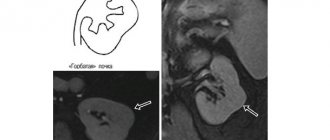
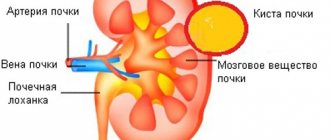
Hydronephrosis, hydronephrotic transformation
– a kidney disease in which the enlargement of the calyces and pelvis of the kidneys occurs.
With hydronephrosis,
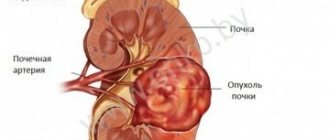
hypotrophy is observed - thinning of the kidney tissue, which has the most negative effect on the functioning of the organ.
Women suffer from hydronephrosis
almost 1.5-2 times more often than men; children are also quite often susceptible to the disease.
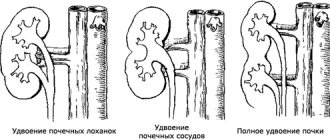
Depending on the cause of the disease, a distinction is made between primary or congenital hydronephrosis
, which usually develops as a result of a congenital anomaly of the upper urinary tract, and secondary or
acquired hydronephrosis
, which can be caused by various diseases.
Classification of hydronephrosis
First of all, it is worth noting that hydronephrosis can be a congenital or acquired pathology. Congenital hydronephrosis is caused by various changes in the anatomical structure of the structures or vessels of the kidney itself. In children, only congenital forms of this disease are diagnosed and they speak of primary hydronephrosis. Secondary forms of this pathology arise as a consequence of inflammatory processes of various etiologies in the urinary system and other diseases (prostate adenoma, prostate cancer, etc.). Secondary nephrosis is more common in men over 60 years of age.
According to the nature of the clinical course, this disease can be acute or chronic. If a pathological acute condition is stopped in time, it is possible to completely restore all kidney functions. If the disease becomes chronic, then the pathological processes become irreversible.
It is customary to distinguish between unilateral and bilateral hydronephrosis. The bilateral form of the pathology is quite rare; hydronephrosis of the right kidney or hydronephrosis of the left kidney is more often observed.
Hydronephrosis, according to the severity of the pathological process, can have the following forms:
- mild form, in which only the renal pelvis expands, and renal function is not impaired or slightly impaired;
- a moderate form, which is characterized by an increase in the pelvis by 15-20%, and a significant thinning of its walls is observed. The functions of the organ are significantly reduced;
- a severe form of hydronephrosis, in which the kidneys increase in size by approximately 2 times, and the pelvis and cups are significantly dilated. Kidney function decreases by 70-80% or the kidneys lose their ability to function. This condition is life-threatening for the patient.
Hydronephrosis, the degree of which determines the medical prognosis of the disease, can have both reversible and irreversible consequences.
It is also customary to distinguish between infected and aseptic types of the disease.
Diet
A significant role in the course of treatment is given to proper nutrition, which helps reduce the load on organs and normalize water and electrolyte balance. During treatment, it is necessary to exclude legumes, fish and fatty meats, spices, salt, chocolate, coffee, alcohol, and canned food.
Instead of prohibited foods, give preference to vegetables and fruits, cereals, lean fish, eggs, dairy and fermented milk products. Ensure adequate fluid intake. It is recommended to drink more than 2 liters of liquid per day, giving preference to water, natural juices, compotes, fruit drinks, and herbal teas.
Hydronephrotic transformation is a pathological process characterized by an increase in kidney size. It goes through three stages, each of which has its own characteristic clinical picture. To eliminate the pathology, medications and surgery are used. For therapeutic purposes, a special diet is also prescribed.
Causes of kidney hydronephrosis
As already mentioned, renal hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. Each of these forms of pathology has its own etiology. Congenital hydronephrosis is associated with the anatomical features of the child’s body. Certain changes can be noticed by an experienced specialist during an ultrasound examination of the fetus. Even then, the renal pelvis can be enlarged to varying degrees. Depending on how serious the deviations from the norm are, a decision is made to carry out appropriate treatment or even terminate the pregnancy if doctors assess the functions of the fetal kidneys as incompatible with life.
The causes of hydronephrosis can be divided into external, internal and functional. Pathological changes can affect both the ureter and the bladder. From the ureter, internal causes of hydronephrosis can be:
- blood clots;
- tumors of various etiologies;
- narrowing of the mouth of the ureter (urethrocele);
- endometriosis;
- tuberculosis;
- fibroepithelial polyps, etc.
Among the external causes that can cause ureteral dysfunction are the following:
- pregnancy;
- oncological diseases of the female reproductive system (cervical cancer, polycystic ovary syndrome, etc.);
- uterine prolapse;
- prostate tumors of various etiologies;
- aortic aneurysm in its abdominal section;
- anatomically incorrectly located renal artery, which in this case compresses the ureter.
If we are talking about the bladder, then among the internal factors contributing to the development of hydronephrosis, the following can be identified:
- contracture of the bladder neck;
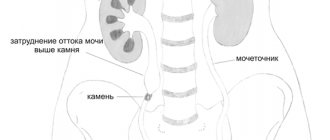
- urolithiasis disease;
- prolapse of the bladder into the vagina in women (cystocele);
- carcinoma;
- bladder diverticulum, etc.
An external obstacle to the physiological outflow of urine from the bladder can be pelvic lipomatosis. Functional disorders include various disorders of bladder filling and emptying and retrograde vesicoureteral movement of urine (reflux).
From the urethra, the cause of hydronephrosis can be prostate cancer, its hyperplasia (external causes), as well as urethral strictures (pathological narrowing of the urethra) or urethral diverticula (internal causes).
Hydronephrosis can also be caused by various injuries, postoperative conditions, inflammatory diseases of various origins, obstruction of the urinary tract, etc.
Hydronephrosis: symptoms of the disease
If a patient is diagnosed with hydronephrosis, the symptoms directly depend on the degree of expansion of the pyelocaliceal complexes, the rate of development of the disease over time, and the duration of urinary tract obstruction.
Acute hydronephrosis manifests itself in the appearance of paroxysmal pain in the lumbar region, which can radiate to the thigh, groin, genital area, or spread along the ureter. There may also be a frequent urge to urinate, and the process of releasing urine becomes painful. Phenomena of general intoxication of the body (nausea, vomiting, general weakness, etc.) may be observed. Blood may appear in the patient's urine. In some cases it is visible to the naked eye (macrohemoturia), in others it can only be detected by microscopic examination of urine (microhemoturia).
The danger of unilateral chronic hydronephrosis is that for a long time the disease can occur without pronounced symptoms. The patient may experience periodic dull pain in the lumbar region, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, etc. With the development of pathology, the patient may experience a sharp increase in blood pressure and hematuria. Women often tend to mistake hemoturia for uterine bleeding and seek help from specialists too late.
If the patient's body temperature rises, then there is a possibility of developing infected hydronephrosis. Often in this case, the patient experiences symptoms of pyuria (the presence of pus in the urine), as well as symptoms of general intoxication.
By interviewing the patient, you can find out that he prefers to sleep on his stomach, since this position promotes the outflow of urine from the kidney that is involved in the pathological process. In the terminal stage of the disease, kidney function is impaired and signs of renal failure may appear.
Diagnosis of hydronephrosis
First of all, the patient is examined and anamnesis taken. During the survey, factors predisposing to the occurrence of hydronephrosis can be identified. Palpation may reveal an enlarged kidney or a distended bladder. These data are subjective, so the patient is prescribed additional examination.
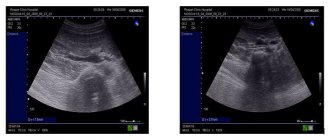
Imaging research methods are of great importance, the most informative among which is ultrasound, namely ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. X-ray and radiopaque studies are also used:
- urography;
- retrograde urethropyelography;
- X-ray examination of the renal arteries.
Radiological and endoscopic research methods are also relevant:
- urethroscopy;
- nephroscopy;
- cytoscopy;
- chromocytoscopy;
- renoangiography, etc.
It is important to examine the patient’s blood and urine to identify typical signs of renal dysfunction. The results of urine tests according to Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky, etc. can be used. A general urine test may reveal the presence of blood or purulent discharge, as well as leukocyturia.
Differential diagnosis of conditions with similar clinical manifestations that are not associated with hydronephrotic changes in the kidney is necessary. Similar symptoms may be a consequence of the presence of kidney stones, nephropathosis, or cancer.
Folk remedies
Photo: thebiglunch.ru
Hydronephrosis cannot be eliminated using traditional medicine recipes. Self-medication can lead to irreversible impairment of kidney function and its subsequent removal.
Folk remedies are included in the treatment regimen only to eliminate or mitigate individual symptoms and do not replace drugs from official medicine.
Parsley can be used as an additional medicine with a uroseptic effect. One tablespoon of finely ground plant root is poured with boiling water and left for twelve hours. The resulting infusion is drunk one tablespoon four times a day, twenty minutes before meals. If parsley root is not available, you can use the seeds. In addition, the following herbal preparations are used as uroseptics:
- Burdock root, wormwood, chamomile, celery root and rose hips. All ingredients should be one hundred and fifty grams.
- Adonis, nettle, oats, bearberry and horsetail - just one teaspoon each. You will need to add three teaspoons of birch leaves to the mixture.
- Currants, cranberries, knotweed, raspberry leaves, calamus root, meadowsweet inflorescence, string and chamomile.
- Fireweed, alder, marshmallow, celandine, coriander, knotweed and mint.
All components are crushed. The collection in the amount of two tablespoons is steamed with boiling water and left overnight. In the morning, filter the liquid and take a third of a glass three to four times a day.
Self-treatment of hydronephrosis with folk remedies is strictly prohibited due to the risk of developing severe complications. Before using traditional recipes, you should consult with your doctor to make sure there are no contraindications, the compatibility of herbal remedies with the prescribed pharmaceuticals and the safety of their use at this stage of therapy.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.
Complications of hydronephrosis
A pathological condition such as hydronephrosis is quite dangerous to human life and health. Due to pathological disorders, the kidneys lose their ability to function normally, and the following complications may arise that threaten the patient’s life:
- renal failure is a syndrome of dysfunction of all kidney functions, which leads to disruption of all metabolic processes in the patient’s body. In this situation, the development of severe general autointoxication of the body is possible, which can cause the death of the patient;
- sepsis (or blood poisoning) can occur against the background of infected hydronephrosis;
- hypertonic disease;
- urolithiasis disease;
- inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis);
- sudden rupture of the pelvis, leading to spillage of contents into the retroperitoneal space. This condition is characterized by high mortality.
Stages
Hydronephrosis goes through three stages: pyelectasia, hydrocalycosis and terminal stage. With pyeloectasia, there are no disturbances in the process of urine discharge. Changes in the organ are minor.
At the stage of hydronephrotic transformation, a slight stretching of the pyelocaliceal system and renal parenchyma occurs, and the organ enlarges. Due to the stagnation of urine, which puts pressure on the tissues, the cells of the organ slowly die and its performance decreases.
At the terminal stage, the kidney enlarges excessively, the tissues atrophy, and the functioning of the organ practically ceases. As a result, all cleansing functions are assigned to the working kidney, which cannot always cope with the volume of incoming urine. At the last stage, renal failure joins hydronephrosis.
Treatment of kidney hydronephrosis
Unfortunately, there are no conservative treatment methods that can cure hydronephrosis. Drug therapy is used aimed at eliminating pain, treating concomitant infectious diseases, normalizing blood pressure and correcting renal failure in the preoperative period.
Emergency care for acute hydronephrosis consists of emergency removal of accumulated urine and normalization of pressure in the kidney. For this purpose, nephrostomy is used.
Surgical treatment methods are aimed at reconstructing, removing or preserving the organ. If it is possible to eliminate the cause of hydronephrosis, then reconstructive surgery is performed. If this is not possible, then all possible measures are taken to preserve the organ. In this case, individual affected areas of the urinary system can be removed. In case of urolithiasis, stones can be surgically removed. Bougienage of the ureter can be performed, which helps to expand the pathologically narrowed canal of this organ, endotomy, balloon dilatation, etc.
In cases where such surgical intervention is impossible or unjustified, a decision is made to completely remove one affected kidney. This operation is performed when the organ completely loses its functional load.
Medical prognosis of the disease and preventive measures
The key to successful treatment and the main method of prevention is periodic ultrasound examination of the urinary system. Only in this way can the first “alarm bells” be detected in a timely manner.
The medical prognosis of the disease is defined as serious, but conditionally favorable. However, you can only hope for a complete recovery if you consult a specialist in a timely manner. Remember that the main symptom of the disease is the presence of blood in the urine. If you notice something like this, immediately consult a urologist. Self-medication is unacceptable and can cost the patient his life.
Medicines
Photo: etodiabet.ru
The drug therapy regimen for hydronephrosis is determined by the cause of the disease and the existing complications. Patients may be prescribed:
- Antibacterial agents . Indicated in the development of the inflammatory process, the threat of infection. At the initial stage, broad-spectrum drugs are used, reaching the highest concentrations in the organs of the urinary system. After urine culture results are obtained, the medication is changed based on antibiotic sensitivity.
- Plant uroseptics . Prevents the development of complications. Recommended after eliminating acute inflammation and stopping taking antibiotics or as an adjuvant during antibiotic therapy. Prescribed in drops, syrups, capsules. Some products are approved for use in children and pregnant women.
- Antispasmodics . Reduce the tone of the smooth muscles of the walls of the urinary organs. When relaxed, the lumen of the ureters increases, the outflow of urine improves, sand and small stones are released. In some cases, the drugs are effective in the treatment of renal colic - they eliminate the painful spasm, which allows the stuck stone to pass into the underlying sections and come out with urine.
- Other medicines . Immunomodulators, vitamin-mineral complexes, and antioxidants are useful. In case of urolithiasis, to prevent the formation of stones, medications are prescribed to reduce the level of uric acid, restore oxalic acid and phosphorus-calcium metabolism. For malignant neoplasia, chemotherapy may be required.