Parameters and indicators studied
An ultrasound of the kidneys will help the doctor see such a standard set of indicators and parameters as:
- number of organs;
- location of the kidneys;
- dimensions;
- shape and contours;
- structure of the renal parenchyma;
- blood flow condition.
Quantity
Normally, a person should have two kidneys, but there are also anomalies that may be associated with
- congenital absence;
- duplication of one of the organs;
- removal of a kidney due to surgery.
Location
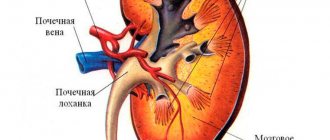
The kidneys are located quite high, at the level of the first and second lumbar vertebrae. Normally, the right kidney is located slightly higher than the left - this is due to the fact that it is pushed upward by the liver. A kidney that is too drooping is considered a deviation from the norm.
Location of the kidneys (dorsal view)
Dimensions
For adults, the normal kidney sizes are:
- length – 100-120 mm;
- width – 50-60 mm;
- thickness – 40-50 mm.
In children with:
- height up to 80 cm - only length and width are determined;
- height above 100 cm - all indicators are measured.
Inflammatory processes such as pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis can increase the size of the kidneys and increase the risk of organ loss.
Shape and contours
The shape of a normal kidney is bean-shaped and has clear, even contours. In some cases, a “humpbacked” or “lobed” kidney may be the norm. Most often, these are congenital anomalies associated with abnormalities in the structure of the organ, which do not require treatment, provided the patient does not have any associated ailments.
It is also possible to identify the following features of the organ:
- uneven contours;
- changes in shapes, pelvis and cups;
- kinking of the ureter.
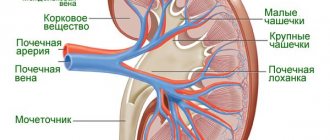
Anatomically, the appearance of the kidneys resembles beans with slightly rounded poles, upper and lower
Structure of the renal parenchyma
Normally, the structure should be uniformly porous. If the kidneys are affected by the disease, then this parameter in the ultrasound interpretation can be described as “increased echogenicity” or “decreased echogenicity”.
In the parenchyma there may be cysts - bubbles with fluid. They are not treated if they are small and do not change in size over time. If they cause symptoms or are unusual in appearance, a tumor may be present.
Blood flow condition
A detailed diagnosis of blood vessels is most easily obtained using Doppler.
The Doppler ultrasound method allows you to determine:
- condition of the walls of blood vessels;
- the presence of stenoses and intravascular obstructions;
- blood flow speed (normally from 50 to 150 cm/sec).
Visualization of renal blood flow. Dark colors are considered normal, bright colors are an increase in blood flow. This indicates the presence of stenosis, in which the blood flow speed can reach 200 cm/sec.
Ultrasound indicators and their standards are described in the video. Provided by the channel “Clinic of Aesthetic Gynecology”.
What factors influence the size?
As described above, the size of a person’s kidneys is influenced by certain factors. First of all, the gender of the person.
As research data show, the thickness and size, as well as the length and width of the cortical connective layer, significantly exceed those of the female sex.
This is simply explained by the difference in body structure, because a man’s body is also more massive than a weaker female’s.
In addition, studies have shown that there is a difference in the size of a person’s kidney from each other, depending on whether it is left or right. An explanation was also found for this fact - the liver interfering with the development of the right kidney.
Age also produces significant differences in kidney size. This organ grows until the age of 27, after which its development stops and it remains at the same level. With advancing age, the kidneys begin to decrease in size.
What does an ultrasound show and why is it done?
Ultrasound makes it possible to identify pathologies such as:
- formations on the kidneys (tumors benign and malignant);
- diffuse change or damage to the renal parenchyma;
- urolithiasis (kidney stones);
- nephroptosis (organ prolapse);
- inflammatory diseases, acute and chronic (pyelonephritis, as well as changes in glomerulonephritis);
- hydronephrosis;
- MKD (urolithiasis) of the kidneys;
- blockage of the ureters and expansion of the renal pelvis;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the kidney and the blood supply system of an underdeveloped organ;
- cysts of various etiologies and localizations;
- pyeelectasis in childhood;
- kidney abscesses;
- kidney tuberculosis.
Kidney changes can be diagnosed and recognized using laboratory tests, but an ultrasound examination allows an accurate diagnosis to be made. With its help, you can observe changes in the state of organs over time, and use the results obtained during the pre- and postoperative period.
Normal indicators
For adults and children, the ranges of normal kidney health indicators are different. There were no differences between the normal readings in men and women. Based on the special condition, the norms for pregnant women differ from the usual ones.
In adults
Normal indicators in the structure of the kidneys in adults are shown in the table:
| Height, cm | Length, mm | Length, mm | Width, mm | Width, mm | Parenchyma thickness, mm | Parenchyma thickness, mm |
| Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | |
| 150 | 85 | 82 | 33 | 29 | 13 | 13 |
| 160 | 92 | 90 | 35 | 33 | 14 | 13 |
| 180 | 105 | 100 | 38 | 37 | 17 | 15 |
| 200 | 110 | 105 | 43 | 41 | 18 | 17 |
In children
The norms for children are given in the table:
| Age | Right | Right | Right | Left | Left | Left |
| Thickness, mm | Length, mm | Width, mm | Thickness, mm | Length, mm | Width, mm | |
| 1-2 months | 18,0-29,5 | 39,0 — 68,9 | 15,9-31,5 | 13,6-30,2 | 40,0-71,0 | 15,9-31,0 |
| 3-6 months | 19,1-30,3 | 45,6-70,0 | 18,2-31,8 | 19,0-30,6 | 47,0-72,0 | 17,2-31,0 |
| 1-3 years | 20,4—31,6 | 54,7—82,3 | 20,9—35,3 | 21,2—34,0 | 55,6—84,8 | 19,2—36,4 |
| up to 7 years old | 23,7—38,5 | 66,3—95,5 | 26,2—41,0 | 21,4—42,6 | 67,0—99,4 | 23,5—40,7 |
Acceptable standards for pregnant women
If the results of an ultrasound scan of pregnant women show that the organ is elongated to 2 cm or there is a slight expansion (with the pelvis and ureter), this is normal.
Organ development and size
Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) is used to detect kidney pathology. This device is able to detect abnormalities and the size of this organ.
In addition, an ultrasound will show the functions and structure of the kidneys. True, when receiving the results of the study, some additional data can be calculated according to the table.
As experts say, body weight and organ size are closely intertwined. The greater the weight of a person, the larger the kidney and its height and width. What is the norm for adults and their normal size?
Adult organ size
The normal size of the kidneys in an adult is from 75 to 135 mm. Taking the anatomical dimensions, you can determine the length using the vertebrae.
Indeed, according to confirmed data, the size corresponds to the height of 3 lumbar vertebrae, while the width reaches 75 mm.
As for the thickness of the organ, it will be up to 55 mm. Some begin to measure the size by a person’s fist.
The data was verified experimentally, which confirms this statement.
In young men, the thickness of the kidney and its tissues ranges from 12 to 27 mm. With old age, the connective tissue of the organ significantly reduces its size. In people over 60 years old, the thickness becomes 12 mm, and in some cases even less.
Kidney organ size in children
As stated above, the kidney organ and its size depend on body weight and gender. Taking into account that children develop according to individual characteristics, clear criteria for determining sizes have not been established.
Doctors are beginning to navigate statistical data in the context of age development groups.
The kidney pelvis in a newborn has a normal kidney size of 5 mm; up to 4 years, this figure increases by 1 mm. According to statistics, the average size of a person’s kidneys at birth is 48 mm.
- As for ages from 3 to 12 months, the size reaches 60 mm.
- From one to five years, the size of the organ corresponds to 72 mm.
- From five years to 10 years, the size is already 86 mm.
- Age ranges from 10 to 14 years, size up to 100 mm.
- From 14 to 20 years old – 107 mm.
For a more accurate determination, the doctor calculates the height and weight of the patient, a small person.
Traumatic injuries
Kidney damage implies a violation of the integrity of the organ due to physical impact. It varies in severity: from minor injuries to those that pose a threat to human life.
In medicine, two types of injuries are distinguished: closed and open kidney injuries.
Closed damage
These include:
- bruise (there may be hemorrhages in the parenchyma, but there is no rupture of the hematoma);
- contusion;
- subcapsular rupture, with a hematoma present;
- crushing;
- separation of the ureter, complete or partial damage to the vascular pedicle (rupture of tissue and fibrous capsule of the kidney).
Open damage
The causes of open damage can be:
- gunshot wounds;
- knife wounds;
- possible damage to the abdominal cavity with subsequent development of peritonitis.
Photo gallery
Bruise (hematoma) of the kidney
Kidney crush
Kidney injury
Interpretation of kidney ultrasound results
To decipher the kidney ultrasound indicators, it is better to contact a specialist who will also take into account the patient’s medical history as a whole.
Special terms in the conclusion
The ultrasound report contains special terms that are incomprehensible to most patients:
- Severe pneumatosis of intestinal loops. This means that the study was difficult due to the large amount of gases in the intestines.
- Pelvis. This is a small cavity in the middle of the kidney where urine collects. Urine from the renal pelvis enters the ureter, and from there it is completely eliminated from the body.
- The fibrous capsule is the membrane that covers the outside of the kidney. Normally, it should be smooth and clearly defined.
- Echotenosis, hierechogenic inclusion, echogenic formation indicates the presence of stones or sand.
- Kidney microcalculosis means that small stones up to 5 mm or sand were found in the kidneys.
Signs of Healthy Kidneys
Signs of healthy abdominal organs:
- the shape of the kidneys is bean-shaped, the outlines of the organ are clear, there are no signs of changes in urinary outflow;
- the aortic diameter is normal, there is no aneurysm;
- The abdominal organs are normal, there is no proliferation of tissue and fluid;
- The thickness of the gallbladder is normal, the ducts are not dilated, there are no stones;
- the liver is normal, the structure is not changed.
Changes indicating pathologies
The examination may show deviations from the norm; therefore, the conclusion of the kidney ultrasound indicates the following description of the anomalies:
- the size of the organ is increased, urinary outflow is impaired, the ureters are dilated, kidney stones are present;
- the aorta is dilated, there are symptoms of an aneurysm;
- there are signs of inflammation, infection, disease;
- organs are displaced, tissue is growing, or there is fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- the walls of the gallbladder are thickened, the ducts are dilated, stones are present;
- there are signs of heatomegaly, the structure of the organ is changed.
What do the colors mean on a kidney ultrasound?
In addition to blood flow, the structure of kidney tissue can also allow it to be visualized in color, an ability called echogenicity.
Echogenicity of tissues and pathological formations on ultrasound:
| Color characteristic | Color | Formations corresponding to color characteristics |
| Anechoicity | Black | Renal pelvis, cavities filled with fluid |
| Hypoechogenicity | Dark grey | Tissues containing a lot of fluid, medulla |
| Echopositivity (normoechogenicity) | Grey | Most soft tissues of the abdominal cavity, kidney parenchyma (cortex) |
| Increased echogenicity | Light gray | Tissues with low water content, kidney capsule |
| Hyperechogenicity | Bright white | Kidney stones (formations of such density are not found in a healthy kidney) |
Characteristics of the pathology
Description of how ultrasound will show pathology in conclusion:
- If the kidney is too mobile or its position is displaced, a diagnosis of nephroptosis is made.
- A wrinkled kidney indicates nephrosclerosis.
- Hyperechoic inclusions on ultrasound (darkening, darkening) look like neoplasms in the form of sand or stones. In this case, microcalculosis is diagnosed.
- Neoplasms in the form of cysts or abscesses are diagnosed with low echogenicity.
- Seals and neoplasms in the form of tumors may indicate oncology or renal hemangioma. This pathology is usually diagnosed even when the tumor is located in the organ bed. Kidney cancer can be more accurately determined with additional cancer tests.
- Structural changes, uneven contours, enlarged kidneys or low mobility - the patient has pyelonephritis.
- Uneven contours, increased echogenicity, decreased blood flow - renal failure is diagnosed.
- The thickness of the parenchyma decreases, there is no visualization of the hydronephrotic sac - characteristic of hydronephrosis.
- If a decrease in the size of the kidneys is visible, a diagnosis of glomerulonephritis or a congenitally hypoplastic kidney is made.
- An increase in size indicates hydronephrosis, tumor processes, and blood stagnation.
- An increase in the width of the renal pelvis is inflammation or signs of diseases of the urinary system.
- A spongy kidney indicates deformation of the renal canals - Malpighian pyramids, which are affected by many cysts.
- A horseshoe-shaped kidney indicates a congenital anomaly of the fusion of the two poles of the kidney with each other. In this case, a diagnosis of pyelonephritis, nephrolithiasis, hydronephresis or arterial hypertension is made.
How to prepare a child for a kidney ultrasound?
During an ultrasound of the kidneys, the child does not need to prepare for the procedure. The most important thing is to drink still water or tea about twenty minutes before the test (the volume depends on age), since the procedure is performed on a full bladder.
The day before the examination, do not give your child foods that promote gas formation: white bread, raw vegetables and fruits, carbonated drinks, legumes. If a child is overweight or has flatulence, then this diet should be started three days before the examination.
Photo gallery
The photo clearly shows kidney pathologies on ultrasound images.
Coral kidney stones on ultrasound
Angiomyolipoma of the kidneys on ultrasound
Multicystic kidneys on ultrasound
Kidney tumor on ultrasound