Causes of kidney duplication
Kidney duplication occurs most often compared to other anomalies in the number of kidneys.
This anomaly is explained by the simultaneous growth of two ureters from two ureteric shoots of the nephrogenic blastema or by the splitting of a single ureteric shoot. The first option explains to a greater extent the occurrence of ectopia of the opening of one of the ureters with complete doubling of the urethra and its splitting. Doubling can be one- or two-way. Unilateral pathology is more common. Separately, complete and incomplete doubling of the kidney are distinguished:
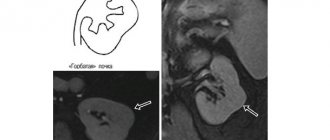
- complete doubling is characterized by the presence in each half of the kidney of the pyelocaliceal system and the ureter; the pelvis is located one above the other and is in no way combined with each other, while they are united by a connective tissue isthmus; usually the upper pyelocaliceal system is underdeveloped, and the lower one is normal; a ureter departs from each pelvis, which means that each half of this type of double kidney is anatomically and physiologically supposedly an independent organ;
- incomplete doubling of the kidney is represented by doubling of the parenchyma and vessels of the kidney, but the pyelocaliceal system remains in a single quantity; the upper part of the double bud is smaller than the lower part.
The blood supply to both halves of the kidney during doubling of the bowls and ureters is carried out by two renal arteries. Lymph circulation in each half of the doubled kidney is separate. Most often, both ureters of the double kidney open into the bladder. In some cases, splitting of the ureter occurs. If the ureter splits, it is in the upper section, where it connects with the pelvis, and in the pelvic section, as normal, there is one opening and one trunk of the ureter.
If there are two ureteral openings on one side of the bladder, the opening of the lower renal pelvis is adjacent to the opening of the ureter of the upper renal pelvis. In this case, the splitting of the ureter can cross several times along the course from the bowl to the opening of the ureter. In addition, one of the ureters may end blindly or be located outside the vesical triangle:
- in women - in the back of the urethra or in the vagina,
- in men - in the back of the urethra, seminal vesicles or vas deferens.
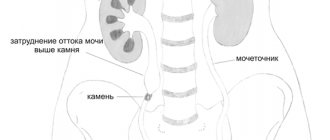
Even with preserved anatomical patency of this section of the ureters at the level of their confluence, urodynamics are changed, and the upper half of the kidney is often affected. The outflow of urine from the upper bowl is disrupted because its ureter flows into the ureter of the lower bowl at an acute angle. This impedes the continuous flow of fluid and partially contributes to the hydronephrotic transformation of the upper part of the kidney.
Clinical observations indicate a high incidence of various anomalies and diseases on the side opposite to the duplication of the renal pelvis and ureter.
The anatomical prerequisites for reflux in a kidney with a doubled pelvis and ureter or with incomplete duplication of them are lateral (lateral) or caudal displacement of the ureteral opening, a ureterocele in the terminal part of one of the ureters, asynchronous contraction of a split ureter.
Vesicoureteral reflux is most often observed in the ureter of the lower half of the kidney. The ectopic opening of the ureter is located lateral to the bladder neck. Reflux in this segment contributes to the ureterocele, which breaks the closure mechanism of the ureteral opening of the lower half of the kidney due to stretching of the bladder wall.
Along with the reverse flow of urine into the lower half of the double kidney, with ectopia of the ureteral opening into the neck of the bladder, urine reflux into its upper half is observed.
Kidney duplication is a fairly common abnormality of the urinary system. Based on the name of the disease, it is clear that one of the kidneys doubles. The parameters of such a kidney will slightly exceed the parameters of a regular kidney, and sometimes a double kidney has two lobes in its structure. A bifurcated kidney leads to inflammation. The diagnosis code for “double kidney” according to ICD-10 is Q63.0-63.1.
When a normal kidney is doubled, the final result is the lower and upper buds separated by a groove, with the upper one being smaller in size compared to the lower one. We can say that in the process of doubling one kidney, two separately functioning kidneys were formed, although they represent a single whole.
Each of the resulting kidneys has its own separate renal artery, its own ureter. The ureters are separated from each other and adjoin the bladder with separate orifices.
This anomaly occurs during the embryonic development of the embryo. The cause may be: infections, radiation, drugs, bad habits during pregnancy. Or this pathology is transmitted by heredity.
Symptoms of kidney duplication
1. One of the main symptoms of kidney duplication is an increase in the upper urinary canals.
2. Pain in the lumbar region
3. Urine becomes cloudy
4. Temperature rises
5. Weakness with bouts of vomiting
6. Headaches are common
Although, cases of asymptomatic disease are not uncommon. The anomaly of a double kidney can be detected completely by accident during an ultrasound examination.
Diagnosis of the disease.
It is possible to detect the presence of an abnormal kidney in the body using the following methods:
1. Ultrasound diagnostics;
2. Cystoscopy;
3. Excretory urography.
Preventive measures.
Since kidney division begins to form in the embryonic state of a person, the expectant mother must avoid ionizing radiation during pregnancy, stop using hormonal drugs, and lead an exclusively healthy lifestyle.
Methods of treating double kidney disease
As such, the anomaly does not require treatment, but it can provoke the occurrence of other diseases, such as urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis. Therefore, treatment of emerging diseases is prescribed. For pyelonephritis, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
The main condition of treatment is adherence to a special diet aimed at reducing or completely destroying kidney stones.
If a double kidney is detected in a child, a set of measures is taken to reduce the risk of complications.
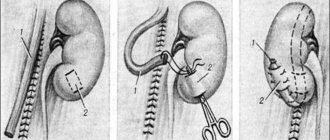
If complications occur, surgery may be required. During operations, they always try to save the kidney and remove it only in case of complete loss of its capacity. In some cases, part of the kidney is removed.
Disease code according to ICD-10
Q63.8 Other specified congenital anomalies of the kidney
You should not give in to panic when you discover such an anomaly in your body. A consultation with a doctor is necessary, but you also need to add proper nutrition, giving up bad habits, and taking medications prescribed by your doctor. In this case, it is important to prevent the doubling of the kidney from “giving impetus” to a new disease.
Next news Home Previous news
How to treat kidney duplication?
Patients with kidney duplications do not require specific treatment. Therapeutic measures are taken in the event of the development of chronic pyelonephritis and/or vesicoureteral reflux. Initially, preference is given to conservative methods, and if there is no effect from them or the process relapses, the prospect of surgical intervention is considered.
If, when one half of the kidney is damaged, it is necessary to remove the pathological focus (hydronephrosis, significant dilation of the ureters due to reflux, the presence of stones in the pelvicaliceal system), it is advisable to carry out surgical treatment immediately, regardless of the patient’s age.
In case of lack of function of the affected half of the double kidney, heminephrectomy is performed with complete excision of the refluxing ureter. This is necessary in order to prevent even a small stump, which will preserve the conditions for reflux. With age, the size of the stump will increase, which means empyema will develop and the need for repeated technically complex surgical interventions.
If the function of the affected part of the kidney is preserved, it is possible to perform uretereroanastomosis, ureteropyeloanastomosis, or antireflux ureterocystoneostomy on one or both ureters. These surgical methods are used for hydronephrosis of one half of the kidney. The timing of the operation depends on many factors. In each specific case, tactics must be individual.
Etiological factors influencing the development of the anomaly
Kidney duplication occurs due to the formation of two induction foci at once in the metanephrogenic blastema. Complete separation does not occur in the blastema, even despite the formation of two pyelocaliceal systems, therefore the integrity of the fibrous capsule of the organ is not compromised.
Each half of the bifurcated kidney has a separate blood flow. Its vessels can exit in one common column, and the division is located directly next to the sinus. Also, the vessels can exit separately from the aorta. Some of the arteries are located inside the organ and are capable of connecting one organ to another. All this is important to consider when performing organ resection surgery.
What diseases can it be associated with?
Anatomical and functional inferiority of the kidney with doubling of the calyces and ureters, urodynamic disorders create an additional background for the occurrence of a chronic inflammatory process - pyelonephritis. If a pathological process does not occur in a double kidney, it is often not accompanied by clinical manifestations.
The pathological process often develops with complete duplication of the ureter. This form of anomaly manifests itself with severe symptoms and is often combined with duplication of the urinary tract, ectopic ureteral orifices, uregerocele, vesicoureteral and ureteral reflux. When the opening is ectopic into the proximal urethra, ureteral reflux occurs during urination. The presence of a ureterocele, which leads to obstruction of the urethral neck.
In the case of bilateral duplication, congenital or acquired pathology (dysplasia, dystopia, hydronephrosis, lithiasis) is often detected.
Causes
Nephrological pathologies that arise against the background of systemic diseases are the result of complex metabolic changes. As a result, a progressive immunoinflammatory process develops in the renal tissues, accompanied by urinary syndrome, which is often associated with arterial hypertension.
The course of systemic kidney damage has several stages of development:
- asymptomatic (latent),
- pronounced clinical manifestations,
- terminal stage.
Also, the course of these pathologies is characterized by a certain phase pattern:
- proteinuria,
- development of nephrotic syndrome,
- edematous-proteinuric phase,
- development of arterial hypertension,
- pronounced uremia (terminal phase).
Frequent stress, poor environment, sedentary work, physical inactivity, unbalanced diet - the combination of these factors is a trigger for the development of secondary nephropathies. Recently, experts are faced with the fact that the percentage of kidney damage in systemic connective tissue diseases has increased significantly. In order to promptly diagnose pathology and minimize possible damage, it is very important to undergo systematic examinations by a nephrologist.
Which doctors should you contact if you have a double kidney?
- Nephrologist
- Urologist
The diagnosis of kidney duplication is established based on the results of cystoscopy, excretory urography and ultrasound. Due to hypoplasia of the parenchyma of the upper kidney, for its examination it is often necessary to administer a double dose of radiopaque contrast agent.
Excretory urography allows you to assess the functional state of each half of the double kidney, structural and anatomical changes in them. In recent years, ultrasound and computed tomography have occupied an important place in diagnosis.
As a rule, diagnosing duplication of the pelvis and ureters does not present great difficulties. With complete doubling of the ureters and placement of their openings in the bladder, cystoscopy is sufficient. If the interpretation of its results is difficult, chromocystoscopy is recommended.
In the case of ectopia of the additional opening of the ureter, the diagnosis is often made on the basis of complaints of characteristic urinary incontinence. To clarify the diagnosis, retrograde ureteropyelography is performed.
It is much more difficult to detect duplication of the renal pelvis and ureter when the ureters merge before they flow into the bladder. The diagnosis can only be made by x-ray examination. Excretory urography with delayed images allows us to draw a conclusion about the structural changes, anatomical position and functioning of each half of the kidney.
Treatment of other diseases starting with letter - y
| Acne treatment |
| Treatment of polyarteritis nodosa |
| Treatment of erythema nodosum |
| Treatment of nodular goiter |
| Treatment of ureaplasmosis |
| Treatment of ureterohydronephrosis |
| Treatment of urethritis |
The information is for educational purposes only. Do not self-medicate; For all questions regarding the definition of the disease and methods of its treatment, consult your doctor. EUROLAB is not responsible for the consequences caused by the use of information posted on the portal.