What is PINA (habitually excessive tension of accommodation) in ophthalmology
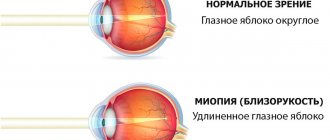
Accommodation is the unique ability of the human eye to perceive equally clearly objects located at different distances from it.
Disruption of this mechanism leads to a pathology called PINA, in which clarity of vision is lost due to the inability to focus on things near and far.
ICD code
In accordance with the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), this disease is classified as “Impairments of Refraction and Accommodation.” In this section it is coded as H52.5.
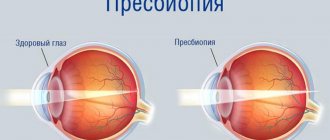
Accommodation disorders such as internal ophthalmoplegia (impaired functioning of the oculomotor nerves with subsequent loss of function of the eye muscles), spasm and paresis are also identified here. Presbyopia (age-related loss of elasticity of the lens) has a separate code - H52.4.
Mechanism of the problem
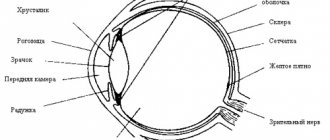
The clarity of perception of an object depends on the ability of the lens to refract light, as well as the ciliary muscle and ligament of zinn, to change its tension and shape.
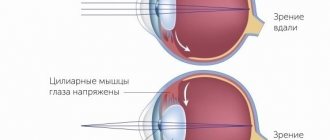
If a person looks at something located in the distance, the ciliary muscle relaxes, and at the same time, the ligament of Zinn is tensed, which pulls on the elastic lens. It becomes almost flat and its refractive power decreases.
When the eye focuses on a nearby object, the ciliary muscle tenses, and the ligament of Zinn, on the contrary, relaxes. At this moment, the lens takes on a convex shape, its refractive power increases.
When the accommodation process is disrupted, the lens loses its elasticity, and when viewing distant objects, its refractive power becomes insufficiently small, and when looking at nearby things, it becomes too strong.
Types of pathological conditions
Only a specialist can diagnose the causes and type of violation. To do this, the doctor measures the visual acuity of each eye, checks the reaction of the pupils, performs ophthalmoscopy, ultrasound, and skiascopy. In some cases, an MRI of the brain and a consultation with a neurologist are required.
What pathological conditions can diagnostics reveal:
- Paresis of accommodation. Its characteristic feature is the inability to see small details and small objects. The condition occurs due to paresis of the ciliary muscles. Can be peripheral or central. Paresis is often caused by infectious diseases, poisoning and metabolic disorders, as well as diabetes.
- Spasm of accommodation. Due to dysfunction of the ciliary muscles, a person loses the ability to see objects both near and far. In addition, the spasm is accompanied by painful sensations: the eyes begin to “sore” when working at the monitor or reading. This disorder is caused by excessive load on the organs of vision. The eyes of school-age children and adults whose work involves computers are especially affected. In such people, a spasm of accommodation is most often recorded. Additional symptoms of the disorder are excessive lacrimation, redness of the eyelids and conjunctiva, headaches and decreased performance.
- Paralysis of accommodation. This disorder is associated with improper passage of nerve impulses. It leads to the fact that the near point of clear vision almost merges with the far one. This causes serious vision problems, especially at close range. Paralysis of accommodation can be caused by an overdose of pharmacological drugs, neurological and infectious diseases, or eye injury.
Modern medicine makes it possible to identify and eliminate all types of pathologies. But this must be done by a qualified doctor.
Symptoms of PINA in both eyes
This pathology has characteristic signs:
- rapid fatigue when working close;
- unpleasant sensations in the eye area (from ordinary discomfort to burning, and even stinging);
- tearfulness;
- excessive dryness of the surface of the eye;
- loss of clarity of vision (distant objects blur and may appear double);
- often dazzles the eyes;
- headache.
Symptoms are not always pronounced. But 3-4 simultaneously occurring symptoms are enough to warrant a visit to the doctor.
Causes
There are several sources of origin for PINA:
- genetic predisposition (children whose parents have eye problems have a high risk (almost 80%) of developing PINA;
- high strain on the eyes when working close;
- continuous communication with a computer, smartphone or tablet;
- failure to comply with basic eye hygiene rules;
- incorrect work with gadgets (lying down, in low light, while moving, etc.);
- inactive lifestyle, lack of fresh air and exercise;
- unhealthy diet, for example, consumption of large amounts of carbohydrates due to a deficiency of protein, vitamins and microelements;
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system (various injuries, scoliosis).
And these are only the main reasons that provoke accommodation disturbance. There are also motivators that indirectly influence the occurrence of PINA.
Risk factors
Violation of accommodation is promoted by:
- lack of daily routine;
- incorrect posture;
- weakness of the neck and back muscles;
- presence of somatic diseases.
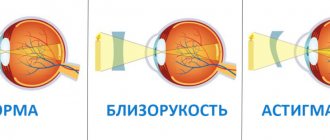
PINA can aggravate conditions such as farsightedness and astigmatism that the patient already suffers from.
Diagnostics
In order to establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination, including:
- appointment with a specialist (questioning and examination of the patient);
- determination of visual acuity and pupil reaction;
- examination of the visual field using special devices;
- skiascopy and ophthalmoscopy;
- measurement of absolute and relative accommodation.
In some cases, additional research is required: consultation with a neurologist, ultrasound of the orbits, MRI of the head, etc. instrumental and laboratory examinations.
Other types of accommodative apparatus disorders
In addition to PINA, which most often manifests itself in adolescence in children who violate the rules for using tablets, smartphones and computers, experts distinguish 3 more types of ocular accommodation disorders:
- accommodative spasm, accompanied by acute excessive accommodation tone, which contributes to the manifestation of myopia;
- weakness of accommodation, characterized by prolonged insufficient and unstable accommodation;
- accommodative paralysis, which is a disorder that makes it difficult to see small objects.
All these ailments require adequate treatment methods.
Symptoms of the disorder
The most characteristic sign of eye accommodation disorders is blurred images when looking into the distance or at nearby objects. In some cases, it may be difficult for a person to focus his gaze on any object. Sometimes double vision occurs.
Other possible symptoms of pathology:
- rapid eye fatigue;
- severe pain, stinging, burning sensation;
- watery eyes and redness of the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity at distance or near.
In some cases, severe headaches, nausea, and weakness may appear. Patients of working age quickly get tired at work, and schoolchildren cope poorly with classes.
Treatment at home
The fight against accommodation disorders begins with the correct organization of the daily routine, workplace and nutrition process.
Then a gymnastic complex for the eyes is selected, vitamins are taken, it is possible to use Sidorenko glasses and other additional methods.
Auxiliary procedures
Therapeutic gymnastic complex for the eyes consists of exercises:
- Close your eyes tightly for 2-4 seconds. and open them again. Repeat up to 10 times.
- Frequent blinking, perform 7-8 approaches for 5-7 seconds. every.
- Movements of the eyes vertically from top to bottom, then horizontally from right to left. Do up to 10 times.
- Circular eye movements, first clockwise, then counterclockwise. Perform 10-12 times.
- Fixing the gaze on a near object, and then on a distant one, and so on 7-8 times.
For the last exercise, you can use a pencil, moving it closer and then moving it away. As an auxiliary procedure, massage of the eyeballs through closed eyelids is also recommended. It can be done without outside help:
- Close your eyes loosely and relax.
- Using light touches of the pads of your middle fingers, first make 10 strokes clockwise, then counterclockwise.
- Using your thumbs, slightly stretch the eyelids towards the temples, and so on 5 times.
- Press slightly on the eyes with your thumb and middle finger and release. Repeat up to 7-8 times.
- Perform stroking movements with the middle phalanx of slightly bent thumbs in the direction of the temples, then to the bridge of the nose, and so on 6 times.
At the end of the massage, do not immediately open your eyes sharply. It’s better to sit for another half a minute with your eyelids lowered.
Medication
To treat PINA, Atropine eye drops are used, which have an antispasmodic effect. They also improve the ability of the eye muscles to contract and the pupil to dilate.
Sometimes Digofton or Irifrin are prescribed. Additionally, vitamin complexes are prescribed.
In a clinical setting
The hospital provides comprehensive treatment, including physiotherapy, laser and hardware therapy, and also prescribes glasses or contact lenses.
Selection of optics
The procedure for selecting glasses is individual and is carried out by an ophthalmologist, taking into account all the nuances of visual impairment identified by diagnostic tools.
If necessary, monofocal glasses with one corrective lens are prescribed, or bifocal glasses, where both zones are working, sometimes progressive glasses are prescribed, in which 1 lens corrects the image near, and 2 - at a distance.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy procedures prescribed for accommodation disorders are aimed at improving blood circulation and stimulating the work of the eye muscles:
- electrophoresis with a medicinal composition (exposure to current improves the penetration of medicinal drugs);
- magnetic therapy (magnetic field strengthens vascular tone, improves blood flow);
- reflexology - exposure to active points with special needles or current;
- massage of the cervical-collar area improves blood flow to the head.
Electrophoresis and massage are most often prescribed.
Laser
Vision correction with laser beams, the therapeutic effect of which is aimed at restoring the eye’s ability to refract light, is used if other methods are unsuccessful.
Hardware
Special devices aimed at correcting the functioning of the neuromuscular and sensory systems of the eye have a normalizing effect on the ability of the ciliary muscle to contract and also relieve spasm.
Treatment methods
Treatment is selected in a complex manner and prescribed strictly in accordance with the type of pathology.
If accommodation is impaired, doctors often prescribe eye drops. Mydriatic and cycloplegic drugs are used. They help bring the ciliary muscles into a relaxed state, strengthen their contractility, improve eye mobility and dilate the pupil.
In some cases, there are not enough minerals and vitamins. They must be in balance to stimulate accommodation.
Depending on the type of disorder and the degree of refraction, the ophthalmologist selects glasses. In some cases they need to be worn periodically, and in others constantly. Sometimes special contact lenses are used to improve vision.
An excellent alternative is laser correction. It allows you to change the thickness of the cornea, eliminate defects and irregularities that led to disruption of eye accommodation. This treatment improves refractive power and increases image clarity.
Sometimes physical therapy is effective. It includes several techniques. These are magnetophoresis, magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, electroreflexotherapy, acupuncture, as well as massage of the cervical-collar region.
If the accommodation disorder is caused by injuries, neurological, infectious or psychological lesions, then therapy will be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease.
Features of treatment in adults and children
In children, unlike adults, both drug treatment and laser therapy are used with caution. For preschoolers, the emphasis is on corrective optics and additional treatment methods, such as eye gymnastics and massage. In elderly people and patients with chronic heart disease, magnetic therapy is excluded.
PINA in childhood often develops due to excessive exposure to the computer, TV, or tablet, and therefore such entertainment should be minimized during therapy.
It is equally important that the child’s work area is properly equipped during treatment:
- good lighting;
- furniture (table and chair) must correspond to height, so that from the eye to the book lying on the table, with correct posture, there is at least 35 cm.
In addition, the TV should be located no closer than 3 m.
Types of accommodation spasm
With a spasm of accommodation, the muscles responsible for focusing are in a tense state even when this is not necessary. In this condition, a person loses his usual visual acuity, so the symptoms are similar to true myopia. Due to the development of digital technologies, the percentage of adults with such visual impairment is increasing, whereas previously this problem was more common among schoolchildren and students.
Depending on the reason that caused such a violation, a spasm of accommodation occurs:
- physiological - occurs as a self-correction for farsightedness and astigmatism;
- artificial - paralysis of the ciliary muscle caused by the effects of drugs;
- pathological - with such a disorder, there is a sharp deterioration in visual acuity due to constant tension of the ciliary muscle after long work at close distances, with small objects;
- mixed - occurs when several types of violations are combined.
Can a spasm of accommodation lead to myopia? A pathological, prolonged spasm of accommodation when the body’s alarm signals are ignored and the lack of adequate treatment can lead to the formation of not false myopia, but true myopia. Without correction, a person will experience constant malaise, irritability, and fatigue. Children in this condition experience a significant decline in academic performance.
Preventive measures
Any disease is easier to prevent than to cure. You can prevent not only the occurrence of PINA, but also a number of other eye diseases, if you follow simple rules aimed at organizing a healthy lifestyle:
- proper nutrition;
- active lifestyle;
- proper rest in case of daily severe strain on the eyesight, including mandatory breaks from work and eye exercises.
If problems with the eyes occur, it is important to promptly consult a specialist to determine the type and cause of the disease. Today, a sufficient number of methods for treating PINA have been developed, and constant ignoring of the problem will certainly lead to even greater deterioration of vision.
Watch a video about how accommodation of the human eye works:
How does eye accommodation occur?
Accommodation is responsible for focusing vision at different distances. If you look into the distance, the ciliary muscle will be relaxed. At the same time, the ciliary girdle, on the contrary, tenses. It stretches the outer layer of the eye lens, making it flatter. Therefore, the refractive power of the visual organ is noticeably reduced. This is the mechanism of accommodation. Looking into the distance is considered one of the main methods of relieving eye strain.
If you look at an image or object at a close distance, the ciliary muscle will tense. At the same time, the ciliary band enters the relaxation phase, and the standard round shape returns to the eye lens. That is, viewing close up forces the muscle to always be in a tense state.
If we look at the description of the structure of the eye, we can understand that the function of accommodation is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. One of its sections promotes contraction of the ciliary muscle. Sometimes accommodation is disrupted. Why is this happening?