Is it inherited?
The genes that cause this disease are located on the X chromosomes and are inherited to a greater extent by males.
The type of inheritance of color blindness is called sex-linked. Color blindness is inherited only from mothers to sons, and not from fathers. If the pathology is present in both parents, the disease is transmitted from parents to daughter. The color blindness gene is considered recessive. Women are less likely to be affected by the disease, since the female body has two XX chromosomes. In men, due to a deficiency in chromosomes, color blindness is fully manifested.
Main reasons
As a rule, color blindness in a child is congenital. The difference in color between objects depends on intrauterine development, during which chromosomal mutation occurs. The disease is transmitted through the mother. A gene localized on the X chromosome is responsible for color perception, of which women have 2 and men only have 1, so more often than not a boy is colorblind. Not only genetic factors can influence the development of the disease, but also external causes, which include:
- eye injury of varying severity and nature;
- myopia, manifested by cataracts;
- diabetes;
- age characteristics of the child.
The perception of a specific color depends on the protein pigment. Each person has several types of cones, which include a certain protein pigment. The perception of a specific color depends on the presence of the latter:
- Type I - red spectrum;
- II - green;
- III - blue.
If the child is healthy, then all light-sensitive cells contain all types of pigments. In this case, there are no vision problems and there are no signs of color blindness. If any of the pigments is missing, then the functioning of the visual apparatus is disrupted and it is not able to normally distinguish colors and their shades. The more pigments are missing, the more severe the form of the disease.
Is color blindness a hereditary disease?
There are two forms of the disease: hereditary and acquired from a primary disease. The first type includes a breakdown of a gene located on the X chromosome. This is the female sex chromosome. If a woman has a pathological gene, most often she does not suffer from color blindness, but is a carrier. The disease will be inherited by her son, who receives a Y chromosome from his father and a defective X chromosome from his mother.
When a child receives a defective chromosome, the formation of nerve endings that are located on the retina of the eyes is disrupted. They are called cones. Their pigments are able to perceive all filters: green, red, blue. When they act together, a nerve impulse is sent to the brain, which converts the signal and leads to the perception of many shades. If the recognition of one of them is impaired, this can lead to serious disturbances in a person’s perception of the world around him.
The following disorders lead to secondary color blindness:
- cataracts, glaucoma, which interfere with the flow of light to the retina;
- a brain disease that damages the center of color perception (tumors, hematomas, neuralgia) or impairs the transmission of nerve impulses;
- mechanical damage to eye or brain tissue.
Diagnostics
To determine or exclude color blindness, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Ishihara test. Presents a series of pictures depicting multi-colored spots. They are folded in the form of letters, numbers and geometric shapes.
With normal visual perception, a person can easily identify them. For a colorblind person, completing the task is impossible. The color of the figure or figure does not differ from the main background. Patients with impairments see only the rear plan, as it is difficult for them to differentiate subtle color changes. - FALANT test. In order to carry it out, a beacon is placed far from a person. A couple of lights turn on. The subject names the color he sees. The lighthouse glow includes 3 colors, muted using a filter. The method is justified when hiring a job with special requirements. For example, the test is used in the United States to test those wishing to enroll in military service. Interestingly, 30% of patients with a mild form of color blindness pass the test successfully.
- Anomaloscopy. A special device is used - an anomaloscope. During the test, the person being examined looks through the device's peephole. He sees streams of light. Using the regulator, they are adjusted so that a uniform color is obtained. The results are interpreted by the doctor taking into account how different the shades are to the test subjects. Using the method, it is possible to establish not only the presence of color blindness, but also to indicate the influence of the brightness level, the process of adaptation to color, the pressure indicator, and the effect of medications on the retina. The technique is used to establish standards for visual perception and color discrimination, as well as assess professional suitability in certain areas of employment and monitor therapy. It is one of the most accurate diagnostic measures. Allows you to identify the smallest deviations. For an accurate assessment, the eyes are examined one at a time.
- Holmgren's method. 3 skeins of thread of different colors are laid out in front of the person. The examinee must arrange them in accordance with the color palette.
- Pigment method of Rabkin tables. Mugs of different colors of the same brightness are used. Numbers and shapes are depicted in the centers of the figures. The colorblind will not see them. The method has a high degree of accuracy, as it determines the degree of pathology by the number of correctly given answers.
- Abney and Girenberg apparatus. The research method is used very rarely. In front of the subject there are 3 illuminated fields - yellow, red and red-green. From the shades of 2 fields you should create a yellow color. Not only the presence of color blindness is determined, but also the degree of visual acuity.
- Ophthalmoscopy. The method is carried out using a slit lamp. Allows you to identify abnormalities of the fundus, nerves, conjunctiva, cornea, vitreous body of the lens and other components of the visual apparatus.
The price of studying visual perception of color according to Rabkin’s tables in ophthalmological centers in Moscow will be 500 rubles. Ophthalmoscopy will cost from 400 to 1100 rubles. The cost of anomaloscopy will be 500 rubles. In Samara, the price of an examination using the Rabkin table will range from 200 to 550 rubles. Ophthalmoscopy will cost from 200 to 1000 rubles. Anomaloscopy - 350 rub.
Is it possible to somehow find out about predisposition to diseases?
Yes, with the help of pedigree. True, now this method is most often used by future parents who want to make sure that their offspring are not at risk of any hereditary diseases. A pedigree is compiled by a geneticist to assess the likelihood of having a sick child in a family. At first glance, this study looks simple (square, circle, arrows), but in reality everything is very serious. The pedigree is based on the medical history of all relatives known to the family. The doctor is interested in cases of serious illnesses that are repeated from generation to generation, and consanguineous marriages. The doctor will definitely clarify whether any of the relatives have had infertility, miscarriages, or whether children were born with developmental defects and mental retardation. Therefore, before you go to see a geneticist, you should seriously talk with your parents and grandparents and clarify all the details. As you can see, genealogy is not only a look into the past, but also into the future.
If there are hereditary diseases in the family, using the compiled pedigree, the doctor will determine how they are transmitted in the family and what is the likelihood that these disorders will be transmitted to the unborn baby. When the risk of inheriting a genetic pathology is high, the doctor will tell you what can be done to detect it in time. We are talking about a variety of examination methods before conception and during pregnancy.
Karyotyping is the mapping of a person's chromosomes. In some countries, by the way, this study has become as common as determining blood type and Rh factor. It is given to both parents, because the child receives half of the chromosomes from the mother and half from the father. A karyotype helps to detect rearrangements in the chromosome set, when all the genetic information is preserved, but during division one “piece” of the chromosome is “transplanted” to another. These changes do not interfere with future parents' lives, but they are dangerous for the child. The problem is that the future baby may inherit a chromosome that is missing a piece or has an extra one. If rearrangements in the chromosome set of spouses are detected in time, special examination during pregnancy can prevent the appearance of a sick baby. Already from the 11-12th week of his life, many developmental defects and changes can be detected inside the mother during an ultrasound, which indicate that the child has inherited a chromosomal pathology. For example, thickening of the collar area in a small child in 30% of cases indicates Down syndrome. One of the additional research methods will help dispel doctors’ suspicions or, alas, confirm them: chorionic villus biopsy (analysis of cells of the future placenta), amniocentesis (examination of amniotic fluid), cordocentesis (analysis of the baby’s blood from the umbilical cord). The second ultrasound is performed on the expectant mother at 20-22 weeks, and at this time most deviations in the development of the face, limbs and malformations of the baby’s internal organs are determined. At 30-32 weeks, ultrasound can detect delays in its development. A change in the concentration of proteins in the mother’s blood (they are produced by the placenta and the baby’s organs) can also indicate chromosomal pathology and some malformations of the baby. This test is called a biochemical blood test.
How to determine color blindness
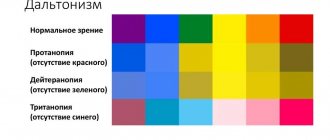
Color vision disorders are most often determined during examination using Rabkin's polychromatic tables. During the verification process, specialists use tables, and in some cases spectral equipment may be used.
Polychromatic tables allow you to explore color perception
Polychromatic test using Rabkin tables: the subject is shown 27 color tables with pictures on them. They are made using colored circles or dots with different colors, but the same in brightness. Colorblind people will not be able to distinguish the drawing. They only see a field that is filled with dots or circles.
Ishihara test: specialists ask the patient to read a letter that consists of colorful spots. Based on the results, the presence of a color perception disorder and which one is determined. These tests are usually used for adults with mental disorders.
Children and mentally retarded persons may distort the results. That is why experts use separate tests for them that will help determine the presence of color blindness based on indirect signs. With normal color vision, patients give over 90% correct answers, and colorblind people give no more than 25%. In some cases, before conceiving, a girl wants to determine the risk of color blindness in her child. In this case, a genetic test will be required.
Using DNA testing, it is possible to identify a gene with a mutation, but since it is currently impossible to eliminate a gene mutation, this expensive method simply has no practical significance.
If you are interested, then you can read about female color blindness.
Colorblindness - how to improve quality of life
Since color blindness is a hereditary disorder, the number of people suffering from it is not decreasing. Public organizations representing the interests of Internet users with hereditary color blindness are calling on website designers to use blue colors when creating resources, since this shade is perceived by most people with color vision disorders. Many sites are now being tested to determine how easy the site is to use for people with colorblindness.
It is important that the colors of objects and backgrounds have the proper level of contrast
Inheritance of color blindness
Gene mutations or abnormalities lead to the development of color blindness. Most often, men (9%) and women (about 0.4%) suffer from color blindness. The inheritance of color blindness in a person depends on which parent is the carrier of the defective gene and on the gender of the child. The disease occurs when there is a defect in the X chromosome at the genetic level. This pathology is caused by a recessive trait, since with a healthy gene the disease does not manifest itself.
Causes of color blindness
Special nerve cells called cones, located in the center of the eye shell, are responsible for distinguishing individual colors by humans. These cells show sensitivity to three colors such as green, red and blue. If one of the three types of pigments does not function, dichromasia occurs. This means that a person ceases to distinguish colors. Patients with dichromasia are divided into two groups. Patients may be blind to red (protanopia) or only green (deuteranopia). People who are blue blind are quite rare. Monochromasia is damage to all three types of pigment. In this case, a complete lack of perception of the color gamut occurs, a recessive gene appears that causes color blindness.
There are acquired and congenital color blindness. The impetus for development can be:
- brain injury or disruption of the nervous system;
- motion sickness;
- dry eye syndrome;
- optic nerve disorder;
- self-medication.
Is it inherited?
The type of inheritance of color blindness is called sex-linked. Color blindness is inherited only from mothers to sons, and not from fathers. If the pathology is present in both parents, the disease is transmitted from parents to daughter. The color blindness gene is considered recessive. Women are less likely to be affected by the disease, since the female body has two XX chromosomes. In men, due to a deficiency in chromosomes, color blindness is fully manifested.
A study by scientists at the University of Cambridge showed that colorblind people are able to distinguish shades that are the same for people with normal vision.
Scheme and mechanisms
If a healthy gene is present in the body, which is located on the sex chromosomes in humans, the disease does not manifest itself. In men, color blindness is more common due to the presence of only one X chromosome. Below is a diagram of how a hereditary disease can be transmitted from parents to children with different genotype options. The genotype for a colorblind person is designated X*Y, for a woman - X*X*.
Colorblindness diagram
How pathology is inherited is presented in detail in the table:
If a man is colorblind and the woman is healthy, then the daughters become carriers of the colorblind gene (X*X), but will not get sick. The chromosome is not passed on to sons. In such a family, all children are healthy and hereditary diseases will not manifest themselves. If a man does not have the disease, and a woman is a carrier of the color blindness allele, half of the daughters will become carriers. In 50% of cases, sons will be healthy and sick in the same ratio. Parents should not always worry about pathology, since it is rare. Daughters have a 50% chance of inheriting a recessive trait if the mother is a carrier and the man is colorblind. The second half will be sick. If a man is healthy and a woman is color blind, then the girls will become carriers of the pathology gene, but will not get sick. In this case, the sons will be color blind. If both a woman and a man are sick, the disease is passed on to daughters and sons.
Prevention methods
If color blindness arose as a hereditary disease, it is impossible to prevent its occurrence. The best thing parents can do during pregnancy is to calculate the likelihood of the recessive gene being present in the unborn child. There is also an option to correct color perception with special glasses or lenses that are painted in a unique color. This invention will help convey a huge number of shades of colors, but may slightly distort objects. Glasses with multilayer lenses are a new development by scientists. Unique devices significantly improve color vision in patients with the initial form of the disease.
You can achieve excellent results if you eliminate the very cause of the disruption of the lens of the eye. However, if a violation of color perception occurs due to aging of the body, the changes cannot be reversed. Stopping medications that negatively affect your color vision may improve the situation. Treatment for diseases such as cataracts and glaucoma can restore the ability to distinguish colors, and early diagnosis and treatment will help prevent the onset of this disease.
How is color blindness inherited in humans?
Home » Other »
Loading…
Question for experts: how is color blindness inherited? What color perception will children have whose mother is colorblind and whose father has normal vision?
Best regards, ZveR
Best answers
The inheritance of color blindness is associated with the X chromosome and is almost always transmitted from a mother who carries the gene to her son, as a result of which it is twenty times more likely to occur in men who have a set of XY sex chromosomes.
In men, the defect in the only X chromosome is not compensated for, since there is no “spare” X chromosome. 2-8% of men suffer from varying degrees of color blindness, and only 0.4% of women.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with How to donate your share of an inheritance in 2020?
Some types of color blindness should not be considered a “hereditary disease”, but rather a feature of vision. Co
Mothers are not color blind. Only men are affected by the disease. If a woman carries the gene for color blindness (linked to one of the X chromosomes), then her son is more likely to get this hereditary disease. If the daughter is not (maybe she will become a carrier, maybe not)
Video response
This video will help you figure it out
Answers from experts
The type of inheritance of color blindness is called SEX-LINKED. The appearance of color blindness is based on the action of a number of genes. Long before the advent of genetics, it was established that color blindness is inherited according to completely natural rules.
So, if a woman suffering from color blindness marries a man with normal vision, then their children exhibit a very peculiar pattern of cross inheritance. All daughters from such a marriage will receive the sign of their father, i.e.
they have normal vision, and all sons, receiving the mother’s trait, suffer from color blindness (a-color blindness linked to the X chromosome). In the same case, when, on the contrary, the father is color blind and the mother has normal vision, all children turn out to be normal. .
In general, the presence of color blindness is more common in men.
Color blindness is one of the variants of color blindness - red-green blindness
Color blindness is when a person cannot distinguish colors, men are especially susceptible to this.
The inheritance of color blindness is associated with the X chromosome and is almost always transmitted from a mother who carries the gene to her son, as a result of which it is twenty times more likely to occur in men who have a set of XY sex chromosomes. In men, the defect in the only X chromosome is not compensated for, since there is no “spare” X chromosome. 2–8% of men suffer from varying degrees of color blindness, and only 0.4% of women.
Some types of color blindness should not be considered a “hereditary disease”, but rather a feature of vision.
According to research by British scientists [1][2], people who find it difficult to distinguish between red and green colors can distinguish many other shades. In particular, khaki shades that appear the same to people with normal vision.
it is inherited, but it is not transmitted to everyone because it is a recessive gene
The woman is healthy and not colorblind (XX), the man is colorblind (X'Y). In this case, all daughters will be carriers of the color blindness gene (XX'), since they will receive one X chromosome from the mother and the other from the father.
But her father has color blindness. Since color blindness is recessive, the daughters will be healthy. All sons will also be healthy, but will not be carriers of the defective gene (XY), since they can only receive a Y chromosome from a sick father.
So, in this case, the manifestation of the disease is 0%.
In this matter, the problem of color blindness among children is very acute.
This is due to the fact that, due to its physiological characteristics, a child does not perceive most colors until the age of three.
Only after crossing the age threshold of three years, color discrimination gradually begins. In turn, only then can it be determined whether the child is hereditary color blind.
To determine or rule out color vision disorders, the doctor examines the patient using the Ishihara color test. This is a series of photographs showing spots of different colors. A certain number of these spots differ from the rest in a shade of color and form a certain figure, number or letter.
Color blindness is a disorder of color vision. This disease occurs when there is a defect in the X chromosome. Color blindness is a recessive trait, therefore, if the allelic “healthy” gene is present, the disease does not manifest itself.
However, due to the fact that the gene is localized in the sex chromosomes, there may not be a healthy gene that will overlap the sick one. Men have only one X chromosome. Therefore, color blindness most often manifests itself in them.
Let's consider how color blindness is inherited with different variants of the genotype of the parent carriers of this defect. (X is a “healthy” chromosome, X' is a color-blind chromosome).
The woman is healthy and not colorblind (XX), the man is colorblind (X'Y). In this case, all daughters will be carriers of the color blindness gene (XX'), since they will receive one X chromosome from the mother and the other from the father.
The woman is color blind (XX'), the man is healthy (XY). In this case, all daughters will be healthy, but 50% of them will be color blind. Some will have XX, others will have XX'. Sons have a 50% chance of being either healthy (XY) or sick (X'Y). So, in this case, the manifestation of the disease is 25%. And only boys can get sick.
The woman is colorblind (XX'), the man is sick (X'Y). Here, half of the daughters will only be carriers of the disease (XX'), since they will receive a healthy chromosome from their mother, and a sick one from their father.
Both boys and girls can get sick.
The woman is color blind (X'X'), the man is healthy (XY). In this case, all daughters will only be carriers (XX'), since they will receive a healthy chromosome from their father. But all sons will be sick (X'Y), because in any case they will receive a chromosome with a defect from their mother. Here the manifestation of the disease is also 50%. Moreover, all the boys will be sick.
The woman and the man are color blind (X'X' and X'Y). There is no chance here, all children will be color blind.
Related articles: Sex-linked inheritance, Inheritance of blood types
Treatment
If this is a genetic disease, the positive dynamics are completely absent, and the patient remains colorblind forever. There is nothing you can do about it, you have to live in your condition and adapt to the perception of incorrect tones and shades. When diagnosing acquired color blindness, the clinical outcome is more optimistic, but the proposed treatment is long-term and not always successful. In modern ophthalmology, the problem of color perception can be compensated by the following publicly available methods:
- Lenses. This optical device is painted in special colors that allow you to see the world normally. The use of lenses does not improve visual acuity; moreover, it can distort visible objects.
- Colorblindness glasses. This optical device has special shields or wide frames on the sides. A prerequisite is that there is less bright light, and the shades are perceived more realistically.
- Almedis device. This is an innovative development of quantum medicine, which is extremely popular. The impact on the body and its individual systems is carried out at the gene and cellular level.
Ways of transmission of color blindness
The transmission of color blindness depends on which parent has the defective gene and the gender of the child who receives the gene. The disease occurs more often in men, although it is transmitted through the female line. The gene is found on the sex chromosomes and is recessive.
The mother may be a carrier of a recessive gene, but since she has two XX chromosomes, the second chromosome blocks the defective one and she will not get sick. But the father has XY chromosomes, and his disease is fully manifested.
X chromosomes are sex chromosomes that contain the color blindness gene. Inheritance of color blindness by sons occurs only from the mother. If both parents suffer from this disease, then the gene is passed on to the daughter. But this happens quite rarely.
In some cases, this type of disease is acquired. Color vision impairment occurs in people due to:
- brain injuries or disorders of the central nervous system,
- prolonged motion sickness in transport or on a ship,
- constant work at the computer (temporary violation),
- eye injuries that damage the optic nerve,
- darkening of the lens or cataracts,
- taking a number of medications without a doctor’s prescription.
The impairment may be temporary or permanent depending on the origin of the disease or its cause.
How is color blindness inherited?
Let's see how color blindness is inherited with different types of combinations of defective and healthy genes:
- The woman is healthy (XX), and the man is color blind (X*Y). The daughters will get the recessive gene and they will become its carriers (X*X), but they will not get sick. The sons will grow up healthy, as they inherit only the Y chromosome from their father. The disease will not manifest itself in such a family.
- The woman is a carrier of the diseased gene (X*X), the man is healthy. In 50% of cases, daughters will be carriers of this gene, but the disease will not manifest itself. Sons will be healthy in 50% of cases (XY) and sick in 50% of cases (X*Y). Inheritance occurs in 25% of cases and only in boys.
- The woman is a carrier of the color blindness gene (X*X), the man is sick (X*Y). Half of the daughters will receive a defective chromosome, but will not get sick (X*X), the other half will be sick (X*X*). The disease will be transmitted to sons in the same proportions: 50% (XY) and 50% (X*Y). The disease will manifest itself in 50% of cases, i.e. Half of the children will get sick.
- The woman is colorblind (X*X*), the man is healthy (XY). Girls in the family will be carriers of the diseased gene, since they will receive a second, healthy gene from their father, and the transmitted diseased gene will be in the sons. All boys in the family will be sick (X*Y).
- If both parents are colorblind, then all children will be sick, since the colorblind gene will be passed on to daughters and sons. The disease is 100% inherited.
To identify the disease, polychromatic tables are used, on which figures or numbers are depicted using multi-colored dots. The patient will not see different colors; for him it will be a blurry, gray background. Inheritance affects both eyes.
The inheritance of color blindness is related to the sex of the child. The risk of getting this disease is much greater in boys, while girls for the most part do not get sick, but their genotype may contain a diseased gene. Color blindness is inherited from generation to generation, it can be traced through the family tree.
How to test a child for color blindness
To know how to check your child for color blindness, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. He will collect anamnesis from the parents’ words and may suspect the presence of color blindness.
To confirm it, the following methods are used:
- a table with color scales arranged in the form of figures or numbers, according to which the child tells what shades he sees;
- the use of special automatic devices that emit a different spectrum of colors that the child must perceive and tell what he sees.
Since it is possible to have secondary color blindness, which develops as a result of a primary disease, it is necessary to confirm the hereditary pathology.
Color blindness test
The following studies are used for this:
- general clinical studies of biological fluid, blood biochemistry;
- examination of the fundus with assessment of the condition of the lens and retina;
- measuring intraocular pressure to exclude its increase and the formation of glaucoma;
- CT and MRI of the brain.
Having excluded all primary systemic diseases, the doctor makes a diagnosis of “hereditary color blindness”. At the same time, he must explain to his parents what it is and how to deal with it.
How colorblind people see
The main symptom is that the patient does not distinguish between tones and their shades. Instead of green, blue or red, a colorblind person sees gray. If this is a small child, then he does not always inform his parents about such visual defects, so the task of adults is to monitor the younger generation and their worldview, promptly respond to alarming symptoms and report them to the pediatric ophthalmologist. There are no such serious problems with the diagnosis of adult patients. The main symptoms of this disease are as follows, both single and complex:
- uncontrolled frequent oscillatory eye movements (nystagmus);
- difficulty distinguishing colors;
- low visual acuity as a temporary or permanent symptom.
How to understand that a child is color blind
Before reaching 4-5 years of age, it is almost impossible to understand that a child is color blind. Kids remember information received from their parents, so they know that the sky is blue, the grass is green, and the sun is yellow. They repeat this information. Therefore, parents need to know how to understand that a child is colorblind.
In the process of growing up, your own opinion appears, to which parents should listen. Here it is possible to understand that the child is not able to perceive some colors. This is the only external sign of the disease.
Related and recommended questions
Father's heart disease when planning pregnancy Natalya. My husband has a congenital problem...
Epilepsy in the male line I will be very grateful to you for your answer. The situation looks like this...
Planning children with a second cousin, the likelihood of a positive outcome? Situation…
Can be avoided I wanted to know if it is possible to genetically test children! Since in the family...
The birth of a child from a fourth cousin, consequences. Recently it turned out that my husband...
Planning a pregnancy I am 23 years old, planning a second pregnancy, my son is 3 years old...
The risk of inheriting a seizure disorder, Hello, my husband had up to 6...
Schizophrenia My husband's mother's brother has schizophrenia. My husband and I are planning...
Hearing loss mutation in the GJB2 gene My younger brother suffered hearing loss, in 2012...
The child’s TSH is elevated. On the third day of life, blood was taken from the child’s heel at five...
Hippel-Lindau disease in the father of the child My wife is pregnant, 12 weeks, my father has...
Interpretation of the coagulogram The child was removed from adenotomy, the aphtv was elevated. Sent to...
Autism and schizophrenia heredity I am 23 years old, my younger brother is 15 years old and he...
What critical diseases are transmitted from the father? Can you tell me what diseases...
Perthes disease in a child treatment My 6 year old boy was diagnosed with Perthes disease...
Pyloric stenosis My eldest child was diagnosed with CONGENITAL PYLOROSTENOSIS. 4 years…
Do I need to take any medications to plan a pregnancy? I have one like this...
Six-fingered by inheritance or accident I am worried about such an unusual question...
Heredity of mental disorders Please write what is the probability of manifestation...
The second child in the family is born disabled. My sister has two children, a girl...
Is color blindness inherited?
Genetic diseases
or color blindness is a reduced ability to perceive the differences between certain colors that healthy people can distinguish. Typically, the origin of this disorder is genetic. but the disorder can also occur due to damage to the eyes, nerves, brain, or exposure to certain chemicals.
English chemist John Dalton published the first scientific work on this topic in 1798, it was called “Extraordinary Facts Concerning the Vision of Colors.”
Color blindness - types, causes, diagnosis and treatment
Color blindness (color blindness) is a vision disorder that manifests itself in the inability to distinguish colors or shades of color. The term first appeared in 1794 after the publication of the work of the Englishman John Dalton, in which the scientist described the features of color perception based on his personal experience.
type of inheritance. Color blindness is inherited through the X chromosome.
Color blindness and its types
The human eye is thought to have 3 types of retinal cells that perceive color: red, green and blue-yellow cones. Each of them contains special visual pigments, collectively called iodopsin. If there is not enough iodopsin in any of the types of cones, then blindness to the corresponding color occurs. The absence or insufficient amount of iodopsin in cones is inherited and almost always from a mother who carries the gene to her son, as a result of which color vision impairment is 20 times more likely to occur in men.
Some types of color blindness, although they are inherited, should not be considered a “hereditary disease”, but rather a feature of vision.
Color blindness in women and men
Color blindness is considered an anomaly that arose in the X chromosome, according to experts. It is believed that both men and women can be color blind. However, in practice this is extremely rare. After all, representatives of the fair sex have XX chromosomes, and men have XY chromosomes.
A colorblind woman must have two chromosomes with an anomaly. This is possible, but practically never occurs.
Colorblindness: forms and causes
Color blindness is a disease that is characterized by impaired perception of certain parts of the color gamut, as a result of which the patient cannot distinguish or confuses some colors. The disease has various types, forms and causes.
Color blindness has been called color blindness since 1974 thanks to John Dalton. He always wore a gray jacket, which he loved very much. But then it was discovered that the robe was actually burgundy.
Is color blindness curable today?
Color blindness or color deficiency is a genetic disease. It can be inherited and is mainly common among men. It can also be acquired if it develops as a result of glaucoma or cataracts and color perception is impaired.
The disease is detected using Ishihara tests or Rabkin polychromatic tables. The patient must read colored text on a colored background.
Curious facts about color blindness
One of the effective methods of restoring emotional and physical balance in naturopathy is chromotherapy - color treatment. According to the followers of this teaching, color is an integral part of our life. However, this method of relieving fatigue is not applicable to all people. Thus, chromotherapy is not suitable for monochromatic people with black-and-white vision, and colorblind people - people suffering from color blindness.
Is color blindness inherited?
Color blindness is the inability to distinguish one or more colors. Color blindness was first described by John Dalton in 1794. As a rule, the disorder is inherited, but acquired diseases associated with the inability to distinguish colors are also identified.
The structure of the average person's eye allows us to distinguish all colors in both low-light conditions and normal lighting.
Factors influencing the heredity of color blindness
Factors that influence the heredity of color blindness vary depending on a person's gender and which parent has the defective gene that causes the condition. Men are more susceptible to color blindness than women, although the disease is passed on to sons from their mothers. Some very rare forms must be passed on by both parents, although this does not happen often.
Color blindness is a condition in which a person cannot distinguish between certain colors or confuses some colors with others.
Color blindness - interesting facts
The name of such a disorder as color blindness is associated with the name of the English physicist and chemist John Dalton, who first described the case of color blindness. There is a version that previously people were not able to distinguish colors at all and only the process of evolution influenced the appearance of color vision. The ability to differentiate shades was very useful for people to find ripe fruits during the period of gathering and hunting.
One of the creators of quantum mechanics, Erwin Schrödinger, spoke of color only as electromagnetic waves that are perceived by the optical system of the eye. This is probably why physicists believe that the colored world is illusory. It is made this way by photoreceptors that can distinguish between electromagnetic waves of different lengths. Therefore, colorblind people just need to adapt to life in a society where the interests of such people have not been taken into account for a long time.
Types of color vision disorders
Color blindness is a hereditary, less commonly acquired disease. Based on the nature of the lesion, a distinction is made between complete and partial color blindness. With complete color blindness, there is a black and white vision of the world. The reason is that the pigment is not completely produced by the body or it is not enough to produce a multi-colored image. The most common is partial color blindness.
With this type of genetic disease, there is an inability to see one color due to the absence of pigment or its reduced activity:
- protanopia is a type of disease in which red pigment is lost or reduced;
- deuteranopia is a manifestation of this type of color blindness, expressed in the inability to correctly identify shades of green, which can be perceived as red or orange;
- tritanopia - this type of disorder is associated with difficulty perceiving the color blue, which appears red or green.
The presence of such a predisposition can be confirmed or refuted by undergoing specialized DNA tests. They are used when diagnosis by visual tests is difficult. For example, if you need to check the optical system of a newborn's eye. In other cases, if hereditary color blindness is suspected, a complex of examinations is carried out, consisting of checking the retina using machines, tests, studies using an anomaloscope and polychromatic Rabkin tables.
Kinds
This disease in the field of ophthalmology is rare, but, in any case, requires detailed diagnosis using clinical methods. The predominant types of color blindness are determined according to several evaluation criteria. By type of inheritance:
- congenital (transmitted from sick parents during the prenatal period);
- acquired (the diagnosis appears throughout life under the influence of pathogenic factors).
When the perception of only one color is impaired (abnormal trichomacy), color blindness has the following conditional classification, which facilitates quick diagnosis:
- protanomaly, characterized by problems perceiving the color red;
- tritanomaly with impaired blue color perception;
- deuteranomaly with problems distinguishing the color green.
A disease in which the patient is unable to distinguish between two colors is officially called dichromatism . The diagnosis classification is as follows:
- deuteranopia, in which the problematic colors are green mixed with light pink;
- tritanopia, in which there are certain difficulties in perceiving the blue part of the spectrum, and a loss of violet tint occurs;
- protanopia, in which there is an absence of the red part of the spectrum, the mutation occurs in dark green or brown shades.
- Eye stroke - first manifestations and types of pathology, drug therapy and preventive measures
- Fungus in the nose in humans: symptoms and treatment
- What is a microstroke: symptoms and treatment
The presumptive diagnosis can be clarified only after a detailed diagnosis using clinical and laboratory methods. The main classification of color blindness according to the characteristics of color perception is presented in the following list:
- achromasia (achromatopsia), in which the patient has black and white vision;
- monochromasia, when a person distinguishes only one color (usually blue);
- dichromasia, in which two primary tones (yellow or orange and blue) are problematic for perception;
- abnormal trichromasia, in which patients see 3 primary colors, but one of them is distorted.
Causes of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a non-contagious disease, therefore it is not transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person (for example, through the use of personal items, through saliva, sexually). Unfortunately, scientists are still studying the etiology of the dermatological disease, despite its increasing popularity.
However, experts in this field voice one of the main factors in the occurrence of the disease - a genetic predisposition to skin disease. There is a possibility that psoriasis can be inherited.
In those suffering from skin pathology, mutational changes occur within the skin cells of the body. Psoriatic papules develop mainly in individuals who have a predisposition to the disease. Sometimes the disease manifests itself in grandchildren. A characteristic feature of psoriasis is that a person does not even imagine that the disease can develop at any time.
Along with the genetic factor of the origin of the disease, several more reasons can be identified:
- Consequences of past infectious diseases. Pathogenic microorganisms that have a negative impact on the general condition of the body negatively affect human skin. At the same time, scientific studies have shown an insignificant likelihood of developing pathology without a pre-existing predisposition to psoriasis. According to scientists and distinguished doctors in the field of dermatology, infection can speed up the process of the disease emerging from its latent state.
- Allergic reactions. Some medical luminaries believe that psoriasis is one of the types of allergic manifestations due to the influence of certain foods or viruses.
- Metabolic and immune system disorders. The occurrence of problems with metabolic processes leads to the accumulation of an excessive number of lymphocytes in some places of the epidermis, and then a rash and inflammation appear. At the same time, the patient, as a rule, has a genetic predisposition to the pathology. In addition, a person’s weak immunity exposes him to the development of many serious infectious diseases (tonsillitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, and so on) and allergic reactions.
- Hormonal imbalances. Disturbances in the natural activity of the endocrine system lead to deviations in the regenerative functions of the human skin epithelium.
Psoriasis takes people who are unaware of the development of this pathology by surprise. It is usually a consequence of severe nervous shock, prolonged depression or other nervous system failure. Psychosomatic disorders trigger a mechanism of metabolic disturbances in the human body, which in turn leads to the development and exacerbation of skin diseases.
In addition to psychosomatics, the situation is negatively affected by the presence of an infectious disease in the patient, such as influenza, ARVI, sinusitis, tonsillitis, otitis media, caries and other diseases.
According to the above, we can conclude that dermatological pathology is contagious only if a person has a genetic inheritance for the disease or has suffered severe forms of infections. In this connection, it is obvious that with weak immunity, the likelihood of the disease occurring is much higher.
Find out more