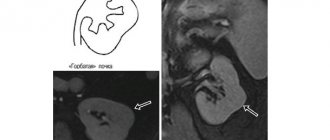
Kidney prolapse, or nephroptosis, is a pathological condition that occurs when there is abnormal mobility of this organ. In this case, the kidney moves downward from its usual location and goes beyond the natural bed. Women are much more susceptible to this pathology than men. In addition, prolapse of the right kidney is more common than displacement of the left.
The kidneys should not move more than 5 cm even with breathing and physical activity. Often, a pathological displacement is found during an ultrasound of the abdominal organs completely by accident (for example, when checking the liver and gallbladder). A person is unaware of the disease, since it provokes pain only in 10% of cases.
Fact: The disease is more common in women aged 30-55 years, as well as in young children. It develops with a sharp drop in body weight and a low percentage of adipose tissue.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a urologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,000
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Indications
Surgical treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- Decreased ability to work due to pain.
- Significant mobility of the kidney.
- Hydronephrotic transformation.
- Lack of results in the treatment of pyelonephritis.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Venous hypertension and bleeding in the kidneys.
Contraindications
Surgery is not recommended for exacerbation of chronic diseases, pregnancy, intolerance to medications and anesthesia.
If a pathology is detected, it is strictly prohibited:
- To engage in the gym.
- Consume more than a gram of protein per 1 kg of body weight.
- Attend sparring in contact martial arts.
- Eat sour, spicy, smoked, fried foods.
What is the cause of kidney prolapse?
Nephroptosis is a consequence of weakening of the supporting apparatus of the kidney.
This may occur when:
- loss of elasticity of the abdominal wall due to repeated pregnancies;
- rapid and significant reduction in body weight;
- constant physical activity associated with lifting and carrying heavy objects;
- chronic severe cough;
- injuries with damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the kidney.
- genetic predisposition.
- prolonged stay in a high vibration zone.
- lack of timely treatment of infections.
- severe injuries (impacts to the kidney area or falls on the back from a great height).
- low intra-abdominal pressure due to lack of physical activity.
What are the symptoms of kidney prolapse?
The most common manifestation of nephroptosis is pain in the hypochondrium or iliac region. The intensity of pain directly depends on the degree of prolapse of the kidney.
- Severe pain in the lower back due to the accumulation of urine and blood in the kidney tissues. Pain is more pronounced in a standing position. Lying down they go away completely.
- Blood during urination appears due to the destruction of blood vessels, as strong twisting occurs.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, thighs, or pelvic organs is caused by pressure on the nerve endings due to the displacement and enlargement of the kidney.
- Significant disruption of the gastrointestinal tract is caused by increased stimulation of the nerve endings located near the displaced kidney.
- The flu-like state and weakness are caused by an increase in the volume of toxic substances in the blood due to the fact that the kidney gradually loses its basic function.
- With further development of the disease, the pain becomes constant in an upright position of the body, but weakens when lying on the back.
- A severe degree of kidney prolapse is characterized by constant severe pain, sometimes reminiscent of renal colic. In addition, periodic nausea and vomiting may bother you, and complications may appear in the form of pyelonephritis, arterial hypertension, neurological pain radiating to the buttock or leg, etc.
Types of palpation
There are superficial and deep palpation.
Superficial palpation
Superficial palpation of the kidneys is an approximate palpation that allows one to draw preliminary conclusions. The doctor places his hands on the patient’s body and feels the body with symmetrical strokes. Thus, the doctor can:
- Determine the temperature, sensitivity, density and humidity of the skin.
- Determine the tone of the body muscles, identify their tension.
- Detect subcutaneous infiltrates and compactions.
Superficial palpation is carried out with a straightened hand; the doctor does not apply any pressure deep into the body. You can perform a superficial examination with both hands at the same time.
Deep palpation
Deep palpation is used for a detailed examination of internal organs. The doctor performing it must not only have a good understanding of the anatomical projection of the internal organs, but also have sufficient experience in performing the manipulation. Deep palpation of the kidneys and other organs is performed with one or more fingers and involves significant pressure on the body. The method is divided into the following types:
- Deep sliding. This is a methodical palpation, which involves feeling the internal organs in a certain sequence. The doctor's fingers penetrate deep inside the body and feel the organ pressed against the back wall.
- Bimanual. This is a feeling with both hands of the doctor. The optimal method for examining the kidneys. The doctor's left hand holds the kidney in a certain position, and the right hand, moving towards it, palpates. With bimanual palpation with your left hand, you can, as it were, “hand over” an organ for examination with your right hand.
- Jerky. Used to diagnose pathologies of the spleen and liver. This type is not used for renal examination.
How is kidney prolapse diagnosed?
There are 4 diagnostic methods used:
- General urine analysis.
- Ultrasonography.
- Urography.
- Palpation.
The main method for detecting nephroptosis, which is used in the multidisciplinary CELT clinic, is ultrasound examination. With its help, you can determine the presence of the disease, the stage of kidney prolapse, and also assess the impairment of its function. Additional information to clarify the diagnosis is also provided by an X-ray examination of the kidneys using a contrast agent - excretory urography.
Methods and techniques
To palpate the kidneys, use:
- The technique of deep sliding palpation is that the kidney is pressed against the posterior surface of the abdominal cavity, after which it is palpated with sliding movements.
- Bimanual method - palpating simultaneously with both hands. The doctor's left hand holds the kidney in a comfortable position, and the right hand palpates.
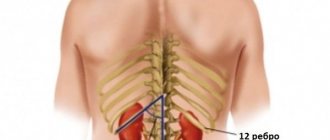
- Balloting is palpation using short pushes. The doctor places his hands on the abdominal area below the twelfth rib. The left hand pushes in the direction of the right. When the organ prolapses, the kidney is felt partially or completely.
Based on these techniques, a number of palpation techniques for examining the kidneys have been developed.
Palpation according to Obraztsov-Strazhesko
The Obraztsov-Strazhesko study is most often used by doctors. Performed using deep sliding palpation:
- The patient lies on his back with his legs extended, his arms folded loosely on his chest, and his abdominals relaxed.
- The doctor sits to the right of the patient, places his left hand under the lower back below the ribs so that the fingers are close to the spine, but do not touch it. To palpate the left kidney, the doctor moves his hand behind the spine under the right kidney.
- The right hand is placed on the stomach below the costal arches, perpendicular to them.
- The patient is relaxed, breathing deeply and evenly.
- During exhalations, the specialist plunges his fingers gradually deeper until he reaches the back wall.
- With your left hand, apply pressure on your lower back towards the fingers of your right hand.
- When the hands are as close as possible, the doctor asks the patient to inhale using the abdominal muscles, but without tension. If the kidney is located below the anatomical bed, it drops even further and is palpated with the fingers of the right hand.
- Then the doctor presses the kidney and slides his fingers down its front surface.
Palpation of the kidneys according to Obraztsov-Strazhesko is used for any pathologies of the kidneys, since it is considered highly informative.
Thus, it is possible to get an idea of the size, nature of the surface, shape, location, consistency, and pain of the kidney.
Botkin technique
Features of palpation according to S.P. Botkin is that it is performed with the patient standing or sitting. The disadvantage of this technique is that it is not informative for overweight people.
If the patient is standing, his torso leans forward slightly. From the side of palpation, the patient bends his leg. The rest of the execution technique is similar to the previous one.
The advantage of palpation of the kidneys according to Botkin is that the organs are examined under the influence of gravity. This makes it possible to identify the wandering kidney and the degree of nephroptosis.
Palpation according to Glenar
Glenard palpation is used to diagnose kidney prolapse, as well as to identify tumor formations and organ enlargement.
Technique:
- The patient is placed on his back.
- With his left hand, the doctor clasps the side of the person being examined so that the thumb goes into the hypochondrium and the rest are on the lower back.
- The right hand is placed in the hypochondrium, continuing the thumb of the left hand.
- The patient exhales. The kidney moves with its lower part to the thumb of the left hand.
- The organ is captured, and under pressure it moves up to the hypochondrium.
- Using the fingers of the right hand, sliding palpation is performed along the anterior surface of the kidney.
Palpation according to Glenard is more suitable for patients with asthenic and normal physique
Video: features of palpation of the kidneys
Our doctors
Perepechay Dmitry Leonidovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
40 years of experience
Make an appointment
Kochetov Sergey Anatolievich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
Khromov Danil Vladimirovich
Urologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
35 years of experience
Make an appointment
Mukhin Vitaly Borisovich
Urologist, Head of the Department of Urology, Candidate of Medical Sciences
34 years of experience
Make an appointment
What is the treatment for nephroptosis?
Laparoscopic nephropexy
- Cost: 100,000 - 135,000 rubles.
- Duration: 90 – 120 minutes
- Hospitalization: 3-4 days in hospital
More details
If kidney prolapse is diagnosed early, therapy includes wearing a bandage. Our specialists select it on an individual basis, which guarantees the best results.
If nephroptosis has already reached a pronounced stage and leads to serious dysfunction of the kidney or surrounding internal organs, then the question of surgery is raised. Usually it involves fixing the kidney in its natural position.
Why is palpation of the kidneys needed, what does it reveal?
Palpation of the kidneys is carried out for patients in whom the doctor suspects diseases of the urinary system. Initially, the specialist listens to the patient’s complaints, finds out the presence of kidney pathologies in the past, and then begins a palpation examination.
By palpation it is revealed:
- location of the kidneys relative to other anatomical structures;
- size;
- shape;
- consistency;
- mobility;
- soreness.
Palpation is not the main, but important diagnostic method. Guided only by it, the doctor does not make a final diagnosis, but raises the question of the following ailments:
- Nephroptosis is prolapse of the kidneys. At the first stage of the disease, the lower part of the organ can be felt, but only when inhaling. The second stage is characterized by the organ descending beyond the lower rib in a standing position. When the patient lies down, the kidney returns to its place. In the third stage, the prolapse is pronounced, so the specialist can easily palpate the diseased organ well below the ribs or in the pelvis.
The higher the degree of nephroptosis, the lower the kidney descends relative to the costal arches - Hydronephrosis is a pathological expansion of the internal renal structures, as a result of which the organ becomes overfilled with fluid. Over time, the kidney increases in size, and due to atrophy (death) of its cells, the consistency of the tissue is disrupted.
With hydronephrosis, an enlarged kidney is clearly palpable - A single kidney cyst is a formation that can be palpated when it is of impressive size and located closer to the lower pole. Feels like a bulge or thickening.
A kidney cyst can be detected to the touch, but often does not cause pain in the patient. - Malignant kidney tumors. They are able to change the consistency, shape, size of the organ, and provoke its fusion with surrounding tissues.
- Polycystic, multicystic. Multiple formations disrupt the kidney structure, shape, and size of the organ.
Multiple cysts can significantly change the size and structure of the kidney, so palpating it is not difficult - Nephritis (kidney inflammation), urolithiasis. With these pathologies, palpation provokes pain.
Soreness of the kidneys during palpation is characteristic of diseases associated with inflammation in the urinary organs
Along with palpation, percussion is used. The method involves effleurage (tapping) of the kidney area. The patient is in a standing position. The doctor places his left palm horizontally on the lower back in the projection of the kidney. Using the edge or fist of the right hand, the specialist performs tapping on the left palm. First, weak blows are applied, then stronger ones.
While performing percussion of the kidneys, the doctor monitors the correct movements of his own hands, gradually increasing the tapping
The study is carried out on both sides alternately. If the patient feels pain, this indicates a unilateral or bilateral positive tapping test. Guided by it, a specialist may suspect inflammation of the kidneys or perinephric tissue, or an exacerbation of urolithiasis. At the same time, pain when tapping may indicate the presence of other pathologies - radiculitis, osteochondrosis, myositis, pancreatitis, etc. Percussion of the kidneys is informative only in combination with characteristic complaints and relevant examinations.
Percussion is needed not only to detect pain. When you tap the kidney with your fingers, sounds arise that will tell an experienced doctor about the diseases the patient has. For example, if there is a tumor in the projection of the organ, a dull percussion sound is heard. If fluid has accumulated in the kidney, a tympanic (loud) sound is characteristic.
Tapping to evaluate percussion sound is performed with the index and middle fingers of the left hand along the middle finger of the right hand, which is located on the lower back in the projection of the kidney
Indications and contraindications for palpation examination
Palpation of the kidneys is a safe and accessible method of physical examination. Palpation is carried out:
- if the patient expresses complaints characteristic of nephrological diseases: swelling, pain in the lumbar region, difficulty urinating, persistent increase in blood pressure;
- if you have a history of kidney disease;
- for differential diagnosis with diseases of other abdominal organs - liver, pancreas, intestines, etc.
- during a routine medical examination in a clinic or upon admission to a hospital.
Palpation of the kidneys is contraindicated in cases where the area to be palpated is affected by burns, extensive wounds, purulent formations, or there are fresh postoperative sutures on the abdomen and back.
Palpation is carried out with caution:
- if there is a threat of internal bleeding;
- people with stiffness (excessive tension) in the muscles of the lower body;
- if the doctor suspects a purulent process in the abdominal cavity (abscess, phlegmon, peritonitis, etc.);
- during pregnancy for more than twelve weeks, with a threat of miscarriage.
The examination is difficult if the patient:
- obesity with excess deposits in the abdominal area;
- bloating;
- ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity).
Surgery for prolapsed kidneys
In the absence of contraindications and stable results with conservative treatment, surgical intervention is prescribed. There are 4 types of operations in total:
- Attaching the organ to the ribs with muscle flaps.
- Fixation with synthetic materials.
- Attachment of the fibrous capsule by connective tissue.
- Fixation to the ribs using a suture in the kidney.
After surgery, you must remain in bed for 14 days to avoid relapse.
Timely detection of nephroptosis and its adequate treatment is the key to a quick and effective solution to any problems associated with kidney prolapse. To diagnose the disease, you must consult a urologist at the CELT multidisciplinary clinic.
Results and norms
If the kidney is located within its own anatomical bed and is not enlarged, it is impossible to palpate it. In people of asthenic physique, during deep palpation the doctor can feel the lower renal pole. This is not a pathology. In some cases, the lower surface of only the right kidney is palpable, since anatomically it is located below the left.
Normally, the kidneys are located within the ribs, have a bean-like shape, a smooth capsule, and a uniform consistency
Table: palpation characteristics of the kidneys in normal conditions and diseases, indicated by deviations
| Characteristic | Norm | What diseases do deviations indicate? |
| Location | within the costal arches, therefore not palpable | position below the costal arches and excessive mobility indicate nephroptosis |
| Mobility | insignificant; during deep breathing, running, bending and jumping does not exceed 2–3 cm | |
| Form | bean-shaped | Changes in shape, size and consistency occur when:
|
| Consistency | homogeneous, moderate density | |
| Size | bud length - about 12 cm, diameter - about 6 cm | |
| Surface | smooth and even due to the dense capsule | tuberosity may indicate:
|
| Soreness | absent | pain is present in pathologies such as:
|
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Ultrasound of the kidneys and adrenal glands | 2 700 |
| Urography intravenous | 6 000 |
| Laparoscopic nephropexy | 100 000 — 135 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions