Characteristics and types of method
A device with attached electrodes for echo-encephalography.
The study is based on recording vibrations generated by plates applied to the head, which are exposed to ultrafrequency electrical impulses. From the bone tissue of the skull, vibrations are transmitted inward, and echolocation occurs at the boundary of environments of different densities - the impulse returns with a certain time delay. The nature of the resulting images on the encephalograph monitor gives the doctor the opportunity to judge the state of the brain tissue and the presence of various pathological formations in it.
Echography is performed in two modes:
- one-dimensional - this is how an echoencephalogram is created;
- MMA readings (graphic representation of reflected signals);
- two-dimensional - ultrasound scanning: the image obtained as a result of scanning the brain simultaneously in two planes (echoencephaloscopy) is displayed on the screen.
Echo-encephalography allows you to observe the work of the brain in real time.
One of the varieties of a two-dimensional encephalogram is neurosonography, which consists of conducting an echo of the head of a newborn child through the large fontanelle - a section of the cranial vault at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones of the skull. In the first months after the baby is born, it is covered with a soft film, under which a pulsation is felt. Due to this, the bones of the fetal skull can shift as it passes through the woman’s birth canal. By the end of the first year of life, the soft part of the skull gradually ossifies. Until this point, ultrasound easily passes through the fontanel, which makes possible a detailed study of brain structures, which has a high degree of information content. Pediatricians recommend mandatory neurosonography for every child in the first year of life.
Experts divide the process of displaying an impulse when taking an echogram into several types:
- The initial complex is a set of reflected high-frequency pulses, showing the location of the external tissues of the head (skin, muscles, bones).
- M-ECHO is a signal reflected from the third cerebral ventricle and the pineal gland.
- The final complex is an echolocation signal from the bone tissue of the skull on the side opposite to where the initial complex comes from.
- Lateral echo signals are recorded in the interval between the initial and final complex - before and after M-ECHO.
If pathological changes are detected, for a full diagnosis it is necessary to carry out several ECHO-EG procedures of the head while monitoring the patient’s condition. This gives the doctor the opportunity to observe the dynamics of the severity of damage to the brain and its blood vessels at different stages of the disease.
What is echoencephalography?
ECHO of the head is a safe and quite informative method of studying the brain using ultrasound in both adults and children.
Such waves, having a frequency of 0.5-15 MG c/s, easily pass through various tissues of the body and are reflected from any surfaces located near the boundaries of tissues with different compositions (brain matter, skull bones, blood, cerebrospinal fluid, soft tissues of the head). As a result of such a study, formations that are pathological in nature (various hematomas and abscesses, foreign bodies, crush areas, cysts) may also turn out to be reflective surfaces. Using echoencephalography, the patient’s arteries and veins are also examined and the patency of the brain vessels is checked. This procedure easily reveals blood flow disturbances, which can subsequently lead to serious illnesses.
Indications and contraindications for EchoEG
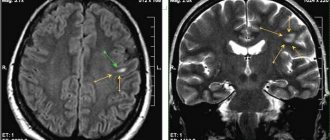
On the left is a normal ventricle, on the right is hydrocephalus
Despite the advent of modern diagnostic techniques, such as magnetic resonance and computed tomography (MRI and CT), echoencephalography is still actively used in examining the brain in children. Most often it is prescribed for various problems of cerebral etiology in infants. The main indications for EchoEG are:
- Hydrocephalus is an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles and subarachnoid parts of the brain. It occurs due to its excess production or poor outflow.
- Intraventricular hemorrhage in the brain.
- Oxygen deficiency leading to the development of periventricular leukomalacia - the main cause of cerebral palsy.
- Craniosynostosis is premature fusion of the bones of the skull.
- Intrauterine and postnatal neuroinfections.
- Prematurity.
- Birth injury.
- Muscle hypertonicity, cramps.
- Developmental disorders - both physical and mental.
- Dynamic monitoring of previously diagnosed brain pathologies.
For older children, echoencephalography is prescribed for complaints of dizziness, nausea and frequent headaches, as well as for enuresis, nervous tics, logoneurosis (stuttering), hyperactivity, and sleep disorders. It helps identify concussions, space-occupying formations (tumors, cysts), edema and foreign bodies in the area of brain tissue. EEG also makes it possible to diagnose intracranial hypertension and at an early stage to recognize post-traumatic complications of traumatic brain injury - intracranial hematomas.
There are practically no contraindications to echoencephalography - the examination can be carried out on a patient in any condition. The only reason for a temporary ban is the presence of open wounds on the head.
In what cases is echoencephalography prescribed for children?
Like adult patients, children do not need any preliminary preparation. It is advisable that the child does not eat anything for three hours before the test, because with a full stomach, the diaphragm is high, which can distort the result.
Parents should take with them the results of the electrocardiogram performed the day before, as well as the results of studies that were carried out previously. Without fail, the baby should be psychologically prepared for the procedure, explaining that no one is going to hurt him.
In order to carry out the procedure, the baby is undressed to the waist and placed on the left side on the couch. After moving the sensor across the chest, the doctor examines the resulting image.
Echoencephalography of the brain in children is one of the optimal methods of neurological examination. This is primarily due to the absence of contraindications, as well as the painlessness of the procedure. In addition, echoEG does not require special preparation and is an informative method. The indications for its implementation are the same as for adults. In addition, there are other complaints that are usually characteristic of the pediatric population. Among them:
- Growth retardation. The process may be associated with a violation of hormonal regulation, which occurs in the brain.
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. This disease is psychological in nature, but its cause can also be structural disorders. This syndrome is manifested by disobedience, lack of concentration, poor academic performance, and defiant behavior. Most often diagnosed at the age of 5-8 years.
- Enuresis is urination at night.
- When diagnosing hydrocephalus, an echoEG is necessary to assess the severity of the pathology.
Neurosonography is performed in newborns and infants. What's different about this study is that it looks at the entire structure of the brain. This is ensured due to the fact that young patients have open areas of the skull - fontanelles. Indications for NSG are sleep disturbance, sudden screaming, holding one's breath, and excessive regurgitation. In general, this study is no different from echoencephalography. The mechanism of action of the devices and the technique for performing both methods are identical.
In children under 1.5 years of age, the fontanel has not yet become overgrown, so this procedure can be used to completely examine all areas of the brain.
ECHO of the child’s head is prescribed in the following cases:
- to assess the degree of hydrocephalus;
- if sleep is severely disturbed;
- to assess the effectiveness of therapy for neurological diseases;
- if nervous tics bother you;
- with delayed physical development;
- if muscle hypertonicity is detected;
- for stuttering and enuresis;
- in case of head injury.
There are billions of nerve cells in the human brain. Neurons have a unique feature - the ability to generate and conduct electrical impulses. The total activity of a large number of neurons forms the bioelectrical activity of the brain. Neurophysiologists record it during EEG recordings for children and adults.
An EEG recording is a reflection of the functioning of the brain. At what age is EEG performed? EEG is performed on both infants and older children. In children, EEG allows one to correctly assess not only the state of functional activity of the brain, but also the stages of development of bioelectrical activity of the brain during the first years of life.
By analyzing the EEG, doctors receive valuable information about the presence of pathological changes in the bioelectrical activity of a child in various diseases of the central nervous system. Thanks to the availability of modern equipment, neurophysiologists have the opportunity to do EEG in newborns. The study makes it possible to assess the severity of disorders and predict the outcome of brain lesions.
Preparation and conduct of the survey
The places where the electrodes are attached are moistened with water.
No special preparation of the patient for an echoencephalographic study is required; the main requirement is the absence of damage to the skin on the head. For infants and children under three years of age, it is done in a supine position, while parents must ensure their complete immobility during the procedure; older children can sit. Patients do not experience pain or any discomfort.
Sensors are placed on the head, fixed on one axis and connected to a diagnostic apparatus. They are attached on both sides of the head above the external auditory canal, at the temple above the superciliary arch and 4-5 cm behind the ear vertical. Before applying the plates, the surface of the head is moistened with water to improve their adhesion to the skin and improve the conductivity of electrical impulses by tissues. The gel is absolutely harmless and can be easily washed off at the end of the diagnostic procedure, which takes no more than a quarter of an hour. When conducting EchoEG in children, currents with a frequency of 2.6 MHz are used, which easily penetrate the outer membranes of the head. During the examination, the doctor smoothly moves sensors over the head, while simultaneously monitoring the encephalograph monitor. The procedure begins with the right side of the skull, then examines the left side, moving from the frontal part to the back of the head.
Conditions for the existence of an echo
Several conditions are required for an echo to appear. Have you ever wondered why echo is not heard in an apartment or a store, but at the same time it is extremely easy to hear in the mountains? The fact is that the human ear hears an echo only when the reflected sound sounds separately from the spoken sound, and is not layered on top of it. To create such an effect, it is necessary that the time elapsed between the influence of the sound itself and the reflected wave on the ear must be at least 0.06 seconds. In a normal environment (for example, in an apartment) this will not happen due to the short distance and various objects that also absorb sound.
Decoding the results
Electrical indicators of brain function, which are displayed on the monitor.
Decoding the results of an echoencephalogram takes no more than an hour. It is printed out in paper form and given to the patient or his parents, if this is a minor. The following indicators are taken into account:
- M-ECHO – signal with the highest amplitude. Normally, it occupies a middle position, but its displacement in one direction or another up to 5 mm is considered acceptable. A displacement of more than 6 mm indicates the presence of pathological changes in the brain.
- A dilated or disrupted signal coming from the third ventricle is a sign of high intracranial pressure (ICP).
- The pulsation of M-ECHO signals should be within the range of 30-40%. If the value of this indicator exceeds this figure, reaching 50-70%, hydrocephalic syndrome is diagnosed.
- The SI indicator - the average sellar index - should not go beyond the range of 3.9-4.1. A lower SI indicates a high ICP
The correct interpretation of EEG results depends on the joint efforts of the diagnostician and the attending physician. In some cases, their opinions on this issue differ, then additional studies are needed - MRI or CT scan of the brain.
An electroencephalogram is a fairly accessible diagnostic technique for patients. Services for its implementation are provided in specialized diagnostic centers in many large cities, which have the appropriate equipment and qualified specialists who can use it competently. Prices for EchoEG are higher, the higher the status of the clinic and the professional level of its employees. On average, the cost of this diagnostic procedure is about 3,000 rubles.