The article talks about calicoectasia, a pathology of the pyelocaliceal system of the urinary organs. The causes of occurrence and characteristics of symptoms are described.
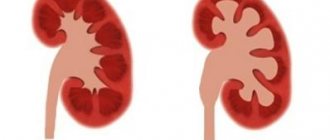
Renal calicoectasia, or hydrocalycosis, is a pathology involving the pyelocaliceal system. It is characterized by expansion of the renal calyces, leading to disruption of the outflow of urine. The disease is not life-threatening, but can provoke the development of other kidney diseases.
People of all ages are susceptible to the disease
The essence of pathology
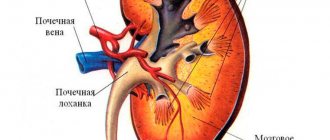
What is calicoectasia of the kidney and how does this pathology develop? Calicoectasia or hydrocalicoectasia of the kidneys is a pathological condition of the organ in which the accumulation of urine causes expansion of the renal calyces, and as a result, compression of the remaining tissues. Thus, kidney function is impaired.
The ICD 10 code for this disease is Q62.3.
Accumulation of urine in the pelvis and calyces leads to their expansion
Causes
This disease is not an independent pathology, but develops against the background of diseases that cause persistent disruption of the outflow of urine or injury. The pathology can also be congenital.
The main reasons leading to the development of the disease:
- intrauterine anomalies in the development of the kidneys, arteries and vessels of the organ;
- urolithiasis, tuberculosis, nephrolithiasis, prostate adenoma, cancer;
- prolapse of the kidney and torsion of the ureter;
- postoperative adhesions;
- organ injuries.
Pregnancy is one of the factors predisposing to the development of the disease. In pregnant women, the kidneys are subject to double stress; in addition, in the third trimester, the urinary tract begins to be compressed by the enlarging uterus.
Mechanical impact on organs and increased stress can cause disease. Calicoectasia of the right kidney mainly occurs during pregnancy, due to pressure on the ureter on the right.
The cause of calicoectasia in children is a congenital anomaly - an additional vessel inside the organ.
Compression of the ureter by the uterus can cause disease during pregnancy
How it manifests itself
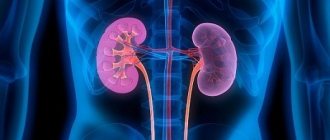
Calicoectasia of the right kidney occurs many times more often than in the left. Calicoectasia occurs against the background of other diseases, so the symptoms of the underlying disease are more pronounced. In the early stages, there are virtually no symptoms; there may be only moderate pain over the area of the affected kidney or in the groin.
As the disease progresses, the symptoms intensify, and the following signs appear:
- fever;
- general intoxication;
- painful vomiting;
- intense pain on the right or left in the lower back, less often on both sides;
- increased frequency of urination with decreased volume of urine excreted;
- cutting pain during urination;
- change in urine.
Calicoectasia of both kidneys - what is it? This is a simultaneous enlargement of the calyces of both kidneys. Usually has a congenital origin or is a consequence of an autoimmune disease.
With unilateral damage, symptoms appear after about 2-3 months, as the healthy organ compensates for the work of the affected one. Bilateral renal caliectasis is less common, its manifestations are more pronounced and appear a month after the onset of the disease.
Lower back pain from the affected organ is one of the first signs of the disease
Characteristic symptoms of pyelectasis
Let us remember that pyeelectasis is not a disease, but a concomitant condition resulting from some kind of kidney pathology.
Such diseases include:
- urolithiasis, which manifests itself as renal colic (recurrent intense pain in the lower back);
- kidney tumors, which cause aching pain in the back, radiating to the groin and abdomen; possible appearance of scarlet blood in the urine;
- chronic inflammation of the kidney, which leads to intoxication, lower back pain, cloudy urine with the appearance of sediment and mucus in it.
It happens that pyeelectasis occurs without symptoms and is accidentally discovered on an ultrasound.
If the dilated collecting apparatus is infected, this can lead to the following symptoms:
- fever up to 38.5-41 ° C;
- chills;
- dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief;
- loss of appetite;
- increased fatigue.
Diagnostics
To establish a diagnosis, the patient must undergo a complete examination. First of all, the doctor collects an anamnesis, where he describes complaints and analyzes previous diseases and injuries.
Then additional diagnostic methods are carried out.
- Blood analysis. It will show the presence of inflammation in the body - an increase in ESR, an increase in the number of leukocytes.
- Analysis of urine . An increase in the number of leukocytes is detected, protein and blood impurities appear.
- Ultrasound . Pathology is indicated by expansion of the boundaries of the pyelocaliceal system and deviations in the structure of the organ (photo).
- Angiography, excretory urography. They are carried out using a contrast agent, which makes it possible to track the distribution of the substance through the vessels and urinary tract and determine the cause of the disturbance in the outflow of urine.
- . The most accurate, but also the most expensive method, the price of which varies in different medical institutions. Using the procedure, the exact location and nature of the obstacle is determined.
Since the disease is characterized by nonspecific symptoms, it must be differentiated from acute appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and urolithiasis.
Enlargement of the renal calyces is diagnosed using ultrasound
How is calicoectasia detected on the left and right?
Symptomatic diagnosis of calicoectasia presents a certain difficulty for doctors, since its symptoms described above are similar to the symptoms of many other common diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: cholecystitis, appendicitis, pancreatitis. However, with the help of laboratory tests, calicoectasia easily reveals itself through increased levels of leukocytes, red blood cells and certain types of epithelium. As a rule, with the laboratory diagnostic method, the patient is prescribed a biochemical blood test.
Another effective method to detect this disease is an ultrasound of the problem area, which will clearly show an enlargement of the renal pelvis, precipitation of salts in the urine (microlites), and an increased size of the cups. This diagnostic method is necessary to correctly determine the causes of difficulty in passing urine, as well as the affected area (left, right, or both kidneys).
Instrumental diagnostics are quite effective in the following ways:
- Urography is the injection of a contrast agent into large blood vessels, with the help of which the functioning of the kidneys and urinary tract is monitored.
- Angiography is a procedure similar to urography. The only difference is that the substance is injected directly into the renal artery without involving other blood vessels.
- Retrograde pyelography - a contrast agent is injected into the kidney through a ureteral catheter.
The final stage of examining the patient is to conduct various types of radiation diagnostics, for example, magnetic resonance imaging. This diagnostic method can provide information:
- About the functional activity of organs and the presence of complications and anomalies.
- About the presence or absence of malignant or benign neoplasms.
- About the presence or absence of fistula connections with neighboring organs.
Treatment methods
Treatment for calicoectasia should begin as early as possible. Since stagnation of urine in the kidneys can lead to the development of complications - hydronephrosis, urolithiasis, renal failure.
The method of treatment - conservative or surgical - is selected depending on the root cause of the pathology and its severity. It is known that renal calicosis is a disease that develops due to an existing pathology of the organ.
Therapy is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and normalizing renal function. The conservative method involves taking medications and adjusting nutrition. A specialist will talk about surgical methods for treating calicoectasia in the video in this article.
Causes of development and types of pathology
Based on the nature of hydrocalycosis, it can be argued that it is associated with a violation of the flow of urine from the kidneys due to blockage of the duct to the bladder.
Depending on the location of the pathological process, calictoectasia occurs:
- right kidney,
- left kidney,
- bilateral (15-20% of cases).
Hydrocalycosis of the left kidney is found less frequently than the right kidney, which is caused by physiological characteristics. The right kidney is more mobile, located approximately 1 cm lower than the left. Pathology of the right kidney can often be observed in women during pregnancy. In this condition, the uterus deviates to the right, pressing on the bladder, which leads to difficulty in the outflow of urine. As a rule, after the birth of the baby, everything returns to normal.
Unilateral hydrocalycosis is easier to treat than bilateral hydrocalycosis. The course of a bilateral process has a more unfavorable prognosis, and its treatment regimen is more complex. Kidney failure may develop.
The causes that cause pathology can be renal (direct) and enterorenal (indirect).
Learn about the likely causes and home treatments for kidney cysts.
For a list of the latest generation of antibiotics for kidney pyelonephritis, see this article.
Immediate causes include diseases:
- urolithiasis disease,
- kidney tuberculosis,
- tumors
- nephroptosis,
- anomalies of the cup, in which it is compressed,
- kidney prolapse,
- trauma and inflammation.
Enterorenal causes:
- abnormalities of the vascular system,
- defects of the lymphatic system, including enlarged lymph nodes that compress the urinary organs,
- neoplasms in the abdominal cavity,
- congenital defect of the entire urinary system.
Reference! Renal diseases cause deterioration of the patient's condition more quickly than enterorenal diseases. But recovery occurs faster with the treatment.
Prognosis and prevention
Timely diagnosis and treatment allow us to hope for a favorable prognosis. Lack of therapy leads to irreversible atrophic changes in the organ. Prevention consists of annual examinations, tests, timely treatment of concomitant diseases and adherence to the principles of proper nutrition.
Renal calicoectasia is a disease that occurs due to stagnation of urine in the renal pelvis and calyces and is characterized by a latent course in the initial stages. It can be congenital or acquired, and can affect the left, right and both kidneys. The pathology is dangerous due to its complications, but can be easily treated in the early stages of development.
Consequences
In the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, caliectasis can provoke very serious complications. One of the dangerous conditions is considered to be a bacterial infection, which can cause death. In addition, with this pathology, the kidney loses its functions, shrinks, and its parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue.
With calicoectasia, stagnation of urine occurs, increasing the risk of stone formation and the development of urolithiasis. Hydronephrosis or renal failure can also be a consequence of the disease. In order to reduce the risk of complications, it is important to diagnose the disease in time and take all necessary measures to treat it.
Questions for the doctor
I am 32 weeks pregnant and have been diagnosed with kidney disease. How dangerous is caliectasis of the kidney in a pregnant woman for a woman and her unborn child? Anastasia U. 30 years old, Belgorod.
Hello, Anastasia. Calicoectasia is not uncommon in pregnant women, when the kidneys are under increased stress. If detected in time, the disease is not dangerous if treated correctly. Ignoring symptoms can lead to the development of urolithiasis in a woman, complications during childbirth and problems in the postpartum period.
What folk remedies can be used to treat caliectasis of the right kidney? Victor S. 47 years old, Volzhsky.
Hello, Victor. Not only medications, but also traditional medicine recipes will help alleviate the condition. It is useful to eat watermelons, melons, and drink non-concentrated juices from red currants and raspberries.
Traditional healers advised eating fresh, boiled, or baked pumpkin. Collections are available in large quantities in pharmacies. Conveniently, each pharmacy package contains detailed instructions for making decoctions and infusions.