Prostatitis is an exclusively male disease. Previously, men over forty years of age suffered from it, today even 20-30 year old men are diagnosed. After 50 years, almost 50% of the male population suffers from this disease. The most common cause of prostatitis is infection. Bacteria that enter the prostate can lead to the development of an inflammatory process.
Many men do not experience anxiety for several years, but the inflammation becomes more pronounced and deeper. Men need to closely monitor their health, visit a urologist at the first signs of disease and strictly follow his recommendations. A prerequisite for curing prostatitis is changes in your usual lifestyle. Factors that contribute to the development and complication of prostatitis should be avoided.
Nutrition
First of all, you should reconsider your gastronomic preferences. Prostatitis requires a balanced diet. The consumption of fatty meat and fish, meat broths, strong tonic drinks, canned and smoked foods, baked goods, carbonated drinks, hot seasonings, and large amounts of salt is contraindicated.
The diet should contain a sufficient amount of liquid (at least two liters per day). Proper nutrition can reduce pressure on the prostate by normalizing the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and timely emptying the intestines and bladder.
Complaints with prostatitis
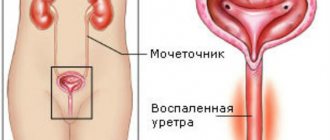
- Various urination disorders associated with narrowing of the lumen of the urethra:
- difficulty starting urination
intermittent urination
- weak stream of urine
- urination drop by drop
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
- involuntary leakage of urine
- Symptoms caused by irritation of nerve endings:
- frequent urination
frequent urination at night
- urgency to urinate
- urinating in small amounts
- urinary incontinence with the urge to urinate
- Pain in the lower abdomen, groin areas, inner thighs or lower back; various sexual disorders may also occur.
Remember that urinary disorders
and
pain symptoms
can occur not only with prostatitis, but also with adenoma (benign hyperplasia) of the prostate. Unfortunately, prostate cancer is also often diagnosed. That is why, in order to early diagnose possible prostate pathology, all men over 50 years of age are recommended to donate blood for prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle provokes congestion in the prostate gland and contributes to excess weight gain. Impaired blood supply to the prostate reduces the body's ability to fight infection and leads to an increase in the disease. In addition, prostatitis has a close connection with metabolism, and extra pounds only worsen the situation. Therefore, race walking, running and swimming have a positive effect in treating the disease.
Riding a horse is also beneficial. The rider's leg muscles are massaged, blood flow increases, and the pelvic area is warmed up. But to ride a bicycle, you need to take care of an anatomically correct saddle without a spout, which eliminates the negative impact on the genitals.
Chronic prostatitis: symptoms, causes of development, treatment and prevention
Category: Medical prevention.
- Exacerbation
- Causes
- Popular questions
- Prevention
Prostatitis is diagnosed exclusively in men. This is one of the most common diseases among diseases of the male reproductive system; 4 out of 5 men have experienced symptoms of prostatitis at least once in their lives.
Most often, men aged 20–40 years are susceptible to prostatitis at the peak of their sexual activity. Chronic prostatitis is diagnosed in every 10 men. It is characterized by periods of exacerbation and remission and disguises itself as a number of other diseases.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis include the following:
- Discomfort and aching pain in the lower abdomen, with periodic cramps that do not go away for a quarter or longer. Pain may appear in the lower back, legs, scrotum, and anus. It becomes especially painful during urination and ejaculation.
- Penile erection worsens and sexual desire weakens. First, premature ejaculation develops, but over time, on the contrary, ejaculation practically does not occur; this becomes very difficult to achieve.
- Urination becomes painful and incomplete. There is always a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
- A man’s quality of life deteriorates significantly.
There are 2 types of chronic prostatitis: bacterial and abacterial.
Bacterial (infectious) prostatitis occurs with a constant alternation of sharp exacerbations and remissions, while the prostate secretion contains infection and bacteria.
In this case, nearby organs, such as the urethra, bladder neck, and vas deferens, may also be affected, which is why the disease manifests itself in different ways. An accurate diagnosis can be made after a thorough examination.
Most often the disease manifests itself as follows:
- Frequent and painful urination.
- Burning in the urethra.
- Premature ejaculation.
- Small mucous discharge from the urethra.
- Serious sexual dysfunction.
All this greatly affects the performance and mental state of a man, which leads to long-term depression and neurasthenia.
Abacterial chronic prostatitis is a disease in which bacteria are not found in the prostate secretion. This form is very difficult to diagnose, as evidenced by numerous reviews from men on various forums. It is also very difficult to choose the right treatment regimen.
Important
Until now, doctors are faced with many unclear factors in the origin of this disease. This greatly complicates the treatment process.
Even ultrasound and laboratory tests of secretions may not show the presence of an inflammatory process. According to the recommendations of the European Association of Urological Specialists, the main signs of abacterial prostatitis are identified:
- It appears in middle-aged men.
- Prolonged pain in the pelvic area and groin.
- Impaired urinary function and frequent imperative urges.
- Erectile dysfunction and pain during ejaculation.
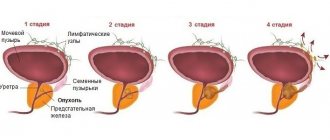
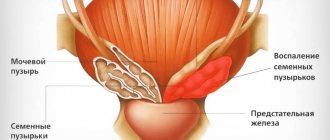
- Chronic congestive prostatitis: exacerbation and remission
- Chronic congestive prostatitis is characterized by several stages of development, which manifest themselves with different symptoms:
- Exudative - a man feels a cutting pain in the groin, scrotum and pubic area.
- There are problems with erection and accelerated ejaculation.
- Alternative - the patient complains of discomfort in the groin, scrotum and pubis.
- There is a frequent urge to urinate and rapid ejaculation during sexual intercourse.
- Proliferation - the patient notes frequent urination with a weak stream, a constant feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder. On the contrary, ejaculation becomes difficult and slow.
- Scar changes - at this stage, the prostate tissue begins to intensively thicken. The patient complains of discomfort in the pelvic and pubic area, frequent urge to urinate with a thin stream and incomplete emptying. The erection is very weak or absent altogether, ejaculation becomes almost impossible, and the orgasm is weak, without vivid impressions. Prostatitis passes into the stage of chronic prostatitis of unstable remission, in which constant pain is observed and remission occurs for only a few hours.
As for classification, it is customary to use the US NIH classification, which divides the disease into types: acute and chronic bacterial, chronic without signs of inflammation and congestive, as well as histological.
Factors and causes of chronic prostatitis in men
Despite the fact that some microbes of chronic prostatitis are present in the body of almost every person, only a few get sick. How can one explain the development of such a disease in a particular case?
Experts determine the occurrence of chronic prostatitis not only by the presence of infection in the body, but also by the conditions that influence the development of the disease.
The most common causes of chronic prostatitis in men include:
- stagnation of blood contained in the prostate, caused by a sedentary lifestyle;
- unstable sex life;
- uncomfortable and rather tight clothes;
- frequent hypothermia;
- injuries, as well as infections of various organs of the genitourinary system;
- poor nutrition;
- constant stressful state;
- frequent drinking and smoking.
Diagnosis begins with a conversation with the patient, who must accurately and completely tell what is bothering him. The doctor must find out why the patient developed chronic prostatitis, find out all the possible causes and symptoms, how they manifest themselves. The doctor should tell you everything down to the smallest detail; this will determine how correctly the diagnosis will be made and effective and comprehensive treatment prescribed.
Next, you need to palpate and submit the secretion for bacteriological analysis, through which you can determine the presence of infections and determine the resistance of the bacteria to antibiotics.
Attention
Palpation is carried out by a urologist through the rectum. This procedure makes it possible to find out the size and pain of the prostate. When palpated, hemorrhoids, adenoma or prostate cancer can also be detected. An ultrasound of the prostate will provide accurate data on the condition of the organ.
Determining the level of PSA in the blood makes it possible to exclude or confirm the presence of adenoma and prostate cancer.
If the urologist suspects the presence of a tumor, he will have to submit pieces of prostate tissue for a biopsy, which will show its presence or absence.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis is a complex and time-consuming process. Today, various methods are used to treat this disease.
Treatment with antibiotics. In this case, macrolide antibiotics and tetracycline are used.
Only the attending physician can correctly select the drug, its dosage and duration of treatment.
Usually the medications are taken for 10–15 days. After that, repeated tests are taken, based on the results of which the doctor will determine whether the patient has been cured or whether additional treatment is required.
Prostate massage is necessary so that prostate secretions do not stagnate and microcirculation occurs. This greatly contributes to a quick recovery.
However, massage is prohibited for acute prostatitis, hemorrhoids and rectal fissures.
Massage is usually prescribed as an additional therapy to antibiotic treatment.
Physiotherapy is prescribed to improve the condition of prostate tissue, thereby speeding up the healing process.
Laser therapy and ultraphoresis are used for treatment. The use of mud and enemas with mineral waters rich in hydrogen sulfide is also effective.
Herbal medicine is used as an additional stimulation for the patient’s recovery and is always used in combination with other methods. Pygeum africanum, peponen and other herbal remedies are used for treatment.
In some cases, surgical intervention may be indicated if the urethra is severely narrowed or the presence of abscesses or prostate adenoma is detected.
Important
Diagnosis and treatment must be carried out in a medical facility under the constant supervision of qualified doctors.
By consulting a doctor in time, you can achieve a quick cure. Once treatment is started, long-term remission will be observed. We can talk about complete recovery when all the symptoms of the disease disappear and laboratory tests show good results.
The most popular questions from patients about chronic prostatitis
How to cure chronic prostatitis with folk remedies quickly and effectively?
Treatment can be carried out using folk remedies. In folk medicine, the most popular is the use of infusions of chamomile, yarrow, and sage. These microenemas very well relieve inflammation that occurs in the prostate gland.
To prepare such a microenema, take two tablespoons of chamomile and pour 100 grams of the herb. boiling water You can also use horse chestnut peel for treatment, which is filled with alcohol and kept for 10 days in a dark place.
A decoction of the onion also helps. You need to finely chop two large onions and pour boiling water over them in a half-liter jar. Wrap the jar in a terry towel and let it brew for 2 hours. Then, every hour you need to drink 50 grams of the decoction.
How to cure impotence with chronic prostatitis?
Impotence can be cured at home if you follow a set of measures.
It is necessary to choose suitable drugs that will help fill the corpora cavernosa of the penis with blood. But before this, consultation with a urologist is required. Modern drugs to enhance potency - Levitra and Viagra.
You need to adjust your diet and go on a diet. You should not eat fatty foods or foods that reduce testosterone. You need to eat porridge and lean meat, drink juices and green tea.
Also, do not forget about physical activity. Walking and light running in the fresh air are very effective in this regard. You also need to swing your legs. This promotes contraction of the muscles of the anus and perineum.
How long does it take to treat chronic prostatitis and how to get rid of it forever?
Antibiotic therapy lasts 1–3 months, depending on the advanced stage of the disease. If necessary, additional treatment with small doses of antibiotics may be prescribed. Lipophilic antibiotics cope best with this task.
To forget about this problem forever, you need to change your lifestyle, eat right, avoid hypothermia and give your body rest.
Why is chronic prostatitis dangerous?
Chronic prostatitis is characterized by sharp exacerbations of the disease, which are replaced by remissions. When the pain subsides, it becomes easier and the man decides that he can cope with this problem on his own, instead of quickly turning to a urologist. However, delay will not help here, since with each exacerbation the inflammation will increase.
Inflammation can affect nearby organs, leading to cystitis, pyelonephritis and vesiculitis. As a result, a man may develop infertility.
What antibiotics should I take for chronic prostatitis?
A number of penicillins (Amoxilav, Amoxicillin) are often used. Tetracycline antibiotics are often prescribed for mycoplasmas and chlamydia.
Fluoroquinolones are very effective and penetrate well into prostate tissue (Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin). Macrolides accumulate well in the tissues of the prostate gland and quickly remove toxins.
Is it possible to have sex with chronic prostatitis?
If the disease is caused by an infection, then it is better to abstain from sex so as not to infect your partner. Although you can use a condom. It is simply necessary to have sex, because when aroused, blood rushes to the prostate gland, and it begins to contract. Also, during ejaculation, the pelvic muscles contract strongly, which is considered good self-massage.
Prevention of chronic prostatitis in men and its features
Prevention of chronic prostatitis in men involves a healthy lifestyle and daily exercise. You can constantly tense and relax your scrotum from time to time.
Each time you urinate, pause the stream a little, this way the bladder sphincter will be hardened. Such high-quality exercises will allow blood to circulate well through the veins of the prostate, as well as enhance metabolic processes in the body.
Print Email
Sex life
Prostatitis reduces sexual desire, but regular sex life with this disease is necessary. Abstinence disrupts the production of seminal fluid. If sperm is not consumed, then stagnation occurs in the prostate ducts, aggravating the situation. Stagnation of blood and testosterone negates the treatment of prostate inflammation even with the most effective drugs. Sexually active men should not forget that prostatitis often occurs as a complication of urethritis, which in 90% of cases is of a sexually transmitted nature. Therefore, the cause of inflammation of the prostate can be sexually transmitted infections.
Diagnosis of prostatitis
Chronic prostatitis is an insidious disease. Very often the disease develops latently and gradually becomes chronic. If you do not pay attention in time, then a seemingly minor ailment can develop into a real nightmare. In the acute stage, it sometimes gives a fairly high temperature (38-39° C), pain in the perineum turns the process of urination and defecation into a feat. An abscess may form, that is, purulent melting of the prostate tissue, with all the ensuing consequences.
In neglected form
Prostatitis leads to the most serious complications, which create many problems not only for the man himself, but also for his entire family. With prostatitis, not only libido decreases and erectile function is impaired. The saddest thing is that approximately 40% of patients face some form of infertility, since the prostate gland can no longer produce enough high-quality secretion to ensure sperm motility. This is why it is so important to treat prostatitis in the early stages of development. The success of prostatitis treatment largely depends on this.
Viral prostatitis
Herpes viruses
,
cytomegaly
,
papillomaviruses
often cause the development of urethritis, complicate the course of prostatitis and cause male infertility.
For example, in men without any manifestations of genital herpes on the skin and mucous membranes, the virus can only be detected during laboratory diagnostics in semen or prostate secretions. The patient infects his sexual partner, developing sperm pathology and, as a result, infertility. Often, patients with non-bacterial forms of prostatitis receive a variety of massive antibiotic therapy without the expected positive effect, whereas in fact, the cause of the disease may be viruses, which requires completely different treatment tactics (antiviral treatment, immunotherapy, etc.).
Herpetic:
According to various authors, prostatitis is caused or supported by the herpes simplex virus in 2.9 - 21.8% of cases. Typically, chronic prostatitis is characterized by frequent and persistent recurrence. In clinical practice, the diagnosis of chronic herpetic prostatitis is rarely made by urologists. The reason, apparently, is that virological diagnostic methods are not included in the standard examination of patients with chronic prostatitis. The reason is the doctor’s stereotype of thinking, and patients are traditionally screened for sexually transmitted infections of a non-viral nature.
In the clinical course of prostatitis, functional changes are noted - reproductive changes, pain (with irradiation to the external genitalia, perineum, lower back) and dysuric syndromes. Often in patients with recurrent genital herpes, prostatitis occurs subclinically: in these patients, the diagnosis of prostatitis is made based on the appearance of leukocytosis in the prostate secretion and a decrease in the number of lecithin grains.