Indications for use of the duochrome test
The duochrome test is used if the patient complains of decreased visual acuity.
As a rule, patients complain of dull color and blurred outlines of objects. If a patient has a color vision disorder, this does not affect the diagnostic result. The perception of images on the left and right is assessed. Indications for the use of the duochrome test exist in the following cases:
- eye injuries;
- the presence of hereditary diseases or a predisposition to them;
- if the patient begins to experience age-related changes in the retina (this phenomenon is called presbyopia);
- corneal burn;
- retinal detachment.
This technique is also used to select corrective agents and check the effectiveness of treatment procedures.
Test features
Light-refracting media for people who have undergone surgery on the lens, cornea, vitreous body or who suffer from cataracts and some other eye diseases, including age-related changes. may bend light waves incorrectly, causing this test to be inaccurate.
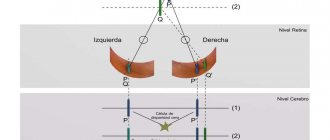
The duochrome test is a type of subjective examination methods for studying the refraction of the eye. It is mainly used to check the correctness of the selected optical systems. This test is based on the effect of chromatic aberrations (deviations) in the eyeball.
This effect is that rays with different wavelengths are refracted differently by the optical media of the eye. For example, shorter green waves experience more refraction than longer red waves. That is why the focus for green rays is located closer to the corneal layer, while for red rays it is closer to the retina. Another way to put it is that the emmetropic eye is essentially myopic for green objects, while it is hypermetropic for red objects. In this regard, several focusing points are simultaneously formed in the eyeball. Due to the fact that their range is not significant, the middle point corresponding to yellow light falls directly on the retina, that is, the eye focuses correctly.
The purpose of the duochrome test is to determine on which background (green or red) a person is better able to distinguish optotypes (usually letters). There are several options for test objects, which are represented by two fields (red and green) and black optotypes on them (Landolt rings, numbers, letters). If the patient recognizes optotypes better on a red background, then the average focusing point is shifted closer to the cornea, that is, it is located in front of the retina. Therefore, correction in this case should be carried out using a negative lens. That is, in this case we are talking about insufficient correction of myopia or overcorrection of hypermetropia.
In the event that the patient better recognizes optotypes located on a green background, the average focal point is located behind the retina, that is, we are talking about hypermetropia, insufficient correction of it or hypercorrection of myopia. To move the focus directly to the retina, use a plus lens.
With correct focusing of the eye, the patient equally accurately recognizes optotypes on both green and red backgrounds, since the focal point is located on the retina. That is, in this case we are talking about optimal correction of refractive error. This test can be performed both near and far. In addition, there is a monocular option to clarify the strength of the sphere and a binocular option to determine balance.
In some cases, the doctor installs an additional fogging lens (+0.5 diopters), which is necessary to eliminate the influence of accommodation (the red background is more suitable for determining optotypes).
In addition, the duochrome test can be used to assess the accommodative abilities of the eye in patients when looking at near, as well as to identify the amount of addiction (that is, the increase for near). This is necessary to check optical systems when correcting presbyopia.
Interestingly, such a test is suitable for diagnosing patients with color vision impairment, since the presence of color anomalies is not associated with chromatic aberrations of the eye. In this case, the doctor determines not the color in which it is easier for the patient to distinguish optitypes, but the corresponding area of the table (right or left halves).
When carrying out the test, it is necessary to remember that some age-related changes and eye diseases (cataracts, surgery) can lead to distortion of chromatic aberrations. This is due to the inaccurate results obtained when performing a duochrome test in such patients.
Contraindications for the duochrome test
Contraindications to the duochrome test exist in the following cases:
- after eye surgery;
- in old age;
- if the patient has diseases such as glaucoma, color blindness, cycloplegia;
- for eyeball injuries, corneal burns, retinal detachments.
Due to age-related changes or certain diseases, such as cataracts, the light refractive medium changes. The light waves are not refracted correctly and the test results will not be reliable. The duochrome test does not have any unpleasant consequences after the study is carried out.
The technique is not used if the patient is under the influence of drugs or alcohol. Also, this procedure is not possible for people with mental disorders if they are experiencing an exacerbation of psychosis.
Methodology for conducting a duochrome test
The duochrome test is carried out using a two-color screen.
You can also use a computer monitor for this purpose. The room where the test is carried out should have good lighting. The poster or monitor should be placed at the patient's eye level. Conditions under which the test result is considered valid:
- the distance between the eyes and the screen should be 1 m. If a monitor is used, it is reduced to 70 cm;
- the screen should be in line with the eyes;
- if the patient uses lenses or glasses, he does not remove them during the test;
- it is necessary to ensure uniform illumination of the surface;
- each eye is tested separately;
- During testing, the clarity of perception of signs on the side of one color is assessed by comparison with the other.
The methods for performing the duochrome test are as follows:
- From close range.
As a rule, this method is used to diagnose young people. - At a great distance.
This method is used to organize complex eye treatment. - Using optical instruments.
Used in cases of vision correction. - Binocularly.
The ability to perceive an object simultaneously with both eyes is tested. - Monocular.
In this case, the left and right eyes are checked separately.
In order to assess visual acuity, it is worth considering the line that the patient can see without eye strain. There are often cases where the ophthalmologist can install a “fog” lens. It will eliminate the influence of accommodation and make it possible to correctly analyze the results of the study.
Sometimes, during this test, color blindness is revealed, which the patient may not have been aware of.
If the patient does not have problems with visual perception, or the correction is selected correctly, then he should see letters or other signs equally clearly on both red and green backgrounds.
When signs on a red background have clearer outlines, the light wave is focused to the retina. This indicates that myopia is not corrected enough, or hypermetropia is corrected too much.
When letters that are on a green background are visible better, it means the light wave is focused after the retina. This result indicates that myopia is overcorrected, or hypermetropia is undercorrected.
Diagnostic methods
So how can you determine whether you have farsightedness without visiting a clinic? This requires simple online duochrome tests that you can take at home, and they will help diagnose eye problems with reasonable accuracy. But diseases determined in this way can only be definitively confirmed by a specialist, and such a diagnosis itself is only suitable as a periodic check of one’s visual acuity, for the timely detection of any abnormalities. The latter can help you save yourself from farsightedness at an early stage.
People may often not notice that they have developed certain health problems until the correlation with their previous condition becomes so striking that they pay attention to it. Therefore, if you have recently begun to notice that squinting is necessary to view objects close up, or you need to move the newspaper to arm’s length and only then can you read it, then you should definitely have your visual system diagnosed.
You must understand that problems identified by tests may not always turn out to be such, which is why you should contact an ophthalmology clinic for a residual diagnosis. But even if you really have them, you can solve them in the same way at home, which is what doctors most often advise, prescribing certain therapy if vision with farsightedness can still be saved. To do this, it is enough to use special mesh training glasses, which almost every person has seen. Or simple warm-up exercises, but you should do them, regardless of how busy you are, once every half hour.
Attention! Self-medication for farsightedness in itself cannot cause harm, but without consulting a doctor and looking for optimal solutions, you can only make things worse, wasting time on therapy that will not help in your case.
Decoding the results of the duochrome test
After the procedure is completed, the doctor writes a report on the condition of the visual apparatus.
The interpretation of the duochrome test results is as follows:
- If the signs on a green background are clearer, then this indicates farsightedness, or hypermetropia.
- Better readings on a red background indicate myopia or myopia.
- With emmetropia, or normal vision, the images on the left and right should have the same clarity.
The test consists of several lines that can characterize visual acuity. If the patient can read letters with a value of 0.7, then visual acuity is 70%. In addition to the meaning of the symbols, the patient must indicate the color background on which the image clarity is higher. In cases where the patient does not perceive color, he names the side in which there are changes and the contours are blurred.
The test procedure does not pose any danger to the patient, is carried out very quickly, and allows you to obtain the result at the time of the examination. If necessary, based on the results of this test, correction with lenses or glasses is prescribed.
The duochrome test is carried out very quickly, it is safe and informative. But in order to find out why disturbances in visual perception occurred, it is worth using other diagnostic methods.
Duochrome test
The duochrome test refers to subjective methods for studying eye refraction and is used to clarify and verify the selected optical correction. It is based on the phenomenon of chromatic aberration (from the Latin aberratio - deviation) in the eye, which consists in the fact that rays with different wavelengths are refracted differently by the optical media of the eye. Thus, shorter light waves (green) are refracted more strongly than longer ones (red). Based on this, the focus for green rays is closer to the cornea than for red ones, that is, the emmetropic eye is myopic for green objects and hypermetropic for red ones. This phenomenon is associated with the formation of several focal lengths in our eye. But their range is small and if its midpoint, corresponding to yellow light, hits the retina, the eye focuses correctly.
Click on the picture to enlarge
The purpose of the test is to determine on which background - red or green - the subject distinguishes optotypes better. Various versions of test objects have been developed, representing a red and green field with black optotypes placed on it (Landolt rings, letters or numbers). If the patient sees optotypes better on a red background, it means that the midpoint of the focal lengths of his eye is in front of the retina. That is, for correction in this case a negative lens (“minus”) is required. And this indicates that the eye alignment is myopic and we are dealing with undercorrection of myopia or overcorrection of hypermetropia.
If optotypes are better visible on a green background, this means that the midpoint of the focal lengths is behind the retina, which corresponds to hypermetropia. In order to shift focus to the retina, it is necessary to use a positive (“plus”) lens (or eye accommodation). This means that this patient has overcorrection of myopia or undercorrection of hypermetropia.
If the subject sees optotypes equally well on both red and green backgrounds, this means that the middle point of the focal lengths is located on the retina and the eye focuses correctly. Based on this, we can conclude that the optical correction for this patient was chosen correctly. The test can be carried out both far and near, monocularly - to clarify the power of the sphere and binocularly - to determine the binocular balance and once again check the compliance of the prescription with the true data.
Sometimes the doctor places a “fogging” lens (+0.5D) on the subject in order to eliminate the influence of accommodation, which causes optotypes to be distinguished more clearly on a red background, and to obtain undistorted data during testing, gradually reducing the “fogging” until a balance of red and green is achieved background colors of test objects.
This test can also be used to evaluate the accommodative ability of the eyes in young patients for near vision and to determine the amount of addition (called "near gain") when checking a prescription for glasses to correct presbyopia.
Despite the fact that color plays a major role in the duochrome test, such a test can also be performed with patients who have color vision disorders, since the presence of color anomalies is not associated with chromatic aberrations of the eye. In such cases, the doctor asks the patient not on which background - green or red - he distinguishes optotypes more clearly, but on the left or right half of the test table, correlating his answers with the location of the color background and drawing the necessary conclusions.
However, it should be taken into account that age-related changes in the eyes, the presence of diseases such as cataracts, and some surgical interventions can affect chromatic aberrations. Therefore, the duochrome test may give inaccurate results in such patients.
The duochrome test is a special method for studying the refractive power of the eye, allowing one to assess the adequacy of the selected correction.
It is subjective, so the results obtained are rather of a general information nature.