The ureter is a long tube that extends from the renal pelvis and connects to the bladder. This creates an outflow for urinary fluid. Its length is 29-35 cm, and it is located in the retroperitoneal part. But the length of the right and left ureter differs, because. the right kidney is lower than the left.
The most common disease is inflammation of the genitourinary system. This also includes inflammation of the ureter in women and men. The female sex suffers more often, not only due to pathologies, but also due to the special structure of the urinary system.
Causes of occurrence and development of pyelonephritis
Kidney inflammation occurs when a lower urinary tract infection spreads upward through the urethra to the bladder and from there along the ureters to the kidneys.
The main cause of pyelonephritis is infection in combination with impaired urine flow. Any problem that interferes with the normal flow of urine increases the risk of acute pyelonephritis. For example, urinary tracts that are unusual in size or shape are more likely to lead to acute pyelonephritis.
Also, local hypothermia of the lumbar region can cause the development of pyelonephritis, even in the absence of anatomical features and with normal urine outflow.
Treatment methods
Officially, there are two types of treatment:
- medicinal,
- surgical.
But there is also traditional medicine , which improves the functioning of the urinary system and eliminates inflammation.
Medication
The specialist prescribes antibiotics to the patient:
- furadonin,
- furagin,
- nitroxoline.
anti-inflammatory drugs are also included in the treatment . For severe pain, no-spa, drotaverine or driptan help.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
The disease can have a different clinical picture, the pathology can affect one or both kidneys, and be acute or chronic.
Acute pyelonephritis
The acute form occurs with pronounced symptoms, including:
- heat;
- pain in the abdomen, back, side or groin;
- painful urination;
- cloudy urine;
- pus or blood in the urine;
- frequent urination;
- trembling, chills;
- nausea, vomiting.
Chronic pyelonephritis
Patients with the chronic form of the disease may experience only mild symptoms or no symptoms at all.
Chronic pyelonephritis is more common in people with urinary tract obstruction. It can be caused by infections, vesicoureteral reflux, or anatomical abnormalities. Chronic pyelonephritis is more common in children than in adults.
Who's at risk
High-risk groups include:
- patients with kidney stones or other kidney or bladder diseases;
- aged people;
- people with a suppressed immune system (for example, diabetes, HIV/AIDS or cancer, taking hormonal medications);
- patients with vesicoureteral reflux (a condition in which small amounts of urine return from the bladder into the ureters and kidneys);
- men with prostate diseases;
- people who tend to wait a long time before going to the toilet due to psychological characteristics or profession;
- people with urinary incontinence - when, for various reasons, the muscles that hold the contents of the bladder inside weaken, and when coughing, sneezing, or laughing, a small amount of urine may be released involuntarily.
There are a number of factors that make the body more vulnerable to infection, such as the use of a catheter or surgery in the urinary tract.
Despite the fact that people of any gender and age group can experience the disease, most often they suffer from it:
- Children under seven years old - due to the peculiarities of anatomical development.
- Young women. Several factors can provoke pathology: the onset of sexual activity, pregnancy, childbirth.
- Men with prostate adenoma.
Symptoms of the disease
Any inflammatory processes occur due to the presence of bacteria and viruses.
If the patient has a chronic case, the symptoms will be more pronounced:
- Sharp pain in the lumbar region;
- pain moves to the stomach, external genitalia;
- body temperature and fever rise;
- nausea and vomiting;
- frequent urination;
- pain when urinating;
- The color of the urine changes to more cloudy with sediment.
If the disease is due to pyelonephritis, then one of the main signs will be aching pain in the lower back. Intoxication and general malaise may occur. Sharp pain can surround the entire lower back.
The cause of the disease may be hidden in helminthic infestation . And the most common helminth is the pinworm. It penetrates the urethra, then the ureter and causes inflammation. The main symptom is itching in the anus.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis
- Initial consultation with a doctor and general examination. The doctor will check for fever, tenderness in the abdomen and lower back, and other general symptoms.
- Analyzes. The first and most important is a general urine test. A complete blood count is usually necessary. It is also often advisable to culture urine to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to drugs.
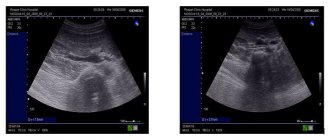
- The doctor may also order an ultrasound to look for cysts, tumors or other obstructions in the urinary tract, a blood test for creatinine and urea, uric acid, and a biochemical urine test.
Why and how does the bladder hurt?
The content of the article
Bladder pain is most often caused by a urinary tract infection, leading to inflammation of the organ. In most cases, urinary tract infections affect women, who, due to anatomical conditions, are more likely to become infected with pathogenic microorganisms. The short urethra and the proximity of the urethral opening to the vagina predispose bacteria to enter the urinary tract more easily.
The development of the disease occurs as a result of the penetration and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms in the urinary tract. The most common pathogen responsible for the development of the disease is Escherichia coli. In addition to pain, cystitis is characterized by a burning sensation when urinating, a sense of urgency, and frequent urination.
Treatment of pyelonephritis
Antibiotics are the first remedy against acute pyelonephritis.
The antibiotic is selected only by a doctor based on the results of an analysis of the type of bacteria and its sensitivity to drugs. In acute cases, if it is not possible to wait for test results, a broad-spectrum antibiotic is used. Although with proper treatment, symptoms may subside within 2-3 days, the course of antibiotics must be completed to the end, as recommended by the doctor (usually treatment lasts from 10 to 14 days). If the course of therapy is interrupted prematurely, the pathogen may develop resistance to the antibiotic - this will complicate further treatment and increase the risk of chronic pyelonephritis.
Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis is possible. It is carried out according to the principles of treatment of acute pyelonephritis, only it requires more time and effort. Treatment involves eliminating the cause that led to stagnation of urine, restoring renal circulation, destroying pathogenic bacteria using antibiotic therapy, and strengthening the general immune system. Even if sustained remission is achieved, maintenance intermittent antibiotic therapy may be required. Treatment of a chronic disease is a serious challenge for doctors and a long journey for the patient, which is why it is so important to consult a doctor promptly at the first symptoms of illness and not waste precious time on self-medication.
Without proper treatment, acute pyelonephritis becomes chronic. If the infection continues to spread, the kidneys may be permanently damaged. In rare advanced cases, the infection can enter the bloodstream. The consequences of this can be extremely serious, including sepsis and bacterial shock.
Causes of urethritis
Another name for inflammatory processes is urethritis . It can become chronic if the first symptoms are ignored.
Attention! The causes of inflammation in men and women are almost the same, there are no significant differences. The most important of them is injuries.
If there are stones in the kidneys and they cannot pass through the duct, then inflammation of the organ occurs. Urine stagnation begins and infection and sepsis occur. The main thing is to diagnose urolithiasis in time and eliminate it.
The following reasons also contribute to the occurrence of urethritis:
- Cystitis (cold disease of the bladder);
- inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- paelonephritis or pyelitis;
- innervation;
- bladder infections;
- anatomical structure, narrow excretory canal;
- promiscuity.
Pyelonephritis in pregnant women
Pregnancy causes many transformations in the body, including physiological changes in the urinary tract.
Elevated levels of progesterone (a hormone that supports normal pregnancy) and increased pressure on the ureters increase the risk of pyelonephritis. Pyelonephritis in pregnant women may require hospitalization if this condition threatens the life of both mother and child. Also, untreated kidney infections in pregnant women increase the risk of premature birth, placental abruption, intrauterine infection of the fetus and damage to its nervous system. With proper and timely treatment, all these consequences can be avoided, childbirth occurs on time, and the prognosis is favorable for both the woman and the child.
During pregnancy, it is extremely important to understand whether this is the first case of the disease in a woman’s history, or whether the disease was chronic in nature, and an exacerbation occurred during pregnancy. Statistics show that primary kidney inflammation in pregnant women is treated successfully and without complications.
To prevent pyelonephritis in pregnant women, it is necessary to be tested for infections when planning pregnancy. Urine cultures are also performed at the beginning of the second trimester. Early detection of UTIs can prevent kidney infections.
The following will also help prevent problems:
- Moderate physical activity, walks in the fresh air, gymnastics for pregnant women. The goal is to strengthen muscles and improve the tone of internal organs, improve blood flow.
- Compliance with drinking regime. Pregnant women should consult their primary care physician.
- Empty the bladder at least every 3-4 hours to prevent congestion.
- Following a special diet that promotes the flow of urine (if there was kidney inflammation before pregnancy).
Sick bladder - what tests to do?
Additional tests are needed to find out the cause of bladder pain. A characteristic medical history and a general urinalysis are usually sufficient to diagnose cystitis. But since cystitis is not the only cause of pain in the bladder, it can be associated, for example, with a tumor, the urologist must prescribe an ultrasound of the pelvis with a detailed examination of the bladder.
Pelvic ultrasound
With a urinary tract infection, leukocytes, squamous epithelium and numerous bacteria are found in the urine. In addition, cultural analysis provides an answer to the question of whether Escherichia coli is the causative agent of the infection.
If, despite therapy, symptoms persist or the patient experiences frequent recurrent cystitis, it is necessary to perform another test - urine culture, that is, a bacteriological examination. This will help identify the bacterial strains responsible for the development of the disease, as well as determine the antibiotic to which these pathogens are sensitive.
Urine for culture should be collected in a sterile container. Before taking a sample, you must thoroughly wash the area of the urethra, and then release the first portion of urine into the toilet so that only medium-flow urine enters the container.
If cystitis is suspected, blood tests are required to show signs of inflammation: high levels of CRP or leukocytosis (increased white blood cells).
It is also useful to perform an abdominal ultrasound when diagnosing bladder pain. The examination will rule out the presence of kidney stones, obstructions in the outflow of urine, or disturbances in the anatomy of the urinary system.
Pyelonephritis in children
This is a common disease among children, ranking second in frequency of cases after ARVI.
The main risk group among children is preschool children. Due to their anatomical characteristics, the disease affects girls more often than boys. The most common causative agent of childhood pyelonephritis is Escherichia coli. In addition to it, proteus (protozoa), Staphylococcus aureus, and enterococci are often found in smears.
Acute pyelonephritis in children noticed in time is completely cured in most cases. After complete recovery for three years after the illness, regular examinations are required (the first three months - once every 10 days, then monthly) and medical supervision. After three years, an examination is required every 3 months so as not to miss an important asymptomatic pathology.
Prevention
General recommendations for the prevention of pyelonephritis:
- Compliance with hygiene measures, regular and thorough toileting of the genitals.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Prevention of dysbacteriosis.
- Compliance with the drinking regime (if there are no other indications, then about two liters of water per day).
- Timely prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted infections.
- Toilet after sexual intercourse.
- Preventive ultrasound of the kidneys.
- Annual medical examination, including laboratory diagnostics (general blood test, general urinalysis, flora culture).
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General practitioner (family doctor), ultrasound diagnostics doctor, chief physician
Bladder pain - how to prevent it?
To prevent a recurrence of a urinary tract infection, it is recommended to remember a few rules.
- If you have an inflamed bladder, drink at least 1.5 liters of fluid per day. Women are advised to drink a glass of water immediately before sexual intercourse.
- Do not hold urine in your bladder - you should go to the toilet as soon as you need to urinate. Women should urinate immediately after intercourse.
- It is necessary to ensure daily hygiene of intimate places.
- Do not wash or wipe the perineal area from front to back. In this way, bacteria can be transferred from the anal area to the urethra.
- It is recommended to avoid swimming in public pools and hot tubs.
A good way to prevent cystitis is to drink cranberry juice. It has the effect of inhibiting (suppressing) the adhesion of bacteria to the mucous membrane of the urinary tract, as a result of which these microorganisms are excreted in the urine without delay.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter