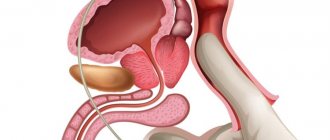
Who is at risk?
Today, prostate cancer ranks among the leading causes of mortality from malignant diseases.
All men are at risk, especially those who have crossed the threshold of maturity, that is, after 40-45 years.
The older a man is, the more likely he is to develop prostate cancer.
Those men whose close relatives have been diagnosed with this disease are especially at risk.
Men who abuse alcohol, suffer from chronic diseases, and do not undergo regular examinations raise the risk level.
Kinds
Based on histological characteristics, prostate cancer is divided into the following types:
- adenocarcinoma, which, in turn, is divided into large and small acinar, solid and cribriform forms;
- squamous;
- transitional cell;
- undifferentiated cancer.
Adenocarcinoma occurs in approximately 90-95% of clinical cases of the disease, other types of tumors occur much less frequently.
In addition, to classify prostate cancer, a special indicator is used that shows the level of malignancy and is called the Gleason score. In accordance with it, tumors are distinguished:
- moderate malignancy – Gleason score up to 6 points;
- average – with an indicator of 7 points;
- high – with an indicator of 8 to 10 points.
What might be a concern?
- frequent urge to urinate, especially at night;
- weak intermittent stream;
- pain, burning sensation during urination;
- blood in urine or semen;
- urinary retention, which is associated with compression of the urethra by a tumor;
- pain in the pelvic area, etc.
Painful manifestations turn a man’s life into a real test. Impaired potency, nervous exhaustion, weakness, chronic fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss - these symptoms can accompany an adenoma, and especially prostate cancer.
Only regular examinations will help to recognize the disease in time and increase the patient’s chances of a long and productive life.
Questions and answers
How long do you live with prostate cancer?
About 80% of men treated for prostate cancer live more than 10 years. In the absence of treatment, life expectancy depends on the stage of the disease and the aggressiveness of the tumor, and death becomes inevitable within several years.
What does prostate cancer look like?
There are no external signs of a tumor, so it is impossible to independently detect the presence of cancer pathology. Initial symptoms resemble those of prostatitis or prostate adenoma. For diagnosis, you need to contact a urologist or oncologist.
Is there a cure for prostate cancer?
Currently, malignant prostate tumors can be successfully cured in most cases if they are detected in a timely manner. If any signs of deterioration in urinary function appear, you should visit a urologist as soon as possible and undergo a quality examination.
Attention! You can cure this disease for free and receive medical care at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of Academician Roitberg) under the State Guarantees program of Compulsory Medical Insurance (Compulsory Medical Insurance) and High-Tech Medical Care. To find out more, please call +7(495) 775-73-60, or on the VMP page for compulsory medical insurance
Can an adenoma turn into cancer?
This is impossible! Adenoma and prostate cancer usually affect different parts of the prostate gland.
But at the same time, prostate cancer can develop both asymptomatically and against the background of the development of adenoma, that is, with the same symptoms.
Thus, both cancer and prostate adenoma can exist in the body at the same time .
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis based on the examination.
But for this you need to regularly undergo preventive examinations by a urologist and undergo a set of special laboratory tests.
This applies to both men over 40 years of age and younger ones, even in the absence of symptoms of the disease.
In particular, to exclude prostate cancer, regular prostate specific antigen (PSA) tests are performed.
Causes and risk factors
The only cause of prostate cancer is a malignant modification of cells that lose their original function and direct the generated energy to uncontrolled division. How the biological mechanism that triggers this process works has not yet been established. However, the main factors that increase the likelihood of developing a tumor are well known:
- age over 65 years – up to 75% of patients belong to this age group;
- hormonal imbalances associated with age-related changes in the body;
- unbalanced diet, excessively saturated with animal fats;
- inherited predisposition to the disease;
- the presence of pathologies of the prostate gland - adenoma, prostatitis, hyperplasia, adenosis;
- prolonged exposure to sunlight or exposure to artificial ultraviolet radiation;
- work in hazardous industries with prolonged exposure to carcinogenic compounds.
Win a victory!
The urologists-andrologists at ON CLINIC have the most modern methods of laboratory and instrumental diagnosis of prostate diseases.
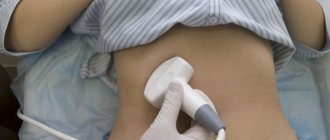
Diagnosis of the prostate gland includes: TRUS (transrectal ultrasound), tests for tumor markers, in particular, determination of PSA levels.
According to indications, the following are carried out: targeted biopsy followed by histological examination, diagnosis of distant and immediate metastases (ultrasound, X-ray, CT, MRI, etc.).
The most advanced method for diagnosing male problems is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
ON CLINIC has unique MRI equipment, developed by SIEMENS, which has increased magnetic field power and a full set of high-tech MR coils.
In particular, a special MR coil is used, designed to examine space-occupying formations in men in the pelvic area .
Unique technologies make it possible to perform MRI of the whole body in a matter of seconds.
ON CLINIC provides comfortable dynamic observation of all men, including those at risk.
Dynamic observation - regular examinations, diagnosis and treatment of concomitant diseases, monitoring the activity of the tumor process.
At ON CLINIC you can take all tests in 1 visit, get results within 1 day, as well as certificates, extracts, state-issued sick leave certificates.
In the early stages, prostate cancer can be successfully treated.
The most important thing is to recognize the disease in time!
Stages
Oncologists distinguish four stages of prostate cancer.
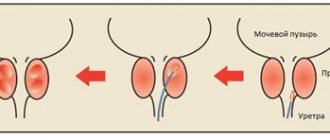
- The size of the neoplasm is very small, so it cannot be felt and is not detected by ultrasound of the gland. Signs of the disease are detected only with the help of a special prostate antigen (PSA) test.
- The tumor increases in size, but does not extend beyond the prostate. It can be detected: with a digital examination, compactions are felt, which are detected by ultrasound. There are problems with urination and painful sensations.
- Malignant tissue affects the bladder, rectum and other nearby organs. An admixture of blood appears in the urine, and severe pain is felt when urinating.
- The tumor metastasizes to other organs: lymph nodes, liver, lungs, bone tissue. The patient's condition worsens, he feels a loss of strength, and excretory processes are disrupted.
Sources
- Dowlatshahi AS., Constantian MB., Deng A., Fudem G. Defining the Histologic Support Structures of the Nasal Ala and Soft Triangle: Toward Understanding the Cause of Iatrogenic Alar Retraction. // Plast Reconstr Surg - 2021 - Vol146 - N3 - p.283e-291e; PMID:32842101
- Kaplama ME., Ak S., Yukkaldiran A. Is Rhinoplasty Surgery a Risk Factor for Low Back Pain among Otorhinolaryngologists? // Facial Plast Surg - 2021 - Vol37 - N1 - p.102-106; PMID:32838440
- Schall JL., Rogers TL., Deschamps-Braly JC. Reprint of: Breaking the binary: The identification of trans-women in forensic anthropology. // Forensic Sci Int - 2021 - Vol314 - NNULL - p.110356; PMID:32758678
- Dey JK., Recker CA., Olson MD., Bowen AJ., Hamilton GS. Predicting Nasal Soft Tissue Envelope Thickness for Rhinoplasty: A Model Based on Visual Examination of the Nose. // Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol - 2021 - Vol130 - N1 - p.60-66; PMID:32627568
- Rohrich RJ, Mohan R. Male Rhinoplasty: Update. // Plast Reconstr Surg - 2021 - Vol145 - N4 - p.744e-753e; PMID:32221209
- Schall JL., Rogers TL., Deschamps-Braly JC. Breaking the binary: The identification of trans-women in anthropological forensics. // Forensic Sci Int - 2021 - Vol309 - NNULL - p.110220; PMID:32200173
- Sykes JM., Dilger AE., Sinclair A. Surgical Facial Esthetics for Gender Affirmation. // Dermatol Clin - 2021 - Vol38 - N2 - p.261-268; PMID:32115136
- Borujeni LA., Pourmotabed S., Abdoli Z., Ghaderi H., Mahmoodnia L., Sedehi M., Hasanpour Dehkordi A. A Comparative Analysis of Patients' Quality of Life, Body Image and Self-confidence Before and After Aesthetic Rhinoplasty Surgery . // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2020 - Vol44 - N2 - p.483-490; PMID:31832733
- Kim HJ., Lee SJ., Lee JH., Kim SH., Suh IS., Jeong HS. Clinical Features of Skin Infection After Rhinoplasty with Only Absorbable Thread (Polydioxanone) in Oriental Traditional Medicine: A Case Series Study. // Aesthetic Plast Surg - 2021 - Vol44 - N1 - p.139-147; PMID:31797043
- Parab SR., Khan MM. Do Aesthetic Average Nasal Parameters Matter For Rhinoplasty in India? // Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg - 2021 - Vol71 - NSuppl 3 - p.2011-2018; PMID:31763285
Prostate cancer treatment
At the beginning, it should be noted that the chances of cure are quite high, reaching 90% in cases of early detection of the disease. Treatment is divided into several types: observation, surgery, radiation therapy.
Medical observation method
For patients suffering from serious concomitant diseases, a system of constant medical supervision without active treatment has been adopted. The use of this system is gradually becoming more popular, but it is only suitable in cases where the volume and nature of the tumor does not pose a danger to the patient. This is an option that requires extensive dialogue with the patient and his family members, since awareness of the disease in the absence of active treatment can create great psychological difficulties.
According to doctors from various sources in the United States, approximately a third of such patients decide to begin the process of active treatment within two to three years because they cannot withstand the stress that accompanies the method of medical supervision.
Operating method
During the operation, the prostate gland is completely removed and the bladder is directly connected to the urinary canal.
The operation itself can be performed in several ways - from abdominal surgery through the abdomen (the most popular method), through the perineal method (through the area between the scrotum and anus), to the laparoscopic method (point-invasive method).
The operation can also be performed using a robot, a system that was developed in the USA and then adopted in Europe, and has also appeared in several clinics in Israel in the last few years. In the United States, more than a third of all prostate cancer surgeries are performed this way. But despite all its advantages, this system is not very accepted in Israel, mainly due to the high cost of the equipment.
If a surgical method of treatment has been chosen, then the operating surgeon must, according to the indications and condition of the patient, select the optimal type of surgical intervention, which is expected to give the best results and maximum chances of recovery for this particular patient.
Radiation therapy method
The use of external and internal radiation exposure, the purpose of which is to simultaneously affect the tumor formation, and at the same time not damage the surrounding tissue.
External radiation exposure – is based on gradually increasing doses of radiation exposure to the prostate gland, according to a computerized treatment program and with the control of three-dimensional imaging. Medical research proves that when using modern equipment, exposure to high doses of radiation is more effective in the long term (5-10 years, and apparently even longer - research is ongoing). External radiation is performed without anesthesia, lasts about two months and requires daily visits to the radiation treatment center.
Another possibility is the use of internal radiation - brachytherapy, a technique based on radiation from the inside through a puncture, using small radioactive crystals (about the size of a grain of rice) placed directly - temporarily or permanently - into the prostate gland.
Unlike external radiation, brachytherapy uses radiation from the inside, implanting radioactive material (iodine 125) into the prostate. With this method, it is possible to use a much higher dose of radiation (twice or even more) relative to external radiation, since with this method there is no danger of irradiation of neighboring healthy tissues (skin, bladder, anus). This is a one-time procedure that requires anesthesia for about an hour (general or local). The patient is discharged from the clinic on the same day and can return to normal activities 24-48 hours after the procedure. The crystal emits radiation for several months.
Brachytherapy was “imported” to Israel about 15 years ago. To date, approximately 1,200 patients have been treated with this method, with a cure rate of 95%.
It should be noted that in some patients, but not all, hormonal treatment (with tablets and several injections three months after irradiation) has been proven to increase the chances of cure. Of course, the decision on such treatment should be made by the attending physician.
How to properly treat metastatic or advanced inoperable prostate cancer
Treatment options for advanced prostate cancer include hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
All types of treatment are prescribed mainly to stop the development of the malignant process, relieve or significantly reduce the symptoms of the disease, and also improve the patient’s quality of life. Choosing the type of treatment
Here in Israel, each patient is treated by a multidisciplinary team consisting of specialists in radiation, chemotherapy and hormonal therapy (oncologists, urologists, pathologists and radiologists). The team may also include nurses, social workers, psychologists and physiotherapists.
The decision about the most appropriate method is made based on: general health, the patient's age, the location of the tumor and the symptoms it causes, the likelihood of side effects, and the patient's medical history.
Treatment Options
When cancer spreads beyond the prostate to other parts of the body, treatment can be given to keep the disease under control for as long as possible, relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
For most patients with advanced prostate cancer, hormone therapy is recommended to lower testosterone levels through pills, injections, or orchiectomy. If hormonal therapy does not cope with the progressive disease, chemotherapy is prescribed, possibly together with radiotherapy.
Consent to treatment
Before administering any treatment, the doctor must explain to the patient its purpose. You will receive full information about the type and extent of the recommended treatment, its advantages and disadvantages, other types of treatment that can be used in this case, and all significant dangers or side effects of the treatment.
Hormone therapy for metastatic prostate cancer
Hormone therapy is the mainstay of treatment for patients with advanced prostate cancer. Treatment can reduce the volume of a malignant tumor, delay its development and alleviate symptoms.
In order to develop, prostate tumor cells need the hormone testosterone, produced by the testicles. A course of hormone therapy reduces the level and suppresses the effect of testosterone in the body.
Hormone therapy is prescribed through injections or tablets (antiandogens). Some drugs stop the production of male hormones by reducing the amount of hormone produced by the pituitary gland, others bind to proteins (receptors) found on the surface of cancer cells and block the flow of testosterone into cancer cells.
The doctor will monitor the response of the malignant tumor to hormone therapy using special diagnostic methods. If a malignant tumor develops despite treatment, the doctor changes the type and method of hormone therapy.
Despite the availability of various and varied drugs, at a certain stage the cancerous tumor stops responding to hormone therapy. This condition is called hormone-resistant prostate cancer. When hormone therapy stops working, then the doctor switches to chemotherapy.
Types of hormonal therapy for metastatic prostate cancer:
LHRH agonists - stop the production of male hormones in the testicles by reducing the level of hormones produced in the pituitary gland. This group includes the following drugs: Leuprorelin - Leuprorelin acetate (Eligard® - Ellgard®), Goserelin - Goserelin (Zoladex® - Zoladex®)*, Leuprorelin - Leuprorein (Prostap®K - Prostap®)* Triptorelin - Triptorelin (Decapeptyl® - Decapeptyl®)*, Buserelin (Suprefact®)*.
After a course of treatment with these drugs, there may be a temporary increase in testosterone levels, which can lead to an exacerbation of symptoms.
This phenomenon is called “tumor aggravation.” To prevent this, you will be asked to take anti-androgen drugs for some time.
LHRH blockers - block the transmission of information from the brain to the testicles, thereby interfering with the production of testosterone, as a result of which cancer cells begin to grow more slowly or stop growing altogether. In this way, the size of the tumor can decrease.
LHRH blockers act faster than LHRH agonists and do not worsen the tumor. A representative of this group is the drug Degarelix (Firmagon® -Firmagon®)*, which is administered by subcutaneous injection into the abdomen once a month.
Antiandrogens
Hormone therapy is based on the fact that the drug binds to proteins on the surface of cancer cells and blocks the effect of testosterone on these cells.
Antiandrogens are taken orally (in tablets), and the most common types are: Bicalutamide (Casodex®), Flutamlde (Drogenil)*, Enzalutamide (Xtandi)*. Often, a course of antiandrogens alone is prescribed as hormone therapy for metastatic prostate cancer.
They are sometimes given a week or two before the first injection of LHRH agonists to help prevent the tumor from worsening.
Second-line hormone therapy
Currently, there are new second-generation hormonal drugs that act by suppressing the production of hormones in the testicles and adrenal glands, for example, Abiraterone (Zytiga®)
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses anti-cancer (cytotoxic) drugs to kill cancer cells. For metastatic prostate cancer, chemotherapy is prescribed in an attempt to reduce the volume of the malignant tumor, bring the disease under control, relieve its symptoms, thereby maintaining a decent level of quality of life and prolonging it.
Two large studies with a large number of participants and a control group have proven that combining chemotherapy and hormone therapy from the very beginning of the latter in patients with metastatic prostate cancer can markedly and significantly increase the life expectancy of patients compared with hormone therapy alone.
Chemotherapy drugs are usually taken intravenously (by injection), most often Docetaxel _ Docetaxel (Taxotere®)* is used. Steroids (such as prednisone) are usually prescribed in parallel with chemotherapy. It has been proven that this drug prolongs the patient’s life even after the end of hormone therapy as a second line of treatment. Another drug, Cabazitaxel (Jevtana®), was tested in patients who underwent treatment
Targeted (molecular targeted) therapy
Prostate cancer may change after treatment. One such change is the occurrence of an acquired mutation in combination with a congenital one, which occurs in 15 percent of patients with metastatic prostate cancer after multiple lines of treatment. BRCA type 1 and 2 mutations are the most common, but other similar mutations exist. The discovered mutations respond well to so-called PARP inhibitors. These medications are currently undergoing clinical trials to determine their effect on the life expectancy of patients.
Other treatments
Immunotherapy can help increase life expectancy by reducing the expression of proteins responsible for correcting errors in the genetic material of tumor cells (MS/H, MS/). This type of treatment is also being studied in advanced clinical trials.
Treatment with radioactive drugs
- Radium treatment - Radium chloride [223Ra] (Xofigo® - Xofigo®)* is recognized as life-prolonging and is included in the health care basket.
- Therapy with lutetium isotope (Lu-177)-PSMA (details here )
- Radiation therapy for metastatic prostate cancer
- Radiation therapy to relieve symptoms of the disease (palliative radiation)
Isotope therapy
Cancer cells respond to isotope therapy better than healthy cells, thus receiving a higher dose of radiation. This technique is especially effective for targeting specific areas of bone affected by cancer.
The most commonly used isotopes are radium 223 or strontium 89, and more recently PSMA-lutetium is also used.
CTCs - an innovative test for patients with metastatic prostate cancer
The circulating tumor cell test (CTC) is a new test for patients with metastatic prostate cancer. The test looks for the few cancer cells that have separated from the primary tumor and are circulating in the bloodstream. Newer technologies make it possible to detect these cells using a simple blood test.
Unlike imaging studies, which provide information about the size of the tumor and new areas of metastases every few months, this test allows you to obtain a biological characteristic of the malignant tumor, learn about the state of the disease (remission or progress) and the effectiveness of the treatment prescribed to the patient already in the first week after it. started. A doctor's referral is required to undergo testing.
CtDNA
A test for detecting genetic changes (mutations) in tumor DNA fragments freely circulating in the blood. This test can identify mutations that are amenable to targeted (molecular-targeted) therapy.
Relief of symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of the disease can be relieved by treating the tumor itself. Sometimes the effects of treatment appear very quickly and after a few days you can notice an improvement. In other cases, it takes longer for the effects of treatment to begin to take effect, and it may take several weeks before the effects are fully felt. In addition to treating the disease itself, there are other ways to help relieve symptoms.
Radiation therapy to relieve symptoms of the disease (palliative radiation)
Radiation therapy may be given if the tumor has spread to other organs, such as the bones. In this case, treatment may not destroy all cancer cells and cure the disease, but it can relieve symptoms such as pain, thereby making the patient feel better.
This type of treatment is used less and less due to the possibility of using Xofigo.
Xofigo® , a drug used in the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer, relieves symptoms caused by bone metastases and is recognized as prolonging life.
RANKL inhibitors are drugs that target the RANKL protein in bone cells to reduce the rate of cancer growth in the bones and reduce the risk of fractures and bone damage. Of the drugs of this type, Denosumab (Xgeva) is used, which is prescribed for the same indications as zoledronic acid. It is more effective for the consequences of bone metastases.
How to resolve issues with organizing a trip to us for treatment
You will only need medical documents or an extract from them for this CASE, which can be prepared in Russian. You send them to our email: [email protected]
We translate them into Hebrew, leading specialists hold a consultation in absentia on them, and after a few days you receive an answer. Where is it reported about the advisability of coming (there are such advanced cases that we are powerless), what length of stay is required, the list of diagnostic and treatment measures that we offer, accommodation conditions, the cost of medical measures, accommodation, transfer and other organizational issues.
We have a special department that deals with organizational issues: meeting at the airport, transfer, ordering accommodation, accompaniment of an interpreter at all stages of treatment and diagnosis, excursion services.
We also have our own housing stock: these are fully equipped 2-3 room apartments. The apartments have everything: TV with satellite TV and Russian channels, washing machine, refrigerator, air conditioning, equipped kitchen, internet. Typically, staying in apartments is cheaper than staying in hotels.
Our patients are provided with the following free of charge:
- accompanied by an interpreter in the medical center.
- transfer place of residence - medical center - place of residence
- mobile phone and local SIM card
- translation into Russian of medical documents received in Israel
Payment methods: no prepayment required, because... Payment for the medical program is made during the implementation of the program to the center’s accounting department.
Payment methods: cash (US dollars, Euros, Israeli shekels), credit card, bank transfer.
Control after treatment (after departure)
After treatment, you leave with documents that are translated into any of the languages you choose. But we are not saying goodbye to you - we continue to monitor your health. To do this, we maintain contact with our specialists, with whom you can contact on any issue regarding your recovery and receive the necessary recommendations.