If a couple is having trouble conceiving despite trying to conceive for over a year, both partners should be tested for problems leading to infertility. The assessment of infertility varies between men and women.
To identify possible causes of infertility, the doctor will begin with specific questions about the medical history. Based on the answers received, various diagnostic tests will be recommended for the couple. This article discusses the typical tests needed to diagnose male infertility.
Sperm testing – spermogram
Male infertility can occur if:
- insufficient production of sperm to fertilize the egg;
- if the sperm does not have the correct shape;
- if the sperm cannot swim and move freely.
To check if any of these problems exist, a sample of the man's sperm is needed, collected in a special container by ejaculation. The resulting sample is examined in the laboratory to determine the number of sperm, their health, shape and motility. A spermogram should answer all questions regarding the composition and quality of sperm.
Spermogram
Any abnormalities in sperm morphology should be checked along with signs of other problems and infections. Since the sperm count may vary from one sample to another, to obtain accurate results, a spermogram may be ordered several times over a period of time.
Causes of the disease
There are a variety of factors that can lead to infertility in healthy men - from temporary external influences to severe systemic diseases. First of all, it is necessary to highlight deviations in the functioning of the genitourinary system: sexually transmitted pathologies, chlamydia, prostatitis - all of them can cause dysfunction.
You also need to take into account the following diseases:
- complications of infectious diseases - mumps and rubella;
- diabetes;
- viral hepatitis;
- antisperm antibodies;
- exposure to various radiations and chemicals.
It is important to know! It is obvious that living conditions have a serious impact on male fertility.
We are talking mainly about addiction to bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol. Also at risk are patients with obesity, a sedentary lifestyle and a lack of two components in the body - vitamin C and zinc.
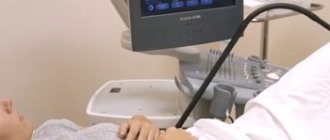
Ultrasound of the scrotum
Ultrasound produces fairly clear images of the internal organs, which allows the urologist to check for structural problems in the testicles. Scrotal ultrasound can easily diagnose problems such as varicoceles, which are enlarged veins in the scrotum. Since nearly 40% of male infertility is caused by varicocele, it is important to rule out this condition before moving on to other possible problems.
Ultrasound of the scrotum
Ultrasound also allows the doctor to diagnose torsion or twisting of the testicles in the scrotum. This leads to tumors and infertility. The pathology must be eliminated surgically, otherwise the man faces permanent infertility.
Causes of infertility in men
The following factors contribute to the development of male infertility:
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- abnormal structure of the pelvic organs;
- anatomical features of the external genitalia;
- inflammatory processes and complications after serious illnesses;
- varicocele – varicose veins of the spermatic cord;
- hydrocele - a congenital pathology in which fluid inside the scrotum puts pressure on the testicle, disrupting the blood circulation in it and reducing sperm production;
- cryptorchidism is an abnormal deviation in the development of the reproductive system, when the testicles do not descend into the scrotum, but remain in the abdominal cavity of the man;
- hormonal disbalance;
- autoimmune mechanism;
- genetic and hereditary diseases;
- erectile dysfunction (impotence);
- premature ejaculation;
- ailments in which soft tissues of the whole body are damaged (tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, thyroid pathologies, mumps, and the like);
There are also additional causes of male infertility that are indirectly related to the development of such pathology. These include:
- bad habits such as smoking, alcohol and drug abuse;
- unbalanced diet;
- frequent stress;
- injuries to the external genitalia;
- lack of vitamins in the body;
- prolonged exposure to toxicological fumes or direct contact with hazardous toxic substances;
- infantilism – a man’s reluctance to have children;
- sexual illiteracy.
It happens that a man has completely no indications for the development of infertility, but his partner never becomes pregnant. Then doctors can make a disappointing diagnosis - infertility of unclear history. Dealing with this problem is difficult, but possible.
Testing hormone levels
Spermatogenesis is driven by hormones.
The hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This acts on the anterior pituitary gland, signaling the release of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). FSH enters the bloodstream and prompts the seminiferous tubules to begin producing sperm. LH stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone.
Each hormone in the chain plays an important role. If the hormones are not balanced, spermatogenesis does not occur and only Sertoli cells are visible on testicular biopsy.
To see if there is a problem with sperm production, urologists check hormone levels using blood tests.
Blood test for hormones
Prevention rules
It is possible to resist male infertility, but you need to be prepared to follow a number of recommendations. Here are some preventive measures that can help avoid this problem:
- You need to lead a healthy lifestyle: moderate physical activity, giving up alcohol and smoking, a proper diet (in particular, foods containing zinc and selenium are useful).
- Regular sex life.
- Sexually transmitted diseases need to be treated promptly.
- Tight underwear should not be worn. Avoid overheating the testicles.
It is necessary to understand that infertility is not a death sentence, so if there are no serious congenital pathologies, then it is quite possible to improve the functioning of the reproductive function. Therefore, taking care of men's health is the work of men themselves.
Testicular biopsy
This test is used to determine whether sperm can be produced normally. This is not the most common test for male infertility, as it is traumatic and unpleasant. But sometimes it is simply necessary to undergo such a procedure.
The process involves obtaining a sample of sperm from the testicle using a needle. The sample is examined in the laboratory for structural problems. With this diagnostic test, it is easy to identify damage to the outer layer of sperm, sperm with fragile DNA and impaired motility.
Testicular biopsy
If the sperm is normal and healthy, then infertility may be caused by blocked ducts or a sperm transport problem.
Sexual activity and infertility
According to doctors, male infertility is the inability of a sexually mature man to conceive a child. Moreover, this pathology has nothing to do with the ability of representatives of the stronger sex to sexually satisfy women.
It should be understood that the presence of an erection does not mean that the male reproductive cells contained in the sperm are viable and active. That is why the detection of male infertility is carried out on the basis of a complete examination of the patient.
Transrectal ultrasound
High-frequency transrectal ultrasound provides images of the prostate, seminal vesicles and ejaculatory ducts. This allows the practitioner to check for any blockages in the ducts along the way the sperm is transported.
Transrectal ultrasound
To perform the procedure, a lubricated probe is placed in the rectum. This allows real-time imaging of the seminal vesicles and ejaculatory ducts. This diagnostic test can confirm or correct the problem of blocked ducts.
History taking
To select further examination tactics and predict the results, the doctor conducts a conversation with the woman, collecting information about past diseases, surgical interventions, existing chronic pathologies and the presence of genetic abnormalities in family members.
During the conversation, the doctor finds out how the woman’s sexual development proceeded:
- at what age did menarche occur?
- at what age did a regular menstrual cycle become established?
- what is the duration and nature of menstrual flow;
- whether the woman experiences intermenstrual bleeding or menstrual-like discharge.
In order to find out the cause of infertility, the doctor needs to know when the woman began sexual activity, what is its regularity, and whether contraceptives are used.
To determine whether infertility is primary or secondary, the doctor needs information whether the woman was pregnant before the previous pregnancy ended: whether the woman had spontaneous abortions or childbirth.
Diagnosis of male infertility – other tests
There are a number of other tests used to detect fertility problems in men, but most of them will not be recommended by a urologist unless strictly necessary due to their high cost or invasiveness.
These tests include:
- Vital Staining test – shows the number of sperm in a semen sample
- Antisperm antibody test – checks for the presence of sperm antibodies.
- Sperm culture – checks if there is an infection affecting the sperm.
- Hypoosmotic swelling test – checks whether the outer layer of sperm is damaged.
- Chromosome analysis is a test for genetic defects.
- Specialized sperm function tests - see how well the sperm moves, attaches to the egg and whether it is able to penetrate the egg.
Once the underlying problem is identified, the urologist practitioner will provide the couple with possible solutions to overcome infertility.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
About the effectiveness of home methods
To date, there are no reliable laboratory methods to determine infertility in men at home. However, there are some useful tips that can help you identify indirect signs of loss of fertility. A visual assessment of his ejaculate will help to understand whether a man is infertile. The following signs will indicate that sperm quality is below acceptable levels:
- excessive viscosity or wateriness;
- the presence of yellowish or other impurities;
- presence of lumps;
- appearance of whitish threads.
A significant symptom may be a dull and aching pain in the lower abdomen that appears after walking or physical activity. It can indicate varicocele, a pathology affecting the testicles. It is worth paying attention to such everyday disorders as frequent urge to urinate or a burning sensation during this process.
It is imperative that men who have a female body type: with wide hips, narrow shoulders and a characteristic distribution of subcutaneous fat need to be tested for infertility. In such a situation, we are talking about a systemic endocrine failure, due to which the body does not receive male hormones in the required volume.
Finally, it is strongly recommended to undergo a check-up or laboratory test if the orgasm after intercourse is not accompanied by ejaculation at all. Any of the listed pathologies is a reason to get tested for infertility in a situation where we are talking about a chronic manifestation and not a single disorder.
Endoscopic examination methods
Endoscopic examination during pregnancy is carried out using methods such as hysteroscopy and laparoscopy.
Hysteroscopy
This study allows you to detect pathologies of the uterus - endometriosis, polyps, intrauterine adhesions, fibroids and adenomyoma. A doctor can assume the presence of these diseases based on a number of characteristic symptoms: intermenstrual bleeding, the appearance of spotting after sexual intercourse.
Using hysteroscopy, metrorrhagia is diagnosed and the causes of menstrual irregularities are determined.
Gas or liquid can be used as a means of dilating the uterine cavity during hysteroscopy. Gas hysteroscopy is typically a diagnostic procedure performed on women when they are not menstruating.
Hysteroscopy using liquid to expand the uterine cavity is used more often than gas.