Symptoms
The disorder progresses acutely or subacutely.
Patients often combine the appearance of symptoms of paralysis of accommodation with stress, infectious diseases, or the use of eye drops. There are complaints about changes in near vision, less often complaints about distant vision. A factor in turning to an ophthalmologist is considered to be the inability to carry out normal visual work at a sufficiently close distance and to focus the gaze on one object.
Patients clearly indicate the time of formation of the first signs of paralysis of accommodation and spasm. More often, vision decreases symmetrically, but episodes of unilateral damage are also described. The disease is predisposed to a relapsing course. If brain damage becomes a factor, the overall clinical picture is dominated by meningeal symptoms, manifested by nausea, uncontrollable vomiting, and intense headache.
Symptoms of paralysis of accommodation
The main symptom of the disease is the inability to clearly see objects that are close to the patient. At the same time, nearsighted people do not feel this process as keenly as farsighted people. But with farsightedness, distant vision also decreases. Visual acuity in myopic people is not lost so sharply, and sometimes does not occur at all. An enlarged pupil with an inability to see close objects also indicates paralysis of accommodation. When near vision decreases, patients often complain of headache, redness of the eyes and eyelids, burning and itching in the eyes. Sometimes these symptoms are accompanied by vomiting.
Causes of pathology
There are actually a lot of conditions that provoke the development of false myopia, all of them are mainly associated with too high a visual load. Although the reason may well lie in diseases of the internal organs. Doctors identify several of the most common causes of pathology:
- excessive eye strain, for example, while working at a computer or while watching TV for a long time;
- disturbances in the daytime routine - lack of sleep, lack of useful exercises for tired eyes, too infrequent walks on the street;
- lack of natural or artificial light while reading or writing;
- vitamin deficiencies, lack of vitamins and minerals in consumed foods;
- impaired blood flow in the cervical region;
- muscle weakness in the neck and back;
- reading lying on your side;
- too close a distance when reading literature and writing notes;
- incorrect ratio of chair and table to the child’s height.
In adults, false myopia can be caused by neurological stress, frequent stress, closed head injuries, impaired metabolism, and menopause in women. But still, visual fatigue is the most common cause of spasm. But be that as it may, before starting treatment, you should undergo a full examination.
Spasm of accommodation of the eye
The most common accommodative disorder in children and adults is spasm.
Spasm of accommodation of the eye is a deterioration in visual perception, associated with excessive tone of the eye muscles. Symptoms of a spasm of accommodation may be:
- disturbances in distance visual acuity;
- there is pain, pain, dryness in the eyes;
- headache in the temporal and frontal region;
- rapid visual fatigue.
Spasm of accommodation is called “false” myopia or tired eyes syndrome. The time frame for the duration of visual impairment associated with spasm can last from one month to several years, and if you do not undergo examination and start treatment in time, the spasm can turn into myopia.
With timely complex treatment using hardware and medication, it is possible to restore clarity of vision. The spasm can be relieved by applying conservative treatment with special drops to relax the muscles.
Spasm of accommodation most often occurs in schoolchildren; according to statistics, more than 15% of students suffer from visual impairment.
The causes of spasm of accommodation of the eye can be:
- excessive visual stress associated with long periods of time at the computer or TV screen;
- bad light;
- close reading;
- deviations from the daily routine;
- chronic lack of rash.
Among ophthalmological diseases, spasm of accommodation of the eye confidently holds second place after myopia. A temporary spasm caused by prolonged tension of the extraocular muscles, the process is reversible.
Spasm of accommodation of the eye in adults is extremely rare. This is associated with physiological age-related changes in elasticity and thickening of the capsule of the eye lens. The causes of the disease may be related to a person’s professional activity: intense, monotonous work with small details, with high visual load.
Treatment of accommodation spasm
If it is impossible to immediately determine what were the reasons for the development of accommodation pathology in a child or adult, then the patient is referred for additional examination to an orthopedist or neurologist to find out the causes of spasm of the ciliary muscles. Treatment of accommodation spasm in adults and children involves complex therapy, which includes the following measures:
- instillation of eye drops into the conjunctival sac, which have a relaxing effect on the smooth muscles of the ciliary muscle and ligaments;
- the use of vitamin and mineral complexes that have a beneficial effect on vision restoration;
- eye gymnastics classes;
- electrophoresis;
- correction course with magnetotherapy;
- massage of the cervical spine and frontal region, therapeutic exercises, manual or acupuncture sessions.
Drops to relax the eye muscles
Drug therapy with special drops that relax the ciliary muscle allows you to quickly restore the accommodation apparatus. However, they need to be instilled regularly, and there is a high probability that after some time accommodation will be disrupted again. Doctors recommend not only instilling drops for spasms, but also taking other measures to restore vision. Anti-spasm drops include:
- Irifrin;
- Cyclomed;
- Lutein;
- Mydriacyl;
- Tropicamide;
- Atropine (rarely used).
Irifrin
- Pumpkin - benefits and harm to the body. Healthy recipes for preparing pumpkin vegetables
- Pumpkin jam with lemon: recipes with photos
- Radish with honey for cough
Being an adrenergic agonist, Irifrin drops help dilate the pupil, relaxing the eye muscles, relieving spasm. These eye drops to relieve spasms are used for children over six years of age and adults. Instill Irifrin for spasms at night, 1 drop in each conjunctival sac for at least one month to achieve optimal results. The drug is contraindicated in the following cases:
- presence of closed-angle glaucoma;
- with arterial aneurysm;
- patients with acute heart failure and cerebral blood supply disorders;
- with hyperthyroidism;
- children under 6 years of age.
Cyclomed
The drug is used to relieve symptoms associated with spasm - eliminates eye pain, burning and stinging, reduces redness of the eyeballs, has a calming effect, eliminates myopia. For adults and children, 1-2 drops of solution are instilled into each eye once. The effect should occur in 10-20 minutes, and if this does not happen, then another 1 drop of solution is instilled into each eye. Cyclomed is not recommended for the following pathologies:
- allergies to the main substance or auxiliary components;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- intestinal obstruction;
- post-traumatic paresis;
- under 3 years of age.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Ophthalmologists recommend eye gymnastics for accommodation spasms as a method that brings good results. However, you should know that you will have to do gymnastics regularly, perhaps for a year or two. The effect of the exercises will not be immediate, but will last for a long time, the ability to accommodate will return again. Exercises for the eyes are done once a day, in the evenings, so that later the eyes no longer strain when reading or working. You can do the following exercises:
- Stick a small piece of plasticine on the window, at eye level, slowly moving your gaze from it to the distant future.
- Close your eyes tightly and open your eyes, repeating this 10 times.
- Blink quickly and frequently for 30 seconds.
- Move your eyeballs in a circle 10 times, then the same amount diagonally.
Causes and treatment of accommodation spasm
Accommodation is the ability of the eye to clearly see objects at different distances, which occurs due to the coordinated work of the lens, ciliary ligament and ciliary (eyelash) muscle.
Spasm of accommodation is a vision pathology, which is also called false myopia or tired eyes syndrome.
Spasm of accommodation most often occurs in children, but adults can also suffer from it.
It appears when there is prolonged stress on the eyes - frequent and long work at the computer, prolonged reading, work that requires visual strain (work as a watchmaker, jeweler, embroidery).
The main symptoms of accommodation spasm are very similar to the symptoms of myopia - pain in the eyes, rapid fatigue, decreased distance visual acuity.
The eye is an optical system that is in a moving state to correctly focus on the selected object. Its operation is similar to that of binoculars equipped with a special device for adjusting image clarity.
In each eye, this function is performed by the ciliary muscle. With its help, the lens of the eye is able to move to select the appropriate focus of the image on the retina.
With prolonged visual strain, the ciliary muscle “gets tired,” causing the eye to lose its ability to respond to changes in focal length.
Accommodation spasm occurs as a result of visual fatigue, as a result of which a person has difficulty seeing into the distance. This is a reversible process, which is why the spasm of accommodation is called false myopia. However, if a person does not pay due attention to the spasm of accommodation, postponing a visit to the ophthalmologist, false myopia can become true.
Causes of accommodation spasm
- Increased eye strain (watching television programs, working at the computer).
- Incorrect daily routine (insufficient time for sleep, failure to do eye exercises, lack of walks in the fresh air).
- Insufficient illumination of the workplace.
- Weakness of the neck and back muscles.
- Problems with blood supply to the cervical spine.
- Poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis.
- Failure to maintain the optimal distance from the eyes to the book being read (30 – 35 cm).
- The desk and chair do not match the child’s height.
The main stimulus for the appearance of the accommodation reflex is the defocusing of the image on the retina. Under optimal lighting conditions, light rays emanating from a nearby object are focused away from the retina. The defocus perceived by the brain turns on the accommodation mechanism.
The nerve impulse transmits the signal to the ciliary muscle. It contracts, the tension of the zonules of Zinn decreases, as a result of which the lens changes curvature, and the focus of the image moves to the retina.
If you move your gaze into the distance, the focus of the image returns to the retina, there is no defocusing signal, no nerve impulse is received, the ciliary muscle relaxes, the tension of the zonules of Zinn increases, the lens reduces its curvature and becomes flat again.
Symptoms of false myopia
- Redness of the eyes, pain, pain, burning sensation.
- Rapid eye fatigue when working close.
- Less clear perception of nearby objects; distant objects take on a split and blurry shape.
- Headache.
- Decreased performance at school, rapid fatigue of the child in class.
Age and accommodation
The main condition for normal accommodation is the elasticity of the lens, which changes with age. In childhood, the lens exhibits the highest accommodation properties.
Causes
Children have to constantly “load” their eyes with reading at school, and then at home when doing their homework. Added to this load is the constant use of gadgets, computers, and watching TV. There are many more factors that can provoke a spasm of accommodation in schoolchildren than the reasons that cause symptoms of false myopia in adults.
- unbalanced diet and lack of vitamins in the body;
- incorrect body position when reading;
- poor circulation in the spine, especially in the cervical region, disorder of the cervical and spinal muscles;
- using a table and chair that is not appropriate for the child’s age;
- increased strain on the eyes in the absence of eye exercises;
- improper organization of the workspace: poor lighting, too large or too small a distance from which the child reads, etc.
These are the most common reasons. False myopia can also be caused by head/eye injuries and neurological diseases.
The main stimulus for the accommodation reflex to appear is the defocusing of the image on the retina under optimal lighting conditions - light rays from a nearby object are not focused on the retina (defocusing on the retina), this defocusing, perceived by the brain, is an impulse to turn on the accommodation mechanism.
A nerve impulse passing along the oculomotor nerve gives a signal to contract the ciliary muscle. The muscle contracts, the tension of the ligaments of Zinn decreases, and as a result the lens changes its curvature. As a result, the focus of the image moves to the retina. If the gaze is moved into the distance, the focus of the image will return to the retina, there will be no defocus signal, there will be no nerve impulse, the ciliary muscle will relax, the tension of the zonules of Zinn will increase, the lens will eventually reduce its curvature and become flat again.
The development of accommodation spasm is promoted by:
- excessive visual stress (TV, computer, doing homework in the evening);
- poor workplace lighting;
- non-compliance with the daily routine (lack of walks in the fresh air, playing sports, insufficient sleep);
- the desk and chair do not match the child’s height;
- failure to maintain the optimal distance to the book (30–35 cm);
- weakness of the neck and back muscles;
- impaired blood supply to the cervical spine;
- poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis;
- insufficient physical activity.
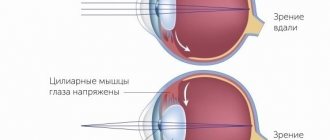
The picture clearly shows the mechanism of accommodation of the eye in accordance with the distance of the object focused by the eye
Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs against the background of excessive psycho-emotional stress. The relationship between the occurrence of pathology and metabolic disorders and diabetes mellitus of any type is also noted.
Since this disease is very rare, medical scientists are constantly studying its triggering factors. As a result of this work, the main causes of accommodation paralysis were established. These include:
- Diseases of infectious etiology: botulism, diphtheria, syphilis, influenza.
- Frequent exposure to cycloplegics and mydriatics.
- Traumatic injury to the ciliary muscle.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Eye contusion.
- Brain pathologies: neoplasms, cysts, abscess, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Damage to the ciliary nerves during surgical treatment with a laser.
These causes cause constantly developing paralysis. A temporary paralytic phenomenon can occur against the background of severe alcohol intoxication.
The reasons for the development of the disease may be different. Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs due to injuries and microtraumas. A temporary spasm may occur when the brain is contused or when looking at the sun. If severe damage occurs in the form of a burn, then the disease develops on an ongoing basis.
There are the following causes of paralysis of accommodation:
- age-related changes;
- tumors;
- inflammation;
- tuberculosis;
- meningitis;
- previous injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- intoxication with drugs or chemical elements;
- diabetes;
- constant physical overload.
The development of paralysis of accommodation also occurs naturally with aging. After forty-five years, the lens becomes inelastic and takes on an irregular shape. Eye strain and physical strain also influence the development of pathology. In order to avoid unpleasant manifestations, it is necessary to visit the doctor more often.
What could be the reasons?
The picture clearly shows the mechanism of accommodation of the eye in accordance with the distance of the object focused by the eye.
Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs against the background of excessive psycho-emotional stress. The relationship between the occurrence of pathology and metabolic disorders and diabetes mellitus of any type is also noted.
Since this disease is very rare, medical scientists are constantly studying its triggering factors. As a result of this work, the main causes of accommodation paralysis were established. These include:
- Diseases of infectious etiology: botulism, diphtheria, syphilis, influenza.
- Frequent exposure to cycloplegics and mydriatics.
- Traumatic injury to the ciliary muscle.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Eye contusion.
- Brain pathologies: neoplasms, cysts, abscess, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Damage to the ciliary nerves during surgical treatment with a laser.
These causes cause constantly developing paralysis. A temporary paralytic phenomenon can occur against the background of severe alcohol intoxication.
Diagnostics
Causes of accommodation disturbance:
- disturbance of sleep and rest patterns;
- lack of necessary physical activity, sedentary lifestyle;
- excessive visual stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- injuries, tumors, vascular disorders.
Accommodation disorders also have physiological causes. Due to the natural aging of the lens, which can no longer perform its accommodative functions, vision deteriorates. In young people, problems with accommodation are more often associated with abnormal eye strain. Spending a long time at a computer in a forced position leads to disruption of the blood supply to the cervical spine and organs of vision, which negatively affects eye health.
The disease most often manifests in adolescence
The clinical symptoms of paralysis of accommodation have common features with other diseases such as: optic neuritis, infiltration of the optic nerve in glioma and sarcoidosis, Chiari syndrome, Foster-Kennedy syndrome, Lyme disease, drug intoxication, medulloblastoma, lymphoblastic leukemia.
To exclude these pathologies, a differential diagnosis of paralysis of accommodation is carried out. It includes a complex consisting of:
- Hardware refractometry.
- Rheophthalmography
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Perimetry.
- Sonography.
- Visometry.
- Microscopic examination with a slit lamp.
- Computed tomography of the brain.
- MRI of the eyeball and brain.
- Accommodation studies using sets of negative and positive lenses.
Based on the results of this examination, the ophthalmologist will be able not only to accurately determine the presence of paralysis of accommodation. Such an examination will also help to establish the reasons for its development.
The following research methods are carried out:
- accomodometry is carried out with a special device to study the reaction of the eyes;
- biomicroscopy using this procedure examines the patient’s fundus;
- viziometry reveals visual acuity thanks to special plates;
- pachymetry makes it possible to find out the thickness of the cornea of the eye;
- Ergography This research method checks the mobility of the ciliary ligament.
It happens that a specialist may prescribe an ultrasound or MRI. If there are suspicions of neurological changes, the doctor will refer you for a consultation with a neurologist. In order to prevent further development of paralysis of accommodation, you need to consult a doctor at the first sign.
| Type of medical service | Service price in rubles |
| Complete ophthalmological examination | 1000 |
| Complete ophthalmological examination of children | 1100 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye disease in an adult | 500 |
| Consultation with an ophthalmologist for eye diseases in children over 3 years of age | 700 |
| Selection of simple glasses with a prescription | 500 |
| Selection of progressive, office glasses with prescription | 700 |
| Selection of contact lenses with training and prescription | 1000 |
| Selection of contact lenses without training | 600 |
| Training in the use of contact lenses | 400 |
Treatment methods
Treatment with ophthalmological devices makes it possible to achieve a lasting therapeutic effect in young patients. In some cases, it is possible to completely get rid of pathologies such as amblyopia, impaired binocular vision, and false myopia.
The lenses have a corrective effect for myopia. Perifocal models are aimed at correcting central and peripheral vision, which provides excellent visibility and a pronounced therapeutic effect.
The device is a system in which light emitters are located at different distances from the patient’s eyes. Training is carried out by adjusting the image position and the speed of changing “pictures”.
Impact on the visual function of the eyes with light and color stimuli that dynamically move over a certain distance in a closed tube. Particularly effective for accommodation disorders and restoration of binocular vision.
The ophthalmic myotrainer relaxer has a complex effect on the organ of vision and oculomotor muscles. Particularly effective for eye accommodation disorders, as well as during myopia, hypermetropia and computer syndrome.
Paralysis of accommodation: what it is, how it manifests itself, diagnosis and treatment
The work of a person's eye must correspond to his daily needs. This is facilitated not only by the structure of the eyeball, but also by accommodation. This term refers to the ability of the eye to have good quality vision at different distances.
In some pathological conditions, the functionality of the eye can be impaired by paralysis of accommodation. What it is, how it manifests itself, and who is at risk can be found out at a consultation with an ophthalmologist or ophthalmologist.
Most often it appears in children aged 7 to 15 years. It is very rarely detected in middle-aged and elderly people. The disease has no gender and develops equally in both women and men.
Spasm of accommodation of the eye
The most common accommodative disorder in children and adults is spasm.
Spasm of accommodation of the eye is a deterioration in visual perception, associated with excessive tone of the eye muscles. Symptoms of a spasm of accommodation may be:
- disturbances in distance visual acuity;
- there is pain, pain, dryness in the eyes;
- headache in the temporal and frontal region;
- rapid visual fatigue.
Spasm of accommodation is called “false” myopia or tired eyes syndrome. The time frame for the duration of visual impairment associated with spasm can last from one month to several years, and if you do not undergo examination and start treatment in time, the spasm can turn into myopia.
With timely complex treatment using hardware and medication, it is possible to restore clarity of vision. The spasm can be relieved by applying conservative treatment with special drops to relax the muscles.
Spasm of accommodation most often occurs in schoolchildren; according to statistics, more than 15% of students suffer from visual impairment.
The causes of spasm of accommodation of the eye can be:
- excessive visual stress associated with long periods of time at the computer or TV screen;
- bad light;
- close reading;
- deviations from the daily routine;
- chronic lack of rash.
Among ophthalmological diseases, spasm of accommodation of the eye confidently holds second place after myopia. A temporary spasm caused by prolonged tension of the extraocular muscles, the process is reversible.
Spasm of accommodation of the eye in adults is extremely rare. This is associated with physiological age-related changes in elasticity and thickening of the capsule of the eye lens. The causes of the disease may be related to a person’s professional activity: intense, monotonous work with small details, with high visual load.
Spasm of accommodation of the eye in adults is extremely rare. This is associated with physiological age-related changes in elasticity and thickening of the capsule of the eye lens. The causes of the disease may be related to a person’s professional activity: intense, monotonous work with small details, with high visual load.
Causes
The reasons for the development of the disease may be different. Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs due to injuries and microtraumas. A temporary spasm may occur when the brain is contused or when looking at the sun. If severe damage occurs in the form of a burn, then the disease develops on an ongoing basis.
When neurological pathologies occur, paralysis of accommodation is a sign and can be treated if the root cause is eliminated.
There are the following causes of paralysis of accommodation:
- age-related changes;
- tumors;
- inflammation;
- tuberculosis;
- meningitis;
- previous injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- poor nutrition;
- intoxication with drugs or chemical elements;
- diabetes;
- constant physical overload.
The development of paralysis of accommodation also occurs naturally with aging. After forty-five years, the lens becomes inelastic and takes on an irregular shape. Eye strain and physical strain also influence the development of pathology. In order to avoid unpleasant manifestations, it is necessary to visit the doctor more often.
The volume of accommodation of the eye and its definition
To determine the performance of the eye, diagnostic procedures are carried out using special medical equipment (an accomodometer) using medicinal relaxation of the eye muscles. The purpose of the study is to identify discomfort in the visual system caused by visual fatigue.
To calculate the volume of accommodation, ophthalmologists use a special calculation formula, which takes into account all indicators of the elasticity of the lens at the farthest and closest points.
The volume of accommodation of the eye is conventionally designated by the letter “A”; the resulting difference in the refraction of light rays between the closest and most distant point of clear vision will be the volume of accommodation.
With good vision, the human eye clearly recognizes small print on 4 lines from the table used in near vision studies at a distance of 1 meter.
A full examination using the ergography method (assessment of the performance of muscle dynamics) reveals the ability to maintain the focus of vision when moving objects.
The rate of adaptation of the eye organs at different ages is different. Newborn babies lack the ability to focus on one object; after two weeks of life, this skill manifests itself.
In adulthood, the normal area of accommodation is considered to be clarity of distance vision at a distance of at least 5 meters, near vision of at least 15 centimeters.
Treatment and symptoms of accommodation paresis
Accommodation paresis is an eye disease, but to understand what it is, you need to understand what accommodation is. In fact, this is a feature of the eye organ that allows you to recognize objects that are located at different distances. You could even say that accommodation is an unconditioned reflex.
When a person begins to experience blurred images, the muscular system of the eyes either relaxes or, on the contrary, tenses. For example, in order to see a picture close up, the muscles tense and vice versa, for distant viewing, they relax. Thanks to this, accommodation of the eye occurs. Such changes occur due to the fact that the lens and eyeball change their parameters: they lengthen, round, and so on. As a rule, with age, the fibers of the lens lose their elasticity and therefore become unable to change curvature. Thus, age-related pathologies appear.
Asthenopia
It occurs in patients with myopia, farsightedness and other refractive errors of the eye, in the absence of vision correction or with incorrectly selected lenses or glasses. It manifests itself in the form of excessive fatigue of the visual system when working at close range, discomfort in the eyes, and is also accompanied by headaches.
| Pathology is not a disease, but if untimely correction can lead to abnormal development of the eye. |
Working with objects at close range leads to inevitable accommodative overstrain and can develop myopia.
Avetisov's technique
The patient stands in front of the window at a distance of 30-35 cm from the window glass, on which a round mark with a diameter of 3-5 mm is pasted. In the distance, along the line of sight passing through this mark, it designates some object for fixation. Then he alternately looks at the mark on the glass, then at an object in the distance.
The exercise is performed for 10 minutes twice a day for 2-3 weeks. Repeat the exercises after 10-15 days until normal accommodative ability of the eyes is achieved.
With exercises, it is necessary to increase the volume of accommodation to 2/3 or 3/4 of its volume, depending on the patient’s age.
Paralysis of accommodation: what is it, the etiology of the disease and methods of treating the pathology
The work of a person's eye must correspond to his daily needs. This is facilitated not only by the structure of the eyeball, but also by accommodation. This term refers to the ability of the eye to have good quality vision at different distances.
In some pathological conditions, the functionality of the eye can be impaired by paralysis of accommodation. What it is, how it manifests itself, and who is at risk can be found out at a consultation with an ophthalmologist or ophthalmologist.
Paralysis of accommodation - what is it?
Depending on the cause, surgery may be required to correct the paralysis.
Accommodation paralysis defines a pathological condition in which the near and far points of clear vision of objects and images merge into one. This pathology of neurogenic origin is not widespread.
Most often it appears in children aged 7 to 15 years. It is very rarely detected in middle-aged and elderly people. The disease has no gender and develops equally in both women and men.
Paralysis of accommodation is accompanied by a loss of the ability of the ciliary muscle to tension. With the development of this pathology in people with normal refraction and farsightedness, the ability to recognize close-up small print disappears.
The disease has a certain classification. In medical practice, the types of paralysis of accommodation are clearly defined.
According to the nature of the lesion, paralysis of accommodation is divided into:
- Unilateral - paralysis develops in one eye.
- Bilateral – characterized by paresis of accommodation with pathological changes in the lens, size of the eyeball and its muscles.
Ophthalmologists also distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- Peripheral - caused by dysfunction of the ciliary ganglion.
- Central - accompanied by an inadequate reaction of the pupils and is associated with damage to the midbrain.
- Isolated – caused by damage to the central nervous system, has a central and peripheral form.
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the presence of accommodation and establish its type, form and stage of development.
What could be the reasons?
The picture clearly shows the mechanism of accommodation of the eye in accordance with the distance of the object focused by the eye
Most often, paralysis of accommodation occurs against the background of excessive psycho-emotional stress. The relationship between the occurrence of pathology and metabolic disorders and diabetes mellitus of any type is also noted.
Since this disease is very rare, medical scientists are constantly studying its triggering factors. As a result of this work, the main causes of accommodation paralysis were established. These include:
- Diseases of infectious etiology: botulism, diphtheria, syphilis, influenza.
- Frequent exposure to cycloplegics and mydriatics.
- Traumatic injury to the ciliary muscle.
- Traumatic brain injuries.
- Eye contusion.
- Brain pathologies: neoplasms, cysts, abscess, meningitis, encephalitis.
- Damage to the ciliary nerves during surgical treatment with a laser.
These causes cause constantly developing paralysis. A temporary paralytic phenomenon can occur against the background of severe alcohol intoxication.
Symptoms of the disease
Paralysis of accommodation has its own clinical symptoms. The main signs of pathology include:
- Constant pupil dilation.
- Redness of the sclera.
- Tearing in rare cases.
- Sensation of burning and foreign body in the eye.
- Inability to recognize text at close range.
- Looking at objects in the distance is accompanied by squinting of varying intensity.
- Feeling the urge to rub your eyes frequently.
- Chronic headache.
- Pain in one or both eyes.
- Fatigue quickly when working with text documents.
This condition is often complemented by an unstable psycho-emotional state and chronic fatigue.
Signs of paralysis of accommodation can appear complexly or individually. Their severity depends on the stage of development of the disease.
Differential diagnosis
The disease most often manifests in adolescence
The clinical symptoms of paralysis of accommodation have common features with other diseases such as: optic neuritis, infiltration of the optic nerve in glioma and sarcoidosis, Chiari syndrome, Foster-Kennedy syndrome, Lyme disease, drug intoxication, medulloblastoma, lymphoblastic leukemia.
To exclude these pathologies, a differential diagnosis of paralysis of accommodation is carried out. It includes a complex consisting of:
- Hardware refractometry.
- Rheophthalmography
- Ophthalmoscopy.
- Perimetry.
- Sonography.
- Visometry.
- Microscopic examination with a slit lamp.
- Computed tomography of the brain.
- MRI of the eyeball and brain.
- Accommodation studies using sets of negative and positive lenses.
Based on the results of this examination, the ophthalmologist will be able not only to accurately determine the presence of paralysis of accommodation. Such an examination will also help to establish the reasons for its development.
Prevention methods
To date, preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of paralysis of accommodation have not been developed. But as preventive measures, ophthalmologists recommend:
- Avoid uncontrolled use of ophthalmic drops.
- Minimize eye and head injury.
- Reduce eye strain by limiting your work with the computer and small print.
- Be examined by an ophthalmologist after suffering from infectious diseases.
The best preventive measure is an annual preventive consultation with an ophthalmologist.
Palsy of accommodation requires timely diagnosis and adequate treatment. To identify the disease at an early stage, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations by an ophthalmologist.
An experienced ophthalmologist will tell you about the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of accommodation spasm in the video:
Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Paralysis of accommodation - what is it?
Depending on the cause, surgical intervention may be required to eliminate the paralysis.
Paralysis of accommodation is a pathological condition in which the near and far points of clear vision of objects and images merge into one. This pathology of neurogenic origin is not widespread.
Most often it appears in children aged 7 to 15 years. It is very rarely detected in middle-aged and elderly people. The disease has no gender and develops equally in both women and men.
Paralysis of accommodation is accompanied by a loss of the ability of the ciliary muscle to tension. With the development of this pathology in people with normal refraction and farsightedness, the ability to recognize close-up small print disappears.
The disease has a certain classification. In medical practice, the types of paralysis of accommodation are clearly defined.
According to the nature of the lesion, paralysis of accommodation is divided into:
- Unilateral - paralysis develops in one eye.
- Bilateral – characterized by paresis of accommodation with pathological changes in the lens, size of the eyeball and its muscles.
Ophthalmologists also distinguish the following forms of the disease:
- Peripheral - caused by dysfunction of the ciliary ganglion.
- Central - accompanied by an inadequate reaction of the pupils and is associated with damage to the midbrain.
- Isolated – caused by damage to the central nervous system, has a central and peripheral form.
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the presence of accommodation and establish its type, form and stage of development.
Treatment of accommodation spasm
Spasm of accommodation is treatable, but it all depends on the level of neglect of this disease. Correction, medication and surgery are the main methods of vision restoration.
Use of Irifrin for spasm of accommodation
Irifrin is one of the most common medications for the treatment of spasm of accommodation. The medicine is an alpha-adrenergic drug and therefore is used in the treatment of children and adults, but naturally, after consultation with a doctor. When used topically, the drug helps to constrict blood vessels, dilate the pupils and improve the functioning of the eyeball. Eye drops are used for myopia, accommodation spasm, iridocyclitis and glaucoma, but the medicine is useless against infectious or viral diseases.
This medicine is sold in the form of drops for topical use. When instilled, the patient’s pupils dilate for 4–6 hours, after 10–40 minutes. After taking the medicine, it is recommended to stay at home and not overload your eyes.
Relieving spasm of the eye muscles
At an early age, many medications or operations are not allowed. That is why the spasm of eye accommodation should be relieved using secondary methods. For example, a child should constantly conduct relaxing exercises that will help restore the functioning of the ciliary muscle.
Work on the visual apparatus will, after a while, begin to produce significant results and vision can even be completely restored without medications, surgeries or correction. There are many methods that help remove spasm of accommodation in children. Treatment must be timely and correct.
In addition, vision treatment is facilitated by a healthy lifestyle, sports, fresh air, proper sleep, nutrition, and low levels of eye strain over a long period of time.
On the issue of spasm of accommodation
Sometimes this pathology is called false myopia due to the similarity of symptoms and the reversibility of the process. Other factors that provoke a spasm of accommodation include insufficient lighting, incorrect posture, the presence of cervical osteochondrosis (and associated vertebral insufficiency), poor nutrition, insufficient physical activity, and so on.
Accommodation spasm can have a different nature; there is no single classification; the structure of the disease includes several clinical forms:
- The physiological or accommodative form is most often recorded in schoolchildren and students due to the close connection and overload of the accommodative apparatus. Leads to weakened vision both at close and long distances. Often accompanies other forms of visual impairment (myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism).
- A transient form associated with the use of ophthalmic drugs such as atropine, pilocarpine, eserine. More often than not, it does not require active treatment and goes away on its own after stopping the medications.
- Neurogenic form (paresis of accommodation, paralysis of accommodation). It is provoked by neurogenic and psychoemotional factors, toxins, and injuries. In this case, the degree of myopia may not change or increase insignificantly, but visual acuity decreases at close distances. In any case, paralysis and paresis lead to a reduction in accommodative reserves and a decrease in the total volume of accommodative capabilities.
- Accommodative asthenopia. Most often it develops in people with farsightedness or astigmatism in the absence or incorrectly selected correction with glasses. It is characterized by rapid eye fatigue, symptoms of chronic blepharoconjunctivitis (hyperemia, burning, itching, foreign body sensation), cerebral symptoms (headaches, vomiting). Associated with excessive tension of the visual apparatus, with sharply limited reserve capabilities of accommodation.
- Presbyopia or age-related accommodation disorders. They develop as a result of gradual involution of the lens under the influence of external factors and inhibition of metabolic processes in old age. With age, the lens loses elasticity and becomes denser. The eye muscles are no longer able to give it the necessary curvature and provide sufficient optical refractive power with such changes.
- Habitually excessive tension of accommodation (PINA). Chronic, gradually developing, long-term (in contrast to acutely developing spasm of accommodation) hypertonicity of accommodation, causing myopization of manifest refraction, but not reducing maximum corrected visual acuity. It develops in both children and adults whose work involves intense visual stress.
For any clinical variants, etiopathogenetic therapy is necessary. Symptomatic treatment, which allows you to relieve clinical manifestations and increase accommodation reserves, is indicated for any form of accommodation spasm, but especially for functional disorders. Such drugs, for example, include the alpha-adrenergic agonist Phenylephrine-Optic . The drug causes dilation of the pupil, improves the outflow of intraocular fluid and constricts the vessels of the conjunctiva. After a single instillation, mydriasis occurs within 10-60 minutes. A convenient dosage regimen (once a day) makes the drug not only effective, but also comfortable for course use.
How does accommodation occur?
The quality of the image we perceive depends on the tone of the eye muscles. When we look at something close, the muscles are tense, and if the object is far away, they relax. Thus, our eyes adapt to different distances between the image and the retina. When a person wants to look at something at a long distance, the ciliary muscle relaxes, and the ligament of Zinn, on the contrary, tenses. Thanks to this, the lens capsule stretches, and light rays fall directly on the lens.
In the reverse order, when the ligament is relaxed and the muscle is tense, the lens takes on a more convex shape. Objects located at a small distance are focused on the retina. The autonomic nervous system (its sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions) is responsible for the mechanism of accommodation.
Prevention
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to deal with its consequences. Prevention of vision pathologies includes:
- eye accommodation training with the help of special exercises and devices;
- strengthening the joints and blood vessels of the cervical-collar area;
- a diet rich in microelements and vitamins;
- general health of the body.
Serious visual impairment begins with small reversible pathologies. Measures taken in time can stop the disease and significantly improve the quality of life.
You need to work at a computer at a distance of 60–70 cm.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the iris, what eye color says
You must also adhere to the following rules:
- Rest your eyes - avoid prolonged strain, take five-minute breaks.
- Nutrition – a person’s diet should be enriched with foods high in fiber, blueberries are recommended.
- Gymnastics – perform a special set of exercises for the eyes every day.
- Hardening the body - spending as much time outdoors as possible, playing sports (swimming, running).
- Massage – disorders can occur due to diseases such as osteochondrosis, scoliosis; in such cases, doctors recommend a course of massage.
- Daily routine – it is necessary to normalize sleep and rest patterns.
- Visit an ophthalmologist regularly.
- Wear glasses only with a doctor's prescription.
Gymnastics
The complex allows you to prevent the development of all accommodation disorders.
- Close your eyes at a fast pace 10–25 times.
- Focus your gaze on objects that are at different distances. The duration of the exercise is 5 minutes.
- Massage closed eyelids for 1-2 minutes.
- Draw a circle with your eyes, 8 times to the left, 8 times to the right.
- On the street, it is recommended to perform the “SURVEILLANCE” exercise; you need to find an object that is moving and follow it (cat, bird, car).
- Do head tilts with your eyes closed, tilt your head to the left shoulder and then to the right, duration 2 minutes.
- To relax the eyes, a massage of the superciliary area for 2 minutes is recommended.
- Move your eyeball left/right and then up/down. The duration of the exercise is 20–30 seconds.
You should know that the complex should be selected by an ophthalmologist after examining the patient, since in some cases contraindications are possible.
The best prevention of accommodation spasm is considered to be proper nutrition with sufficient levels of vitamins and proteins, as well as eye exercises. It is based on exercises aimed at strengthening the eye muscles.
Place a small sticker 15 mm wide on the window glass. Take a place next to the window at a distance of about 40 cm from it. Stop your gaze on the sticker, and then move it to any object on the street, located 7-10 meters from the house. Perform the exercise 10 times.
Take a sitting position, press the eyelids with 3 fingers of one hand, holding for 5 seconds. Repeat 7 times.
Move your eyes up and down, left and right, making the maximum possible turns. Perform up to 10 times without allowing tension.
While standing, extend your index finger forward, then slowly bring it closer to your nose until the finger begins to double. Repeat 10 times.
Standing, extend your arm to a distance of 0.3 m from your eyes. Stay with your gaze on the tip of your finger for 7 seconds, then cover one eye with your hand and continue looking at the finger, then open the first one and close the other. Repeat the exercise seven times.
Blink quickly for 2 minutes.
Performing these exercises will help prevent the development of accommodation spasms and maintain eye health for many years.
The basis for preventing any disease is proper nutrition and exercise. It is necessary to fully rest, take breaks during visual stress, and perform eye exercises.
Myopia in children often develops due to excessive exposure to a computer, TV, or tablet. Such entertainment should be kept to a minimum
It is important to properly equip the child’s work area. It should be well lit, the table and chair should be adjusted to the height of the child
When reading, the distance from the eyes to the book should be at least 35 cm. You cannot read lying down, in dim light, or while driving. The TV should be no closer than 3 meters.
The article may be useful to your friends, share it on social networks. Tell us about your experience in treating accommodative disorders. Be healthy.
Accommodation paresis of the eye
Various neurological diseases, chemical poisoning, and injuries when nerve fibers are damaged lead to paresis and paralysis of accommodation. Accommodation paresis of the eye differs from paralysis by characteristic pathological disorders. With paresis, there is a partial loss of elasticity of the internal paired muscle fibers, which provide accommodation. With the pathology of paresis, accommodation of both eyes is lost, the person cannot see small objects.
Neurological syndrome is often caused by infectious diseases, diabetes, chemical poisoning, and metabolic disorders.
Palsy of accommodation of the eye
Accommodation paralysis is a rare pathological condition in which the near and far points of clear vision merge into one. Accommodation paresis is neurogenic in origin and can be caused by injury or poisoning. It is expressed by a decrease in near vision in patients with good vision or farsightedness, and a slight decrease in vision in nearsighted people.
Pathologies of the accommodative ability of the visual system are the most common factor in visual impairment in schoolchildren. Scientists are carefully studying and developing methods for treating spasms of accommodation. After all, they are quite often the root cause of the occurrence and development of myopia.
Disorders of accommodative function such as paralysis and paresis, which provoke severe asthenopia in school-age children, have been much less studied.
Pathologies of the accommodative ability of the visual system are the most common factor in visual impairment in schoolchildren. Scientists are carefully studying and developing methods for treating spasms of accommodation. After all, they are quite often the root cause of the occurrence and development of myopia.
In what cases is accommodation impaired?
Quite often, accommodation is disrupted in children, adolescents and young people who are forced to focus their gaze at close distances for a long time. The disease mainly affects people who read a lot and constantly work at the computer. In such people, the ability of the eye to see clearly into the distance is impaired. This condition is called false myopia.
Accommodation may be impaired after injuries to the eyeball, due to neurological or infectious diseases, or taking certain medications.
Disorders often develop in people with encephalitis, syphilis, diphtheria, botulism, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, and brain tumors. Uncorrected refractive errors are a common cause.
Men and women over forty often develop presbyopia, an age-related weakness of accommodation. At the same time, distance visual acuity is maintained, but near reading becomes impossible. To correct the disorder, a person is fitted with glasses for near vision. It should be noted that in persons with high degrees of myopia, manifestations of presbyopia are almost always absent.
Disorders often develop in people with encephalitis, syphilis, diphtheria, botulism, diabetes mellitus, multiple sclerosis, and brain tumors. Uncorrected refractive errors are a common cause.