a year.
Timely therapy always gives hope for a successful result. If you ignore such manifestations, the prognosis may be disappointing. In case of such diseases, it is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol. This negatively affects the patient’s well-being and can provoke the development of unpleasant symptoms.
Prevention
The development of maculopathy can be avoided only by controlling the underlying disease. This is the basic rule of prevention.
You can control the amount of sugar in your blood only with proper and nutritious nutrition, an active and healthy lifestyle. The patient is strongly advised to give up bad habits.
It is important to avoid stressful situations and nervous tension. Depression and emotional stress negatively affect the development of diabetes.
If work activity is associated with physical activity or work with chemicals, then the activity should be changed. If you have diabetes, you must strictly follow your doctor's recommendations. This will help keep your glucose levels under control.
With maculopathy, dystrophic changes in the retina are observed. Therefore, it is better to prevent their development than to treat them. In severe cases, irreversible processes may develop.
A healthy lifestyle and good nutrition are the main prevention of any disease.
Was the article helpful?
Source: //proglazki.ru/bolezni/makulopatiya-setchatki/
Classification and symptoms of the disease
Experts distinguish the following types of diabetic maculopathy:
- exudative;
- edematous (diffuse);
- ischemic.
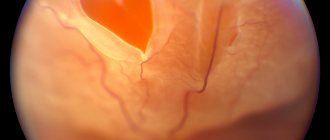
With edematous maculopathy, the following occurs: the retinal tissue of the eye thickens significantly, and its cystic changes develop. Obliteration occurs, accompanied by severe swelling, sometimes with the inability to determine the location of the fovea.
Fluorescein angiography reveals: punctate plural hyperfluorescence of microaneurysms; late edematous hyperfluorescence is more pronounced than during clinical examination.
In the cystic form of macular edema, this area is defined as a flower petal.
This maculopathy manifests as widespread edema, which is seen as diffuse staining on fluorescein angiography in late stages.
Eye maculopathy: causes, symptoms and treatment
Macular degeneration of the retina is a pathology that is accompanied by degeneration of the visual spot and leads to complete or partial loss of vision. Most often, this disorder is diagnosed in people over 50 years of age. At a younger age, this condition is much less common.
Typically, this disorder develops against the background of a narrowing of the lumens of the blood vessels that supply this part of the visual apparatus. Damage to the retina makes it impossible to focus the image. Peripheral vision is practically not affected by this.
In medical practice, it is already well known what macular degeneration of the retina is, so quite effective methods for treating this pathology have been developed. The success of therapy largely depends on the stage of the disease at which it was started. People at risk need to be careful about their health and regularly visit an ophthalmologist.
Causes of development of macular degeneration of the retina
Currently, many factors are known that contribute to the development of retinal macular degeneration. Europeans are most often affected by this disease, while Africans and Asians suffer from it much less frequently.
This indicates a genetic predisposition of certain races to develop such a visual disorder. In most cases, age-related macular degeneration of the retina is detected. It is diagnosed mainly in people over 70 years of age.
This age group has a 30% higher risk of having a lesion in the macula.
Hereditary predisposition is also the most important factor contributing to the development of macular degeneration of the retina. It has now been confirmed that those who have blood relatives suffering from this disease have a 50% risk of developing the disease. Among other things, factors contributing to the development of such a disorder as retinal macular degeneration include:
- smoking;
- abuse of ultraviolet radiation;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- physical inactivity;
- poor nutrition;
- hypertension;
- angina pectoris;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- taking certain medications.
Among other things, atherosclerosis increases the risk of developing macular degeneration, especially if it is accompanied by blockage of small blood vessels.
This leads first to the formation of scars, and then to the launch of degenerative processes. This disruption of the visual apparatus may be the result of rapidly progressing myopia.
Myopia often develops after cataract surgery.
Excess weight and diabetes mellitus contribute to macular degeneration, as they are accompanied by damage to the small blood vessels that supply the retina.
In addition, excess weight and diabetes contribute to increased levels of “bad” cholesterol in the blood.
This substance, deposited on the walls of blood vessels, forms microthrombi, which subsequently cause disruption of the nutrition of the retinal tissue and contribute to the initiation of degenerative processes.
The development of macular degeneration may be facilitated by calcium deposition on the retina at an early age.
This problem is often the result of an unhealthy lifestyle and addiction to monotonous and unhealthy food.
Thus, people who are initially at risk because they have a genetic predisposition need to take into account all factors that can trigger the pathological process.
Types of disease
This disorder has 2 forms: dry and wet. The dry form is considered to be the result of natural tissue thinning, deposition of pigment substances, or a combination of other disorders observed in old age.
When macular degeneration is confirmed, the dry form means that the condition is not accompanied by the appearance of new blood vessels. In 80-95% of patients, this type of damage to the visual apparatus is diagnosed.
It usually does not lead to complete loss of vision.
The progression of dry AMD (age-related macular degeneration) can lead to the development of the wet form. This condition causes new blood vessels to form in the retinal tissue.
This pathological process is extremely dangerous, since new capillaries are fragile. Their damage causes microhemorrhages. This contributes to the accelerated development of the disease.
As a rule, the wet form develops against the background of the dry form only in 10% of cases.
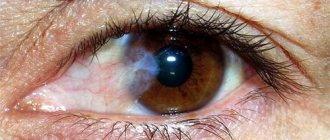
To make a diagnosis and determine the degree of advanced AMD, an ophthalmologist conducts examinations of the macula to determine such a phenomenon as drusen. These are peculiar yellow spots around the affected area.
Such deposits can be found in people aged 50-60 years, when the dry form of the disease is still at the very beginning of its development. Research has now confirmed that there is a clear relationship between drusen and macular degeneration of the retina.
As drusen increase in size, the risk of developing AMD increases.
AMD has 3 stages:
- early;
- intermediate;
- expressed.
The degree of visual impairment depends on the stage. When it comes to a condition such as age-related macular degeneration, the wet form can occur in a classic or latent form.
In the first case, there is a characteristic growth of blood vessels, there are pronounced hemorrhages and the active process of formation of scar tissue. If wet macular degeneration of the eye occurs as a latent type, the signs are smoothed out. New vessels grow slowly.
In this case, there is practically no hemorrhage, so the disturbances are minimal.
Symptoms of pathology
Macular degeneration of the retina is accompanied by a rather slow increase in signs of tissue damage. The most common condition is macular degeneration of both eyes, which is accompanied by characteristic symptoms. At first, patients may complain that objects appear blurry. There are difficulties in recognizing letters when reading, especially if the font is small.
Degenerative processes lead to the fact that an image cannot be formed on the retina of the eyes, which will be transmitted to the brain for processing. Subsequently, pronounced sensitivity to light appears. Painful sensations are usually not observed at all stages of development.
As the disease progresses, a spot forms on the retina of the eye. Patients see it as a kind of veil that prevents them from fully examining any objects. Vision decreases so much that driving a car and reading already pose a certain difficulty. The development of this pathological condition is evidenced by the loss of the ability to distinguish colors.
As macular degeneration of the retina progresses, patients may complain of loss of coordination and the inability to see any objects in poor lighting. When looking directly, whole fragments may fall out. In rare cases of severe cases, patients may complain of hallucinations that are the result of distortion of straight lines.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic test for diabetic eye disease is the previously mentioned fluorescein angiography of the retinal vessels. Its implementation makes it possible to determine zones of ischemia, areas of active filtration, cystic edema, subretinal neovascular membranes, and retinal breaks. Angiography determines the possibility of prescribing laser treatment (coagulation).
Photographing the retinal area in color and without red makes it possible to detect diabetic changes already in the initial stages of the disease. In the future, this study is used to evaluate the results of therapy and dynamic monitoring of the process.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment of edematous maculopathy can be divided into two stages - conservative therapy and laser treatment. A more effective method, however, is laser coagulation, although it cannot guarantee a 100% positive result.
With early diagnosis of maculopathy and taking timely measures - performing focal laser coagulation, you can count on stabilizing the process and improving the condition of the retina.
The most serious pathological changes in this situation occur in the retina of elderly patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. That is why they have a particularly high risk of a significant decrease in visual function, often to the point of blindness.
Treatment of the disease, regardless of its form, requires excluding exposure to factors that cause pathological processes in the retina.
What is retinal macular degeneration: signs and effective treatment
The retina of the eye is responsible for human vision. Due to the development of macular degeneration, this part of the eye is damaged. Therefore, a person sees a blurry picture. In the presence of macular degeneration of the retina, drug or surgical treatment is prescribed depending on the form and severity of the disease.
What is retinal macular degeneration
Macular degeneration of the eye is a lesion of the central part of the retina. The main reason for the development of pathology is insufficient blood flow. A yellow pigment accumulates near the macula. Because of this, the light-sensitive cones are damaged. First, vision deteriorates in one eye, and later in the second.
Dystrophic changes rarely appear at 17–18 years of age. The disease most often occurs in people over 50 due to age-related changes. The disease usually affects both eyes.
With macular degeneration, the first symptoms do not appear immediately. In such cases, people turn to an ophthalmologist when they have the last stage of the disease. Therefore, it is impossible to completely restore vision.
In the presence of macular degeneration, disability is given, but the group depends on the severity and form of the disease. If visual acuity decreases to 0.03, the person is assigned disability group 1. With a slight decrease to 0.1, group 3 is given. In other cases, group 2 is assigned.
Macular degeneration does not lead to complete loss of vision. The disease affects a person’s ability to work. It makes it difficult to drive a car, watch TV, recognize others, or count money.
Conservative
Treatment of the initial stage of macular degeneration of the retina involves the use of drops. To cure the disease, visual pigments, antioxidants and drops containing zinc and copper are instilled into the eye.
A person may be prescribed vitamin-mineral complexes, the task of which is to slow down the development of pathological changes in vision. Complete vitamin-mineral complexes against retinal macular degeneration contain the following components:
- zinc;
- vitamins of groups A, C, E;
- copper;
- lycopene;
- lutein;
- omega-3 fatty acids;
- beta carotene.
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medications containing vitamins and minerals:
- “Complivit Ofthalmo”, prescribed for periodic visual fatigue;
- “Lutein Complex”, used as a food supplement for vitamin deficiency;
- “Metmorphine” is used as a prophylactic against ophthalmic complications for people with diabetes;
- “Vitrum Vision Forte” is prescribed for changes in the macular area in the central or peripheral part.
In addition to taking these medications, a person should eat a balanced diet. If there are dystrophic changes in the central part of the retina, it is forbidden to eat fatty foods:
- rich soups;
- pork;
- smoked meats;
- fried, salty foods.
When sick, it is recommended to eat green vegetables, fruits and berries. Lenten dishes predominate in the diet.
Surgery and laser
Laser coagulation of the retina is used for the wet form of macular degeneration. During the operation, fragile, leaking vessels that have formed over the course of the disease are removed. The laser is aimed at the vessels and destroys them, preventing vision loss.
But sometimes surgery and laser surgery damage healthy blood vessels. Because of this, vision deteriorates. The surgical treatment method is used only when the newly formed vessels are located away from the central fossa of the macula.
about laser coagulation of the retina, see below:
Modern methods
Today, age-related macular degeneration of the retina is treated with progressive methods. This therapy is effective for severe dry or wet forms. The essence of modern treatment is to prevent the proliferation of small vessels and destruction of the macula. For this purpose, special glasses Argus 2 were invented in the UK.
Folk
It is impossible to completely restore vision in the presence of dystrophic changes in the retina. Treatment of macular degeneration of the retina involves the use of folk remedies. Let's look at recipes for non-standard medicine:
- The washed, sorted wheat is laid out in a thin layer and filled with water. After germination, the wheat is washed. The resulting consistency is passed through a meat grinder. The resulting medicine is stored in a cool place. People with macular degeneration should eat up to 5 tsp of this wheat every morning. Berries and honey are added for taste.
- To restore vision you will need mumiyo infusion and aloe juice. 5 g of mumiyo is mixed with 100 ml of fresh juice. The resulting solution is stored on the top shelves of the refrigerator. It is necessary to instill the prepared drops 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 15 days. Then there is a break for a week. If necessary, therapy is resumed.
- Following a diet prevents further development of the disease. It is important to eat foods that are filled with vitamins and beneficial microelements.
Prevention
The main preventive measure for edematous maculopathy is maintaining compensation for diabetes mellitus for as long and stable as possible. Patients with this disease need to carefully monitor glycemic levels in the laboratory and at home, and adhere to effective treatment for diabetes mellitus. Depending on how timely such measures are started, a long-term prognosis for the course of the disease can be drawn up.
To prevent changes in the retinal vessels themselves, as well as for medicinal purposes, angioprotectors can be prescribed: dicynon, divascan, sore throat, trental. Although, if there is insufficient compensation for carbohydrate metabolism disorders, their effect turns out to be ineffective.
Diabetes mellitus is a compelling argument to strictly adhere to a special diet, monitor blood glucose levels on an ongoing basis, be sure to take special medications, and regularly visit an ophthalmologist to examine the fundus of the eye.
The specialists of our clinic have accumulated extensive experience in treating patients with edematous maculopathy, including those of diabetic origin. Thanks to the technological equipment of the center, it is possible to identify the disease at the earliest stages and receive timely, modern treatment of European quality. In addition, in our clinic there is a service of clinical observation of patients with diabetic maculopathy, management of such patients, organization of long-term measures to prevent the development of the pathological process.
maculopathy
The retina is made up of many structures, and one of the most important is the small macula, which, despite its tiny size, is responsible for central vision and the perception of details in images .
Over the years, the macula may not function well and cause central vision problems such as macular degeneration, which interferes with the correct perception of colors and images. Diseases of the macula are known as maculopathy . In addition, there are different types such as myopic maculopathy, diabetic maculopathy due to stress...
maculopathy
The retina is made up of many structures, and one of the most important is the small macula, which, despite its tiny size, is responsible for central vision and the perception of details in images .
Over the years, the macula may not function well and cause central vision problems such as macular degeneration, which interferes with the correct perception of colors and images. Diseases of the macula are known as maculopathy . In addition, there are different types such as myopic maculopathy, diabetic maculopathy due to stress...
Maculopathy is a disease that affects the function of the macula and causes a gradual loss of central vision, as well as difficulty in correctly perceiving details in images. Those who suffer from maculopathy, in most cases, have difficulty performing everyday tasks such as driving and being limited in recognizing people's faces.
The macula measures between 5 and 6 millimeters and is located in the central part of the retina. This tiny structure ensures that the eye can appreciate details, read correctly, drive and recognize people's faces. Damage to the macula, or maculopathy, is one of the leading causes of partial blindness in the world, hence early diagnosis is important.
There factors that increase the risk of maculopathy the most common are age (being over 60 years old), in which case it is associated with a certain form of maculopathy called DMAE Age Associated Retinal Dystrophy - but it can also be associated with family history, smoking, diet low in antioxidants, vitamin and zinc deficiencies, overexposure to the sun, stress and high blood pressure.
Maculopathy mainly affects people, and its main symptom is that it reduces the acuity of central vision, causing difficulty in perceiving colors and details in images correctly . Symptoms of maculopathy:
- Image distortion : Straight lines appear curved and wavy.
- Blurry vision , making it difficult to perform daily tasks such as reading and driving, or any other activity that requires the use of central vision.
- Learning dark spots in the center of the camp or visual . These spots may be small and gradually grow over time.
- It is necessary for more lighting in places so that one can see correctly and to reduce the contrast, which interferes with correct night vision and color perception.
Let us know below the different types of maculopathy:
Myopic maculopathy is what comes from myopia magna, one of the three most common refractive errors in humans. Nearsightedness causes the eye to grow longer than normal, causing images to form before they reach the retina rather than on it, resulting in poor vision.
La Myopic maculopathy affects people causing difficulty looking at objects from afar and lack of sharpness in central vision. Early diagnosis of this disease can help reduce the risk of a patient losing visual abilities.
Diabetes mellitus is a degenerative disease characterized by the body's difficulty controlling elevated blood glucose levels.
Excess glucose in the blood can permanently impact vision health by causing damage to the blood vessels in the retina, causing a condition called diabetic retinopathy, which can interfere with proper blood flow to the macula or thicken the tissue and cause diabetic macular edema, a condition considered serious.
Patients with diabetes should have their eyes examined on a regular basis to prevent or treat delicate eye conditions such as maculopathy and diabetic retinopathy over time.
Stress affects health in different ways, and different parts of the eye are not exempt from harm. One of the consequences of chronic stress is the development of inflammatory processes that can cause central serous choroidopathy, which is expressed in benign inflammation of the macula, also known in ophthalmology as executive disease.
Those who suffer from stress maculopathy or central serous maculopathy usually have blurred vision and they may have temporary and sudden episodes of vision loss, which is known as amaurosis. Before sudden vision loss, it is important to see an ophthalmologist immediately.
The most important thing for the treatment of maculopathy is early diagnosis, which avoids serious damage to the macula and thus prevents irreversible vision loss.
Maculopathy as such is a condition for which, to date, it has no universal treatment . In order to offer an accurate treatment, it is important that a retinologist analyzes the cause of the maculopathy in order to offer appropriate treatment in each case .
Intake of zinc and antioxidants is important for the treatment of maculopathy, as well as a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, which help control factors such as excess cholesterol, high blood pressure and diabetes. It is important to avoid smoking during the diagnosis of maculopathy.
Source: //areaoftalmologica.com/ru/%D1%81%D0%B5%D1%82%D1%87%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%BA%D0%B0/%D0%BC%D0% B0%D0%BA%D1%83%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BF%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%B8%D0%B8/