When a man has problems with urination, this is a reason to seriously think about his male health. Unfortunately, such problems occur quite often in men, and most of them indicate the presence of serious diseases, usually urological.
Usually, when a man complains about problems with urination, he means that it has become too frequent or too rare, painful, accompanied by a burning sensation, or sluggish and difficult, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder .
Most often, men have problems with urination because inflammation of the prostate gland, prostate adenoma, and prostate cancer develops. As the prostate enlarges, it puts pressure on the urethra, blocking it. This is what makes urination difficult, and in severe cases almost impossible. In addition, the cause of painful and difficult urination is an infection in the genitourinary area.
When difficulty urinating is observed in the morning against the background of erectile dysfunction, and this is accompanied by general malaise, these are the first symptoms of prostatitis. In this case, it is this that causes difficulty urinating.
In any case, whatever the causes of problems with urination, this is a serious reason to see a urologist!
What are the types of bladder diseases?
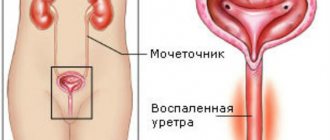
The most common bladder disease is cystitis - inflammation of the walls of the organ, which can be triggered by infection. Cystitis occurs mainly in women and rarely in men. This is due to the fact that the urethra (urethra) in women is several times shorter than in men, which makes it easier for an infection that can cause symptoms of cystitis to enter the bladder.
The next most common problem is bladder stones, which can appear as a result of inflammatory processes in the urinary tract, metabolic disorders or an unhealthy diet. Stones can block the urethra, complicating or making it impossible for urine to flow out.
Overactive bladder is a separate disease in which the walls of the bladder begin to contract uncontrollably, causing a sudden and strong urge to urinate. The cause of the disease may be damage to the brain or spinal cord, diseases of the genitourinary system, or the development of neoplasms.
Leukoplakia is a keratinization of the bladder walls that reduces their plasticity. It can develop under the influence of chemical or mechanical factors.
Bladder prolapse (cystocele) develops as a result of frequent childbirth or its complications, causing frequent urination and incontinence.
Atony is a weakening of the bladder walls that occurs as a result of spinal cord injuries. As a result of this disease, there is no urge to urinate, and the bladder is constantly in a full state.
In addition, papillomas, polyps, and adenomas may develop on the walls of the bladder. In 90-95% of cases, neoplasms are benign, but malignant tumors are also possible.
Causes and risk factors
Why does bladder cancer occur? The disease occurs as a result of abnormal cell growth, the development of mutations and the formation of tumors. It's not always clear why this happens. However, experts identify many possible reasons contributing to the development of cancer, including genetic and environmental factors.
People at risk for developing bladder cancer include:
- People over the age of 40, as aging provokes the development of diseases. 9 out of 10 bladder cancer patients are over 55 years of age.
- Men, as they are diagnosed with this disease more often than women.
- Smokers. Cigarette smoke is one of the main causes of bladder cancer because it contains toxins that pass into the kidneys and urine, where they affect the surface of the bladder.
- Light-skinned persons/Caucasians. People with white skin are twice as likely to suffer from this disease compared to Africans and Hispanics.
- People exposed to chemicals and toxins that can damage the kidneys (for example, at work). Such compounds include arsenic, benzidine, beta-naphthylamine, as well as substances used in the production of paints, rubber, leather, and textiles. The American Cancer Society says that “workers at increased risk of developing bladder cancer include painters, mechanics, printers, barbers (due to exposure to hair dyes and curling products), and drivers (due to exposure to fuel vapors). Arsenic is found even in tap water, but this is quite rare in industrialized countries.
- Persons with chronic infections and inflammation of the bladder. Such diseases can occur due to a genitourinary infection, kidney stones or prostate infection.
- People with a family history of cancer, especially if there is a history of hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (Lynch syndrome). Genetic mutations in the retinoblastoma gene (RB1), or Cowden's disease, also increase risks.
- People who have undergone chemotherapy or been exposed to radiation.
- Persons suffering from parasitic infections. For example, a parasitic infection called schistosomiasis (also known as bilharzia), which occurs primarily in Africa and the Middle East, causes the development of bladder cancer.
- People who have a rare birth defect affecting the urinary tract and bladder (such as exstrophy or urachus).
- Patients suffering from diabetes mellitus and taking the drug pioglitazone for more than one year.
Symptoms of bladder diseases
Patients with bladder disease may complain of the following problems:
- discomfort, aching or bursting pain in the lower abdomen;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- feeling of bladder fullness after urination;
- difficult and painful urination (the pain is cutting);
- intermittent and weak stream of urine;
- darkening or cloudiness of urine;
- blood in urine;
- urinary retention with a constantly full bladder;
- urinary leakage or incontinence.
The severity of manifestations may vary, depending on the specific disease and its severity. The appearance of even one of these symptoms is a sign of an existing disease and a serious reason to consult a doctor.
Where to get diagnosed and treated for bladder diseases in Moscow?
In a multidisciplinary medical center you can always undergo diagnosis and treatment of bladder diseases
. Our medical center is located between the Konkovo and Belyaevo metro stations (South-Western Administrative District of Moscow in the area of the Belyaevo, Konkovo, Teply Stan, Chertanovo, Yasenevo, Sevastopolskaya, New Cheryomushki metro stations " and "Trade Union"). Here you will find highly qualified personnel and the most modern diagnostic equipment. Our clients will be pleasantly surprised by our quite affordable prices.
Diagnosis of bladder diseases
Considering the similarity of symptoms for different bladder diseases, it is better to entrust the diagnosis to an experienced specialist - a urologist or, in some cases, a gynecologist (for women). Diagnostics includes an examination by a doctor and the appointment of additional examinations: ultrasound (bladder, kidneys, for men - prostate) and tests.
If necessary, cystoscopy is performed - an endoscopic examination of the bladder, during which the doctor can examine the condition of its walls. In some cases, an x-ray examination of the bladder may be indicated.
Laboratory diagnosis of bladder diseases may include:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko;
- blood test for urea level;
- blood test for creatinine level;
- bacteriological examination of urine.
Which specific tests from this list may be needed is determined by the doctor, but blood and urine samples for all these tests can be quickly and conveniently submitted to the MedLab laboratory.
Urgent diagnostics
- Ultrasound of the bladder and surrounding tissues is necessary to identify neoplasms, stones, and allows one to assess the integrity of the bladder walls, the size and characteristics of the ureters entering the bladder. If a tumor process in the genital organs is suspected, a comprehensive ultrasound of the genitourinary system is performed.
- Urine tests are necessary to identify formed blood cells, which characterize the degree of inflammation, to assess the functioning of the kidneys.
- Urinalysis in separate portions is indicated for differentiating the inflammatory process in the kidneys, bladder, and urethra.
- If signs of inflammation are detected, bacterial urine tests and PCR urine tests can be performed. To clarify the type of tumor or foreign body, cystoscopy is performed followed by histology of pathological tissues.
You can choose a private clinic to conduct diagnostic examinations of the genitourinary system from the many existing in the capital on the “Your Doctor” Help Desk website.
Useful information on the topic:
- Structure of the bladder
- Cystitis
- Diagnosis of bladder diseases
- Bladder diseases
- Bladder catheterization
- Bladder rupture
- Bladder contusion
- Cystostomy in the bladder
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Kasabov Vadim Vladimirovich Dermatovenerologist
Back to section
Treatment of bladder diseases
Bladder diseases are treated by urologists, and in some cases gynecologists can also do this. If the disease is caused by disturbances in the innervation of the bladder, a neurologist is involved in treatment.
Treatment can be medication, usually used in the early stages of the disease, or surgery. In some cases, such as cystocele, surgery is the most effective treatment. If a patient is diagnosed with stones in the bladder, crushing of the stones with their further independent removal from the body, or their surgical removal, is indicated.
Bladder surgeries are performed using conventional, laparoscopic or endoscopic access. In the last two cases, the interventions are less traumatic and allow the patient to recover faster.
Drug treatment depends on what disease is diagnosed in the patient. The treatment course may include antibacterial drugs, diuretics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics, sedatives and antidepressants. For most bladder diseases, a diet is prescribed to protect the bladder walls from irritation. Diuretic products, such as tea and coffee, are excluded from the diet.
Cost of consultation?
| Name of service | Price, rub.) |
| Primary appointment with a urologist-andrologist | 1800 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a urologist-andrologist | 1300 rub. |
| Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist | 1800 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with the obstetrician-gynecologist | 1300 rub. |
| Primary appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (candidate of medical sciences; doctor of medical sciences) | 1900 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist (candidate of medical sciences; doctor of medical sciences) | 1400 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment (drawing up an individual treatment regimen) | 1000 - 2500 rub. |
All our services and prices
How to treat urinary tract infections?
Simple UTIs are usually treated with a short course of oral antibiotics. A three-day course of antibiotics is often sufficient. However, some infections require longer treatment, up to several weeks. Depending on the type of antibiotics used, take one dose of medication per day or up to four daily doses. A few doses of the medicine may relieve pain or frequent urination, but you should still complete the full course of treatment prescribed by your doctor, even if all symptoms have passed. If UTIs are not completely treated, they can return more than once. You should also remember to drink plenty of fluids.
If you have a complicated UTI, you may need to take longer-term antibiotics and medications to improve your condition. Kidney infections are generally considered to be complications of UTIs.
What can you expect after treatment for a urinary tract infection?
An uncomplicated UTI usually goes away after a few days of antibiotics, and you don't need a urine culture test to prove it's gone. If you have a complicated UTI, a urine culture is required both before and after treatment.
So how do you spot a urinary tract infection?
If you are concerned about this issue, then you should consult a doctor.
The main types of diagnosis of UTI are laboratory tests of blood and urine. A urine sample is examined under a microscope, looking for signs of infection - bacteria or white blood cells in the urine. It is recommended to take a urine culture to determine microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics.
If you find blood in your urine, you should consult a doctor immediately. Blood in the urine may be associated with an infection, but it can also be a manifestation of other serious diseases, such as urolithiasis or tumors of the bladder and kidneys.
Symptoms of a urinary tract infection
If you have a urinary tract infection (UTI), the lining of your bladder and urethra becomes inflamed and irritated, just like your throat does when you have a cold. Possible pain in the lower abdomen and pelvic area, frequent urination with burning in the urethra. During urination, only a few drops of urine may be released, despite a clear urge. You may also find that your urine has a foul odor and is cloudy.
Kidney infections are often accompanied by fever and back pain. These infections must be treated promptly because a kidney infection can quickly spread through the bloodstream and lead to life-threatening conditions.
UTIs are often classified as simple (uncomplicated) or complicated. Complicated UTIs occur when there are abnormalities in the urinary tract or when the bacteria causing the infection are resistant to most antibiotics.