Sometimes, when examining the organs of the urinary system, the patient reveals a deformation of the kidney. He is diagnosed with humpback kidney and tries to find out what it is.
This pathology can have several development options. A kidney anomaly can be a congenital feature of a person and not affect his life, or acquired.
In the latter case, the development of concomitant pathological processes, which are characterized by a clear clinical picture, is possible.
The choice of therapeutic technique depends on the characteristics of the underlying pathology that caused organ dysfunction. It is important to know what a humpback kidney is and what complications arise with such a diagnosis.
General information about the disease and ICD-10 code
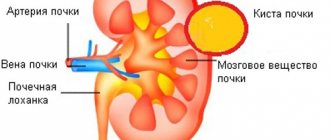
Humpbacked kidney is a condition of the kidneys in which deformation processes begin in the tissues of the organ. In most cases, it is congenital; acquired changes are less common.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition, it has code Q63.9. Congenital anomalies of the kidneys of an unspecified nature.
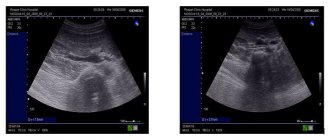
Very often, based on ultrasound results, doctors mistake this condition for a tumor on the kidney. This is due to the peculiarities of appearance: the hunchback seems to stick out from the outer edges of the organ.
Pathology has two main forms:
- congenital;
- acquired.
In the first case, the child is diagnosed with deformation processes after birth; sometimes they can develop throughout life, which is why they are acquired.
Humpback occurs on one or both sides. In an ultrasound image, it can have a variety of shapes: round, crescent-shaped, etc. At the same time, the size and position of the kidneys may also change.
Causes
As a rule, this disease begins to develop during intrauterine development of a person. Unfortunately, to this day the true reasons for this process have not been established. Among the main provoking factors, scientists identify:
- genetic failures;
- taking illegal medications during pregnancy;
- the effect of toxic substances on a woman’s body;
- ionizing radiation;
- intoxication during pregnancy, which are complications of untreated infectious and viral diseases.
Abnormal processes begin when cells divide incorrectly, resulting in many more of them. This leads to a state of tissue hyperplasia in the organs. That this disease does not in any way affect her basic functions.
The impetus for the development of pathology is several factors at once, especially if they are present at the stage of formation of all internal organs of the fetus (the period from 3 to 10 weeks of pregnancy). Sometimes it occurs as an independent anomaly, and in some cases it can cause serious complications.
The acquired form is characterized by the following reasons:
- neoplasms in the spleen, which put great pressure on the kidneys;
- inflammatory processes;
- neoplasms;
- tuberculosis of the urinary system.
Causes of the anomaly
The formation of basic systems occurs in the early period of intrauterine development of the fetus. When malfunctions occur in the functioning of the mother's body, the fetal organs may develop incorrectly.
Deviations relate to various aspects: the anatomical structure of the organ, its structure, tissues. Some anomalies can affect the development of the embryo and cause irreversible consequences of various types.
Other changes in the structure of organs are not dangerous to the health of the unborn child.
A protrusion on the kidney is not a disease of the urinary system. This is a feature of the body that is formed before a person is born.
In medical science there is no exact explanation why this congenital anomaly in the structure of the organ occurs. The reasons for the formation of a humpbacked kidney include the following circumstances:
- genetic failures;
- unfavorable environmental conditions in the area where parents live;
- influence of radiation;
- abuse of certain types of medications before and during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases accompanied by intoxication, suffered by a woman during pregnancy.
Failures occur at the cellular level, and the number of cells increases. As a result, the kidney tissue grows and a protrusion forms.
Most cases of renal protrusion are associated with a congenital anomaly. Acquired pathology is less common. Risk factors that provoke structural anomalies include:
- incorrect position of the organ (more often – its prolapse);
- kidney immobility;
- fusion of organ sections;
- improper blood circulation process;
- traumatic injury with violation of the integrity of the parenchyma.
If a person has kidney disease or a tumor of the spleen, inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, constant medical monitoring of the condition of the humpbacked kidney is necessary.
Uncomplicated cases of diagnosing abnormal organ development do not require close attention from doctors.
Manifestation of the clinical picture
Basically, the humpback kidney anomaly occurs without visible symptoms; it is diagnosed during a routine ultrasound examination. In the presence of concomitant diseases, a number of unpleasant sensations appear.
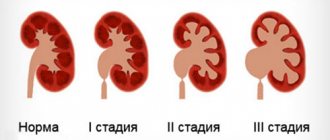
Stages of flow
So, if this pathology is accompanied by urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, cystitis or other diseases, then the symptoms will proceed accordingly. Let's look at the most common signs:
- problems with urination;
- pain in the abdomen, which may radiate to the groin;
- symptoms of the inflammatory process (temperature, intoxication, etc.);
- varicose veins in the lower extremities;
- metabolic disorders;
- problems with bowel movements (constipation, diarrhea).
The risk group includes patients with the following pathologies:
- nephroptosis;
- pinching of blood vessels in the organ;
- injuries.
If one of the unpleasant symptoms appears, it is recommended not to hesitate to consult a doctor.
Possible complications
If a humpback kidney is diagnosed, it is necessary to undergo an examination to identify possible concomitant diseases. Improper organ structure can cause:
- inflammatory processes (glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis):
- urolithiasis;
- hydronephrosis;
- cyst formation;
- disturbances in blood supply due to compression of the renal vessels.
Lack of treatment leads to the development of kidney failure, as a result of which the organ ceases to function normally, and the person’s quality of life sharply deteriorates.
Diagnostic methods
Treatment and observation are carried out by a doctor - a urologist or nephrologist. The following methods are used for diagnosis:
- Ultrasonography. In this case, the specialist studies in detail the condition of the renal parenchyma to eliminate the risk of tumor development.
- MRI, CT diagnostics help to examine the organ in more detail, its shape, size, condition of the pelvis and ureters.
- Contrast radiography (a special contrast solution is used, which makes it possible to examine damaged tissue areas in the organ).
- Urography, retrograde pyelography, arteriography are used to study the state of the circulatory system of the kidney, as well as in case of violations of its normal functioning.
- Scanning using radioisotopes.
The patient must undergo a blood and urine test for general and biochemical parameters. If, using instrumental diagnostic methods, it is not possible to establish true “humpbackedness,” then doctors resort to an extreme method - taking a biopsy. This allows you to confirm the absence of a tumor.
Methods of therapy
Depending on the degree and severity of the pathology of the humpback kidney, as well as the addition of concomitant diseases, the doctor decides on the treatment regimen. Very often it does not cause negative symptoms and does not at all interfere with a person’s exercise, going to work, etc.
If unpleasant signs appear, you should immediately contact a specialist. Either drug therapy or surgery is used.
Drug treatment
This therapy is prescribed if the patient is simultaneously diagnosed with other kidney diseases (urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, etc.). In this case, it is advisable to use:
- antibiotics, they are selected after precise identification of the causative agent of the infectious process, the course and duration of administration is prescribed individually;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- local antispasmodics (to relieve pain attacks);
- uroseptics, which help remove urine accumulated in the body;
- glucocorticosteroids and immunomodulators (used for glomerulonephritis or autoimmune inflammatory processes in the renal parenchyma);
- vitamin complexes to strengthen general immunity.
Surgery
It is used very rarely, only in cases of serious complications that threaten complete disruption of kidney function. For example, in the case of hydronephrosis, a special catheter is installed, with its help excess fluid is removed from the body.
If large mineral deposits are present, the patient undergoes laparoscopic surgery to remove them.
If the patient does not consult a doctor in time, he will develop kidney failure or persistent arterial hypertension. In this case, partial or complete nephrectomy cannot be avoided.
This operation is also prescribed if the inferior vena cava is compressed (in this case, a person’s kidney may fail due to circulatory problems). The doctor decides on the advisability of surgical intervention based on the patient’s clinical picture.
ethnoscience
Since this disease is not a serious pathology, there are no unique folk remedies that are aimed at treating it.
This therapy is used in the presence of concomitant diseases. Most often, patients use infusions or decoctions based on the following medicinal plants:
- rosehip;
- St. John's wort;
- chamomile;
- bear ears, etc.
This anomaly cannot be cured with the help of traditional medicine; in this case, only the removal of acute symptoms is possible. Often these methods provoke the development of serious complications, so you should not get carried away with self-medication.
Forecast
If a diagnosis of “humpback kidney” has been made, this is not yet a cause for concern. If the structure of the parenchyma is preserved and there are no inflammatory processes, the prognosis for the patient is absolutely favorable.
The anatomical feature of the organ does not affect human health and quality of life.
If there are concomitant diseases, the prognosis depends on their severity and the stage of the pathological process at the time of visiting a doctor. With early diagnosis, the risk of complications is reduced.
A humpbacked kidney is a feature of the organ’s condition that does not pose a threat to human health. If an inflammatory process develops in the kidney tissues and blood vessels, you must consult a doctor to prescribe treatment.
Prognosis and prevention
With the correct treatment regimen and uncomplicated pathologies, the result is positive. In other cases, everything depends on the severity of the disease and the moment the patient goes to the hospital.
For prevention, it is recommended to monitor your health during pregnancy, avoid hypothermia, injuries, exercise and lead a healthy lifestyle. An important condition is proper human nutrition. It is imperative to undergo examinations and tests on time.
Humpback kidney is a harmless diagnosis if the patient does not have concomitant pathologies. As a rule, it occurs without symptoms and is diagnosed during a routine ultrasound. In most cases it is congenital.
If this anomaly does not cause any discomfort to a person’s life, then treatment is not required. In all other cases, therapy is selected individually depending on the symptoms and course of the disease (the presence of other kidney diseases).