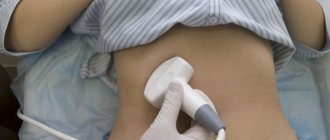
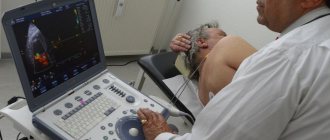
TRUS (transrectal ultrasound) is an ultrasound examination of the prostate through the rectum. It is also possible to examine the prostate through the abdominal wall, but this method is significantly inferior due to its low information content, which is why TRUS is considered the standard for high-quality urological examination.
What is the prostate gland and why is it examined even if there are no symptoms of disease?
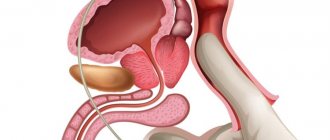
The prostate gland is a small, glandular and fibromuscular organ that covers the initial part of the male urethra. The secretion of the prostate gland is responsible for liquefying the ejaculate, activating the movement of sperm, and having an antimicrobial, buffering and enzymatic effect.
It is this organ that is most susceptible to pathological processes, which is associated with its close location to the urinary tract - the main channel through which pathogens of sexual diseases enter. Another reason for violations is the dependence of the activity of this organ on the regularity and quality of a man’s sexual life, and on his age.
Unfortunately, problems with the prostate do not manifest themselves at first; noticeable symptoms arise only when the process has progressed far in its development. Therefore, andrologists insist on annual preventive examinations of the prostate gland. A man should undergo regular ultrasound examinations starting at age 40. At this age, prostate pathologies appear in every third man, and after 50 years - in every second.
When is a prostate ultrasound prescribed?
An ultrasound may be prescribed if, during a rectal (digital) examination, the doctor finds that the prostate is hardened or enlarged. The study is necessary if there are signs of kidney failure: renal colic, dryness and discoloration of the skin, weakness and weight loss due to frequent urination, nausea and vomiting.
The doctor prescribes an ultrasound if a man has complaints:
- the appearance of blood in urine or semen;
- difficulty, pain when urinating, frequent visits to the toilet, feeling of incomplete emptying, increased frequency of urination at night;
- pain and discomfort in the scrotum, perineum, bladder or anus;
- strange discharge from the urethra;
- problems in the sexual sphere.
An ultrasound is prescribed if the doctor suspects that a man may develop cancer of the gland. The procedure is performed before and after prostate surgery. At the age of over 40-50 years (depending on medical history), doctors recommend including such an ultrasound in the annual preventive examination (screening).
When is TRUS prescribed without fail?
TRUS is prescribed by a urologist, andrologist or oncologist in the following cases:
- if cancer is suspected (after a digital rectal examination or transabdominal examination);
- in case of deviations in the results of blood or urine tests;
- for the purpose of clarification and monitoring during cryotherapy, brachytherapy, ultrasound ablation, drainage of abscesses, prostate cysts or cellular spaces of the pelvis;
- to monitor the extent of cancer during treatment or before other interventions. If a relapse is suspected after treatment;
- for male infertility , erectile dysfunction;
- for pain in the pelvis;
- any type of prostatitis.
The study is not prescribed in cases of exacerbation of hemorrhoids and in inflammatory processes of the rectum until the inflammation is relieved.
Symptoms and diseases for which TRUS is used
Content:
- Symptoms and diseases for which TRUS is used
- The essence of the proposed study
- Preparation for TRUS
- Conducting research
Transrectal ultrasound is one of the most accurate means for identifying or treating severe diseases associated with male sexual health. It is with the help of such an ultrasound that doctors are able to confirm or refute the suspicion of a man’s infertility, which is the most common reason for which patients come to see such specialists. At the same time, experts suggest that only a fraction of truly sick patients reach the doctor’s office, since the majority of men are embarrassed to seek help in such delicate cases or believe that they can turn a blind eye to this problem, which is a big mistake. Also, the basis for performing TRUS is chronic or acute bacterial prostatitis, all kinds of cysts, hyperplasia, stones, prostate adenoma. Any neoplasms in the prostate gland are the reason why a specialist will refer his patient for a transrectal ultrasound examination, as well as various pathological processes in the bladder, erectile dysfunction or varicose veins in the pelvic area, and all kinds of vascular pathologies.
Among the main contraindications to transrectal examination are hemorrhoids, surgical interventions in the rectum or anus, resection of the rectum or its fissures. However, in cases of vital pathologies, TRUS can be performed even in the presence of such contraindications, and before diagnosis the patient is specially prepared for the procedure. In addition to the above limitations, the study has no obstacles, since no type of harmful radiation is used in diagnostics.
The main symptoms in patients, which necessarily require consultation with specialists and, possibly, TRUS, are:
- disruptions in erectile function;
- the presence of various types of seals located in the rectal area;
- frequent and painful urination;
- soreness of the perineum and lower abdomen, which may indicate either prostatitis or problems in the bladder;
- patient's infertility.
What does TRUS show?
TRUS is a highly effective method that allows you to study:
- prostate gland (shape, structure) . A complete description of the contours is possible, which in an unchanged state should be smooth and clearly displayed;
- size, volume of the prostate . Normal length is 25-40 millimeters, width and thickness are 23-43 millimeters. Volume – from 200 to 280 mm³. Exceeding these parameters is a pathology;
- seminal tubercle , which is located in the structure of the prostate, has a triangular shape and a size of no more than 3 millimeters.
Also, at the same time, the doctor examines nearby organs: the rectum, bladder and vas deferens.
Clinical examination 2021
Preparation for TRUS (transrectal ultrasound, i.e. ultrasound examination of the prostate through the rectum)
In order to successfully undergo TRUS, it is necessary to do a cleansing enema 1-1.5 hours before the examination and come to the examination with an empty bladder.
To perform a cleansing enema, the so-called Esmarch mug is used (patients often call it a “hot water bottle” because of its external similarity). At the bottom of the mug there is a nipple onto which a thick-walled rubber tube is placed. The length of the tube is about 1.5 m, the diameter is 1 cm. The tube ends with a removable tip (glass or plastic) 8-10 cm long. The tip must be intact, with smooth edges.
It is preferable to use plastic tips, since a glass tip with a chipped edge can seriously injure the intestine. Next to the tip on the tube there is a tap that regulates the flow of fluid into the intestines. If there is no tap, it can be replaced with a clothespin, clamp, etc.
Contraindications for bowel cleansing with enemas are:
• abdominal pain of unknown nature,
• acute inflammatory diseases in the anus,
• bleeding from the rectum,
• hemorrhoids in the acute stage,
• rectal tumors,
• stomach and intestinal bleeding.
The enema is administered in a lying position on the left side with legs bent and pulled up to the stomach. It is advisable to prepare a basin and oilcloth (towel) in case you cannot hold water.
1-1.5 liters of warm (37-38 C) water is poured into Esmarch's mug, after which it rises up to a height of 1-1.5 meters. The enema can be held in a raised state by one of your relatives, or, if you are doing the procedure without assistants, you can hang it up (for this, as a rule, there is a special hole in the enema).
After this, the tip is lowered down into the basin, the tap is opened (if there is no tap, it can be replaced with a clothespin), air and a small amount of water are released, after which the tap is closed.
The tip is lubricated with Vaseline and, spreading the buttocks, is inserted into the anus with light rotational movements. The first 3-4 cm of the tip is inserted towards the navel, then another 5-8 cm parallel to the tailbone.
If there are obstacles and the tube rests on the intestinal wall or hard feces, the tube is removed 1-2 cm and the tap is opened. Water is pressurized into the large intestine. Almost immediately there is a feeling of “fullness” in the intestines and an urge to stool.
At these moments, reduce the flow rate of liquid from the mug by closing the tap on the tube or squeezing it. Soft circular stroking of the abdomen helps reduce discomfort.
After removing the tip, it is advisable to lie down in the same position for a while, and then you can go to the toilet. With proper preparation, the water should come out without any admixture of feces. After use, wash the tip with soap under running warm water and boil.
Preparation for ultrasound of the abdominal organs
For a successful examination, preliminary preparation is carried out so that the air in the intestinal loops does not interfere with the examination.
· 2-3 days before the examination, it is recommended to switch to a slag-free diet - exclude from the diet foods that increase gas formation in the intestines (raw vegetables rich in plant fiber, whole milk, brown bread, legumes, carbonated drinks, as well as high-calorie confectionery - cakes, cakes);
· For patients with problems with the gastrointestinal tract (constipation), it is advisable during this period of time (2-3 days before the examination) to take enzyme preparations and enterosorbents (for example, festal, mezim-forte, activated carbon or espumizan, 1 tablet 3 times a day ), which will help reduce the manifestations of flatulence;
· Ultrasound of the abdominal organs must be performed on an empty stomach; if the study cannot be performed in the morning, a light breakfast is allowed, in which case the study is carried out no earlier than 6-8 hours after eating.
· If you are taking medications, notify the ultrasound doctor about this;
· The study cannot be carried out immediately after gastro- and colonoscopy, as well as R-studies of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is advisable to bring the results of previous ultrasound examinations, if any, to the ultrasound examination. This will help the doctor assess the dynamics of changes.
Preparation for ultrasound of the pelvic organs in women (uterus, appendages):
· The examination is carried out with a full bladder, so it is necessary not to urinate for 3-4 hours before the examination and drink 1 liter of non-carbonated liquid 1 hour before the procedure.
· No special preparation is required for transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS). If the patient has problems with the gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to perform a cleansing enema the night before.
Preparation for ultrasound of the bladder and prostate in men:
· Transabdominal examination (TAUS) is performed with a full bladder, so it is necessary not to urinate for 3-4 hours before the examination and drink 1 liter of still liquid 1 hour before the procedure.
· Before transrectal examination of the prostate (TRUS), it is necessary to do a cleansing enema. (technique described earlier)
Preparation for ultrasound of the mammary glands:
· Examination of the mammary glands is preferably carried out in the first 7-10 days of the menstrual cycle (phase 1 of the cycle).
Ultrasound of the thyroid gland , lunar glands, lymph nodes, soft tissues, joints and ultrasound of the kidneys - no special preparation is required.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
Method number 1. Preparation for colonoscopy with the drug "Fortrans" (France)
The drug "Fortrans" is intended for preparing the gastrointestinal tract for diagnostic studies (including colonoscopy and irrigoscopy) as well as for surgical interventions on the intestines.
The required degree of cleansing of the large intestine is achieved:
- no cleansing enemas
- without additional laxative intake
- without long-term adherence to a slag-free diet
- without outside help
- no abdominal pain or excessive gas formation
The drug solution has a fruity taste. This type of preparation is ideal for patients with diseases of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
The action of the drug is based on the combination of a high molecular weight polymer with an isotonic solution of electrolytes, which prevent the absorption of water from the stomach and intestines. The solution promotes accelerated bowel emptying. The presence in the solution of electrolytes corresponding to the osmotic pressure of physiological solution replenishes the intestinal secretion of potassium, sodium, chlorine bicarbonate, and therefore there are no changes in the composition of body fluids.
There are two possible types of preparation with Fortrans:
A. One-stage preparation with Fortrans.
The day before (the day before the test), exclude vegetables, fruits, potatoes, berries, mushrooms, and greens from your diet.
On the day of colonoscopy, you can only drink sweet tea and boiled water.
On the day of colonoscopy, depending on your weight (up to 50 kg - 2 sachets, 50–80 kg - 3 sachets, over 80 kg - 4 sachets), the drug is diluted in water boiled at room temperature at the rate of 1 sachet per 1 liter of water, the required amount of solution Drink on the day of colonoscopy from 5-6 to 10 am in fractional portions (a glass every 15-20 minutes). The solution can be washed down with boiled water. The stool begins to pass 1.0-1.5 hours after starting to take the drug and stops 2-3 hours after taking the last dose of the drug.
On the day of the test, before the colonoscopy, you can drink a cup of sweet tea.
Colonoscopy may be performed no earlier than 4 hours after the last dose of the drug.
!!! During the days of preparation for a colonoscopy, you can take the medications you need, with the exception of iron supplements and activated carbon.
Method number 2. Scheme of preparation for endoscopic examination
You should:
On the eve of the study (24 hours before starting to take the laxative), follow a special “cleansing” toxin-free diet. You should not eat meat products, poultry, fish, cereals and cereals, bread and pasta, vegetables and fruits in any form, nuts, etc. throughout the day. It is allowed to consume only clear liquids during the day - mineral water, tea without sugar, clear clarified juices without pulp, clear broth.
Buy Duphalac 200 ml at the pharmacy (sold without a prescription) and at 15:00 dilute 100 ml of the drug in two liters of water or other liquid, gradually as possible, drink this first portion over the next 4 hours. You should have mild, painless diarrhea.
At 19:00 you should gradually drink a second portion of Duphalac - 100 ml, diluted in 2 liters of water or other liquid. You should continue to have mild, painless diarrhea.
The washing liquid coming out of you should gradually become cleaner and have no additional impurities. Remember, the cleaner the rinsing waters are, the easier and better the examination of your intestines will be. The amount of liquid you drink should not be less than 4 liters.
On the day of the study, you should not consume food or any liquids until the end of the study (do not eat or drink anything).
Show up at the appointed time to the endoscopy room. Bring a clean sheet, T-shirt and socks.
Method No. 3. Scheme of preparation for endoscopic examination with Fortrans and cleansing enemas
(if fortrans is not well tolerated)
You should:
On the eve of the study (the day before the appointed date), follow a special “cleansing” slag-free diet. You should not eat meat products, poultry, fish, cereals and cereals, bread and pasta, vegetables and fruits in any form, nuts, etc. throughout the day. It is allowed to consume only clear liquids during the day - mineral water, tea without sugar, clear clarified juices without pulp, clear broth.
Buy the drug Fortrans (2 sachets) at the pharmacy (sold without a prescription) and at 15:00 dilute 2 sachets of the drug in two liters of water. Take 1 glass of the solution over 30 minutes in separate sips. It is advisable to drink 0.5 liters of solution within 1 hour (drink 2 liters of solution within 4 hours). You should have mild, painless diarrhea.
At approximately 20.00 and 21.30, take two cleansing enemas (with a capacity of approximately 1.5 liters).
On the morning of the examination day (at approximately 5.30 and 7.00, take two cleansing enemas (with a capacity of approximately 1.5 liters).
The washing liquid coming out of you should gradually become cleaner and have no additional impurities. Remember, the cleaner the rinsing waters are, the easier and better the examination of your intestines will be. On the day of the study, you should not eat food until the end of the study.
Show up at the appointed time to the endoscopy room. Bring a clean sheet, T-shirt and socks.
Method number 4. Traditional way
This technique uses cleansing enemas in combination with laxatives.
For 3 days preceding the study, the patient must follow a slag-free diet (ideally, the “astronaut diet” with the complete exclusion of dietary fiber). You cannot eat black bread, vegetables and fruits, and nuts. On the day before a colonoscopy, it is recommended to completely avoid eating solid food.
In the middle of the day preceding the day of colonoscopy, laxatives are prescribed (40–60 ml of castor oil once; less commonly, magnesium sulfate 200–250 ml is prescribed).
The evening before and in the morning on the day of endoscopy, two cleansing enemas are performed, on average in the amount of 1.5 - 2.5 liters each.
The end result should be the appearance of clean wash water.
Report to the endoscopy department at the appointed time. Bring a clean sheet, T-shirt and socks.
Preparing patients for x-ray examination of the colon
On the eve of the examination at 10 o'clock - take 2 Bisacodyl tablets, at 12 o'clock - drink, after dissolving one packet of magnesium sulfate (25 grams dissolved in 100 ml of water). In the evening at 20 o'clock, light a candle with Bisacodyl. On the morning of the examination day (at 6:30 a.m.) put a suppository with Bisacodyl (or replace the preparation with Forbrance according to the same scheme).
Meals on the eve of the examination: for lunch only the first course (chicken broth, chicken meat and white bread). Dinner - broth, jelly, grape or apple (clarified) juice. In addition, from 12 to 24 hours, every 2 hours you need to drink 1 glass (200 ml.) of water (that is, at 12-14-16-18-20-22-24 hours, which in total is about 1.5 liters) . In case of increased gas formation - activated carbon, 2 tablets 4-5 times. In the morning - light breakfast (a glass of sweet tea with a sandwich).
Preparation for x-ray examination of the kidneys (excretory urography)
On the eve of the examination, at 10 o'clock - take 2 tablets of Bisacodyl, at 12 o'clock - drink, after dissolving one packet of magnesium sulfate (25 grams dissolved in 100 ml of water) or Glauber's salt (30 grams per 100 ml of water). In the evening at 20 o'clock, put a candle with Bisacodyl (that is, insert it into the anus). On the morning of the examination day (at 6:30 a.m.), place a suppository with Bisacodyl (that is, insert into the anus).
Meals on the eve of the examination: for lunch only the first course (chicken broth, chicken meat and white bread). Dinner - broth, jelly, grape or apple (clarified) juice. In addition, from 12 to 24 hours, every 2 hours you need to drink 1 glass (200 ml.) of water (that is, at 12-14-16-18-20-22-24 hours, which in total is about 1.5 liters) . For increased gas formation - activated carbon, 2 tablets 4-5 times (or Espumisan 2 capsules in the evening). In the morning - light breakfast (a glass of sweet tea with a sandwich).
Preparation for irrigoscopy with Fleet Phospho-soda
Your doctor should know if you are taking anticoagulants or insulin. If you are constantly taking iron supplements, they should be discontinued 4 days before the test. If you are taking anticoagulants, then before undergoing FCS it is necessary to perform a blood test for indicators of the coagulation system. Other medications can be taken until the study.
Three days before the study, a slag-free diet is recommended; fruits and vegetables in any form are completely excluded: cabbage, legumes (beans, peas, beans), potatoes, radishes, tomatoes, onions, etc., milk, jam, grain bread, berries, etc. including in yoghurts and baked goods. You can eat: lean meat, preferably boiled (including poultry), lean fish (carp, pike perch, river trout), eggs no more than 2-3 per day, cheese, cottage cheese, juices without pulp, tea, kefir .
24 hours before the procedure, you should consume only liquids (broth, tea, water, juice without pulp). IT IS IMPOSSIBLE TO EAT! If you suffer from constipation (stool once every three days or less), then a liquid diet should be 48 hours before the test.
If the procedure is scheduled for the first half of the day (before 14.00), then on the day before the study:
At 7 a.m., instead of breakfast, drink at least 1 glass of light liquid (water or soups freed from solid particles, fruit juices without pulp, tea and coffee, clear carbonated and non-carbonated soft drinks, etc.).
The first dose of the drug should be taken immediately after breakfast. The contents of 1 bottle (45 ml) should be dissolved in half a glass (120 ml) of cold water. Drink the prepared solution and wash it down with one (or more) glass (240 ml) of cold water.
At 1 p.m., instead of lunch, you should drink at least 3 glasses (720 ml) of light liquid.
At 19:00 instead of dinner, drink at least 1 glass of light liquid.
The second dose of the drug should be taken immediately after dinner. The contents of the second bottle (45 ml) should be dissolved in half a glass (120 ml) of cold water. Drink the prepared solution and wash it down with one (or more) glass (240 ml) of cold water.
If desired, you can drink more liquid. Light liquids can be drunk until midnight.
If the procedure is scheduled for the second half of the day (after 14.00), then on the day before the test day:
At 13:00 during lunch you can have a light snack, for example, eat a piece (100 grams) of poultry or fish. After lunch, you should not eat any solid food!
At 19:00, instead of dinner, you should drink 1 glass of light liquid. If desired, you can drink more liquid.
The first dose of the drug should be taken immediately after dinner. The contents of one bottle (45 ml) should be dissolved in half a glass (120 ml) of cold water. Drink the prepared solution and wash it down with one (or more) glass (240 ml) of cold water. If desired, you can drink more liquid. During the evening you need to drink at least 3 glasses of light liquid.
And on the day of the procedure:
At 7 a.m., instead of breakfast, you should drink 1 glass of light liquid. If desired, you can drink more liquid.
The second dose of the drug should be taken immediately after breakfast. The contents of one bottle (45 ml) should be dissolved in half a glass (120 ml) of cold water. Drink the prepared solution and wash it down with one (or more) glass (240 ml) of cold water.
Light liquids can be consumed up to 8 hours. This drug usually causes bowel movements within half an hour to 6 hours. The drug should not be used to treat constipation. The drug should be used with caution in elderly, debilitated patients with reduced renal function, heart disease, colostomy, or on a low-salt diet, since there is a possibility of developing hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, dehydration due to hypernatremia, and acidosis. In such cases, please consult your doctor about how you should prepare for the procedure. The drug does not affect the ability to drive vehicles or operate machinery.
Preparing for the examination
After being referred for an examination, the doctor tells the patient about the procedure, benefits and possible complications.
Preparing for TRUS involves having a bowel movement. On the day of the examination or the day before, you must use a cleansing enema. It is also recommended to exclude foods that cause increased gas formation. The day before the procedure, avoid carbonated drinks, dairy products, cabbage, apples, pears and grapes. You can create a menu of cereals, lean meat or fish, and vegetables. Don't forget about personal hygiene.
As for the enema, it is not at all necessary to use “grandmother’s methods” and introduce a large amount of water into the intestines. Pharmacies sell special rectal suppositories called microenemas. Such microenemas, provided you follow a diet, are enough to completely prepare the intestines.
Another important point is psychological preparation. All exciting moments should be discussed with a doctor, because fear can cause additional spasm of the anal sphincter. This will interfere with the examination and time will be wasted.
Before the study, you need to relax and take a deep breath while inserting the sensor. If there are indications (increased suspiciousness, pain in the prostate area), the doctor can use a gel with lidocaine - this facilitates the insertion of the sensor and relieves pain.
Sign up for a prostate ultrasound
Clinic specialists Dr. AkNer offer their assistance in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate diseases. The doctor will be able to prescribe the necessary examinations for you and will tell you exactly what is better – TRUS or MRI of the prostate. Your case may require a different diagnosis. You can make an appointment with a urologist or, if you have a referral, go straight to an ultrasound. With our modern equipment, you will get clear results that will help you understand the cause of the problem. Still have questions? Ask them in the form on the website or by phone +7 (495) 098-03-03.
Urologist, andrologist Akopyan Nerses Grigorievich.
Back to list of articles
How is TRUS of the prostate performed?
Before the procedure, you must drink 3 glasses of water (no later than 30 minutes before the examination), and do not urinate until the examination is completed. A full bladder prevents the organ from leaving and increases the contrast of the prostate.
The patient lies on his left side, bends his legs and brings them closer to his stomach. You need to relax as much as possible and breathe deeply. The sensor is inserted while exhaling. The rectal sensor is protected with a rubber cap (or a special condom), then inserted to a depth of 5-6 cm into the rectum.
The procedure takes several minutes. The doctor carefully examines the organs and makes a conclusion. However, if the purpose of the study is the bladder, then TRUS takes place in two stages:
- examination with a full bladder;
- examination of the pelvic organs after emptying the bladder, measurement of urine residues.
It is worth noting that the amount of liquid you need to drink before the study increases to 1.5 liters.
If during the examination the doctor identifies suspicious areas, then a biopsy is performed using a special needle - taking a piece of tissue to check for malignancy.
In men over 40 years of age, the risk of pathologies of the genitourinary system increases. Therefore, for the purpose of prevention, in addition to an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, you need to regularly take blood tests for biochemistry and tumor markers. These tests detect inflammation and early oncological processes that are not visible on TRUS.
The essence of the proposed study
The transrectal method of ultrasound is based on the same principle as classical ultrasound - a sensor inserted intraintestinal with ultrasonic waves allows you to create echo waves of various lengths, which indicates all sorts of pathologies of the body. From the calculated difference between the reflection length and the length of the ultrasonic wave itself, one can infer the shape, structure or density of the human organ in question. The received data is immediately reflected on the monitor screen of a computer connected to the ultrasound machine, which allows all emerging signals to be assessed in real time.
Transrectal ultrasound also allows for a biopsy, that is, taking affected areas of tissue of various organs for analysis, if such a need arises during the procedure. In this case, a needle is inserted into the area of the prostate gland, with the help of which microscopic samples of the necessary biomaterial are removed. According to doctors, it is impossible to damage organs during transrectal ultrasound, so in this regard the procedure is absolutely safe.
Price
Prostate ultrasound is performed free of charge upon referral from the attending physician at a local clinic. To avoid waiting in line, you can undergo the examination for a fee. The cost of the procedure is low.
| City | Cost, rubles |
| Moscow | 400-1000 |
| Saint Petersburg | 500-1100 |
| Ekaterinburg | 300-800 |
| Novosibirsk | 400-900 |
| average price | 400-950 |
Prostate ultrasound is used to diagnose acute diseases and monitor chronic pathologies. The procedure is painless, has no contraindications, and even minor deviations are detected.
How to do an ultrasound of the bladder
The examination is carried out through the anterior abdominal wall or transrectally. In the first case, a transabdominal sensor is used. The patient is placed on the couch on a clean diaper. A water-based gel is applied to the sensor, which reduces the layer of air between it and the body. The doctor presses the sensor slightly to clearly visualize the structures of the organ. It defines:
- clarity and thickness of walls;
- their smoothness, the presence of outgrowths or uneven contours;
- pathological formations inside the bladder, suspension, calcifications, which may turn out to be stones;
- symmetry of the organ;
- urine volume and residual urine.
An ultrasound of the urinary organs can show the formation of fistulas.
After completing the study, the doctor transfers its results to the conclusion form. The findings are not a diagnosis. Based on these data, as well as other diagnostic methods and the clinical picture, the attending physician will form an idea of the disease and prescribe treatment.
Norm and deviations
Normally, the prostate gland has a uniform or heterogeneous structure with uneven contours. The weight of the organ does not exceed 18 g. Dimensions: longitudinal corresponds to 4 cm, transverse ranges from 2.7 mm to 4.1 cm, anteroposterior 2.5 cm.
The urinary reservoir is normally ovoid in shape with a volume of 350 to 750 ml, with an echo-negative structure. The contours of the organ are smooth, the walls are of the same thickness.
The presence of pathological processes in the genitourinary system is indicated by:
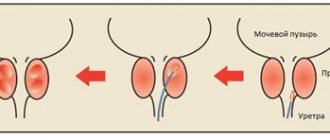
- changes in organ volumes are a sign of benign neoplasms;
- increased echogenicity is a symptom of oncology, chronic prostatitis or cystitis, as well as urolithiasis;
- decreased echogenicity indicates inflammatory processes and cystic formations;
- enlarged lymph nodes and blurred contours of the organ indicate neoplasms of a benign and malignant nature;
- dark moving areas with low ability to absorb waves - stones, blood clots or pus.