Indications for surgery
Most often, strabismus is detected in early childhood. In this case, the operation is not performed immediately. First, any doctor will advise you to use conservative treatment methods. But there are cases when surgical intervention is unavoidable:
- strong angle of deviation of the eyeball from its normal location in the orbit;
- lack of effectiveness from conservative treatment;
- the patient’s lack of desire to carry out long-term conservative treatment, the need to get the effect immediately;
- a high risk of developing amblyopia - a sharp decrease in the visual function of one eye, as a result of which it is completely turned off.
Before performing the procedure, you must obtain permission from the attending physician.
Treatment of strabismus
- Modern methods of treatment:
- Specialized exercises;
- Computer programs;
- Special prismatic glasses and lenses;
- Pharmacological drugs (for example, botulinum toxin);
- Hardware correction;
- Occlusion: used in children with amblyopia to stimulate the deviating eye;
- Surgical procedure.
To choose the most effective method, ophthalmologists carefully study the type and severity of nosology. When choosing a correction method, the age, health status of the patient and the degree of imbalance must be taken into account.
Therapy in children should begin at an early age, since untimely correction can lead to visual and psychological difficulties.
Conservative therapy takes a long time, but it is more reliable. Surgery should be used when other methods have been used unsuccessfully.
Types of strabismus surgeries
Depending on the type of pathology of the extraocular muscles, there are 2 types of operations:
- reinforcing – tension and strengthening of muscle tissue, due to which it will be able to hold the eyeball;
- weakening - a decrease in the tension of the oculomotor muscle, due to which the eye deviates strongly towards the temple area.
In augmentation surgery, the extraocular muscles are cut and stretched, then sewn back on. If, on the contrary, the muscle is very tense, it is cut in a certain place so that it is less tense.
Procedures are divided depending on the surgical technique:
- recession - an incision in the extraocular muscle and further suturing to the sclera, resulting in normal tension;
- myomectomy - dissection of muscle tissue in a certain place to reduce tension without subsequent stitching;
- resection - the surgeon completely excises part of the muscle, suturing the two extreme sides.
The choice of surgical intervention depends on the patient's diagnosis.
How dangerous is surgery to correct strabismus?
Even the simplest eye surgeries involve certain risks. They exist in this case too. The most common problem is double image, which in some cases may not go away even after the rehabilitation period. To get rid of it, wearing prismatic glasses is prescribed.
Also, the consequences of surgery include retinal detachment, infectious diseases, problems due to anesthesia, and deterioration in the quality of vision. The general health of the patient is important: the stronger it is, the more successful the operation will be and the shorter the rehabilitation period will be. In any case, there is no need to sound the alarm in advance. Medicine does not stand still, so negative developments are practically reduced to zero.
Preparing for surgery
In order for an ophthalmologist to make an accurate diagnosis and give permission for surgery, it is recommended to conduct the following ophthalmological examinations:
- assessment of visual acuity using diagnostic tables;
- Ultrasound of the eyeballs;
- autorefractometry;
- fundus examination;
- ophthalmic perimeter;
- assessment of the angle of deviation of the affected eye from its normal location.
Before surgery, the patient must undergo the following tests:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine, blood biochemistry;
- if necessary, coagulogram;
- analysis for HIV and hepatitis C;
- fluorography;
- electrocardiogram.
Additionally, it is necessary to undergo an examination and obtain permission from doctors of narrow specialties: neurologist, cardiologist, otolaryngologist, dentist. If all tests are normal, the ophthalmologist may give permission to perform the operation.
Also, before the operation, the patient must follow a number of rules:
- within a week, you should not take new medications that the doctor has not been warned about;
- You should not drink alcohol two days before surgery;
- Before the procedure, you must take a shower and thoroughly wash your face and hair.
No special visual preparation is required. You should come to the clinical facility at the time prescribed by the doctor. If any of these rules are violated, this may lead to consequences and complications during or after surgery.
Results of the operation
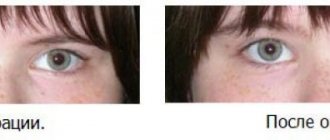
Strabismus surgery helps eliminate the patient’s existing cosmetic defect. It turns out that surgery itself does not always lead to the restoration of normal vision. This is due to the fact that while the patient has strabismus, his brain tries to adapt and compensate for the existing lack of vision in accessible ways: very often strabismus is accompanied by the development of amblyopia, in which the affected eye practically does not participate in the visual process. After surgery and restoration of the normal position of the eyes, the patient must actually relearn how to see with both eyes at the same time (binocular vision), and this can take a lot of time and effort. For the speedy restoration of binocular vision, our specialists, according to indications, recommend that all operated patients undergo a course of hardware treatment.
All photographs of patients before and after surgery
Progress of the operation
The surgical intervention is carried out in several stages:
- the patient lies down on the couch, a disposable cap is put on his hair;
- they give general or local anesthesia, the latter option can only be applied to adults;
- using a scalpel they gain access to the extraocular muscles;
- if the muscle is not stretched enough, it is cut and sewn in the desired position;
- if the muscles are stretched excessively, they are incised, but not sewn;
- closing the tissues, applying an antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agent.
It is possible to perform the operation without making an incision in the extraocular muscles. In this case, it is pulled and sewn in the required position. In this case, tissue healing occurs faster.
Laser correction of strabismus
Source: ophthalmocenter.ru
Today, ophthalmological problems have several treatment options. Innovations in medicine allow you to make a choice in favor of the most optimal option. Laser treatment of eye diseases is not new. It has proven itself to be an effective technique. Is it possible to treat strabismus with laser?
Strabismus is a deviation from the common point of fixation of one eye. This ophthalmological pathology is accompanied by disorders of visual function and impaired binocular vision. It is worth noting that strabismus is a common type of visual impairment. In preschoolers, it usually appears at two to three years of age.
Ophthalmologists distinguish several types of strabismus:
- Imaginary. With it there is a small angle between the visual and optical axes. It does not need treatment. In this case, binocular vision is not affected.
- Hidden. The eyeball tends to deviate when the eye is covered with the palm of the hand. This type also does not require treatment, since it is compensated by binocular vision.
- Friendly. This type of pathology is the most common and is formed during the development of binocular vision in the first years of life. Concomitant strabismus is both a cosmetic defect and a functional disorder that makes orientation and movement in space difficult.
A complication of this type of strabismus is amblyopia, which is also called lazy eye syndrome. In this case, the person mowing is switched off from the vision process, and overall visual acuity decreases.
Important
Treatment of strabismus is a long process, including several stages.
Patients suffering from a similar disease are interested in whether it is possible to restore normal vision with the help of a laser. But, alas, the laser method will not be able to return your eyes to their natural location.
There is no laser method for correcting strabismus. After all, during a surgical operation, a specialist cuts the eye muscle to weaken it or stitches it to tighten it.
It depends on the type of strabismus. And the laser cannot shorten or weaken the eye muscle. As you can see, the laser method, which has proven itself in the treatment of other eye diseases, will be completely ineffective in this case.
Surgical intervention is one of the most effective ways to correct pathology in this case. The operation is performed under local anesthesia, and the person can go home the same day. The ophthalmologist decides which muscles do not work and how to correct the situation during the operation itself.
Most often it is performed on one eye. If we talk about postoperative rehabilitation, then this period is 5-7 days. After surgery, doctors recommend continuing treatment with training on machines.
Hardware treatment or illumination of the retina increases visual acuity and develops the necessary connections between the eyes. Such measures allow you to restore vision completely or partially.
Ophthalmologists emphasize: early diagnosis and initiation of treatment increase the chances of eliminating strabismus. Until three to four months of age, this phenomenon is considered physiological, since muscle balance is just being formed.
If after this period it does not go away, then you should definitely go to an appointment with a pediatric ophthalmologist. He will find out if there are reasons for the development of strabismus. Today, to diagnose and select the correct treatment for this problem, a unique device is used - a pediatric autorefractometer.
It allows you to determine the angle of strabismus and refraction, interpupillary distance and pupil size in infants starting from two months. A pediatric ophthalmologist selects therapy for each child aimed at restoring the correct position of the eyes, increasing visual acuity, and eliminating amblyopia.
Rehabilitation and recovery
After the operation is completed, the rehabilitation period begins. If the procedure was performed on an adult, he is kept in a clinical facility for several hours, then sent home if there are no complications. Children should stay in the hospital for 1-2 days. At home you need to do the following:
- use of medications prescribed by the doctor (antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, moisturizing drops);
- on the first day after surgery, long rest and sleep;
- wearing sunglasses outdoors when exposed to bright sunlight;
- ban on visiting the bathhouse, sauna, swimming in hot water;
- a ban on any physical activity until permission from a doctor is obtained;
- replacing contact lenses with glasses to prevent the risk of damage to eye tissue;
- return visit to the ophthalmologist at the appointed time.
If all stages of rehabilitation have been completed, the risk of complications is reduced.
Cost of the operation
When contacting a public medical institution, surgery to correct strabismus is performed free of charge, for both adults and children with a compulsory medical insurance policy. Treatment is carried out inpatiently. Some private clinics also work with compulsory health insurance policies.
Children under 18 years of age and those with severe visual impairments may require an accompanying person. His stay in the hospital is not always provided for or may require additional payment.
The average cost of strabismus treatment in private clinics in Russia is 20,000 rubles. The price is influenced by the technology used, the complexity of the operation, and the reputation of the clinic or specific surgeon.
If the choice falls on correcting strabismus in an Israeli or German clinic, you will have to prepare from 7,000 euros. When using an intermediary company, the price may increase 2-3 times.
Complications
During the operation or within a few days after it, the following complications may occur:
- hemorrhage in the cornea or inside the eyeball;
- rupture of muscle tissue, damage in this area;
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity up to complete blindness of the affected eye;
- introduction of a bacterial infection into internal tissues, risk of sepsis (infectious blood poisoning that leads to the death of the patient without emergency medical care);
- inflammation of the eyelids, cornea, conjunctiva;
- lack of effect of the operation with further development of strabismus.
To eliminate the risk of complications, it is recommended to undergo a full examination before surgery, a rehabilitation period, and re-visit an ophthalmologist.
Causes of strabismus
The most common cause of strabismus is heredity. About 30% of children with strabismus have a family member with a similar defect.
Other etiological factors:
- Cerebral paralysis;
- Down syndrome;
- Hydrocephalus;
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Diabetes;
- Brain tumors;
- Uncorrected farsightedness;
- Stroke;
- Complications of ENT infections;
- Ophthalmological pathology (retinal detachment);
- Head injuries;
- Neurological disorders;
- Graves' disease.
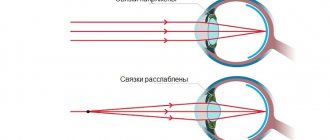
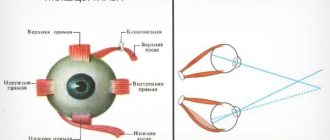
The position of each eyeball is maintained by six extraocular muscles. They receive their innervation from the 3rd, 4th and 6th cranial nerves and move it in different directions.
| Extracular structures have certain characteristics and mechanisms of morphogenesis that are unique to mammals. During the prenatal period, the formation of these muscle fibers is mainly determined by genetic regulatory factors, and it is largely dependent on the development of motor neurons in the brain centers. In the postnatal period, their final structure is established under the influence of epigenetic regulatory stimulators, that is, growth factors, hormones and cell adhesion molecules. There is a critical time for their development, which lasts from 3 to 6 months after birth, during which the extraocular fibers acquire the specific structure and function necessary for stereoscopic perception. |
With this nosology, the displacement of one or both eyes leads to the fact that the visual axes on the fixing object do not intersect. As a result of this, simultaneous merging of two monocular images does not occur in the centers of the cortical structures of the central nervous system. A person does not have a clear and single image; he sees a double or blurry object. This quite often leads to confusion and difficulty in performing many tasks in everyday life.
Diplopia can be a sign of a serious neurological condition such as traumatic brain injury, meningitis, or stroke. The central nervous system tries to protect itself from double vision and therefore constantly suppresses the pathological signals that come from the mowing organ. The result of this aggressive “suppression” is amblyopia. It is characterized by a functional decrease in visual acuity, in which the squinting organ is partially or completely excluded from the process of visual gnosis.
Risk factors for the manifestation of ocular dysfunction are prematurity, disturbances in the central nervous system, low birth weight, genetic predisposition and refractive error.
In some cases, the disease may be iatrogenic. This dysfunction is caused by traumatic damage to oculomotor fibers during operations on the lens and retina.
Patient reviews
Mikhail, 32 years old: My son has a severe form of congenital strabismus. He had surgery. We chose this option, when the muscles are pulled, but not cut, and then they are sewn on. We approached the rehabilitation period seriously and followed all the rules. A re-examination by an ophthalmologist revealed a positive trend towards recovery.
Elena, 22 years old: I have had strabismus since birth. I was treated for a long time using hardware methods. But the result was insignificant. And then two years ago I decided to have surgery. I passed all the tests, there were no contraindications. They cut the muscles around my eyes and pulled them into the desired position. After the operation was completed, it was very difficult and painful; I took painkillers and antibacterial drops. But now the eye has restored its position.
Video with testimonials from our patients
You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by contacting the multi-channel phone number 8 800 777-38-81 (free for mobile phones and regions of the Russian Federation), daily from 9:00 to 21:00 Moscow time or online, use Skype consultation on the website, thoroughly
You can check out the “Prices” section.
Go to the "Prices" section
What is strabismus?
Strabismus can be acquired or congenital. They also distinguish between permanent and non-permanent strabismus, which appears periodically or completely disappears over time. There are two types of this disease.
When both eyes turn away in turn
With concomitant strabismus, as the name suggests, both eyes are affected.
They take turns mowing in approximately the same range. The main cause of this vision pathology is ametropia. Main distinctive features:
- if a person looks at a stationary object, then one eye deviates slightly towards the nose or temple;
- at the same time, the deviating eye may change;
- mobility of the eyeball is preserved in all directions;
- a person does not observe double images before his eyes;
- the patient lacks binocular vision;
- the primary and secondary angle of deviation of the squinting eye are almost the same;
- Deterioration of vision in a squinting eye may occur.
As a rule, a person with concomitant strabismus has other visual impairments: myopia or farsightedness, astigmatism.
When only one eye squints
The second type of pathology is paralytic strabismus. The main difference between this type of visual impairment is that the squinting eye does not move, or moves limitedly in the direction of the affected muscle. The image begins to double, and the person loses the ability to see in volume. The disease is caused by nerve damage, improper functioning of the eye muscles, tumors and injuries.
Signs of this type of pathology include:
- where the muscle is affected, the eye does not move;
- The primary and secondary deflection angles are different: the secondary one is larger;
- double vision, loss of three-dimensional vision;
- dizziness;
- forced slight deviation of the head towards the affected eye.
All age categories are susceptible to paralytic strabismus: it can develop at any age.
Other types of strabismus
In addition to the above, there are convergent and divergent (exotropia) strabismus, as well as vertical. In the first case, the squinting eye deviates towards the nose. Convergent strabismus is diagnosed more often in children than in adults; during the process of maturation, it often completely disappears. As a rule, the pathology develops against the background of farsightedness.
Divergent strabismus in adults is characterized by the fact that the eye deviates towards the temple. Pathology occurs with congenital or acquired myopia. With vertical - one eye is directed up or down relative to the healthy one.
Correction of strabismus in adults using surgery
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW! An effective remedy for restoring vision without surgery or doctors, recommended by our readers! Read more. Strabismus, heterotropia, or strabismus is a malfunction in binocular vision when improper coordination of the eyes on the object in question occurs.
One or two eyes deviate from the center of the visual axis in the direction of the nose or temple, as a result of which the fixation of the eyes on the object is disrupted. If no correction methods help, surgery eliminates strabismus
Strabismus, heterotropia, or strabismus is a malfunction in binocular vision when improper coordination of the eyes on the object in question occurs. One or two eyes deviate from the center of the visual axis in the direction of the nose or temple, as a result of which the fixation of the eyes on the object is disrupted. If no correction methods help, surgery eliminates strabismus.
Definition of strabismus and methods of correction
Strabismus is considered to be a childhood disease, since it manifests itself in childhood. The occurrence of strabismus in adults is much less common, and is often caused by a disruption in the functioning of nerve connections. There are many reasons that contribute to the occurrence of strabismus:
- Traumatic brain injuries;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Psychological herbs;
- Poor blood circulation to the brain;
- Infectious diseases of the brain;
- Incorrect treatment of myopia and farsightedness;
- Excessive strain on the eyes;
- Disruption of the extraocular muscles.
Testing strabismus covers a holistic analysis of the organs of vision - the work and location of the muscles, the fundus and visual acuity, the angle of strabismus and the age of the patient are assessed. If strabismus is present, surgery is not immediately prescribed; they first try to eliminate it without surgery. Treatment has three subsequent stages:
- Optical correction;
- Pleoptic treatment;
- Orthoptic treatment.
Optical correction is treatment through properly selected glasses and lenses to create optimal conditions for the functioning of the eyes. If there are concomitant diseases (myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism, infections), then their treatment is carried out at this stage of therapy.
Pleoptic treatment is aimed at increasing and equalizing the acuity of both eyes to age-related norms.
Orthoptic treatment is essentially a preoperative stage. It is advisable to carry it out only after relative equality of visual acuity between the eyes has been created. Its goal is to develop in the patient the ability to turn on binocular vision (the ability to clearly see an object with both eyes) when looking away in different directions. In the absence of binocular vision, the question of prohibiting the operation may arise. Symmetry of the eyes is possible only with the same spatial perception of objects and objects by both eyes.
Surgery to correct strabismus is prescribed only when maximum visual function has been achieved in both eyes.
Squint surgery
All operations aimed at correcting strabismus involve correcting the work of the extraocular muscles - strengthening and weakening. Manipulations are carried out only as part of traditional surgery; laser correction of strabismus is not practiced. Surgical treatment of strabismus involves cutting the muscle, but this cannot be done with a laser.
The goal of strabismus surgery is to restore muscle balance and binocular vision. But often it is possible to improve only cosmetic defects; restoration of visual functions after surgery requires an integrated approach and active conservative therapy. In ophthalmology, there are three areas of surgical correction of strabismus:
To treat eyes without surgery, our readers successfully use a proven method. Having carefully studied it, we decided to offer it to your attention. Read more.
- Relieving muscle cravings;
- Strengthening traction;
- Changing directions of muscle action.
Muscles that weaken cravings include:
- Recession, which implies a surgical intervention that results in a laxative effect of muscle traction, achieved by shifting the site of muscle attachment to the beginning of the muscle.
- Myectomy is a procedure to remove a specific muscle from its insertion site. The main indication for such an operation is muscle hypercontraction.
- Posterior fixing sutures are a procedure consisting of recession with sequential suturing of the belly of the moved muscle to the sclera, slightly behind the place of its attachment.
Aimed at restoring weakened extraocular muscles:
- Resection is the process of excision of a certain area of weakened muscle at the site of its attachment, followed by its fixation. Essentially, the remaining sections are stitched together.
- Tenorrhaphy is the process of shortening a muscle by creating a fold in the muscle tendon area. As a result, the shortened muscle is significantly enhanced in terms of contractile function.
- Anteposition is the process of changing (transporting) the place of muscle attachment.
Advantages of surgical ophthalmology:
- Low trauma;
- The structure of the eye is preserved;
- Precision of operation;
- Small % of consequences;
- High guarantee of good results;
- A short rehabilitation period.
Surgical intervention to eliminate strabismus does not provide a 100% guarantee of complete correction, but the chances are high - up to 80%. If strabismus persists after the procedure, the operation can be performed again after six months. You should not expect that you will see “correctly” immediately after surgery. During the time that a person suffered from strabismus, the brain lost the habit, forgot how to compare the visions from both eyes into one image, and it will take a lot of time for it to learn. Like any operation, complications may arise. First of all, these are calculation errors that lead to repeated strabismus.
The course of the operation and recommendations in the postoperative period
Strabismus surgery is performed under full or local anesthesia (as indicated) on an outpatient basis, no hospital is required - the patient is sent home a few hours after the operation. Ophthalmological operations, like all others, are performed on an empty stomach. All necessary tests are taken in advance. During the procedure, the patient must be absolutely healthy (no ARVI, fever, infections). The procedure on average does not exceed 30 minutes. After the operation, the patient is given a special bandage, which is left for 12-24 hours. The sutures applied give the sensation of a foreign object in the eye; they do not need to be removed; they dissolve within 6 weeks after application. After surgery, the patient needs to use anti-inflammatory drops. If suppuration occurs, rinsing will be indicated.
The following steps must be taken:
- Carefully protect the eye from contamination;
- Do not engage in physical labor for the first three weeks after surgery;
- Do not swim in public places;
- Do not disturb the eye, do not rub it.
After surgery, careful monitoring of the eye is required. It is necessary to regularly visit an ophthalmologist, use the necessary medications and rest the eyes. To restore muscles, a special system of exercises is being developed that must be performed. The assessment of eye position is checked no earlier than two months after surgery.
Types of convergent strabismus
Convergent strabismus is usually divided into concomitant and paralytic:
- Concomitant strabismus is a condition in which the movements of both eyeballs are completely preserved and the angle of strabismus is the same. This pathology is usually associated with farsightedness. When the accommodative apparatus of the eye is subjected to excessive stress (even when looking into the distance), this leads to excessive convergence, which causes the development of convergent strabismus.
- Paralytic strabismus occurs due to a violation of the synchronous functioning of the extraocular muscles, with an increase in the tone of one or a weakening of the tone of the antagonist muscles.
At the same time, convergent strabismus is divided into accommodative and non-accommodative. Accommodative convergent strabismus occurs in the following types:
- Refractive convergent strabismus with complete and partial accommodation.
- Non-refractive convergent strabismus caused by excess of convergence or weakness of accommodation.
- Mixed convergent strabismus.
- Convergent strabismus of a non-accommodative nature: with an acute onset, sensory, essentially infantile, with excess of convergence, microtropia, with paralysis or insufficiency of divergence, cyclic, secondary.
Such terms are absolutely incomprehensible to the average person, but they can be explained quite clearly. To do this, you need to know that two processes take part in near vision - accommodation and convergence. Accommodation is the process of focusing the eyes on nearby objects, accompanied by a change in the curvature of the lenses. Convergence is the bringing together of both eyes to achieve bifoveal fixation of an object. Both of these processes are quantitatively related to the total distance to the object in question and have a constant relationship with each other. Actually, a change in the index of this ratio is the main reason for the occurrence of a number of forms of convergent strabismus.
Recommendations for the prevention of strabismus
It is best to take preventative measures from childhood. Especially if one of the parents has been diagnosed with the disease. If you consult a doctor in time and follow all the recommendations, you can avoid health problems.
In cases where strabismus is caused by external factors, it is important to take care of the visual organs and regularly visit an ophthalmologist and neurologist at least once a year. Do not neglect the rules of visual hygiene, do not overstrain your visual organs, watch your diet and perform gymnastic exercises for the eyes
At the moment, ophthalmology makes it possible to perform operations to correct strabismus using innovative technologies that minimize injuries to the eyeball and preserve the vascular nerve bundles passing through the extraocular muscles.