Effect of nicotine
The nicotine contained in a smoked cigarette causes harm to the entire body by damaging the cardiovascular system and impairing blood circulation in the organs. The central nervous system is also affected, due to which the regulation of the activity of internal organs deteriorates. Damage to these two systems leads to thickening of the walls of blood vessels, the development of atherosclerosis, increased blood pressure, and systematic malfunctions of organs. The consequences of these violations are often irreversible.
Features of the hormonal background of smokers
The main myth about the benefits of smoking for your figure is based on changes in the hormonal background of the female body. It is believed that by quitting smoking, a woman will begin to gain weight - this opinion is wrong. Nicotine itself has no effect on body weight (it only slightly reduces appetite), but it has a detrimental effect on the endocrine system and causes disruptions in its functioning. This can provoke both weight loss and accumulation of excess fat.
After quitting smoking, some ladies actually get fat, but not because of the lack of tobacco, but because they begin to “eat up” the stress caused by the changes. If you give up additional high-calorie snacks, your weight will quickly return to normal.
Cigarette smoke has a negative impact on the ability to get pregnant. Under the influence of tobacco, the synthesis of the female hormone estrogen is reduced. Its lack provokes disruption of the menstrual cycle, and periods are painful. Menopause occurs earlier than in non-smoking women.
Attention: doctors believe that a smoker's chances of conceiving are the same as those of a woman with one ovary!
Components of inhaled smoke provoke an increase in the level of the hormone FSH in the blood, which affects the activity of the gonads. This further reduces the chance of pregnancy. Increased production of oxytocin vasopressin stimulates uterine contractions, creating the preconditions for miscarriage. A constantly increased level of synthesis of sex hormones leads to premature aging of the body.
The most dangerous misconception (or justification for oneself) is that pregnant women should not suddenly quit smoking, as this will disrupt hormonal levels. There is no scientific damage to this. On the contrary, the functioning of the body’s systems will be normalized, and the process of bearing a child will proceed much easier. If you continue to smoke, great harm will be done to the fetus.
The effect of active and passive smoking on vision
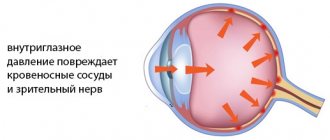
The detrimental effect of smoking on vision is mainly due to the vascular component. Toxins from tobacco smoke, penetrating the body, affect the entire vascular bed, in particular the vessels in the eyes. As a result:
- Vasospasm.
- Increased intravascular pressure.
- Formation of plaques in the lumen of blood vessels due to atherosclerosis.
- Partial or complete closure of the lumen of the vessel, cessation of its functioning.
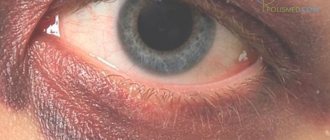
Tobacco smoke also directly affects the eyes. Consequently, a passive smoker, being near a smoking cigarette, is also exposed to harmful effects due to inhalation and direct contact of smoke with the eyes.
Substances contained in tobacco smoke that have a direct effect on the eyes:
- phenol and its derivatives;
- ammonia;
- hydrogen sulfide;
- myosmin;
- acetic and formic acids.
Harm
Systematic inhalation of smoke and tar leads to a deterioration in the functioning of systems in the human body. With each cigarette, the risk of developing cancer of the lungs, palate, and lips increases. The connection between vision and smoking is not the most obvious: first of all, smoke affects the mouth and respiratory tract. Tobacco smoke is a strong allergen and can cause an allergic reaction, so it affects people who smoke actively or passively.
The effect of smoking on vision and its consequences is motivation to quit the bad habit. It brings imaginary peace and harms all the internal organs of the addict. Habit leads to the fact that the whole body is dependent on the ritual: the daily routine, sleep, and food intake are adjusted to it.
The health of a smoker is in constant danger - damage to central vision is only one of the consequences of the habit.
If the body is weakened and the immune system is reduced, you can go blind even without prolonged smoking. Addiction is dangerous for people who have chronic diseases associated with decreased vision.
How does it affect
The main part of smoking mixtures is nicotine. The active substance is a poison that destroys the mucous membranes of the eyes or oral cavity. Nicotine damages blood vessels, and as a result, blood circulation is impaired. Changes occur throughout the body: blood vessels dilate both in the brain and in the eyeball (the retina changes). The addict may be unaware of the complications of the habit and may not pay attention to temporary blurred vision.
The negative effect on the eyes is due to the fact that oxygen starvation occurs. In a smoker, the mucous membrane of the eye dries out, and minor inflammatory processes appear. Changes inevitably occur in the eye tissues due to constant contact with smoke. The risk of lens pathologies increases as a person ages: the older he is, the greater the likelihood of developing senile blindness.
Your Narcologist warns: Why can vision deteriorate in someone who quits smoking?
In heavy smokers, with a constant supply of nicotine, the body triggers defensive responses. Over the course of many years, these defense mechanisms are strengthened, and the functioning of the organ of vision is adjusted to the constant load on the blood vessels. When you stop smoking, the load on blood vessels decreases, but the body's protective reactions continue to work. All this determines decreased vision in smokers who decide to give up the bad habit. To solve any difficulties that arise, you need to contact a specialist.
How to fix the problem and improve vision?
The main way to speed up remission is a healthy lifestyle. By eliminating the intake of toxins, a person provokes the body to normalize the production of necessary substances, and the regeneration of affected cells is accelerated. This equally applies to passive smoking - access to poisons must be stopped by any means .
Walks in fresh air, frequent ventilation of rooms, and regular cleaning are recommended.
However, the body is not always able to recover on its own. If medication is required, it is prescribed by an ophthalmologist and corresponds to the identified diseases. In some cases, the patient can speed up recovery on his own by using special exercises and choosing the right diet.
Eye diseases caused by smoking
Smoking contributes to the development of various diseases.
Eye irritation
It can act as an independent disease or a sign of a more severe lesion.
Symptoms: redness, lacrimation, itching, burning, soreness, possible dryness of the cornea.
Treatment: as a rule, when you quit smoking, it goes away on its own. It is possible to use moisturizing eye drops, for example Visine.
You should consult a doctor if:
- Symptoms do not subside for more than a week.
- Pain and discomfort intensify.
- There was discharge from the eyes.
- Vision has deteriorated.
Destruction of the macula (macula)
The retina of the eye has a heterogeneous structure. On the back wall of the retina there is a collection of cones (vision cells) called the macula. This formation ensures clear images in sufficient lighting.
Symptoms:
- Blurry, blurred vision. In brighter lighting conditions, image clarity may become clearer. If the lighting gets worse, go down.
- Image defect. The appearance of a point in the center of the field of view. As the disease progresses, its size may increase.
- It is difficult to focus on small objects (text, facial features).
- Curvature of straight lines. For example, a straight line of a fence or corner of a house seems curved.
Treatment: consultation with an ophthalmologist is necessary.
Cataract
Cataract is clouding of the lens. The lens is a lens-shaped formation in the eye that is responsible for focusing the image on the retina. Normally, it is completely transparent. Contact with smoke enhances degenerative processes, resulting in accelerated clouding of the lens. A non-smoker can also develop cataracts, but by the age of 70-75, while a smoker can develop it as early as 30-35 years.
2 mechanisms of cataract development:
- Toxins from smoke directly affect the lens. As a result, the protein of which it consists is destroyed. Cloudiness occurs.
- The body produces substances that help restore transparency. But smoking, having a complex effect, reduces the rate of their production.
Symptoms: decreased visual acuity and clarity.
Treatment:
- In the early stages - self-healing when quitting smoking.
- In advanced cases, consult an ophthalmologist. It is possible to replace the lens.
Optic neuropathy
This is damage to the optic nerve.
Symptoms:
- Eye pain.
- Perverted perception of colors.
- Decreased visual acuity, even to the point of blindness.
Treatment: consultation with an ophthalmologist.
Tobacco amblyopia
Literally, this is tobacco blindness. It develops more often in smokers with a lack of vitamin B12. Its deficiency reduces the resistance of the optic nerve to the effects of tobacco smoke. As a result, neuritis develops (usually both eyes are affected).
Symptoms:
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Myopia progresses.
- Scotoma is the loss of areas from the field of view (perceived as dark spots or detected only with a special examination).
- The perception of some colors (usually red, green) disappears.
The disease can lead to complete blindness.
Treatment:
- To give up smoking.
- Consultation with an ophthalmologist.
- Drug therapy accelerates recovery processes.
With continued smoking, pathological changes in the retina and optic nerve become irreversible. The person runs the risk of going blind.
Consequences of diabetes
This is not the first time in this material that we have been forced to draw attention to the connection between smoking, diabetes and vascular damage. Let's look at possible complications associated with different parts of the circulatory system
Microvascular complications
Degenerative processes associated with the vascular system are common to many people suffering from diabetes. Smoking accelerates and significantly increases the risk of developing complications, which include:
- Diabetic microangiopathy. Damage to small vessels of the body, leading to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
- Nephropathy. Complex renal dysfunction directly related to poor vascular function.
- Retinopathy. Impaired blood supply to the retina, leading to optic nerve dysfunction and other negative consequences.
- Diabetic neuropathy. Damage to the body's nerve fibers caused by a decrease in glucose levels.
Any other diseases that are caused by damage to small vessels are also possible.
Macrovascular complications
Along with small vessels, negative effects can also affect large parts of the system. Thrombosis, varicose veins, cholesterol plaques, ischemia and other consequences, which can result in death. All this is not only characteristic of diabetes, but is also provoked and accelerated by smoking.
Research has proven that quitting smoking significantly reduces risk factors, including chronic forms of the disease.
Development of diseases
Over the years, each new puff is the cause of pathology. Vision and metabolic processes in the body suffer due to improper blood circulation. Carcinogens accumulate in the respiratory tract, and it is difficult for the addict to breathe while smoking; oxygen starvation only intensifies. Good eyesight and smoking are two mutually exclusive concepts.
- Diseases of the organs of vision, as a result of addiction:
- macular degeneration;
- cataract;
- blindness.
Smoking affects vision to varying degrees: if one eye suffers from smoke, the other takes on the entire load - both eyes go blind. Trophic processes gradually appear (cells die).
The cells in the center of the eye die first. Passive smoking causes damage to the lens of the eye and allergic reactions. It is difficult to identify the root causes of the disease, and any changes are perceived as natural processes. The smoking experience and how the addict fights it are also important. If he sets himself an ultimatum “you quit smoking, otherwise you will go blind,” negative changes will be prevented.
Macular degeneration
Nicotine is a poison, and the more you use it, the worse the complications. Macular degeneration occurs due to the structure of the eye: the main part of the eye is the macula (the so-called macula), which is the first to be affected by smoking. The macula has special functions:
- it is responsible for vision during daylight hours;
- it contains photoreceptors;
- it contains cones that help you see during the day.