Accommodation spasm is the result of improper functioning of the ciliary muscle, which holds the lens.
Visual perception depends on the functioning of this muscle.
With a spasm of accommodation, it is disrupted, the patient sees a blurry image of objects located in the distance.
Treated with drops. Under their action, the ciliary muscle relaxes when a person looks into the distance. She begins to recover and respond quickly when she shifts her gaze.
What is a spasm of accommodation?
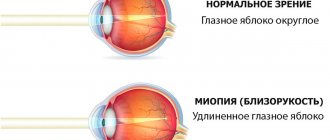
The human eye has a unique structure; it contains a biological lens, better known as a crystalline lens. It is capable of changing optical power depending on the distance at which the object we are trying to see is located. In addition, he transforms his form:
- When a person strains to look at an object nearby, the lens becomes round;
- When trying to see an object located at a great distance, it takes on a flat outline.
The ciliary muscle is responsible for changing the “appearance” of the lens. In some cases, it undergoes spasm. In such situations, the lens cannot change shape and always remains in the form of a ball, which makes it difficult to view distant objects.
Classification
Ophthalmologists distinguish three types of disorders in the functioning of the ciliary muscle:
- Physiological. Spasm occurs as a response of the body to unfavorable conditions (poor lighting, incorrect posture) or to the constant load of the visual apparatus. If the pathology is just developing, then it is enough to normalize the rhythm of life so that it does not return;
- Caused artificially. A similar deviation occurs when taking a certain group of medications - miotics. To get rid of the disease, it is enough to stop using medications;
- Pathologically occurring. In this case, the spasm is caused by refractive problems, i.e. change from farsightedness to myopia. Pathology can be “fresh” or “old”, uniform or uneven. Moreover, not every deviation can be treated with medication.
| Only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis and determine the type of spasm after examination and conducting the necessary examinations. |
Reasons for the development of nystagmus
Cooperative eye movements, performed with extreme clarity, are controlled by the brain. Therefore, the key cause of disorders of this motor function is instability in the functioning and coordinated work of the oculomotor system. These types of problems and job instability can be caused by a variety of factors. Among them the leading ones are:
- An initial predisposition that is passed down through generations;
- Brain injuries, negative effects on the nervous system during childbirth;
- Acquired traumatic brain injuries, especially with damage to the brain or its membranes;
- Visual disorders, predominantly farsightedness or symptoms of astigmatism, the presence of myopia;
- Dystrophic processes affecting the retinal area, the development of atrophy in the area of the optic nerve;
- Formation of Meniere's disease;
- Various infectious, inflammatory lesions of the middle or only the inner ear;
- The use of certain medications, due to which nystagmus will be a side effect;
- Tumor processes affecting parts of the skull, brain tissue or membranes;
- The presence of albinism;
- Various types of stroke (hemorrhagic or ischemic);
- The onset of multiple sclerosis or its progression;
- Chronic exposure to stress;
- Taking alcohol, drugs, psychotropic drugs on an ongoing basis or even occasionally.
Important
Manifestations of nystagmus are often adaptive, as a reaction to certain external changes, then it is not considered a pathology.
Thus, specific nystagmoid eye movements can become the result of significant overstrain in the central parts of the nervous system. This is possible against the background of disorientation as a result of rotation of the body along an axis, riding on a carousel. As a result, due to the flow of scattered impulses, the brain is temporarily lost, which provokes nystagmus. Gradually, when the position of the body relative to space stabilizes, nystagmoid movements disappear.
Important
When nystagmus manifests itself in a completely stable and calm state, when there are no external problems, this is always a signal that the central nervous system is influenced by pathogenic factors.
Causes of ciliary muscle spasm
Most often, the disease occurs in young children and adolescents who spend a lot of time watching TV or computer. Also common causes of spasms of the ciliary muscles include:
- Unbalanced diet;
- Poor illumination of the work area;
- Disturbed daily routine (lack of sleep, lack of walks in the fresh air);
- Passive lifestyle, lack of sports activities;
- Eye fatigue.
The older a person gets, the less elastic his lens becomes. The ciliary muscle contracts less frequently, which provokes the development of farsightedness. However, in adulthood, spasm of accommodation practically does not occur.
Atropine
This medicine belongs to the group of antispasmodics and is a simple anticholinergic blocker. Atropine blocks m-cholinergic receptors, causing paralysis of accommodation and mydriasis. At the same time, the medication increases IOP, so it cannot be used if you have glaucoma or are predisposed to its development. The drug is contraindicated in case of hypersensitivity to the components, in children under 7 years of age.
The duration of treatment is 6–10 days. After this treatment, the spasm of accommodation disappears. Directions for use: 1-2 drops. up to 3 times a day.
There is no data on overdose of Atropine. May cause dry mucous membranes, redness of the conjunctiva, and hyperthermia.
Symptoms of false myopia
The first “distress signal” indicating a disruption in the functioning of the ciliary muscle is rapid fatigue of the organ of vision when reading or working at a PC, i.e. if the object is close to the eyes. Subsequently, the following symptoms appear:
- Burning sensation in the cornea;
- The patient complains of blurry images of objects located at a distance;
- Working capacity decreases in the dark, because in order to look at something you have to strain;
- Differences in pupil size, eyelid nystagmus.
In some cases, depression, hand tremors, and low blood pressure are observed. If you do not give the visual apparatus a rest and ignore the spasm, hoping that over time everything will go away on its own, there is a high risk of “reclassifying” false myopia as true. In this case, therapy will become more difficult and will drag on indefinitely. Return to contents
Diagnostics
| Most often, adults misinterpret children's complaints about poor health and pain in the eyes. They attribute this to increased stress at school and age-related changes in the body. |
Therefore, pathology can only be identified through a mandatory medical examination, which is carried out in all secondary educational institutions. If deviations are detected, you must visit an ophthalmologist so that he can conduct a series of studies and find out:
- How much eye sharpness has decreased;
- The size of the light accommodation reserve;
- Coordination of movements of the pupils of both eyes.
The ophthalmologist also takes a shadow sample and sends it for skiascopy and examines the refraction of the lens.
Features of the pathology
Spasm can be of 3 types:
- Physiological is a response to visual overload when the eye tries to turn on the compensation mechanism. Characteristic of farsightedness and astigmatism.
- Artificial is always temporary, because it is associated with taking certain medications for eye examination, for example, Pilocarpine. This spasm does not require treatment and disappears on its own.
- Pathological – characterized by increased refraction. In this case, vision deteriorates sharply. The most dangerous variety.
In practice, spasm is more often of a mixed nature.
Causes
This type of disorder often occurs among schoolchildren and young people. This is due to high visual loads during this period.
Prolonged work at a short distance from the eyes is the basis of the violations. This could be reading, working on a computer, watching TV for a long time, or using gadgets. Another common reason is imperfection of the eye itself. After all, in order to look at an object better, you have to bring it closer to your eyes and strain your vision. At this moment, an increase in accommodation occurs, followed by a spasm. This often happens when the workspace is poorly lit.
Provoking factors:
- astigmatism;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- unhealthy food;
- lack of vitamins;
- physical overload;
- vascular diseases;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- injuries to the eye area;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- hormonal changes during menopause;
- metabolic disorders;
- incorrect selection of lenses and glasses for astigmatism.
For schoolchildren and adolescents, the reasons may be:
- unlimited time in front of the TV and computer;
- incorrect furniture for working at a desk;
- reading in low light and at close distances - for example, lying down;
- long bright light in the eyes;
- violations of the daily routine: regular lack of sleep, sitting at home without fresh air;
- asthenia;
- poor nutrition – without vitamins and minerals;
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis of the neck.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eye muscle spasm are as follows:
- decreased vision when looking into the distance;
- rapid eye fatigue even with light loads and pain in them;
- dry eyes;
- burning and stinging;
- redness of the sclera and photophobia;
- temporal headaches, dizziness;
- double vision;
- general fatigue and irritability (especially in children).
Useful video
Mechanisms of visual accommodation:
Methods for treating spasm of accommodation
If it is not possible to immediately identify the cause of the dysfunction of the ciliary muscle, then the patient needs to undergo additional examination by a neurologist or orthopedist. Spasm therapy is carried out using conservative methods; surgery will not have any effect.
To achieve maximum results, the fight against pathology must be approached comprehensively; treatment includes the following measures:
- Using eye drops, they have a relaxing effect on the muscle;
- The use of a vitamin complex that has a positive effect on the restoration of the functioning of the organ of vision;
- Conducting special gymnastics;
- Magnetic therapy treatment course;
- Massage or acupuncture.
It is forbidden to use eye drops without first consulting a doctor. Only after he confirms the diagnosis can you go to the pharmacy.
Eye relaxation drops
The main “tool” for eliminating accommodation problems is eye relaxation drops from the group of indirect mydriatics. They must be used on an ongoing basis, and they do not guarantee that the disease will not return.
Atropine
It is highly effective, the result is noticeable two minutes after instillation, and lasts for ten days. The drug is quite strong and at the same time toxic, therefore it has a number of side effects:
- Fear of light;
- Painful sensations;
- Swelling of the eyelids;
- Dry mucous membranes;
- Redness of whites.
| Ophthalmologists rarely use the drug and most often prescribe it to adult patients. The medication is not suitable for people with glaucoma and those suffering from intolerance to the components included in the composition. |
Return to contents
Irifrin
It acts more gently than Atropine. The active substance is phenylephrine. There are a number of contraindications for use:
- Glaucoma;
- Problems with the heart and blood vessels;
- Hyperthyroidism;
- Intolerance to the components included in the composition;
- Congenital pathology of hemoglobin metabolism.
On pharmacy shelves you can find an analogue of Irifrin - Phenylephrine. They are produced with active ingredient concentrations of 2.5 and 10%. The low rate allows the medication to be used even in newborn infants. Eye drops to relieve spasm of accommodation with a high content of active substance can be used by adults and children from twelve years of age.
Depending on the concentration and dosage, instillation time varies from two to seven hours. It also has side effects similar to those of Atropine, but they go away in a short time because they are less pronounced.
Midriacil
The active substance is tropicamide. The result is noticeable five minutes after application and lasts for eight hours. Analogues are “Midrum” and “Tropicamide”. Suitable for use by young patients if they do not suffer from glaucoma or an allergic reaction to the components of the drug.
Cyclomed
Gently but effectively affects the ciliary muscle. The result is visible approximately half an hour after instillation and lasts up to twelve hours. The effectiveness of the drug is reduced if a person has dark eye color, so it is not suitable for them.
The negative consequences of taking it are the same as those of other mydriatics. Contraindications include increased pressure inside the eyes and intolerance to the active ingredient (cyclopentolate). Use the product carefully in children under three years of age. The medication is also not recommended for people suffering from intestinal obstruction.
| In pharmacies you can find drugs such as “Tsiprolet” and “Tsipromed”. They have bactericidal properties and are not part of mydriatics, i.e. They will not be able to relieve muscle spasms. Don't confuse them! |
Cyclopentolate
The drug acts quickly, the effect is felt approximately thirty minutes after use. The result lasts throughout the day. It is forbidden to use the drug for those who suffer from glaucoma or intolerance to the substances included in its composition.
Instill with caution in children under three years of age; use is prohibited during pregnancy and lactation. When using Cyclopentolate, avoid driving a car, as the medication causes a temporary deterioration in visual acuity.
Midroom
The drug is rarely used because it has a short-term effect. Ophthalmologists prescribe it only if the use of other drops is impossible. Typically used as a diagnostic medication to detect refractive errors.
Not recommended for patients with glaucoma and those who suffer from allergies to the components of Midrum. After instillation, side effects such as fear of light and increased intraocular pressure may occur.
Drops and other preparations with lutein
They are not included in the group of mydriatics; the names of the medications may vary, but they always contain the word “lutein”. Most often, the active substance is included in a vitamin complex created specifically to improve visual acuity.
When using the drugs, the pupil does not dilate, since they do not affect the circular and radial muscles, they directly affect accommodation and help relax the lens.
Eye drops consist entirely of natural ingredients, therefore they have no contraindications and there will be no negative consequences from taking them. They can be given safely even to small children. The only exception is an allergic reaction to the components of the drug. Return to contents
Midriacil
Midriacil blocks receptors in the sphincter of the pupil and the ciliary muscle. It causes expansion of the pupil and paralysis of the ciliary muscle. The maximum effect after using the drops occurs within 20 minutes. The drug is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to the components, a tendency to glaucoma and at its initial stage. Eye drops are used for diagnostic purposes.
They are used in preparation for surgery, laser surgery in the prevention of synechiae.
Instructions for use:
- 1–2 drops of a 1% solution for skiascopic examination, repeat the procedure after five minutes;
- 1–2 drops 0.5% solution if fundoscopy is required.
Side effects include blurred vision, sensitivity to light, dry mouth, increased IOP, and hypotension.
How long does the treatment last?
On average, the duration of therapy ranges from fourteen days to one month. After this, the spasm goes away, the muscles smooth out, and visual acuity returns. However, at the end of the course, the disease will not go away completely; the effect will be noticeable only after some time.
When using eye drops, see your eye doctor regularly to prevent side effects. In some situations, such medications are not suitable at all or do not give the desired result.
Preventive actions
To avoid spasm of the ciliary muscle, just follow a few simple recommendations:
- When working at a computer, take breaks every thirty minutes (or at least once every hour). The duration of rest is at least five minutes. During this time, you can perform several exercises to relax your eyes;
- Make sure the work area is well lit. Don’t forget to control the brightness level of your PC monitor; saturated tones and dull colors are equally bad for the visual system;
- Watch your posture. There should be at least sixty centimeters between the eyes and the screen. The back and neck are straight, the shoulders are relaxed and straightened;
- Consult your doctor and choose the best option for visual exercises that is right for you;
- As temperatures rise, minimize eye strain.
Don't forget about proper nutrition, add more vegetables and fruits to your diet.
Tropicamide
Blocks receptors of the sphincter of the iris and ciliary muscle. The medicine causes temporary paralysis of accommodation. Tropicamide is prescribed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
To relieve spasm of accommodation, the medicine is used before bedtime for 1 month. In severe cases of the disease, use 1-2 drops up to 2 times a day.
Tropicamide cannot be used with neuroleptics and antidepressants, intraocular pressure increases.