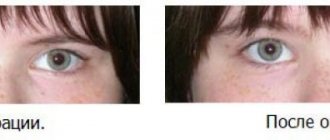
According to medical statistics, alternating strabismus is the most common type of strabismus. In the presence of such a violation, there is an alternating deviation of the eyes from the central axis. The basis of the pathological process is a disruption in the functioning of the oculomotor muscles.
The main category of patients suffering from alternating strabismus are preschool children. Mostly the symptoms of the disease appear after reaching 2-3 years of age. Less commonly, the anomaly develops in infants.
If a newborn has squints in one or both eyes, this condition is not considered a pathology until the age of 6 months. During this period, the oculomotor muscles are not yet strong enough, which causes periodic connection of the irises. If manifestations of strabismus are observed even after six months, there is a need to visit an ophthalmologist and examine the baby.
In case of an unfavorable course of the disease, it is not always possible to completely restore the normal state of the visual apparatus. In such situations, doctors focus their main efforts on improving the quality of life of a patient with strabismus and reducing discomfort.
Reasons for appearance
Ophthalmologists are not always able to determine with 100% accuracy the cause that caused the development of convergent strabismus. According to modern medicine, the occurrence of pathology can be caused by:
- Malfunctions of the central nervous system.
- Injuries to the visual apparatus.
- Uneven structure of the visual organs.
- Deviations in the functioning of the eye muscles.
- Negative heredity.
In childhood, strabismus can manifest itself against the background of cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, as a result of premature birth of the mother, or severe stress. Provoking factors also include smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking prohibited medications by a pregnant woman.
Sometimes the development of alternating strabismus is associated with pre-existing diseases in the patient. The list of disorders that can lead to the appearance of strabismus includes myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, retinal detachment, cataracts, and cataracts.
Pathology can also be triggered by myasthenia gravis, central nervous system disorders, and tumor processes. Sometimes the disease develops after infectious diseases (influenza, measles, diphtheria, scarlet fever).
Prevention of strabismus
It is impossible to protect a child from strabismus 100%, but parents can minimize the risk by implementing prevention. The basis for preventing strabismus is visual hygiene. Toys can only be hung at a sufficient distance from the child’s eyes. You must constantly ensure that the baby does not get injured. It is important to avoid shocks and impacts.
If symptoms do not disappear when the child reaches six months of age, you should consult an experienced ophthalmologist. If symptoms of an infectious disease occur, you should consult a doctor and prescribe proper treatment, because often convergent strabismus becomes a complication of infection.
Children over three years old should be prohibited from squinting their eyes: during deliberate squinting, a muscle spasm occurs, which provokes a violation. It is necessary to protect the baby from fear and stress, as well as from certain types of games.
You need to start treatment for strabismus only with the permission of your pediatrician. You should make sure that the child has no contraindications from other body systems. This is especially true for herbal treatment, since children often develop allergies.
Sources used:
- Treatment of eye diseases: Vision correction. Optics: monograph / M.V. Kuropatkina. - M.: Ripol Classic, 2010.
- Clinical ophthalmology / E.E. Somov. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2012.
- D. Hubel. Eye, brain, vision. — ed. A. L. Byzova. - M.: Mir, 1990.
- Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov
Varieties of the disease
There are two types of alternating strabismus:
- divergent;
- convergent.
The first form of the disorder is less common (up to 30% of cases). The rest of the patients exhibit convergent strabismus.
Alternating strabismus can be permanent or temporary. Sometimes the pathology appears after severe stress and disappears on its own as the psycho-emotional background normalizes.
Divergent alternating strabismus
With divergent alternating strabismus, the patient suffers from divergence of the irises towards the temples. The eye muscles are relaxed on the inside.
This form of disorder occurs against the background of damage to the optic nerve and retina diseases. Patients with neoplasms in the brain, eyes, paranasal sinuses, and hearing organs are susceptible to divergent strabismus.
With divergent strabismus, the pathological eye sees worse than the healthy one. Diplopia (split images) is mostly absent.
Convergent alternating strabismus
The presence of converging alternating strabismus is indicated in cases where a child or adult has an approach of the irises to the nose. A similar phenomenon occurs when the external eye muscles relax. The main causes of convergent strabismus are myopia, farsightedness, and astigmatism.
Sometimes several variations in the divergence of the visual axes are detected simultaneously. This anomaly occurs in isolated cases.
Diagnostics
How to determine the presence of a deviation? To do this, you need to contact an ophthalmologist, who, after listening to the patient’s complaints and collecting an anamnesis, will prescribe the following diagnostic measures:
- external examination, test for symmetry of eyes, face;
- determination of visual acuity;
- perimetry;
- biomicroscopy;
- synoptophore;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- computer refractometry.
If the detected heterotropia is paretic in nature, then EEG, electromyography and electroneurography are additionally prescribed. In addition, your eyes should be checked by a neurologist.
Clinical picture
The main symptoms of alternating strabismus take the form:
- Double vision.
- Headache.
- Coordination problems.
- Deterioration of visual perception.
If the deviation from the norm is mild, the patient often retains a binocular image and normal orientation in space. If the disorder is significant, children experience difficulties during classes in kindergarten or school, and often lag behind their peers. Adults suffering from noticeable strabismus are deprived of full working capacity and cannot cope with complex mechanisms or control vehicles.
As the patient gets older, the symptoms of strabismus tend to worsen. It is possible to stop the progression of the pathology only through properly selected therapy.
People's Councils
Dark Chocolate – Dark chocolate is believed to be very beneficial for vision health. It is recommended to eat several pieces of chocolate every day. Within a month the condition will noticeably improve.
Calamus root - pour hot water over the calamus root, let it brew, then strain the broth. Drink three times a day. Daily dose 250 ml.
Chinese lemongrass is one of the most effective remedies for strabismus. You need to pour 100 grams of the plant with alcohol or vodka, 500–600 ml is enough. Let it brew for two days, shake the tincture every day. Directions for use: dilute 20 drops of alcohol tincture with water. Drink before meals.
Treatment with traditional methods should occur with the permission of a doctor.
Treatment
Timely diagnosis of strabismus is of utmost importance. Examination of the patient, carried out at an early stage of the disease, makes it possible to carry out effective treatment measures and avoid the development of complications.
Therapy for alternating strabismus is always complex and takes a long period of time. The main methods used by modern ophthalmologists are:
- Hardware treatment.
- Gymnastics for the eyes.
- Surgical intervention.
Additional ways to eliminate strabismus include correction with special optics (only glasses are used until the age of 18), minimization of visual stress, and prevention of infectious and other diseases that can aggravate the condition of the visual organs.
The main goal of the treatment is to restore binocular vision and normal visual perception. If the patient’s central nervous system has retained the ability to coordinate the sensory and motor systems of the visual organs, restoration of visual function is successful, and the eyes gradually take the required position.
Hardware treatment
Hardware treatment means the use of special devices aimed at eliminating and preventing ophthalmic pathologies. For alternating strabismus, the following devices are used:
- Synoptophore;
- Monobinoscope;
- Amblyocor.
The synoptophore is a universal device used in the treatment and diagnosis of strabismus. The device contains several movable tubes with lenses at one end and an illuminated socket at the other. During the session, objects are moved, forcing each eye to focus in turn, creating an even load on the visual apparatus. The method strengthens the extraocular muscles and normalizes the performance of the sensory systems of the brain, which serve to fully image surrounding objects. Exercises also allow you to carry out diagnostics and determine the degree of strabismus in each eye.
Monobinoscope is a new generation device that affects the inner lining of the eyeball with laser radiation. The device is used for diagnostic purposes, as well as for the prevention of pathologies arising from strabismus (amblyopia, nystagmus). The device stimulates the central recess located in the center of the macula of the retina and exerts a laser effect on the eye cornea (often using medications).
Amblyokor looks like a specialized computer for conducting therapeutic auto-training. The device stimulates the parts of the central nervous system responsible for the state of the human binocular optical system. Therapy using this device is carried out in a playful way, consisting of watching cartoons or films. The method is safe for children and is well accepted by younger patients. Exercises on this device help to normalize the acuity of visual function not only with strabismus, but also with other diseases of the visual organs.
Contraindications to hardware therapy are acute or chronic inflammation of the eyelids, eyeball, malignant formations in the visual structures, glaucoma with uncompensated intraocular pressure.
Eye gymnastics
Special eye exercises are not intended to completely eliminate strabismus and restore binocularity. The main goals of ophthalmic gymnastics are to strengthen the eye muscles, increase the effectiveness of the main treatment, and prevent complications.
Patients with strabismus are recommended to perform simple passes:
- Extending your hand in front of you and raising your index finger up, fix your gaze on the tip of your finger and smoothly move your hand towards your face. They don’t look away until the finger touches the nose.
- Draw the number “8” with your eyes. Gaze movements are performed alternately vertically and horizontally.
- Follow a monotonously moving object. To perform this exercise, you can use a clock hand or a tennis ball.
Gradually, the described complex is complicated by adding passes agreed upon with the attending physician.
If strabismus is diagnosed, eye exercises are carried out daily, in a prolonged course. You should spend at least 30-60 seconds on each exercise.
After gymnastics, the organs of vision should rest. To relieve fatigue from training, it is recommended to stay in the dark for a while.
Surgical correction
If basic treatment methods become ineffective or alternating strabismus provokes serious complications, the patient is prescribed surgical intervention. Surgery also becomes necessary in cases where a significant deterioration in vision occurs against the background of the disorder.
All types of operations to eliminate strabismus are divided into strengthening and weakening. The first type of intervention is aimed at strengthening muscles that are deprived of the ability to ensure the correct position of the eyeball. Weakening methods suppress the action of stronger muscles that deflect the problematic organ of vision.
Modern ophthalmologists use the following types of surgery:
- recession of the extraocular muscles, the essence of which is the removal of tissue at the site of its attachment, the subsequent fusion of the muscle with the sclera and tendon;
- partial myotomy, which involves cutting off the muscle without further suturing;
- shortening the muscle using partial resection and attaching it to its anatomical location;
- suturing the muscle directly to the sclera using non-absorbable threads.
Intervention for strabismus involves general or local anesthesia. When performing an operation, the surgeon uses low-traumatic devices that do not cause dangerous bleeding - a laser or a radio knife.
An adult patient can be sent home within a few hours after surgery. Children who have undergone surgical procedures remain under medical supervision for 1-2 days.
After the procedure, a recovery period is required, lasting 4-5 weeks. To successfully undergo rehabilitation, you must use the medications prescribed by your doctor:
- eye drops;
- antihistamines, anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics.
You will need to give up intense physical activity, avoid smoking, and staying in smoky or dusty rooms for long periods of time. It is important to carefully maintain personal hygiene and regularly visit a doctor to monitor the condition of your vision organs.
Symptoms
The main symptom of convergent strabismus is the deviation of the iris and pupil of the eye towards the bridge of the nose when trying to focus your gaze directly on any object. In addition to the visible deviation of the cornea, alternating heterotropia of central origin is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- rapid fatigue of the visual organs;
- discomfort, heaviness in the eyes;
- increased sensitivity to light;
- lack of three-dimensionality of the picture (the patient sees a two-dimensional image);
- blurred, double (diplopia) visible image;
- migraines, dizziness.
Children and adults with monolateral convergent strabismus, when trying to see something, tilt their heads to the side and squint. Over time, accommodative esotropia leads to other vision problems and the development of torticollis.
Without proper treatment, progressive strabismus of central origin leads to amblyopia (exclusion of the visual function of the squinting eye).
Treatment prognosis in children and adults
The most favorable prognosis remains in the case of early treatment of strabismus. To rid the patient of strabismus, persistent, consistent and long-term therapy will be required.
In case of late seeking medical help, correction of the ophthalmological defect becomes insufficiently effective, and the patient may develop irreversible vision loss.
Strabismus diagnosed in a young child is best treated. In adults with a fully formed visual apparatus, it is much more difficult to eliminate the pathology.
Is it possible to cure convergent strabismus?
If the problem is identified in a timely manner, the treatment prognosis is favorable. It is recommended to treat strabismus until the age of 18-25, until the visual system is completely stabilized. It must be remembered that strabismus does not go away on its own, so the problem cannot be ignored. Without treatment, strabismus is complicated by amblyopia, decreased visual acuity, and even developmental delays.
Even if the course of strabismus goes without complications, the pathology constitutes a serious cosmetic defect that can greatly complicate the life of even an adult. Children with strabismus are often withdrawn and complex.
If you have strabismus, you cannot hold positions that require prolonged strain on the visual system. This includes control of transport and potentially dangerous equipment, rifle units of troops, etc. The pathology disrupts binocular vision (combining images from different eyes into a single picture), which helps a person see the three-dimensional world, correctly determine the distance between objects, perceive the physicality and depth of the environment.
A person with strabismus, who lacks binocular vision, cannot work with moving objects when it is necessary to instantly assess the depth of something. If you do not treat strabismus in a child, you can block his path to becoming a pilot, machinist, athletes, artist, surgeon, and even dentist.
Peculiarities
structure of a healthy human eye
One of the most well-known forms of this eye pathology is concomitant convergent strabismus. It is determined by the fact that one or both eyes immediately look towards the nose and do not allow both eyes to focus on the object. Surgery is recommended to treat eyelid chalazion.
This is an independent ailment, with its own separate etiology, a type of which is concomitant strabismus. The disease is so common that it has found its place in the International Classification of Diseases, which is updated every 10 years. Its ICD-10 code is H50.0.
There are several types of convergent strabismus, which are determined by different causes.
It is easily determined visually. In addition, many adults and children experience migraine attacks, pain and strain in the eyes, they experience dizziness, and double vision. There are patients who, in order to see clearly, squint and tilt their head towards the poorly seeing eye. Photophobia in children can be congenital.
types of strabismus
Anyone who really wants to recover and does everything necessary for this will definitely overcome such a pathology as strabismus.