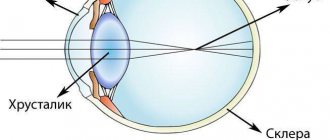
Visual disability groups
It is installed by an ophthalmologist after a thorough examination of the patient. There are a variety of ways to determine the severity of visual loss.
We recommend reading: One eye cannot see - is there a disability?
Determination of disability due to poor visual perception is based on the degree of damage to the optical system. They are formed in the ICD 10 revision.
There are 3 official groups of disability due to complete loss of vision or moderate impairment:
- 1 - given to patients with degree 4 dysfunction of the optical system. This is absolute or practical blindness. Determined if visual loss is equal to or greater than 90%. Grade 4 is characterized by a bilateral narrowing of the concentric type of space perceived by the visual organ with a fixed gaze; this indicator is less than 10 degrees. The acuity with glasses or lenses on the eye that sees better is no more than 0.04 diopters. There are draining blind spots in the central field. Indicators of electrophysiological research methods: electrical sensitivity threshold - more than 300 μA, lability - less than 20 Hz, critical flicker fusion frequency - less than 20 Hz.
- 2 - given to patients with degree 3 impairment. Changes in visual perception are pronounced, this is a high degree of low vision. This group is given to patients with severe forms of glaucoma and lens opacities. 70–80% of the ability to see is lost, the boundaries are narrowed by 10–20%. 2nd degree of disability is established if the ability of the organs of vision to perceive two points separately is 0.05–0.1 diopters, the peripheral boundaries along the meridian from the point of fixation are less than 20 and wider than 10 degrees. When performing visual campimetry, single absolute or multiple non-confluent black areas are detected. Indicators of electrophysiological research methods: electrical sensitivity threshold - up to 300 μA, lability - up to 20 Hz, critical flicker fusion frequency - up to 20 Hz. When assigning a group, the commission takes into account the patient’s level of adaptation and social factors.
- 3 - given to patients with 40-60% loss of visual perception. Peripheral boundaries are narrowed by 20%. Prescribed for stage 2 functional disorders of the visual analyzer. Acuity is more than 0.1 and less than 0.3 (if it can be corrected using contact or glasses vision correction), the field of vision is narrowed - less than 40 degrees, there are scotomas - single ones. Indicators of electrophysiological research methods: electrical sensitivity threshold - up to 120 μA, lability - up to 30 Hz, HFSM - up to 30 Hz. The patient has difficulty learning or doing work, and has limited independent movement and housekeeping.
When assigning a disability group to children before reaching adulthood, the criteria in 2020 in Russia do not differ from adults. After 18 years of age, the child undergoes re-examination, that is, he again turns to the treating ophthalmologist and receives a referral for an MSE.
Medical and social examination
Medical and social examination and disability in myopia (myopia) High myopia occupies a leading place among the causes of disability in people with eye diseases. The difficulty of solving the problems of medical and social examination in case of high myopia is explained by insufficient knowledge of its etiology and pathogenesis, the variety of forms and types of complications, and the peculiarities of visual perception in this pathology. In more than 80% of cases, degenerative-dystrophic forms of myopia lead to disability. A predisposing factor in their development is impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the retina and choroid, as well as in the great vessels. The progression of various forms of myopia is facilitated by weakened accommodation, scleral pathology and genetic predisposition. Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the membranes of the eyes and disruption of muscle activity occur mainly under the influence of infection, intoxication, eye and head injuries, vascular diseases, neurohumoral and endocrine disorders. The clinical prognosis for myopia is determined mainly by the pathogenetic form of the disease. It is favorable for the stationary, peridiscal form of myopia and less favorable for the progressive, predominantly posterior pole, form. The prognosis is especially unfavorable for the wet type of dystrophic changes in the macular zone. Impaired visual functions in myopia are expressed primarily in decreased distance visual acuity and impaired twilight vision. Subsequently, as the disease progresses, light adaptation decreases, color vision is impaired, and central and paracentral scotomas appear; with myopia over 15.0 diopters, disturbances in binocular, stereoscopic and deep distance vision often occur; with myopia over 20.0 diopters, the volume of accommodation is significantly reduced. Long-term preservation of photopic near vision has a beneficial effect on the development of compensation for myopia. When assessing the state of working capacity, special attention should be paid to the clinical picture of the disease, its form and stage, the presence of complications, the time of their occurrence, the severity of compensation, the patient’s age, and his attitude to work.Taking into account the high possibilities of compensation, persons with myopia up to 10.0 diopters without its pronounced progression, engaged in skilled mental or physical labor, as well as performing accounting, clerical and administrative work, are recognized, as a rule, to be able to work. At the same time, persons with progressive myopia in developed or advanced stages of the disease, characterized by hemodynamic changes, which is most often observed with myopia from 10.0 to 15.0 diopters, need exemption from work associated with severe or moderate (permanent) physical tension, sharp tilts of the head, forced working posture, with shaking of the body and vibration, exposure to radiant energy and ultrasound, the danger of exposure to neurotropic and toxic substances, as well as significant neuropsychic stress. However, patients with this variant of myopia have access to a wide range of jobs in the field of mental, accounting and clerical work of moderate volume and some types of physical labor without exposure to the above unfavorable factors.
The cause of disability due to myopia is usually identified as a “general disease.”
However, if young people who have not yet worked or have worked for only a few years, but with old persistent degenerative-dystrophic changes in the eye, are sent to MSE, “disability since childhood” is established. Progressive myopia is included in the list of occupational diseases for people whose work involves constant visual strain during precise, small work, for example, engraver, spectroscopist, cartographer. However, it must be borne in mind that often the progression of myopia and the appearance of complications can occur spontaneously with this disease and not be associated with working conditions. In view of this, when assessing work ability, one should take into account the length of service and working conditions. Since changes in eye tissues with high myopia are mainly degenerative-dystrophic in nature, the possibilities of medical rehabilitation are limited. At the same time, the creation of favorable hygienic conditions, correct, optimal correction, training of the muscular system of the eyes in young people, and sometimes timely surgical treatment (photocoagulation for cystic retinal degeneration, scleroplastic surgery) can prevent further development of myopia and provide the opportunity for long-term continuation of work in the specialty. In cases where conventional correction does not allow achieving high visual acuity, contact correction is used in the indicated cases. If the means and methods of medical rehabilitation turn out to be ineffective, professional rehabilitation, and if it is impossible to implement, social and labor rehabilitation, becomes especially important. A patient with high complicated myopia must be protected from unfavorable working conditions and favorable conditions for visual work must be created. In such cases, the level of illumination is of particular importance. Most patients prefer high levels of illumination - 500 - 700 lux. However, with significant damage to the photopic visual apparatus, which is manifested by increased sensitivity to light, decreased color sensitivity and light adaptation, it is easier for patients to work in lighting conditions not exceeding 300 lux. In this case, it is necessary to ensure not only a sufficient amount of light, but also its proper quality: the absence of direct and reflected glare, the correct distribution of light in the workplace (no shadows), the absence of significant fluctuations in illumination during the day. Timely treatment and compliance with sanitary and hygienic conditions for visual work contribute to the prevention of severe visual impairment due to myopia. Taking into account that 75% of patients with high myopia become disabled due to the wrong choice of profession at a young age, in order to prevent disability in this disease, it is recommended to pay attention to rational employment and timely training or retraining. CRITERIA FOR DISABILITY IN VISION PATHOLOGY IN ADULTS IN 2020 Disability is not established if the patient has: 1. Visual acuity (better in the visual acuity or in the only eye under conditions of maximum tolerated correction) > 0.3. 2. Concentric narrowing of the visual field of the better-seeing or single eye from 60° to 40° (inclusive) without absolute scotomas in the residual visual fields. 3. Relative paracentral non-confluent scotomas. Disability of the 3rd group is established if the patient has: 1. Visual acuity (better seeing or the only eye in conditions of maximum tolerated correction) correction) more than 0.1 to 0.3 (inclusive). 2. Concentric narrowing of the field of vision of the better seeing eye or the only eye less than 40° to 20° (inclusive). 3. Single, confluent absolute central scotomas up to 5 degrees and confluent absolute paracentral scotomas or ring-shaped scotomas with a concentric narrowing of the visual fields of the better seeing or single eye from 55 to 40 degrees (inclusive). Disability of the 2nd group is established if the patient has: 1. Visual acuity (better seeing with the seeing eye with correction) 0.1 - 0.05. 2. Concentric narrowing of the field of vision of the better seeing eye or the only eye less than 20° to 10° (inclusive). 3. Central absolute scotomas more than 5 to 10 better than the seeing or only eye. Disability of the 1st group is established if the patient has: 1. Visual acuity (better seeing eye with correction) 0.04 - 0 Visual acuity (better seeing eye or single eye with optimal correction) 0 - 0.04. 2. Concentric narrowing of the field of vision, better than the seeing eye or the only eye, less than 10°. 3. Central absolute scotomas more than 10 better than the seeing eye or the only eye. CRITERIA FOR DISABILITY IN VISUAL PATHOLOGY IN CHILDREN IN 2020 Disability is not established if the child has: For children aged 0 - 3 years: the presence of object vision. For children aged 4 - 17 years: visual acuity is better than the seeing (only) eye with optimal correction of more than 0.3. Any degree of concentric narrowing of the visual field is better than the seeing (single) eye up to 40° in the absence of scotomas. The category “disabled child” is established if the patient has: 1. For children aged 0 - 3 years: lack of objective vision.
2. For children aged 4 - 17 years: visual acuity is better than the seeing (single) eye with optimal correction of more than 0.1 to 0.3 inclusive. Concentric narrowing of the visual field of the better seeing (single) eye from 39° to 20° inclusive. Central absolute scotomas are better than the seeing (single) eye, 5° or less. 3. For children aged 4 - 17 years: visual acuity is better than the seeing (single) eye with optimal correction 0.1 - 0.05 inclusive. Concentric narrowing of the visual field of the better seeing (single eye) from 19° to 10° inclusive. Central absolute scotomas are better than the seeing (single) eye less than 10 degrees, but more than 5°. 4. For children aged 4 - 17 years: visual acuity is better than the seeing (single) eye with optimal correction from 0.04 to 0 inclusive. Concentric narrowing of the visual fields of the better seeing (single) eye from 9° to 0° inclusive. Central absolute scotomas are better than the seeing (single) eye by 10° or more. A patient can receive an official conclusion on the presence (or absence) of grounds for establishing disability only based on the results of his examination at the ITU bureau of the corresponding region
.
The procedure for completing documents for undergoing MSE (including the algorithm of actions in case of refusal of attending physicians to refer a patient to MSE) is described in sufficient detail in this section of the forum: Registration of disability in simple language
Source
How to register for a visual disability
To register or re-certify disability due to partial or complete loss of the ability to perceive visual information, adult patients are referred to the regional ITU.
MSE involves undergoing an examination, during which an ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist) gives a certificate about the condition of the optical system.
We recommend reading: One eye is missing - is it a disability?
They choose an institution to obtain a certificate independently; according to the current legislation of the Russian Federation, visual perception testing is carried out in a private clinic or government institution.
The initiator of obtaining disability can be the doctor or the patient himself.
The examination can be provided by the Pension Fund or a social service agency if financial support from the state is necessary.
To register a disability, the following documents are collected before contacting the ITU:
- statement;
- passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation (original or copy);
- referral received from an ophthalmologist for medical examination;
- a copy of the document containing records of the citizen’s employment (the work book must be notarized by a notary);
- medical history and treatment (everything is indicated in the medical record, provide it or make a copy and have it certified by a notary, usually the original is required);
- original certificates from clinics where the citizen underwent examinations and treatment.
If necessary, provide a certified certificate of injury at work while working with dangerous machinery or chemicals. After passing the examination, they will receive a certificate of assignment of a disability group and a program developed by the Russian Federation for rehabilitation (it helps to improve the patient’s condition and raise the level of visual perception).
Disability is granted for a year or more, but on a temporary or permanent basis. The result is influenced by the need to obtain measures to ensure minimal sufficient living conditions, help from outsiders, the cause of the deviation, age, diagnosis, and the ability to reverse the process with treatment.
According to current laws at the federal level, there is a special resolution of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation regulating the conditions for obtaining the right of a disabled person to social protection.
Registration of disability for children
To register the disability of children due to severe deterioration of visual perception, the following documents are required:
- referral from an ophthalmologist;
- birth certificate;
- medical card;
- certificates from other clinics where the child was treated.
With the collected documents, they are sent to the ITU at the place of registration, and an application is drawn up. After which parents will be told the date of the commission.
Stages of registration of disability for myopia
If one eye sees well and the other poorly, the chances of getting a disability are significantly reduced. The same thing happens with moderate myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism - people with these eye ailments are rarely given the status of “disabled”.
When a high degree of this disease is diagnosed and visual vision indicators are 0.1 D or lower, he has a good chance of receiving a disability group. What is needed for this? Contact the treating ophthalmologist, who will conduct a comprehensive examination and refer the patient to other doctors, since registration of an MSE is impossible only based on the opinion of an ophthalmologist.
At the next stage, the person will have to undergo a medical examination, during which other specialists will check whether the documents are filled out correctly and make sure that the patient was correctly referred for a medical examination. Mistakes are also possible.
After the head physician signs the documents and certifies them with a seal, the patient will have to contact a representative of the ITU bureau to set the date and time of the medical examination. There, the patient will be examined by an ophthalmologist and only after this will a final decision be made on the advisability of assigning a specific degree.
If you are denied disability
Citizens who have been denied a degree due to disability have the right to file a complaint about the result obtained by the ITU. Submit an application to the main office. Within 30 days, the citizen is called for re-examination.
You can appeal the decision within 3 months from the date of receipt of the refusal.
If a citizen believes that the group assigned is incorrect, the decision is contested. Submit an application to a higher authority of the ITU.
If the ITU confirms the previously established degree, the citizen has every right to challenge the decision in court in accordance with the code of the Russian Federation.
Benefits for the visually impaired
In addition to social payments and annual one-time benefits, disabled citizens receive free means to adapt to society. They are entitled to the following:
- a dog that is specially trained;
- assistance in obtaining secondary or higher education;
- surgery if necessary to install prostheses.
In addition, the patient is entitled to receive benefits such as a subsidy for utility bills, free travel and treatment at resorts, provision of land, and payments to parents.
The set of benefits is determined depending on the degree of disability.
Vision health group
If you did not find the information you need among the answers to this question, or your problem is slightly different from the one presented, try asking an additional question to the doctor on the same page, if it is on the topic of the main question. You can also ask a new question, and after a while our doctors will answer it. It's free. You can also search for the information you need in similar questions on this page or through the site search page. We will be very grateful if you recommend us to your friends on social networks.
Medical portal 03online.com
provides medical consultations via correspondence with doctors on the website. Here you get answers from real practitioners in your field. Currently, on the site you can get advice in 47 areas: allergist, venereologist, gastroenterologist, hematologist, geneticist, gynecologist, homeopath, dermatologist, pediatric gynecologist, pediatric neurologist, pediatric urologist, pediatric surgeon, pediatric endocrinologist, nutritionist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist, cardiologist , cosmetologist, speech therapist, ENT specialist, mammologist, medical lawyer, narcologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon, nephrologist, oncologist, oncourologist, orthopedic traumatologist, ophthalmologist, pediatrician, plastic surgeon, proctologist, psychiatrist, psychologist, pulmonologist, rheumatologist, radiologist, sexologist-andrologist , dentist, urologist, pharmacist, herbalist, phlebologist, surgeon, endocrinologist.
Payments and benefits
After receiving the group, the state transfers funds to the citizen monthly. The size of the pension depends on the disability group. For 2020 the size is:
- 1 - 10,217.53 rubles;
- 2 - 5,109.25 rubles;
- 3 - 4,343.14 rub.
Disabled children are paid a large allowance of 12,231.06 rubles. Payments may vary depending on various circumstances.
From January 1, 2020, patients with partial or complete loss of visual perception who have received a disability degree will begin to receive an annual benefit depending on the degree of disability:
- 1 - RUR 3,238;
- 2 - 2,341 rubles;
- 3 — 1,824 rub.
Labor activity
The labor activity (LA) of children includes the learning process. It is important that the child adapts to society. Children with the 3rd group can study in regular schools, and with the 1st - in special ones.
It is important for a child to be socially developed even with existing problems, therefore the state must provide effective rehabilitation and education programs.
TD is not prohibited if the patient is partially or completely unable to perceive visual information. Sometimes people stay in the same positions.
They are not able to operate complex mechanisms, work in factories with chemicals and in high humidity.
For example, in group 1, a person is assigned an automated workstation with a speech access program.
What health group? scoliosis 1 degree and vision minus 1
The second group includes people who have chronic diseases, but they do not affect the person’s ability to work and do not have exacerbations. The examination must be carried out about twice a year. Here it is necessary to carry out activities that should be aimed at managing health.
This group includes children who have a chronic disease with various periods of remission and exacerbation. These children have preserved functionality, do not have complications of the underlying disease, and may have physical disabilities with compensation.
This is interesting: Is it possible to withdraw money from maternity capital in 2020 25
One eye can't see
Disability in the complete absence of vision in one organ is not given to everyone. It all depends on how the second organ functions. The registration and passing of the ITU is similar. You just need to provide a certificate indicating the visual acuity of both organs of the optical system.
Disability is sometimes denied. However, if a patient is missing one eye, he is considered disabled because he has certain limitations. They give group 3 disability, but it is extremely difficult to get it.
Health groups: types and characteristics
- First and second groups. Any type of activity and load is allowed. Physical education classes and academic workload are formed according to the general program, without restrictions. All sports standards can be met without harm to health; it is recommended to attend additional sections, participate in Olympiads, competitions, and additionally condition the body. A ban on a particular activity can be imposed by a doctor on an individual basis.
- Third group. For each type of activity, a doctor’s consultation is required to establish certain restrictions. Physical education classes are carried out according to specially developed programs; participation in sports competitions is limited, because there is a high risk of exacerbation of the disease or injury. Regular preventive and corrective treatment in health camps and sanatoriums is recommended.
- Fourth group. The activity mode is significantly limited, the doctor creates a special daytime regimen in which a long time is allocated for rest Exercise therapy (physical therapy) and physical therapy are required.
- Fifth group. The child’s physical and mental activity is significantly limited; the daily routine is accompanied by medical procedures and physiotherapy. Constant supervision of activities by adults is required.
- chronic diseases (their presence or absence), genetic diseases, congenital pathologies, etc.;
- harmonious development (physical and mental) in accordance with age;
- the frequency of occurrence of diseases (from elementary ones like acute respiratory infections to severe ones) and the level of the body’s resistance to them.
This is interesting: Family Square Norm
High myopia
In case of serious visual impairment, when treatment does not bring significant changes, the possibility of obtaining disability is considered.
High myopia means absolute or complete blindness. This is the fourth stage of the development of the disease, when a person is required to pay disability benefits and be given a group.
For degree 4 myopia, disability group 1 is assigned; for degree 3, it is given when self-care is impossible and there is a constant need for outside help.
To pass the ITU, submit an application with the required package of documents.
To apply for disability, you will need the following list of documents:
- application to ITU;
- passport;
- hospital card;
- a certificate from the doctors where you were treated;
- characteristics from the place of work and working conditions;
- income certificate;
- report of injury at work, if any.
The commission requires additional examination of the patient in a hospital or in another clinic specified by the head of the bureau. Information about the person’s living and professional conditions and other examinations may be needed (if the cause of blindness is a serious illness).
Based on the results of the examination, a decision is made on the degree of disability assignment. To appeal, you can contact a higher authority. The court of last resort is the court.
Which health group does a child with vision problems belong to? -2
Wah! A real horseman! I can’t offer him beer for his heroism. I can do this for you
Here, smart is not smart - but statistics show... that children pay for the actions of parents (mothers) with their health. and that's a fact. If a woman smokes, drinks, injects drugs, or catches a sexually transmitted disease, this all affects the fetus... especially taking medications... few people think about it - medications are completely eliminated from the body - from 1 month to several years. any sexually transmitted disease leaves a mark on the immune system (lowering it) and smoking (tar) is generally eliminated from the body - and all this circulates through the blood, then through the fetus - and what will be the results? YOU really are chickens if you don’t realize this
This is interesting: What are the privileges for mothers of large families in the Stavropol Territory reviews
Government programs
The state provides a set of measures to restore visual perception, care for the patient, and professional implementation. In Russia there are special programs for the visually impaired.
Consultation with psychologists and psychological support, training in special schools for the blind, and assistance to parents are provided. There are individual rehabilitation programs, and special conditions for studying at home are created.
The implementation of medical IPRA includes the following programs:
- residential equipment;
- Spa treatment;
- medical rehabilitation.
This program gives the right to receive technical means of rehabilitation. Includes prosthetics.
For adults, there is a government program called Vocational Rehabilitation. Within its framework, a person has the right to assistance in finding employment, vocational training, industrial adaptation and vocational guidance.
If a disabled person or his parents want to make changes to a previously created program, they submit a new application to the ITU and draw it up again.
Disability and myopia
Statistics show that every year about 50 thousand Russians are assigned the status of “visually disabled,” and more than 20% of them are of working age. It is very difficult for people suffering from high myopia to obtain this status and documentation to support it. The fact is that the compensatory capabilities of this eye pathology are quite high, up to -10 D.
Thanks to correct optical correction, carried out with the help of good glasses and contact lenses, patients who do not experience progression of the disease can work if the profession does not involve mental activity or heavy workload.
Another important nuance is radical methods of correction of the retina and lens of the eyes, which often contribute to the complete restoration of vision. Of course, in such cases there can be no talk of any disability.
The main difficulty in assigning the status of “disabled” to myopic people is due to insufficient knowledge of the disease. Yes, when myopia of more than -6 D is diagnosed, a person has the right to obtain it, but there is no guarantee that he will be able to achieve this. And all because the criteria for establishing disability for myopia depend not on diopters, but on:
- visual acuity indicator;
- rehabilitation prognosis;
- degree of loss of professional ability to work.
A guarantee that a person will be referred for medical examination is visual acuity of 0.1 or lower. After passing the examination, medical specialists will decide whether to assign a disability to the patient or not.