Why is tonometry performed?
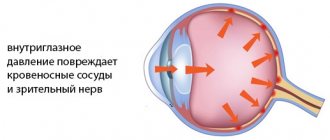
The anterior chamber of the eye, which is limited in front by the cornea, along the back wall by the lens and iris, is filled with a special liquid (aqueous humor).
The fluid (secretes from 3 to 9 ml per day) constantly moves, performing the function of nourishing and protecting avascular structures (lens, cornea), when it stagnates, intraocular pressure increases, while at the beginning of the development of the pathology the symptoms are very scarce.
Tonometry of the eye makes it possible to recognize the onset of changes in time and prevent the development of glaucoma (optic nerve atrophy, which leads to irreversible loss of vision).
The concept of an audiogram, the mechanisms of its decoding
The result of the hearing aid testing is an audiogram - indicators converted into a graph. The frequency of the sound is displayed along its horizontal axis, and the corresponding hearing threshold is displayed along the vertical axis, while the vector axis is at the top. The displayed sound wave threshold ranges from 125 to 8000 Hz.
A separate audiogram is compiled for each ear, which is designated differently: the graph of the right ear is marked as AD, the left - AS. The appearance of the graphs is also different - the audiogram of the right ear is displayed in red, and instead of dots, there are circles on it. For the left ear, the graph is displayed in blue and crosses instead of dots.
The graphs show the level of air and bone conduction: in the first case, the graph looks like a solid line, in the second - like a dotted line. In this case, the bone conduction line is always located higher than the air line. The distance between them is called the air-bone interval, and normally should not exceed 10 dB.
By reading the charts, the audiologist is able to diagnose hearing loss, its degree, as well as the presence and nature of other disorders. The most common types of hearing loss that a doctor can determine on a schedule are:
- conductive (when the air conduction of sounds is disrupted);
- mixed (if both types of sound transmission are impaired);
- sensorineural (in cases where bone sound conduction repeats air sound conduction).
The causes of hearing loss in some cases are also displayed on the graph, for example, if the air-bone interval is more than 20 dB, the doctor draws conclusions about the presence of conductive hearing loss, which appears as a result of otosclerosis or otitis media. The importance of the graph for the final diagnosis cannot be overestimated. Decoding the audiogram does not make it possible to draw absolutely accurate conclusions without further research.
When examining a patient, it is important for the doctor to determine the extent of the lesion and the level of hearing impairment.
To do this, he pays attention to the location of the graph curve. In patients with mild hearing loss, decibel values are between 20 and 40 dB, with moderate hearing loss, the graph values are between 41 and 55 decibels, with moderate-severe hearing loss - from 56 to 70 dB, and severe hearing loss is depicted in values between 71 and 90 dB
The readings for each ear may vary. The range from 0 to 25 dB is considered normal. A graph of loudness above 91 dB indicates absolute deafness.
If the curve tends to go down, this indicates difficulty in perceiving high frequencies, and vice versa. The curve, which is shaped like a hyperbola, indicates that hearing loss is greatest in the middle of the range. In such cases, a person can only perceive very loud sounds. Audiogram indicators are necessary for diagnosing the degree of hearing loss and determining the cause of the impairment; its data is very important for the process of selecting a hearing aid.
Types of tonometry
There are several methods for measuring IOP; the choice of method depends on the availability of special instruments and devices, the condition and age of the patient.
Non-contact eye tonometry
Non-contact (pneumotonometry) tonometry of the IOP of the eye is a procedure in which there is no contact with the cornea. The method is based on the effect of air flow on the visual organ, the device automatically scans the degree of deformation of the cornea, does not require special preparation, pain relief, and the risk of infection and complications is minimized.
The diagnostic manipulation takes a few seconds; for this, the patient sits on a chair, places his chin on a stand, opens his eye wide and focuses his gaze on the burning point, the built-in computer automatically calculates the IOP value.
The method is not accurate, it is not used to treat patients with glaucoma, it is intended for mass examination of people for increased intraocular pressure, for children and people in the postoperative period.
Maklakov method
To measure IOP using the Maklakov method, a metal tonometer in the form of weights weighing 10 grams is used. perform the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient is placed on the couch.
- An anesthetic (pain reliever) is instilled into both eyes one at a time.
- The weight plates are lubricated with special paint.
- The patient looks straight ahead, the colored plates are placed in the center of the cornea and impressions are made.
- An antiseptic is instilled into the patient's eyes.
- The resulting traces are transferred to paper that has been moistened with alcohol, their diameter is measured using a special ruler, and the result is determined using the Polyak table.
The method is the most accurate and is used in the diagnosis of glaucoma.
Goldman tonometry
Goldmann tonometry (applanation) includes the following stages of the procedure:
- The tonometer is installed at the slit lamp.
- An anesthetic and a fluorescein solution are instilled into the patient's eyes to stain the surface of the cornea.
- The patient sits on a chair located behind a slit-shaped lamp, fixes his head on a stand, resting his forehead on the support plate and looks as if through a microscope.
- The device is brought into the correct position, a filter with cobalt blue is turned on on the lamp.
- The prism of the device is placed opposite the cornea, gradually applying pressure to the visual organ, while the colored circles should meet; for this, the screw is rotated (it should reach the 3.06 mm mark).
- The results of the study are calculated using the apparatus scale.
Applanation tonometry is considered the most accurate way to measure IOP.
Daily tonometry
Daily tonometry is a complex diagnostic method, because the procedure should be performed 3 times a day for 7 days or more. The primary measurement is made at 8 am, the second at lunchtime (12-13 o'clock), the last one no later than 8 o'clock in the evening.
For this method, a contact method is used (palpation, applanation), the doctor pays attention to the following indicators:
- difference between measurements;
- IOP level;
- difference in readings throughout the day.
The ophthalmologist calculates the peak number of pressure surges and displays the average daily value.
Impression tonometry
Impression tonometry (Schiotz method) is used for curved corneas when it is not possible to capture a large area. Before the procedure, an anesthetic is instilled into the patient and pressure is applied to the eyeball using a rod with a rounded end.
The amount of indentation is determined using special nomograms, converting the values into mm of mercury.
What is tonometry in medicine?
The most accurate way to measure pressure inside the visual organ is tonometry. The procedure is carried out using a device that, by acting on the cornea, determines how deformed the eyeball is.
If no changes are observed, the pressure reading is normal. In millimeters of mercury it is 10–21. Using the device, one measurement is taken in the morning, the other in the evening. The difference in pressure between them should not be more than 5 mm. Based on these indicators, the ophthalmologist identifies the disorder and selects a treatment method.
Device for measuring intraocular pressure PASCAL
This article will help you understand what problems Polinadim eye drops will help you with.
Indications and contraindications
Tonometry should be performed for such indications as:
- Retinal detachment;
- Disturbances in the development of the eyeball;
- Veil, the appearance of multi-colored circles before the eyes;
- Postoperative complications;
- Neurological diseases;
- Deterioration in clarity and visual acuity;
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- Suspicion of the development of glaucoma;
- Sudden lacrimation, redness of the cornea;
- Painful sensations in the eyes, frequent headaches;
- Endocrine diseases.
The procedure is also prescribed for people whose close relatives suffer from glaucoma.
The procedure is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Viral or bacterial eye infections;
- Drug, alcohol intoxication;
- High degree of myopia (-6 or more);
- Mental disorders in which the patient behaves aggressively;
- Intolerance to anesthetics;
- Injury to the organ of vision, violation of the integrity of their outer shell.
Pathologies of the cornea (keratoglobus, keratomalacia, microcornea) are also contraindications.
How is an ultrasound of the eye performed?
The entire eye can be examined with just a few movements of the probe. The eye is divided into 4 dynamic quadrants and another through a static slice through the macula and optic disc, also known as the longitudinal macula.
The quadrants are designated T12, T3, T6 and T9. They correspond to a dial superimposed on the eye.
An ultrasound examination is performed through the patient's eyelids, applied to the eyelids after applying anesthetic drops.
Before the procedure, a special gel is applied to the surface of the upper eyelid. It ensures contact of the sensor with the tissues of the organ of vision. During diagnosis, the ophthalmologist applies light pressure to the eyeball and asks the patient to make movements in the direction of the quadrant to be assessed.
This ensures optimal position of the eyeballs and makes all structures accessible to detailed examination.
The probe rotates around so that the sound waves always pass through the center. This rotational motion maximizes the amount of retina imaged during the scan.
Cross-sectional view 1 - T12 study:
- the patient looks up;
- the probe is placed on the bottom;
- scanning should begin from the limbus, identifying the shadow of the optic nerve, in order to orientate and make sure that the posterior segment is diagnosed;
- The probe is slowly advanced toward the inferior fornix until visualization of the T12 quadrant is complete.
When examining the T6 quadrant, the person looks down. It is necessary to ensure that the computer is receiving an image of the retina/optic nerve.
When scanning the medial/lateral quadrants, the patient looks to the left
After obtaining an image of the retina and optic nerve, gently move the probe along the anterior portion to complete the assessment of that area. To view the T3 quadrant of the left eye, the patient should still look to the left, but the probe will be placed on the medial limbus
The T9 quadrant scan of the right eye is simply a reverse T3 scan. The patient's gaze is directed to the right side.
Types of ultrasound
There are several types of ultrasound examination. Each of them performs specific tasks and is done using its own technical features:
- B-scan uses sound waves to produce an image. Allows you to get a two-dimensional picture. The ultrasound unit converts sound energy into electrical energy. The patient closes his eyes, the probe with the gel is placed above the eyelid. Ultrasound is non-invasive and the examination is painless. No dilatation is required. Takes about 10 minutes.
- Optical biometrics. This test measures the length of the visual organs so that the correct dimensions of the intraocular lens can be calculated when removing a cataract. An anesthetic is instilled. An ultrasound probe is placed in a saline solution to produce a series of one-dimensional echoes that measure length. No dilatation is required. The procedure lasts about 10 minutes.
- Ultrasound biomicroscopy. Shows a view of the front of the eyeball. Using this technique, it is possible to examine the cornea, iris and ciliary body.
- OCT (optical coherence tomography) uses light waves. Testing is most often performed in patients with macular degeneration. The central visual part of the retina (macula) is examined and its layers are measured. Dilation is necessary for this ultrasound technique for optimal viewing of the macula. The manipulation takes up to 15 minutes after the pupil is fully dilated.
- One-dimensional mode. It is used to obtain information about eye tissues, measurements of various parameters and characteristics.
- Three-dimensional echoophthalmography. Allows you to see all the structural features of the visual analyzer and the location of the vascular system.
Carrying out tonometry of the eye
Before undergoing tonometry, the patient should prepare as follows:
- A day before tonometry, stop using drugs;
- 12 hours before the study, refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages;
- 4 hours before testing, avoid drinking heavily (no more than 2 cups of liquid);
- Tell your ophthalmologist if you or your immediate family have glaucoma;
- Remove contact lenses and refrain from using them for another 2 hours after the procedure, take glasses with you;
- Remove or unfasten anything that compresses the neck area (tie, scarf, jewelry) so that there is no pressure on the veins and the measurement result is reliable.
During the procedure, you need to relax as much as possible and behave calmly. Tonometry of the eye is the simplest diagnostic method of research, which helps to identify or prevent the development of pathological abnormalities in time, while it does not cause serious consequences and does not injure the organ of vision.
When is the ophthalmotonometry procedure performed?
As people age, various health problems arise. After 40 years, checking intraocular pressure cannot be ignored. Tonometry is prescribed if glaucoma is diagnosed in a patient or a close relative. In the first case, it is carried out every 3 months, in the second - once a year.
The indication for the procedure is the presence of:
- neurological problems;
- endocrine disorders;
- abnormal structure of the visual organ;
- retinal detachment;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
See also information about the treatment of retinal detachment.
Tonometry is resorted to when a person complains that his eyes often hurt, the cornea turns red, and tears constantly flow.
An effective local antiviral drug or “dummy” - instructions for Poludan eye drops.
Finger method technique
In case of infectious infections, you should not resort to research! You should first undergo a course of antibiotic therapy, for example, with Tobropt. Instructions for Tobropt eye drops are provided here.
When using a non-contact technique, the procedure is carried out without restrictions. Other methods are not prescribed:
- if you are allergic to drugs;
- if the cornea is damaged;
- eyeball injury.
Tonometry is not done if the patient has a disease of the visual organ caused by harmful bacteria. The procedure is not performed after taking drugs or drinking alcohol.
The article is intended for informational purposes only. The doctor can prescribe medications after learning the results of the examination.
This type of manipulation is carried out using metal weights
Find out what clouding of the cornea of the eye indicates here.
Norm for eye tonometry
The IOP norm depends on the research method; for children and adults under 60 years of age it varies between 10-21 mm Hg; if weights were used, the indicator increases to 25 mm; the most favorable indicators are considered to be 15-16. After 60 years, the limit of normal IOP is 26 mm.
In the morning, IOP is higher than in the evening, but the difference should not exceed 3 mm. If the level exceeds 21 mm for several days, but there is no pathology of the optic nerve, the specialist suspects ocular hypertension, which can develop into glaucoma in the absence of adequate treatment.
When the indicators exceed the norm by several units, the patient is referred for additional examinations; in men the indicators are always higher than in women.
A measurement result of 26 mm indicates glaucoma; a reading of 27 units indicates an advanced stage of the disease.
Increased IOP
The pressure inside the eye can be increased not only due to glaucoma; the following factors can provoke this phenomenon:
- Rupture of blood vessels in the eye, resulting in red spots appearing on the whites of the eyes;
- Blurred vision after sleep;
- Pain in the eyebrows and temples;
- Eye strain (reading, watching TV).
In this case, the nature of high blood pressure can be transient (one-time increase in IOP for a short time), labile (periodic increase), stable (regular increase).
In such cases, increased IOP may indicate both the development of glaucoma and indicate the presence of optical neuropathy (damage and atrophy of the optic nerve) or retinal detachment.
Reduced IOP
Eye pressure can drop for several reasons:
- The presence of infection in the body;
- Diabetes;
- Anomalies in the development of the eyeball;
- Dehydration of the body;
- Surgical interventions;
- Microtraumas of the eye shell.
The patient notes discomfort, dry mucous membranes, frequent blinking occurs, the organ of vision begins to decrease in size, and visual acuity decreases.
A decrease in indicators also indicates the beginning of a pathology of the optic nerve and the need for dynamic observation.
Ultrasound examination of the eye and orbit
Ultrasound examination of the eye and orbit is a highly informative, safe, non-invasive instrumental research method that allows one to obtain a two-dimensional image of the vitreous cavity, the posterior segment of the eye and the orbit. A/B scanning provides high-resolution images and allows measuring the size of intraocular structures with an accuracy of 0.01 mm. Ultrasound examination of the eye is performed for the following main indications:
- Measuring the thickness of the cornea, the depth of the anterior chamber of the eye, the thickness of the lens, the size of the vitreous body, the anteroposterior size of the eyeball. This information is necessary when performing a variety of operations, including cataract removal.
- Identification and determination of the size and topography of neoplasms of the ciliary body, choroid and retina, retrobulbar tumors. Quantitative assessment of their changes in dynamics. Differentiation of clinical forms of exophthalmos.
- Identification, assessment of the height and extent of retinal detachment, detachment of the ciliary body and choroid and their relationship with the vitreous body. Differentiation of primary retinal detachment from secondary retinal detachment caused by tumor growth.
- Detection of destruction, exudate, opacities, blood clots, mooring in the vitreous body. Determination of their localization, density and mobility, relationship with the retina of the organ of vision.
- Detection of foreign bodies in the eye due to trauma to the organ of vision, including clinically invisible and X-ray negative ones. Determination of their location in the eye and relationship with intraocular structures.
- Calculation of the refractive power required for implantation of an artificial eye lens (IOL).
| Recently, a new method of acoustic visualization of intraocular structures of the anterior segment of the eye - ultrasound biomicroscopy - has been introduced into clinical practice. This method allows you to examine the anterior segment of the eye at the microstructural level. Ultrasound biomicroscopy is a scanning ultrasound immersion diagnostic procedure with linear scanning, which provides quantitative and qualitative information about the structure of the anterior segment of the eye (cornea, iris, anterior chamber angle, lens) for the purpose of diagnosing glaucoma, anterior tumors, and the consequences of eye injuries. |
Fluorescein angiography with computer registration
Today, not a single clinic in the world can do without this informative diagnostic study. Fluorescein angiography, based on contrasting retinal vessels with a special dye, is the only method of its kind for accurate and effective diagnosis of diseases of the retina, optic nerve and choroid. It reveals the structure of the vascular bed of the retina, gives a clear picture of hemodynamics, the state of permeability of the vascular walls, pigment epithelium and Bruch's membrane, and allows one to differentiate inflammatory changes from vascular, dystrophic and tumor processes.
Fluorescein angiography is performed on a retinal camera both for diagnostic purposes and to determine the indications, tactics and timing of laser treatment, as well as to evaluate the results of treatment
This study allows us to identify ischemic zones and newly formed vessels, which is important to identify in diseases such as diabetic retinopathy, thrombosis of the central retinal vein and its branches, occlusion of the central retinal artery and its branches, vasculitis, anterior ischemic neuropathy, pathology of the central retinal zone (edema, cysts, ruptures), recurrent hemophthalmos and a number of other diseases