Orchitis, what is it? Symptoms and treatment at home
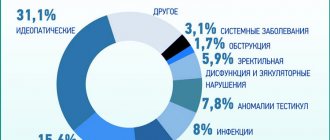
Orchitis is a purely male disease characterized by inflammation of the testicular tissues. The presented pathology began to occur more and more often among representatives of the stronger sex. Previously, only 5% of the population suffered from this disease, today this figure has risen to 15%.
Treatment of orchitis involves taking antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs. But since there are many causes for this disease, the doctor first conducts a thorough diagnosis to establish the etiology of orchitis.
Causes
The causes of testicular inflammation are infections. Depending on the causative agent, orchitis can be specific (caused by pathogens of tuberculosis, syphilis), or nonspecific (caused by any other infection).
Doctors call mumps (mumps) the most common triggering factor for orchitis (about a third of all cases). Typhoid, influenza, and gonorrhea can also cause this disease. Sometimes orchitis develops after injury. Separately, granulomatous orchitis is distinguished, the causes of which have not yet been reliably established.
Among the factors predisposing to the development of orchitis are:
- sedentary work or sedentary lifestyle;
- regular physical or severe mental fatigue;
- overheating or hypothermia, which reduce the body’s protective functions and contribute to the development of the disease;
- sexual abstinence or excess, as well as irregular sexual activity;
- chronic foci of infections - bronchitis, sinusitis, etc.;
- severe diseases (AIDS, diabetes, hepatitis) that reduce the body’s overall resistance;
- obstructed urine outflow, prostatitis, pyelonephritis and other problems of the genitourinary system.
In the case of acute or chronic urethritis and prostatitis, the infection enters the testicle through a descending hematogenous and lymphogenous route, developing inflammation. With mumps, the mechanism of the disease is somewhat different and is associated with the formation of specific antibodies, which, in turn, having an affinity for testicular tissue, are deposited on them and cause damage to testicular tissue.
In any case, orchitis never develops in isolation; there is always some kind of inflammatory focus in other organs or systems of the body.
Treatment of testicular hypoplasia
Currently, accurate knowledge of the etiopathogenesis of pathological conditions makes it possible to carry out fairly effective treatment, which allows not only the male body to function normally and feel full, but also to perform a very successful reproductive function. That is why hormone replacement therapy is used in the treatment of testicular hypoplasia. After all, the main cause of the symptom complex that develops with this nosology is testosterone deficiency. This is exactly what hormonal therapy prescribed to correct the condition compensates for. In the absence of therapy
When testosterone is prescribed exogenously, the boy’s normal growth and puberty are preserved, there is no impotence, the man lives a full life, in which there is room for the birth of his own children. In more complex and severe cases of testicular hypoplasia, replacement therapy can improve spermogram parameters, which, in turn, gives higher chances of using assisted reproductive technologies in the form of ICSI and in vitro fertilization protocol. In some cases, there are indications for cryopreservation of sperm for its subsequent use in the in vitro fertilization protocol.
If a man has unilateral testicular hypoplasia, and he has significant psychological problems about this, doctors can perform an operation such as removing the hypoplastic organ on one side and replacing it with prosthetics. When carrying out such manipulations, the cosmetic defect is corrected one hundred percent. This restores strength and self-confidence to representatives of the stronger half of humanity who have met the corresponding diagnosis.
If doctors diagnose severe bilateral testicular hypoplasia, then doctors often settle on a diagnosis of absolute infertility. It is in this case that men can be offered the option of having a child by using an in vitro fertilization program in a couple using donor sperm. Currently, fertility clinics have a very wide range of sperm donors, which are combined into a sperm bank. It is in such institutions that a couple can choose a sperm donor with their own phenotypic data and the appearance of a man with infertility, and it is for this reason that no one can ever suspect that the child is not biologically his own.
Scientists have long proven the fact that when infertility occurs in a couple, exactly half of the causes come from the male body, as well as from the female. And that is why, in the absence of pregnancy in the family, it is worth examining not only the fair sex, but also the man. It is by using such tactics for managing these patients that it is possible to achieve the fastest possible diagnosis, which will allow prescribing timely and effective treatment. Since in many men, such a pathology as hypoplasia of one testicle can go unnoticed in adulthood. It is for this purpose that a full examination is prescribed to representatives of the stronger half of humanity.
Symptoms of acute orchitis
The disease in men begins suddenly with an increase in body temperature, pain in the testicle of varying intensity and duration. The pain can radiate to the groin, perineum, and lumbar region. The testicle on the affected side increases sharply in size; a few days after the onset of the disease, the skin of the scrotum becomes smooth and may become hyperemic.
The pain may intensify when walking (going down stairs), physical activity, or changing body position. In addition, in the clinic of acute orchitis, general symptoms of inflammation may sometimes be present: dyspeptic disorders, chills, headache.
What is the norm and should we be afraid of deviations?
Despite the fact that men are members of the stronger sex, the weak, fragile and delicate part of their body is the genitals, that is, the testicles and penis.
Almost every man protects his genitals, providing them with maximum sterility and cleanliness, as well as a comfortable condition. Of particular importance are the testicles, which produce sperm for men for procreation and testosterone for sexual activity. In addition, by paying attention to their genitals, everyone knows for sure what size the penis and testicles should be. And any change, be it an increase or decrease, is recorded by the man almost immediately. Moreover, this becomes a cause for anxiety and worry, although physiologically the size of the testicles, for example, should be different. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis of the presence of pathology.
Symptoms of chronic orchitis
Chronic orchitis is much less common than acute orchitis and more often occurs as a consequence of improperly treated acute orchitis.
Pain in the testicle is intermittent and aching in nature, intensifying after long walking, physical exertion, and hypothermia. In this case, the testicle is somewhat compacted and enlarged. The testicle is slightly painful when touched. Symptoms of general intoxication are not pronounced, the temperature rarely rises to 38 C.
Although the manifestations of the disease are not so pronounced and in most cases patients do not even seek medical help. In chronic orchitis, the secretory function of the testicle is significantly impaired, which often becomes the cause of male infertility.
Complications
The consequences of this disease are quite serious. The danger of the inflammatory process is that it can penetrate into neighboring organs, multiplying the infection. If orchitis is not treated promptly, the following may occur:
- Necrosis of testicular tissue (cell death);
- Complete removal of the testicle through surgery;
- Infertility, which in the future cannot be treated.
It is important to understand that orchitis can be successfully treated with antibiotics and there is an adaptive drug for every pathogenic agent. Therefore, you should not hesitate with treatment.
African tribesmen with big testicles
There is more than one tribe in Africa in which males have large genitals. For example, the mysterious Bubal tribe, which roams between Somalia and Kenya. The testicles of their men reach incredible sizes - up to 80 cm. This feature arises as a result of eating the menstrual fluid of a cow. They contain high levels of the hormone that is responsible for the size of the external genitalia.
Africa is a country where deadly diseases are common. By consuming foods unusual for Europeans, the tribe is treated for common diseases - scurvy, leukemia and rickets. The irreversible changes that occur during such hormonal therapy do not affect the male body and do not affect reproductive function.
917
Diagnosis of orchitis
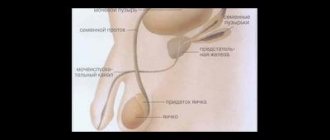
The diagnosis of orchitis is made by a doctor based on examination and the presence of an infectious disease or injury in the patient. Upon examination, the urologist can observe an enlargement of the scrotum; upon palpation, the skin of the scrotum is hot, swollen, the testicle is greatly enlarged in size, swollen and sharply painful.
Of the laboratory diagnostic methods, the most conclusive confirmation of the disease orchitis is the isolation of the mumps virus from the patient’s blood, pharyngeal swabs, cerebrospinal fluid, salivary gland secretions and, of course, urine. Laboratory methods make it possible to detect viruses in a patient at the cellular level within 2 days after the first symptoms. So, to diagnose orchitis, you need:
- microscopic examination of a smear from the urethra;
- general urine analysis;
- antibiotic sensitivity testing, urine culture;
- seeding of ejaculate;
- general blood analysis;
- Ultrasound of the scrotum.
The main method of differential diagnosis of a disease such as orchitis is ultrasound analysis; it is used if the diagnosis of orchitis is difficult due to hydrocele of the testicle, scrotum or periorchitis. A testicular biopsy may also be performed.
Big testicles
For males, the size of the penis and testes has always been important. Information about standards is sought in various medical literature and on the Internet. Some men even seek advice from a specialist if they believe that their external genitalia have a special structure.
Asymmetry, shrinkage, or enlargement of the testicles may be a cause for concern.
Like body structure, the size of testicles varies from person to person and may vary. The main factor that influences their formation is genetic predisposition. It is she who determines the level of testosterone in a man’s body and the size of the gonads. But the cause of non-standard size can also be diseases that lead to an increase in the mass of the organ.
How to treat orthiasis in men?
Treatment of orchitis consists of prescribing medications that are aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation. First of all, antibiotics are recommended. Paracetamol is most often prescribed to reduce fever. To eliminate pain and improve the outflow of sperm, antispasmodics are prescribed.
Treatment regimen for orchitis:
- Pathogenetic treatment - the use of anti-inflammatory drugs “Indomethacin”, “Ibuprofen”, painkillers “Baralgina”, “Ketorol”, angioprotectors “Venorus”, “Detralex”, vitamin complexes.
- Etiotropic treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease. Antibiotic therapy is carried out: patients are prescribed drugs from the group of fluoroquinolones - Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, cephalosporins - Cefotaxime, Cefazolin or macrolides - Azithromycin, Clarithromycin.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures have an anti-inflammatory, local immunostimulating and restorative effect. Patients with chronic orchitis are prescribed UHF therapy, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, acupuncture, electrotherapy, physical therapy, mud and mineral baths.
- Patients with an acute form of the disease are advised to have bed rest, a minimum of movements, rest and an elevated position of the scrotum, and the use of a support bandage that improves blood circulation in the inflamed organ and eliminates congestion in the pelvic organs.
At home, cold compresses are used as a pain reliever. Every 4 hours, a compress is applied to the scrotum for 10 minutes. Treatment of orchitis includes following a diet and giving up bad habits. Spicy, sour and salty foods should be excluded from the diet.
Surgical intervention
If conservative treatment of orchitis does not bring the required results, then the question of surgical intervention is raised.
Indications for its implementation are:
- tuberculous nature of the disease;
- frequent exacerbations in chronic orchitis;
- tissue suppuration;
- acute form, developed as a result of injury;
- severe course of the disease, etc.
Depending on the complexity of the case, surgical intervention can be performed using several methods. With the least consequences for functioning, resection is performed - removal of the inflamed part of the testicle. If the operation is insufficiently thorough and in the case of a number of other factors, complications and relapses are possible.
In case of severe purulent lesions - orchiectomy - removal of the testicle and epididymis. If the operation affects both organs, this leads to a significant decrease in the level of male sex hormones and infertility. The attending physician may also suggest other surgical techniques.
Testicular hypoplasia: what is it?
Both the female and male reproductive systems can have a large number of pathological processes that affect not only the
reproductive function, but also the condition of the entire organism as a whole.
One of these conditions in the field of the male reproductive system is hypoplasia in boys, as well as hypoplasia in men.
Testicular hypoplasia in boys (men) is a pathological process that is characterized by a decrease in the testicles of representatives of the stronger half of humanity, as well as their hypofunction, that is, a decrease in testosterone secretion. Due to the latter, spermatogenesis also suffers, and as a result, the reproductive function of a man also suffers.
Testicular hypoplasia ICD 10 has the code Q55.1.
There are various types of testicular hypoplasia:
- Unilateral testicular hypoplasia, that is, a condition in which only one testicle on one side is reduced. In this state of affairs, the symptoms of the process can be expressed in a somewhat milder form, since its function is taken over by the second testicle
- Bilateral hypoplasia - small testicles in men on both sides. That is, both one and the second testicle in the scrotum are reduced in size. In this condition, testosterone deficiency is severely expressed, which is expressed in impaired puberty, development of secondary sexual characteristics and other signs of testosterone deficiency.