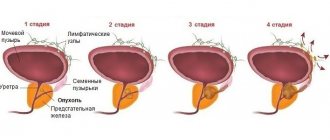
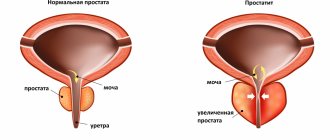
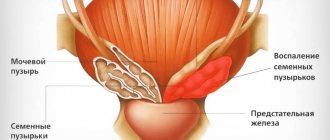
What is prostatitis
Prostatitis is an acute or chronic disease of the prostate gland. This is an inflammation that not only causes pain and problems with urination, but also affects sex life.
The urethra passes through the prostate gland, which begins in the bladder and ends in the head of the penis, which is why all kinds of inflammatory processes occurring in the prostate affect the process of urination and cause burning symptoms.
Prostatitis often occurs in men who have numerous unprotected sexual intercourse. Practice safe sex and use condoms, which will protect you from unwanted infections.
What are the dangers of pregnancy during prostatitis?
b http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;″>r>
- Frozen fruit.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- What caused prostatitis in a man?
- Time of conceiving a child: before or after the start of drug therapy.
- The influence of inflammatory processes on the condition of the male genitourinary system.
Prostatitis and frozen pregnancy
There is a high probability of miscarriage in the early stages or fetal death in the later stages. After birth, the child experiences mental retardation, disruption of the immune system, etc.
Ectopic pregnancy with prostatitis
The consequences of an ectopic pregnancy are rupture of the fallopian tube, leading to peritonitis and, as a result, death. There is a high risk of dying from severe blood loss. The cause of ectopic pregnancy is low sperm motility or a change in the structure and density of the microflora of the female genital organs. After fertilization, the egg develops inside the fallopian tube. Over time, the tissue cannot withstand it and rupture occurs. To prevent consequences, it is necessary to remove the fetus through surgery.
Is it possible to conceive a healthy child with prostatitis?
The chances of getting pregnant and giving birth to a healthy baby during the period of remission of the disease are high
At the same time, it is extremely important to constantly consult with your doctor and avoid common mistakes:
- Trying to conceive a child while taking pills for prostatitis - unprotected sex leads to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, disruption of the woman’s genitourinary and reproductive systems, and the development of chronic diseases. Even if you feel better, you should have sex with a condom.
- Decide for yourself when you can conceive a child after completing a course of drug therapy. It will take 3 months for the body to completely renew itself. Consequently, test results indicating that the man has overcome the disease will be ready only after the end of this period. To conceive a healthy child from a man with prostatitis, you should have open, unprotected sex only after the permission of the attending physician.
We advise you to study - Improving erectile function with 18 means and methods for men, at home
If you follow your doctor's recommendations, it is quite possible to conceive and give birth to a completely healthy and strong baby from a man suffering from prostatitis.
Sex with prostatitis if your wife is pregnant
It is possible to have sex during pregnancy if your partner has prostatitis, but this should be done with a condom, for several reasons:
- There is a possibility of transmission of an infection that affects the development of the fetus and can cause miscarriage or premature birth.
- Even if reproductive function is not affected, bacterial prostatitis easily becomes the cause of candidiasis and the development of cystitis.
Unprotected sexual relations also have a negative impact on a man. They can provoke a new round of exacerbation. To eliminate possible consequences, sexual contact between a pregnant woman and a man with prostatitis is carried out exclusively with a condom. Due to serious complications and a threat to the unborn child and his mother, in each specific case you should contact one of the family planning centers. Getting pregnant from a man who has had prostatitis and giving birth to a healthy child without mental and physical impairment is possible only after completing a full course of therapy and restoring the body.
Causes of prostatitis
Among the many factors predisposing to the development of prostatitis, the following can be distinguished:
• past venereal and infectious diseases;
• unhealthy lifestyle, use of alcohol, tobacco and drugs;
• physical and mental stress;
• irregular sexual relations.
Many men are embarrassed to see a doctor with this problem and try to self-medicate or come to terms with all the inconveniences caused by the course of this disease. But this is absolutely impossible to do, the chronic stage of prostatitis is quite difficult to treat, and irreversible processes can occur, such as infertility and dysfunction of a man’s sexual functions. Our clinic specialists will help you overcome all the symptoms of this disease and ensure complete confidentiality.
Prostatitis and conception of a child
Having prostatitis can significantly affect your ability to conceive a child. Prostatitis leads to a decrease in the number of sperm in the ejaculate and reduces their motility.
From a scientific point of view, this process can be explained as follows: the secretion secreted by the prostate is involved in the process of sperm maturation. When the composition of prostate secretions is disrupted due to inflammation, the motor activity of sperm decreases and the proportion of immature sperm of irregular shape increases. All this affects the ability to conceive, complicating it or leading to the inability to conceive naturally. In this case, the first thing the doctor will prescribe for you is a spermogram, an analysis that will help you find out whether you are able to conceive a child.
Married couples who are unable to conceive a child naturally must undergo a medical examination, during which both partners pass all the necessary tests. If prostatitis is caused by any sexually transmitted or infectious disease, a treatment program should be drawn up for both men and women.
Prostate adenoma and male infertility – is there a connection?
The prostate (or prostate gland) is one of the most “fragile” and vulnerable organs, with which most men have problems throughout their lives.
Chronic prostatitis affects about 40% of men aged 25 to 60 years, prostate adenoma affects more than 50% of men over 60 years of age, and prostate cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in men.
Problems with the prostate have a serious impact on the functioning of the urinary system, causing diseases such as cystitis, pyelonephritis, and urolithiasis. They can also cause a decrease in sperm quality and affect male fertility. Let's try to figure out how prostatitis, prostate adenoma and infertility in men are connected. And will preventing prostate disease help preserve male fertility?
Although problems with the prostate can occur in very young men, and some have a healthy prostate gland at 80 years of age, in general, statistics indicate that the risk of developing prostatitis and prostate adenoma increases significantly with age.
Thus, according to medical observations, men 40-49 years old experience prostatitis 1.7 times more often than those under forty years of age. And upon reaching 50-59 years old - 3 times more often than men 20-39 years old. As for prostate adenoma, at the age of 40-50 years it occurs in every fourth man, at 50-60 years - every second man suffers from this disease, at 60-70 years adenoma is diagnosed in 65%, at 70-80 years - in 80% men.
This is due to the fact that changes occur in a man’s body with age. As a result, the prostate gland also suffers. After 35 years, men begin to develop androgen deficiency, microcirculation in the prostate tissue deteriorates, and the consequences of chronic diseases accumulate, which contribute to the development of prostatitis.
Also, with age, the prostate increases in size, and so-called fibrous tissue appears in some parts of the organ. This is prostatic hyperplasia, the more common name is adenoma. Having grown to a certain size, the adenoma begins to compress the urethra, causing unpleasant, often disruption of erectile and sometimes reproductive function.
The connection between prostatitis and infertility is due to the fact that the prostate gland secretes a secretion, which is one of the components of seminal fluid and makes up approximately half of its total volume. The inflammatory process in this organ can lead to intoxication of the secretion; harmful substances in the secretion have a negative effect on sperm, as a result of which sperm in prostatitis deteriorates . Thus, if a man is diagnosed with chronic prostatitis, sperm become sluggish and inactive, and their morphological structure is disrupted.1
If inflammation is not eliminated in a timely manner, fibrous tissue may form and sperm will not be able to enter the seminal fluid, so-called obstructive infertility will occur in men. Prostatitis often becomes chronic.
Many researchers are inclined to believe that the triggering mechanisms for the development of both chronic prostatitis and prostatic hyperplasia are the excessive formation of free radicals in the body.2
Free radicals are unstable molecules that have so-called unpaired electrons. Trying to compensate for the lack of electrons in their molecules, free radicals attack the cells of the body, including prostate cells. This leads to activation of inflammatory processes, which contributes to the development of prostatitis. In addition, free radicals damage healthy prostate cells and provoke their degeneration into fibrous tissue. Subsequently, this is fraught with the development of not only prostate hyperplasia, but also malignant tumors.
Free radicals also have a destructive effect on the sperm themselves and on the genetic material they contain. This largely explains the fact that with prostate a man’s sperm contains an excessive proportion of morphologically abnormal sperm.
Increased activity of free radicals is associated with the risk of developing hormonal imbalance and deviation of testosterone concentration from the norm, which leads to an increase in the level of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the body, an active product of testosterone metabolism. An increase in dihydrotestosterone provokes increased division of prostate cells and contributes to the development of hyperplasia.
Typically, free radicals are neutralized by the body itself with the help of antioxidants - compounds that somehow interact with free radicals, turning them into low-active molecules. In other words, antioxidants protect cell membranes and other structures, but under certain conditions the number of free radicals increases beyond measure and the body cannot cope with them on its own.
It has been proven that the formation of free radicals increases significantly due to exposure to factors such as polluted air, inhalation of car exhaust, being near sources of electromagnetic radiation, contact with pesticides and other chemicals, poor diet, hormonal disorders, smoking, inflammatory diseases, etc. And if it is completely within our power to give up bad habits and accustom ourselves to a healthy diet, then we cannot influence the state of the environment.
Antioxidants, which should be taken additionally, are designed to help the body cope with excess free radicals, as well as neutralize their destructive effect on prostate cells. The Synergin antioxidant complex includes 6 powerful natural antioxidants: the carotenoids lycopene and beta-carotene, vitamins C and E, rutin and coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone).
All these antioxidants “strangle” aggressive radicals, stop the chain reaction of the formation of new radicals, and they perform better when acted together. Antioxidant vitamins can also break down damaged parts of molecules, replacing old elements with new ones.
In addition to the antioxidant effect, each of the components of Synergin performs additional functions in the male body.
Lycopene is a carotenoid with strong antioxidant properties. It protects prostate cells from damage by free radicals, eliminates inflammatory processes, prevents the conversion of the hormone testosterone to dihydrotestosterone and controls excessive growth of prostate tissue. Lycopene improves sperm quality by increasing the number of normal active forms of sperm.3
Beta-carotene is provitamin A and is converted in the body into vitamin A, which is necessary for the normal functioning of the gonads, maturation and development of sperm. Beta-carotene also increases the body's resistance to stress, improves immunity and reduces the risk of infectious inflammatory diseases, including prostatitis.
Vitamin C strengthens the immune system, inhibits the proliferation of prostate tissue and is effective in the treatment of bacterial prostatitis. Due to its moderate diuretic effect, vitamin C also helps normalize urination in case of prostate diseases.
Vitamin E is needed by the body to produce interleukin-2, a compound that destroys bacteria, viruses and cancer cells, thereby helping to maintain prostate health.
Rutin (or vitamin P) improves the condition of blood vessels, normalizes heart rate and lowers blood pressure. Rutin also helps improve microcirculation, prevents blood stagnation in the tissues and vessels of the prostate gland, which is extremely important for maintaining prostate health, reducing the risk of developing adenoma, prostatitis and infertility . Rutin also stimulates the function of the adrenal cortex, thereby helping to regulate the daily rate of urine output.
Ubiquinone (coenzyme Q10) is a unique lipophilic antioxidant that is necessary to maintain sperm activity. Coenzyme Q10 helps increase the motility and concentration of sperm cells, reduces the content of sperm with irregular structure in the ejaculate. Several studies suggest that CoQ10 may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
The components that make up Synergin improve microcirculation in the vessels of the prostate gland, help eliminate inflammatory processes, strengthen the immune system, and reduce the risk of developing adenoma, prostatitis and male infertility .
An effective preventive course of Synergina should be at least four weeks.
It is important to understand that, despite the fact that there is a certain connection between prostate adenoma, chronic prostatitis and infertility , none of these diseases can put an end to a man’s desire to become a father. Timely consultation with a doctor, competent treatment and adherence to the rules of a healthy lifestyle lead, if not to complete recovery, then at least minimize the risk of complications, eliminate unpleasant symptoms and help preserve male fertility.
1 Reduced semen quality caused by chronic abacterial prostatitis: an enigma or reality? Leib Z1, Bartoov B, Eltes F, Servadio C. - Fertil Steril. 1994 Jun;61(6):1109-16.
2 Oxidative stress in benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review. Minciullo PL, Inferrera A, Navarra M, Calapai G, Magno C, Gangemi S. - Urol Int. 2015;94(3):249-54. doi: 10.1159/000366210. Epub 2014 Dec 5.
3 Lycopene for the prevention and treatment of prostate disease. Ilic D - Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;202:109-14. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-45195-9_13.