Using ultrasound, you can see most of the pathologies of the kidneys and bladder in children, such as:
- Inflammation
- Stones, sand
- Pyelonephritis
- Prolapse of the kidneys (nephroptosis)
- Cysts
- Tumor
- Organ anomaly
- Kidney expansion, etc.
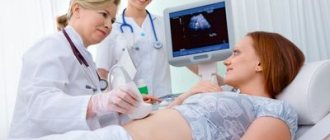
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder in children is carried out after special preparation; the norms depend on the child’s age and gender, height and weight. Three days before the ultrasound, you should not eat spicy, fatty, fried, salty foods, or cabbage and beans. Another important condition for a high-quality procedure is to refrain from eating 7–8 hours before the examination. You can take one tablet of activated charcoal per 10 kilograms of body weight after a meal, 1 hour later (to reduce gas formation).
The examination begins with the abdomen and lower back; the doctor applies a special gel to the sensor for better conductivity of ultrasonic waves. Ultrasound of the kidneys is examined from three sides:
- From the stomach
- From the back
- On the side
After the examination, the doctor will give the result; during ultrasound, the following parameters are deciphered: width, thickness, length.
Preparing for an ultrasound scan of the kidneys
On the day of the examination, it is recommended to refrain from eating food until the diagnosis is carried out. Children with chronic constipation should follow a diet before undergoing the procedure. Otherwise, the information content of the study is noticeably reduced. The diet involves excluding chocolate products, pickled foods, canned vegetables, and fresh baked goods from the diet. Before carrying out diagnostics, you need to stop eating fatty meats and legumes.
Standard Kidney Growth Indicators
The longitudinal size of the organ should be approximately from 80 to 130 mm. In an adult, the length of this internal organ should correspond to the height of three lumbar vertebrae. The width for men can be up to 70 mm, and the thickness up to 50 mm. For any size, the ratio of length to width should correspond to a clear ratio of 2:1. Since all parameters of height and weight of the stronger sex are often greater than those of women, the size of this component of the excretory system is smaller in the weaker sex.
If we compare the dimensions of human parenchyma with standards, then the thickness should be no less than 15 mm and no more than 25 mm. With increasing age and the development of inflammatory and atherosclerotic processes, the parenchyma may become thinner. In most cases, after 60 years of age, the patient's parenchyma decreases to a size of 11 mm.
To find out all the dimensions of this component of the excretory system, ultrasound is used. If we summarize the information about the structure and size, then with relatively good health, the kidneys have a size approximately comparable to the size of a fist.
In childhood, some difficulties arise in determining the standardization and normalization of renal parameters due to the fact that children grow and develop individually. To determine the norm, you need to know the weight and height of the child. Approximate values are as follows:
- in infants it will be 50 mm;
- at 2-3 months it reaches 63 mm;
- at 5 years – 75 mm;
- at 10 years – 85 mm;
- at 15 years old the value is 98 mm;
- 20 years – 105 mm.
An interesting phenomenon is that an infant has a size to weight ratio that is 3 times greater than an adult.
Return to contents
What criteria does the doctor pay attention to when making a diagnosis?
When performing a kidney ultrasound, the specialist pays attention to the following parameters:
- localization of the organ (in order to exclude nephroptosis);
- longitudinal and transverse size of the kidneys;
- state of the organ parenchyma. At the same time, its homogeneity and the occurrence of degenerative changes are assessed;
- structure of the renal pelvis (its size, absence of stones);
- blood supply to the organ (patency of arteries, absence of anomalies in the development of renal vessels).
Location
The right kidney is located lower than the left. Thanks to ligaments and muscles, internal organs are able to move slightly during breathing and movement, otherwise any sudden tilt or turn could cause injury.
But the physiological displacement of the kidneys should not exceed two to three centimeters! If the organ is constantly located lower than necessary, or moves strongly inside the body, the ultrasound report indicates its atypical location - dystopia or right- (left-sided) nephroptosis -.
Ultrasound of the kidneys in newborns
Carrying out an ultrasound scan in children in the first weeks of life involves the following nuances:
- When performing the procedure, smaller sensors are used. Such sensors are ideal for this age category;
- If a mother is breastfeeding, she needs to exclude foods that cause increased gas formation from the daily menu. Otherwise, diagnostic procedures may be difficult;
- The specialist focuses on the developmental defects of the newborn. The doctor should describe them as informatively as possible.
Parenchyma condition
Parenchyma is the name given to renal tissue, thanks to which the kidneys serve as a physiological filter. In its thickness are located the so-called structural and functional units of the kidney - nephrons.
Thickness
The thickness of the parenchyma layer in adults is 18-25 mm, in children over one meter tall - 9-18 mm (left kidney) and 10-17 mm (right). Thinning or thickening of the layer indicates dysfunction of the renal tissue.
- The parenchyma becomes thicker due to edema or inflammation - for example, in acute pyelo- or glomerulonephritis. Thickening of the parenchyma of a single kidney may indicate its hypertrophy.
- The layer of renal tissue becomes thinner during dystrophy against the background of chronic pyelonephritis.
With age, the parenchyma becomes thinner even in people with healthy kidneys. If you are over 60 years old, and when deciphering the results, you heard the number 11 mm from your doctor, do not worry. This indicator is considered the age norm.
Changes in structure
The terms “hyperechogenicity” and “hypoechogenicity” refer to the high and low degree of reflection of sound waves from obstacles - body tissue. It depends on the density of sections along the sound path:
- air and liquid do not reflect sound, they are anechoic;
- “loose”, low-density tissues are hypoechoic and are displayed on the screen as darkened areas;
- dense, hyperechoic tissues are impermeable to sound waves. On the device monitor they are visualized as light contours and spots.
Normal kidney tissue is homogeneous. A change in its “throughput” shows that the parenchyma is affected by a disease process that has affected its density.
“Is this really a tumor?!”
The examination can identify various tumor formations, but not all of them are dangerous. Ultrasound doctors are careful in their conclusions, and in conclusion they describe only what the device shows.
- A malignant tumor is described as a round (oval, other shape) formation, often with unclear contours and a heterogeneous internal echo structure.
- The words “hyperechoic, homogeneous formation, similar in structure to perinephric tissue” are not a cause for alarm. This is probably a lipoma - a benign tumor of adipose tissue.
- The description “homogeneous”, “with homogeneous anechoic contents” means a renal cyst.
However, remember that ultrasound does not give a clear answer about the reasons for the changes! To accurately determine the cause of the disease, after interpreting the results of the ultrasound examination, the urologist will prescribe additional diagnostic procedures, such as a biopsy.
Main indications
One of the main indications for the procedure is cystitis. This disease occurs under the influence of various factors:
- hypothermia;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- chronic kidney disease;
- wearing tight clothes.
An ultrasound examination of the bladder in a child should be performed if there are the following indications:
- the appearance of pain when urinating;
- the presence of oxalates in the urine;
- increased frequency of the urge to urinate;
- cloudy urine;
- discomfort in the lumbar region;
- the appearance of sediment in the urine.
Ultrasound examination not only helps to determine the contours and size of the bladder. When carrying out a diagnostic procedure, it is possible to establish a narrowing of the urinary canal, the presence of stones, and deterioration of blood circulation. Ultrasound is also informative in case of an inflammatory process occurring in the bladder.
Quantity
Even the congenital absence of one kidney (unilateral agenesis) or its underdevelopment (aplasia) sometimes becomes a “diagnostic surprise” on ultrasound. If the kidney is normal in structure, but so small that it cannot fully perform its functions, the conclusion will indicate hypoplasia of the organ.
Congenital duplication of the kidneys can also be unilateral or bilateral. People with complete doubling often suffer from pyelonephritis and other diseases of the urinary system; partial doubling does not always affect the function of the organ.
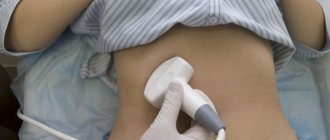
Carrying out ultrasound with an abdominal sensor
The ultrasound examination scheme looks like this:
- The child needs to undress to the waist and sit comfortably on the couch (on his back).
- A small amount of gel is applied to the area of the body located above the pubic bone.
- During diagnostics, an image of the bladder is displayed on the device monitor.
When performing an ultrasound examination, parameters such as the size and shape of the organ and the thickness of its walls are assessed. The specialist also evaluates the condition of the mucous membrane.
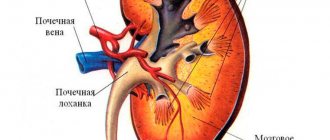
Human kidney anatomy
The topographic anatomy of the kidneys consists of the following features. This component of the excretory system, being a paired organ, is projected differently to other organs. The right component of the system is adjacent to the adrenal gland and liver. The left component is in contact with the adrenal gland, stomach and spleen. At the back, both organs are adjacent to the diaphragm.
Each of these elements of the excretory system is covered on top with a special capsule of connective fibers and a serous additional membrane. The renal parenchyma is formed from the medulla and cortex. The first is approximately 15 pyramids of a conical type with rays at their base. These rays grow into the continuous cortical shell.
Each kidney contains up to 1 million nephrons. They are the main constituent units of these components of the human excretory system. They are formed from tubules, corpuscles and passing blood vessels.
The pelvis is a special cavity that receives urine. The ureter receives urine from the pelvis and then sends it to the bladder.
The renal artery is a blood vessel that arises from the aorta. He brings polluted blood. The renal vein is a blood vessel that carries pure blood to the main vein.
Return to contents
Normal values according to age
According to the results of an ultrasound examination, normal kidney sizes should not exceed the following indicators:
in adults
- in width from 45 to 70 mm;
- in thickness from 40 to 50mm;
- in length from 80 to 130mm;
- in parenchyma thickness up to 25 mm. But this indicator can change with age, so at 65 years old, a parenchyma thickness of 11 mm is the norm;
in children (indicators depend on age, since the body develops most rapidly before the age of 20)
- in the period up to a year, the average length does not exceed 6 cm;
- from one to five years no more than 7.5 cm;
- from five to ten years within 8.5 cm;
- from ten to fifteen top – 10 cm;
- from fifteen to twenty, the size should not exceed 10.5 cm.
It is important to note that the ratio of the right and left kidney plays a key role in deciphering the results. The size of the kidneys according to the criterion of length and width should be in a ratio of 2 to 1. It is also worth noting that the normal sizes of these organs in children are relative, since each child develops individually, therefore, when deciphering, specialists pay special attention to the child’s physique, his weight and age . A typical phenomenon is when the ratio of kidney size to weight in a child is 3 times higher than in an adult. For the most accurate diagnosis, there are tables of normal sizes of the renal pelvis separately for adults and children.
Increased echogenicity
So, what is the basic structure of the parenchyma, you can imagine. But a rare patient, having received the result of an ultrasound examination, does not try to decipher it on his own. It is often written in the conclusion that there is increased echogenicity of the parenchyma. First, let's look at the term echogenicity.
Examination using sound waves is based on the ability of tissues to reflect them. Dense, liquid and bone tissues have different echogenicity. If the fabric density is high, the image on the monitor looks light, the image of fabrics with low density appears darker. This phenomenon is called echogenicity.
The echogenicity of the renal tissue is always homogeneous. This is the norm. Moreover, both in children and adult patients. If during the examination the structure of the image is heterogeneous and has light inclusions, then the doctor says that the renal tissue has increased echogenicity.
With increased echogenicity of the parenchyma, the doctor may suspect the following ailments:
- Pyelonephritis.
- Amyloidosis.
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Sclerotic changes in the organ.
A limited area of increased echogenicity of the kidneys in children and adults may indicate the presence of a neoplasm.
Detection of pathologies using ultrasound
Interpretation of kidney ultrasound helps to identify numerous pathologies associated directly with the urinary system; by nature, such pathologies are divided into anatomical, physiological and functional. Most often, when interpreting sonography, the following types of diseases are diagnosed:
- the presence of sand or stones in the pelvis is diagnosed as kidney stone disease;
- narrowing of the ureters;
- various disorders in the structure of blood vessels;
- the presence of neoplasms, most often of a tumor nature, the formation of a cyst is possible;
- disturbance in the functional state of the urinary system (impossibility of partial or complete failure of the organ to perform its direct functions);
- inflammation, including an infectious nature, in the kidneys (nephritis and pyelonephritis, respectively);
- glycogen degeneration (nephritis).
Ultrasound provides the opportunity to reliably obtain information about the general condition of the kidneys, as well as the presence of possible pathological changes in the patient’s body. This is very important, because kidney diseases can affect a person’s condition extremely negatively, and the possibility of serious complications is a dangerous threat to the patient’s body. Therefore, it is important to regularly
Factors that influence sizes
In general, the size of the kidneys is affected by a person’s gender, age and weight. Scientists have found that a person's mass index affects overall size, volume, height and height.
It was found that the right organ is smaller than the left, which is due to the fact that the liver prevents its growth.
The size of the organ can increase up to 25 years, after which it stops growing, but after 50-60 years it begins to decrease in size.
In diabetes mellitus or hypertension, renal hypertrophy may occur.
It is very important to monitor the size and functioning of the renal structures, because this paired organ is of great importance for the normal functioning of the entire human body.
Of course, its main function is the process of processing blood and removing from its composition substances that have an adverse effect on the body. It further regulates blood pressure, acidity, and the production of vitamin D and hormones.
Kidney size is one of the diagnostic parameters that allows us to reliably establish some human ailments.
Victor Vasilievich Zlatogorsky
The information is relevant for me - I am now 34 weeks pregnant, the doctor, using an ultrasound scan, diagnosed “pyeloetasia of both fetal kidneys”, without giving any explanation. I just said.
I have the same problem. There are continuous drafts at work, and like it or not it will always strain your ribs, your neck, your kidneys. And I also had cystitis myself. I treated him, but he...
Anna, the most important thing is don’t worry. I also discovered a prolapsed kidney, and when I was already pregnant. Yes, I had pyelonephritis, I was kept on guard, and I was on a diet. Rody.
Is it true that after lapparoscopic surgery you are discharged from the hospital within a few days? In addition, I have high blood pressure, there are frequent crises, is this not the case?
The recipe is good, at the age of 50 kidney stones appeared, all this is quite difficult and long to treat. My father advised me to drink and brew rose hips (its root is best), I listened to the recommendation.
More information
Any patient encountering kidney disease for the first time wonders what could be hurting in this small and seemingly solid organ. The doctor, of course, explains in his medical language the origin of the pathology, mentions the nephrons located in the kidney parenchyma, dysfunction, but little is clear from this story to the average person.
So that a person ignorant of medicine can understand what parenchyma is, let us explain - this is the main renal tissue. There are 2 layers in this substance.
- The first is cortical or “external”. There are complex devices here - renal glomeruli, densely covered with vessels. Urine is formed directly in the glomeruli. It is difficult to count the number of glomeruli in the cortex; each kidney contains more than a million of them. The cortex is located directly under the renal capsule.
- The second layer is the cerebral or “internal” layer. Its task is to transport the resulting urine through a complex system of tubules and pyramids, and collect it in the pyelocaliceal system. Each kidney contains from 10 to 18 pyramids, which grow into the cortex as tubules.
It is the kidney parenchyma that is responsible for the water and electrolyte balance of the body. Kidney parenchyma is a unique tissue. Unlike other tissue elements, it is capable of regeneration, i.e. restoration.
This is why treatment of acute renal pathologies is of great importance. The parenchyma tissue of both the left and right kidneys responds positively to health measures.
Glomeruli, pyramids, tubules and vessels form the main structural unit of the kidney - the nephron.
An important indicator of physiological structure is thickness. This is a variable value and changes with age, as well as under the influence of infections and other pathogenic agents.
Normal parenchyma thickness:
When examined by ultrasound, not only the thickness of the kidney parenchyma is important, but also other physiological characteristics of the organ.
Diffuse changes
If the ultrasound report says that you have diffuse changes in the kidney parenchyma, you should not take this as a final diagnosis. The term diffuse in medicine means numerous and widespread tissue changes in adults and children. Diffuse changes in the parenchyma indicate that a person needs additional examination in order to determine the exact causes of physiological abnormalities. Most often, diffuse changes in the parenchyma are observed if the size of the kidney changes. In acute diffuse type disorders, the size of the kidneys of children and adults increases. In chronic diffuse pathology, the parenchyma is thinned.
If diffuse disorders are moderate, this may indicate:
- about congenital renal anomalies in children;
- about age-related changes that kidney tissue has undergone. In this case, diffuse changes may be normal;
- about previous infections;
- about chronic renal pathologies.
That is, any changes that are unusual for the physiological norm of renal tissue are considered diffuse. These are increased echogenicity, thickening or thinning of the kidney tissue, the presence of fluid, etc. The most striking examples of diffuse parenchymal disorders are a cyst of parenchymal tissue or its thinning.
Parenchyma cyst
It can form in both the left and right kidney. It can be congenital or acquired. If a congenital cyst of parenchymal tissue is detected in children, then the formation of an acquired cyst is typical for people over 50 years of age.
A parenchymal tissue cyst is a more serious disease than a cyst located in another area of the right or left kidney. Representing a limited cavity filled with fluid or serous secretion, the cyst compresses the tissue, disrupting the process of formation and excretion of urine. If the cyst in the left or right kidney is solitary, does not grow and does not affect the functioning of the organ in any way, it is enough to monitor it. There is no treatment for such a cyst.
If multiple cysts form in the parenchymal tissue, doctors decide on surgical removal. There is no fundamental difference in the location of the cyst. It requires the same treatment tactics in both the left and right kidneys.
Thinning of the parenchyma
Diffuse changes indicating thinning of the parenchyma indicate not only the patient’s advanced age. If an elderly person is being examined, the doctor will most likely associate the thinning with age-related changes. The symptom also occurs in young people. Here, the main reason for thinning tissue is due to past diseases that the person did not treat or treated incorrectly.
The thinned kidney parenchyma is unable to perform its usual functions in full, therefore, if a person does nothing and continues to be treated, a chronic disease occurs. And he joins the ranks of patients of nephrologists and urologists.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound, sonography) is an effective method for diagnosing various diseases and pathologies of the urinary system. This study guarantees an accurate and reliable diagnosis, and also allows you to clearly visualize the area under study. is aimed at assessing the organization of the structure, identifying pathologies and disorders in volume, shape and contour. Sonography reveals abnormal position of the organ, as well as disorders in the urinary system.
Interpretation of an ultrasound examination provides the most complete picture of the condition of these organs, and can also confirm or refute the doctor’s preliminary diagnosis. In order to correctly decipher ultrasound results, it is important to know the criteria and norms by which the general state of the environment is determined. The main criteria when interpreting sonography results are the shape and size of the kidneys, as well as the size of the parenchyma (the upper layer of kidney tissue, which performs the task of balancing the internal environment).
Acceptable transcript rates by gender
There are no fundamental differences in decoding by gender, but it is worth noting some nuances of such diagnostics. In the normal state, the size of the organs of men is larger than that of women, which is determined by the larger physique of male representatives. The kidneys of men are large in width, length and thickness. The cortical layer is also larger in men.
Differences in organ size indicators will be most noticeable only during a woman’s pregnancy. The length of the organ can increase in size up to two centimeters. This increase is accompanied by enlargement of the pelvis and ureter, which is quite natural during gestation.
For all men and women, there are general standards of normal ultrasound readings. For any deviation from the norm, specialists prescribe additional diagnostics to the patient to establish a detailed picture of the ultrasound interpretation.
For the prevention of diseases and treatment of kidneys, our readers recommend the Monastic Collection of Father George. It consists of 16 beneficial medicinal herbs that are extremely effective in cleansing the kidneys, treating kidney diseases, urinary tract diseases, and cleansing the body as a whole. Get rid of kidney pain..."