Why does cerebral microangiopathy develop?
- Cerebral microangiopathy is damage to small blood vessels in the brain.
- Occurs in more than 30% of people over 60 years of age
- Associated with vascular risk factors.
SAE (subcortical arteriolosclerotic encephalopathy):
- Subcortical atherosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE) or Binswanger's disease
- Diffuse subcortical lesion
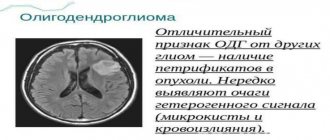
- Evidence of tissue adaptation to hypoperfusion with a decrease in oligodendroglia and myelin content
- Localization: periventricular and subcortical white matter, excluding arcuate fibers.
Lacunar strokes:
- Small strokes caused by occlusion of penetrating arterioles with a diameter of 40-200 µm due to lipid hyaline degeneration and fibrinoid necrosis
- Localization: basal ganglia, thalamus, internal and external capsules, periventricular sections, pons.
Possible complications
Consequences are relatively rare. Years pass from the development of microangiopathy to the final outcome. However, you cannot relax.
Possible problems include:
- Stroke. Acute cerebrovascular accident. Provokes the death of nerve tissue. Severe disability with neurological deficit. The death of a person is possible and even probable.
- Encephalopathy. The process is similar, but there is no destruction of cerebral structures yet.
- Vascular dementia. Dementia due to insufficient brain nutrition.
Complications develop spontaneously. Treatment is the only way to prevent them.
Which method of diagnosing microangiopathy to choose: MRI, CT, angiography
Selection method
- MRI.
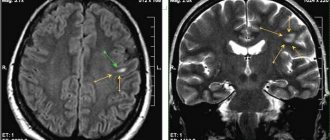
Ischemia of small vessels. Axial FLAIR (a) and T1-weighted ( b ) imaging. In the axial dark-fluid imaging mode, hyperintense zones are identified, consisting of small foci with clear boundaries and/or nodular foci merging with each other. On T1-weighted imaging, these areas are hypointense.
Is MSCT of cerebral vessels informative for lesions of small vessels?
SAE:
- Confluent hypodense zones in the brain parenchyma.
Lacunar strokes:
- Clearly demarcated hypodense lesions measuring 2-5 mm without volumetric effect
- Characteristic localization.
What will MRI images of the brain show in small vessel ischemia?
SAE:
- Confluent hyperintense areas on T2-weighted and proton density-weighted images or hypointense areas in the white matter on T1-weighted images.
Lacunar strokes:
- Well-demarcated hyperintense lesions measuring 2-5 mm on T2-weighted and proton density-weighted images or hypointense areas without evidence of volumetric effect (on T1-weighted images) of the above characteristic location.
Amyloid angiopathy:
- Multilocular microhemorrhages on T2*-weighted images.
Diagnostics
The examination is the task of neurologists. If necessary, a specialist in vascular surgery is involved.
The list of activities is always identical, with minor deviations:
- Oral questioning of the patient. It is necessary to identify complaints and make a list of symptoms. This will allow you to determine the direction of further diagnostics.
- Anamnesis collection. In particular: infectious processes suffered in the recent past, current and chronic pathologies, family history of diseases, bad habits.
- General and biochemical blood tests.
- Electroencephalography. To determine the functional activity of cerebral structures.
- MRI or CT scan of the brain. It is possible to conduct two studies at once. Used to identify the location, number of lesions, and severity of the disorder.
Dopplerography and duplex scanning are also possible. To determine the quality of trophism of nerve tissue.
What diseases have symptoms similar to cerebral microangiopathy
Multiple sclerosis:
- The corpus callosum is often affected
-Younger age of patients
-Results of CSF examination
TsADASIL ( damage to brain blood vessels with subcortical infarctions):
— Subcortical strokes, most often in the frontal and temporal lobes (starting from the poles of the temporal lobe) and in the internal capsule
- Strong family history
— DNA analysis (gene defect on chromosome 19c 12 due to mutation in the 3rd gene
Physiological lines of increased signal intensity in the anterior and posterior horns on FLaIR and proton density weighted images
— Normal subependymal gliosis or increased interstitial fluid
Virchow-Robin spaces:
- Typically found near the anterior commissure
Clinical picture
The manifestation of such symptoms is due to impaired blood circulation in small vessels. For this reason, components are produced that cause damage to brain tissue. Because cerebral angiopathy syndrome occurs slowly, patients do not think about the presence of the disease. Therefore, specialists are often faced with advanced forms of the disease. Patients begin to have headaches so severe that painkillers do not help.
Soon, astheno-neurotic syndrome appears, which is characterized by: constant mood changes, insomnia, fatigue, and deterioration in performance. The disease often leads to depression. In later stages, forgetfulness and inability to concentrate appear. The location of the lesions determines the accompanying symptoms:
- Coordination of movements worsens.
- Vision decreases.
- The diameter of the pupils changes.
- Vegetative polyneuritis appears.
- Thermoregulation worsens.
- The patient does not respond well to pain.
- Aneurysm in the eyes.
- Nose bleeds constantly.
- Pain when walking.
- The skin on the feet is peeling.
- Blood in urine.
Microangiopathy of the brain is accompanied by a coagulation disorder. In the later stages, hemorrhages appear under the skin, from the nose, and in the stomach.
Diabetic form of the disease
Diabetic microangiopathy is a complex manifestation of diabetes. The danger is that the disease affects the strength of tissues and the removal of toxic substances from the body. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner and the patient is not treated, the arteries and veins will become even thinner. This promotes tissue hypoxia.
This form is characterized by:
- Nephropathy. The syndrome resolves in 1/3 of patients with diabetes. It is characterized by impaired renal function and swelling.
- Diabetic angioretinopathy occurs when the blood vessels that help supply blood to the retina are damaged.
- Microangiopathy on the legs contributes to problems with blood supply and tissue nutrition deteriorates. More damage is done to the feet. Sometimes the problem spreads to the legs, knee joints, and hips.
At first, patients experience leg pain and fatigue. Initially, the pain occurs moderately, but as the disease progresses, it becomes more difficult to tolerate. Feeling burning or numbness in the legs. The dimensions of the ankle are expanding. In complex clinical disorders, ulcers form on the skin that do not heal for a long time.
Danger of disease
The most dangerous part of this disease is the lesions of gliosis. That is, those affected areas where glial cells have destroyed brain neurons.
At the junctions of capillaries with foci of gliosis, there is a possibility of vessel rupture, which will lead to hemorrhage on the surface of the brain, or directly into the medulla. In such a situation, the consequences are dire. The person will either die or become disabled. This stage of the disease is called discirculatory microangiopathy.
At this stage the most serious symptoms are:
- Impaired cognitive functions (memory lapses, decreased attention, problems with thinking, even dementia);
- Affective disorders;
- Movement disorders;
- Pseudobulbar disorders (difficulty eating, deepening of voice, slow speech, violent laughter and crying);
- Cerebellar disorders (problems with walking and stability, uneven movements, intermittent speech);
- Vestibular and autonomic disorders (nausea, dizziness, frequent pressure surges);
- In the most advanced stages, pelvic disorders (urinary and fecal incontinence) occur.
In addition, the patient’s life, even in the early stages, becomes significantly more complicated. It is difficult to lead a full life when you constantly have a headache, dizziness, your body is weak, various depressions occur, and so on.
This physical condition can be downright dangerous due to the high likelihood of injury. Therefore, do not suffer, if you have similar symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor.
Healing procedures
Microangiopathy of the brain is treated with complex methods. All stages must be controlled by specialists. First of all, the degree of vascular damage is determined, after which medications are prescribed. Elderly patients require increased attention because their disease progresses more quickly.
If microangiopathy is detected, the pressure should be reduced. Hypertension in patients contributes to rapid deterioration of health. In pharmacies there is a small selection of drugs that can lower blood pressure. If the disease develops, the patient should consult a doctor and not act at his own discretion .
Additional provision of the brain with useful substances is required. Nootropic drugs are used for this. A positive effect can be achieved from drugs containing nicotinic acid. Picammilion is the most effective.
Reducing the amount of lipids is also practiced in the treatment of microagniopathy. Fibrates and statins can achieve this effect. Doctors often prescribe Simvastatin.
A decrease in the amount of oxygen in neurons will affect the intensity of the development of pathology. In order for blood composition to have a beneficial effect, you need to consume antioxidants. The treatment regimen includes blood thinning medications. Physiotherapy, regular massage and swimming in the pool have a beneficial effect on the body.
Rare situations arise when drug treatment does not restore the patency of veins and arteries or compensate for circulatory deficiency. In such situations, the patient's condition requires surgical intervention.
A positive result can be achieved if you use traditional medicine in the initial stages of the disease.
Traditional medicine:
- Herbal decoctions that stimulate metabolic processes and improve blood circulation. The list of useful plants includes: clover, hemlock, herbal preparations from the pharmacy.
- Fasting, raw food diet. Losing weight to improve your well-being.
The use of medications eliminates negative symptoms; tissues damaged by gliosis are not treated. If the causes of these formations are not dealt with, the pathology cannot be eliminated. The benefits of such traditional medicine are long-lasting, but not too noticeable . Therefore, you should not rely on self-medication; you will have to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Surgical procedures are performed in rare situations. Indications for the procedure include: difficulties in restoring vascular patency, problems with blood supply. Hirudotherapy refers to alternative methods of eliminating the disease. Non-traditional treatment methods have been used for a long time. Today it is successfully used to eliminate many ailments.
Leech has the following effects on the body: thrombolytic, regenerative, analgesic, hypotensive. This method of treatment gives a positive result, there are no contraindications, and it is safe.
The active components contained in leech saliva have a general effect on the body, stabilize blood circulation and metabolism, glucose levels decrease, and stabilize microcirculation in the capillaries. Patients with vascular pathology need to undergo herudotherapy twice a year.
Symptoms
In the first stages, the disease does not signal itself with symptoms. When microangiopathy just begins to affect the first capillaries, the areas of the brain that were supplied with blood through them switch to power from neighboring capillaries. Therefore, the appearance of symptoms of the disease will be evidence of pathology in a significant number of vessels.
Symptoms of the disease:
- Headache. It is quite intense and is rarely suppressed by taking painkillers.
- Vestibular disorders. Dizziness, problems with coordination of movements and confusion may occur.
- Asthenoneurotic syndrome. Manifests itself in increased irritability and depression. You may have trouble sleeping.
- At night the patient may suffer from insomnia , but during the day, on the contrary, he may constantly want to sleep. There is a sense of global decline in strength.
- Focal manifestations of microangiopathy . They are caused by a variety of symptoms, depending on the location where the focus of microangiopathy occurs. Changes in pain and temperature sensations are likely.
- Encephalopathy is a disorder in brain tissue. The manifestations of encephalopathy can be different. Here you can read about grade 2 dyscirculatory encephalopathy.
Microangiopathy syndrome does not appear to have specific symptoms. The same symptoms can occur with many other brain problems. This means that timely and accurate diagnosis is important to combat the disease.