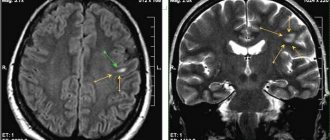
In perinatal practice, a choroid plexus cyst is often diagnosed in a newborn. Most often, it is not the cystic formation itself that has a negative effect on the child’s body, but the diseases that provoked its appearance. Therefore, it is important to undergo a diagnosis in time and establish the cause of the pathology. Taking into account the location of the tumors, their size and structure, the doctor prescribes treatment that will help get rid of the cysts or stop their growth.
What is a choroid plexus cyst?
A cyst is a bubble filled with fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) with clearly defined boundaries. The walls of the bladder may consist of arachnoid tissue, glial or epidermal cells. Most often, cystic formations are benign and do not have a negative effect on the brain. Impaired cerebral circulation and pathological functioning of nerve cells are possible if the cystic sac grows rapidly, squeezing nearby tissues.
A bubble with fluid can form in the lumens of the choroid plexuses in the fetal brain. The formation of tumors during the period from 14 to 22 weeks of pregnancy is considered normal.
The mechanism of cyst formation and the causes of their occurrence
Cystic formations can form in the fetus in the womb, and also occur after the birth of the child.
In the fetus
Cysts of the choroid plexus of the brain in the fetus are detected before the seventh month of pregnancy. The choroid plexus is a paired system formed in the ventricles of the fetal brain. It precedes the development of the nervous system. A pair of choroid plexuses indicates that the child will subsequently develop a left and right hemisphere of the brain. The choroid plexuses themselves do not have nerve cells; they only produce cerebrospinal fluid, which nourishes the brain.
Cerebrospinal fluid can accumulate between the plexuses, forming into vesicles. The accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid does not affect the development of the fetus and does not have a negative effect on the body. If the cystic sac does not subside, but remains in the head cavity, it does not manifest itself in any way; in an adult, the neoplasm can only be detected on MRI or CT images.
In 90% of cases, a brain cyst in the fetus does not cause any harm to the body and resolves on its own by the 28th week of pregnancy.
Some geneticists believe that the appearance of cystic formation of the villous plexuses indicates that the fetus is susceptible to genetic mutations. The neoplasm itself is not the cause of these mutations, but only indicates the possible development of a genetic defect. Experts identify the most common pathologies that can be diagnosed in a baby - Edwards syndrome and Down disease.
It is the failure of chromosome division (non-divergence of the 18th pair, the presence of an extra chromosome) that leads to the formation of bubbles with cerebrospinal fluid in the choroid plexuses of the fetus.
In a baby
A choroid plexus cyst in a newborn usually develops under the influence of various infectious diseases. Cystic formations in the villous plexuses can also form after the 28th week of pregnancy under the influence of negative factors. These include:
- The herpes virus that infected the mother's body.
- Acute infectious diseases.
- Impaired blood flow.
- Prolonged fetal hypoxia.
- Trauma during childbirth.
Often such cysts do not affect the functioning of the brain. Treatment is prescribed only if the cystic bladder grows, causing disruption of brain function.
Is a pseudocyst dangerous and why?
The existing pseudocyst in the head of a newborn in all cases has a second cause of development. The following reasons may act as a catalyst for the appearance:
- lack of oxygen;
- problematic childbirth;
- presence of injury.
A false cyst in an infant is not dangerous to health. This pathology should cause alarm in cases where the formation rapidly increases in size.
There is no need to perform any specific therapeutic procedures in the treatment of pseudocysts in infants. All that is necessary is to regularly visit a neurologist and carry out restorative therapy designed to combat the emergence of possible complications that often appear against the background of injury.
If after 12 months the formation and the baby have not gone away, doctors diagnose a true cyst. In such situations, you should be observed by a neurologist throughout your life.
The course of pathology observed in a newborn child should be monitored by a pediatric neurologist. The following techniques can be used during therapy.
Medicines
As a rule, doctors prescribe a number of drugs to children, the action of which is aimed at improving blood circulation in the brain, and also prescribe antihypoxants:
- Mexidol;
- Cytoflavin;
- Vitamins belonging to group B;
- Mildralex.
If hyperactivity is observed, the use of drugs such as:
- Glycine;
- Pantocalcin, as well as Pantogam.
To strengthen the musculoskeletal system, you should attend massage sessions, but only if they are recommended by your doctor.
If the false cyst was not subject to resorption during the first year of the child’s existence, and it increases in size, surgery will be required. Removal of the formation is carried out through craniotomy using endoscopy and shunting techniques.
Surgery
Endoscopic surgical procedures are by far the best ways to treat tumors in children. But such operations are not carried out in all cases. If your baby has been diagnosed with a cyst of the septum pellucida developing in the brain area, then this technique is perfect for treatment. The treatment is not accompanied by complications and avoids excessive trauma to the small patient.
The recovery period after surgery to remove a cyst is different for each case, and depends on the general well-being and state of health of the child.
Folk remedies
To improve the well-being of children with large cystic formations in the brain, in addition to the use of medications, folk remedies can also be used. The most effective are the following recipes:
- a decoction made from hawthorn fruits. The liquid is taken internally to strengthen the nervous system. This product helps improve baby's sleep;
- horsetail, cinquefoil, as well as capitol and violet are distinguished by their ability to lower intracranial pressure;
- Hemlock is endowed with excellent absorbent properties;
- herbal infusions for taking soothing baths.
From the editor: How to properly prepare for an MRI and what you need to know
To prepare a decoction that has a calming effect, you will need to take raspberry leaves, yarrow, as well as chamomile, licorice rhizome and calamus. The components are used in equal proportions and mixed. Composition in the amount of 2 tbsp. should be placed in a container, pour boiling water (0.5 l) and leave for 8 hours. After this, the liquid is filtered and added to the baby’s bathtub.
Before using traditional medicine in the fight against pseudocyst, you should consult with your doctor.
Types of cysts and their location in the body of a newborn
The following types of cysts can be diagnosed in a child’s body:
Choroidal
A choroidal cyst is nothing more than one of the types of neoplasms of the choroid or choroid plexus of the 3-4 ventricles in a newborn child. The development of pathology is provoked by infectious diseases and oxygen starvation of the child during childbirth.
As the tumor grows, the newborn experiences headaches, twitching of the limbs, and convulsions.
Subependymal
The nature of the development of the pathology is as follows: under the membrane lining the cavities of the brain, small voids and bubbles filled with cerebrospinal fluid can form. A possible cause is damage to the walls of small vessels, which develops as the baby passes through the birth canal. Most often, no more than 2-3 capillaries are damaged. At the same time, a small amount of blood flows under the membrane.
Hematomas are processed by special cells, and the blood is replaced by cerebrospinal fluid. As a result, cystic sacs appear, which, with the normal development of the child, subside and resolve over time.
It is believed that a subependymal cyst in a newborn does not require special treatment. Moreover, given the almost 100% dynamics of self-healing, neurologists do not even consider it necessary for such patients to be re-examined.
Arachnoid
A congenital arachnoid cyst of the brain is a bubble of arachnoid membranes filled with cerebral fluid. The tumor occurs between the upper hard and lower soft membranes. Provoking factors: infectious diseases in the mother, complicated pregnancy, traumatic birth.
When the arachnoid cystic sac does not grow, its presence in the head cavity does not bring any unpleasant sensations to the child. As the tumor increases, it begins to put pressure on the meninges. The patient has:
- Headache.
- Regurgitation, vomiting.
- Loss of appetite.
- Lethargy.
- Restless sleep.
- Convulsions, twitching of limbs.
Treatment involves eliminating symptoms, as well as preventing swelling of brain tissue and normalizing the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
The appearance of cystic formations is also possible on other organs of the baby. Experts diagnose the following types:
- Periventicular cyst of the brain in a fetus.
- Spermatic cord.
- Renal.
- Sublingual a.
- Ovary.
Treatment, if necessary, is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor, since only a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis and select the necessary medications.
How to treat cerebral encephalopathy
- Cream for foot fungus Exomin
- Vetoksik anti-parasite capsules
- Sustalife complex for joint restoration
Description and mechanism of development of the disease “encephalopathy”
This brain damage is not accompanied by an inflammatory process, as with encephalitis. Diffuse-dystrophic changes in the tissues of this main center of the human nervous system ultimately lead to a disorder of consciousness and memory in the patient.
First period. The compensated stage, in which people develop hyperexcitability and increased irritability, is determined solely through a diagnostic study. The patient himself feels some fatigue, but does not fully feel the main symptoms of encephalopathy.
Causes of encephalopathy
Organic brain damage is an accompanying disease that can be provoked by the following factors:
- TBI (traumatic brain injury)
. Quite often, diffuse damage to this main organ of the central nervous system is diagnosed in people who engage in contact sports. Encephalopathy can also occur in those individuals who have experienced an accident, a fall from a height, or a domestic quarrel that ended in assault.
Types of cerebral encephalopathy
Based on the nature of the formation, two forms of organic brain damage are distinguished: congenital and acquired.
Perinatal. It can occur in the womb if pregnancy becomes problematic in the third trimester (after the 28th week of fetal development). The formation of pathology in a child is also provoked by traumatic brain injury during pathological childbirth. We should not forget about genetic predisposition, which is the main risk factor for encephalopathy in a baby.
How does cerebral encephalopathy manifest?
Death of brain cells in children
Due to genetic predisposition, intrauterine infections and pathological births, the child may then experience the following symptoms of encephalopathy:
- Oppression
. Depressed mood in children cannot be the norm when it has become systematic. If a son or daughter tries to be alone and stops making contact, then the parents definitely need to sound the alarm.
Encephalopathy in young and middle-aged people
The older a person becomes, the more clearly the clinical picture of the described disease manifests itself:
Paresthesia. A similar neurological disorder in the form of partial loss of sensitivity is characterized by tingling, burning of the skin and a “pins and needles” sensation on the skin.
Encephalopathy in the elderly
At an advanced age, a person quite often experiences exacerbation of existing chronic diseases. Encephalopathy in older people usually manifests itself as follows:
- Severe migraine attacks
. They take on a systematic nature and do not stop even with the help of strong painkillers.
- Read a review of the complex remedy for hemorrhoids Proctonol
- How to lose 20 kg - real reviews on Guarchibao
Diagnosis of cerebral encephalopathy
You can obtain reliable information about your health only after completing the following procedures:
CT scan . Using cone beam CT, three-dimensional images of the head are taken to recognize the disease at the earliest stage of its development.
Features of the treatment of cerebral encephalopathy
Medicines against encephalopathy
The use of medications by patients in case of brain cell death should be strictly controlled by a specialist. In most cases, encephalopathy is treated with the following drugs:
- Nootropic substances
. They are intended to regulate metabolism and improve blood supply. Among the huge range of drugs in this pharmacological group, experts usually recommend that a patient with a similar diagnosis take Piracetam and Pyriditol.
Therapeutic procedures to combat encephalopathy
In addition to the aforementioned drug treatment, the patient is prescribed the following set of rehabilitation measures:
Massage . Such a reflex effect on a person’s muscular system has a beneficial effect on his overall well-being during progressive migraines and tremors of the limbs.
Editorial: Symptoms and causes of optic atrophy
Folk remedies to combat encephalopathy
Such therapy cannot replace drug treatment, but can be an excellent accompanying tool in the fight against the death of brain cells.
https://tutknow.ru/psihologia/11107-kak-lechit-jencefalopatiju-golovnogo-mozga.html
Signs of cyst growth in a newborn
If there is a cystic formation of the choroid plexus in the baby’s brain tissue that has not previously resolved, most often it does not manifest itself with any symptoms. The baby may show signs of damage to brain structures if the cystic sac appears later, and its occurrence is triggered by infection or injury.
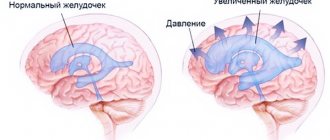
A large cyst is putting pressure on the brain tissue. In addition, due to the structural features of the choroidal cystic formation, it provokes increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. Thus, the pressure inside the child’s head increases and signs of hydrocephalus appear.
Symptoms that are provoked by a growing vascular cyst of the brain in newborns:
- Hypertonicity, hypotonicity of the extremities.
- Nausea, excessive regurgitation, vomiting.
- Inability to coordinate movements.
- Strabismus.
- Convulsive seizures.
The sick baby suffers from a headache and often screams protractedly. The baby's sleep is disturbed; he may be capricious, whiny and at the same time lethargic and apathetic.
What is a cerebral pseudocyst in newborns?
Both a cyst and a pseudocyst are a cavity filled with exudate, which is cerebrospinal fluid or other substances. Brain pseudocysts in newborns are formed due to trauma during childbirth, fetal hypoxia, etc. With adequate help, the formation resolves.
Why do pseudocysts appear in the brain of a baby?
The causes of cerebral pseudocysts in infants are very different, but basically the etiology of the formation comes down to disorders associated with prenatal development of the fetus.
Often the catalyst is:
- Hypoxia.
- Brain hemorrhages.
- Circulatory disorders due to insufficient nutrients for the development of the child.
Particularly dangerous is a subependymal pseudocyst of the brain in newborn infants. The disorder always occurs against the background of hemorrhage, sometimes as a result of birth trauma. The causes of the formation of a subependymal pseudocyst are always associated with an acquired during pregnancy rather than a congenital factor.
Why is a pseudocyst dangerous?
A pseudocyst always has a secondary cause of development. The catalyst for the occurrence is injury, lack of oxygen, difficult childbirth, and not disturbances in the functioning of the body.
No specific treatment is required for cerebral pseudocysts in infants. It is enough to regularly visit a neurologist and undergo restorative therapy aimed at combating possible complications due to injury.
If a year after birth, the formation does not go away in an infant, a true cyst is diagnosed. In this case, a lifelong consultation with a neurologist will be required.
How to identify a pseudocyst
The most informative and safe method for diagnosing abnormalities in a baby is an ultrasound of the brain. Indications for an ultrasound examination are birth trauma, fetal hypoxia and any disturbances in the child’s behavior. Excessive tearfulness, lack of sleep, etc.
Having discovered pseudocysts of cerebral vessels in newborns, the neurologist will order a repeat study to monitor the dynamics of growth.
Upon repeated examination, attention is paid to a decrease in the volume of the tumor. If the dimensions remain the same or there is a tendency to increase, a course of therapy is prescribed to prevent the occurrence of possible complications: seizures, headaches
As you get older, the diagnostic procedure may be replaced by an MRI.
Difference between a cerebral cyst and a pseudocyst
Although some medical reference books indicate that the main difference between diagnoses is the presence of an epithelial lining, not all experts agree with this.
Pseudocysts of the lateral ventricles of the brain are determined by the following criteria:
- Localization - pseudoformations are always located in the area of the lateral corners of the anterior horn or the lateral ventricles of the brain. A cavity may develop between the optic thalamus and the caudate nucleus. In other cases, we are talking about a true cyst.
- Etiology - the cause is always secondary or acquired in nature and is not determined by genetic predisposition. Thus, a multi-chamber pseudocyst occurs due to hemorrhage; during fetal hypoxia, the lateral ventricles of the brain are damaged.
Editorial: Arnold-Chiari malformation
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis is carried out in utero - during the first ultrasound. The doctor may indicate the appearance of cystic formations in the choroid plexuses, continuing further observation of the pathology only if the cystic sac does not subside on its own after 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Newborns undergo neurosonography - ultrasound examination through a non-overgrown fontanel. The procedure is mandatory in many maternity hospitals; it is during this study that a specialist can note the appearance of a neoplasm and recommend a re-examination after 3 or 6 months to determine whether the cyst is growing or remains unchanged.
The doctor may report that the child has a unilateral formation - on the right or left ventricle. Also on ultrasound you can see a bilateral formation, when cysts of the choroid plexus of the brain affect both the left and right ventricles.
Other types of examinations, such as magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography, are not performed on children under one year of age, since the need for them arises only when pronounced symptoms of brain damage occur.
Diagnosis of pathology
Changes are detected by ultrasound or sonography. According to the recommendation of the World Health Society, these studies are performed on all children under one year of age. Neurological disorders are determined using ultrasound.
Sonography is prescribed if there is a history of:
- birth trauma in a baby;
- infectious disease of the mother during pregnancy;
- difficult pregnancy;
- fetal prematurity;
- deviations in size at birth;
- pronounced disturbances in the shape of the head;
- a defect in the structure of the baby’s organs.
There are no signs of a cyst in the infant. This deviation appears and disappears without symptoms. It is not pathological and in most cases does not affect the child’s brain activity.
According to research, such cysts are found not only in children who are developmentally delayed. These formations are equally found in normally developed children.
Features of treatment
Since the prognosis for cystic formation of the choroid plexus is mostly positive, most often the child is not prescribed any treatment. Drug therapy is indicated for young patients only if the cyst in the cranial cavity is growing rapidly, causing an increase in intracranial pressure, impaired cerebral circulation, and the transmission of nerve impulses.
Most often, the cause of the pathological growth of the cystic sac is an infectious disease, so the infection is first eliminated with medication. For these purposes, the use of antiviral and antibacterial drugs is indicated.
For the treatment of choroid plexus cysts of the lateral ventricles of the brain in the fetus, antiviral drugs may be indicated for the pregnant woman to prevent the growth of the cystic formation. Before this, an analysis is required to determine whether the pregnant woman has an infectious disease.
Treatment for a newborn whose cystic tumor is growing is prescribed by a doctor. The neurologist focuses on symptoms, test data and ultrasound.
- For severe headaches, medications that normalize cerebral circulation (Cavinton, Magne B6) are prescribed.
- To reduce intracranial pressure - diuretics.
- If a baby suffers from seizures, he needs to take anticonvulsants (Depakine Chrono).
- If sleep is disturbed and there is increased excitability, the child may be prescribed a sedative (Glycine).
Surgical intervention is carried out only in case of severe pathologies - rupture of the cyst, suppuration, germination into other tissues.
Possible prevention
Basically, preventive measures to prevent the development of pathology depend on the pregnant woman. She needs to avoid general hypothermia, dress appropriately for the weather, and avoid visiting crowded places where she can become infected with chickenpox or another infectious disease.
To avoid the occurrence of choroid plexus cysts in the newborn, the expectant mother should adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat right and improve immunity. Everything else depends on nature.
Forecast
In the vast majority of cases, everything ends well. Typically, choroid plexus cysts in a newborn, which are formed during embryogenesis, resolve themselves by the time of birth.
If the tumor still remains, then depending on the individual characteristics of the diagnosis, therapeutic tactics are chosen. As a rule, with timely removal of large or growing dysplasia, it is possible to achieve its complete cure.
The prognosis for choroid plexus cyst in a newborn is favorable