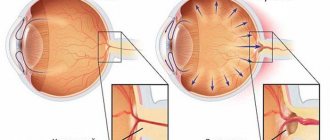
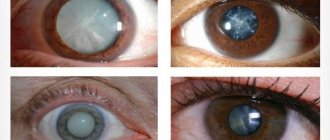
Types of cataracts
The most common type of disease is an age-related or senile anomaly that affects people over forty years of age. However, don't relax if you don't fall into this category. The disease can also affect younger patients.
There are congenital and acquired cataracts. The development of the second is most often provoked by damage to the visual apparatus, complications after illness or prolonged radiation exposure.
The pathology is detected by an ophthalmologist when examining the eyes at a slit lamp; this is the main type of diagnosis of the disease.
What is a cataract?
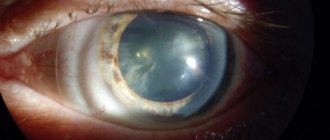
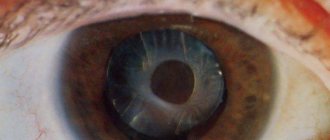
An eye cataract is a clouding of the lens, which causes a decrease in the quality of vision and its complete loss if left untreated. The eye lens is a biconvex lens located between the iris and the vitreous body. In its normal state, the transparent body refracts light rays and passes them to the retina, ensuring the formation of a clear image, which is then transmitted to the human brain.
A healthy lens is highly elastic and can change its shape, allowing vision to adapt to different conditions. With age and under the influence of a number of negative factors, the transparent body becomes cloudy, causing deterioration of vision up to its complete loss. Visual functions decrease gradually, so often a person does not even realize that he has such a problem. Most often, cataracts occur after 60 years of age. And after 80 years, it is present to one degree or another in every person.
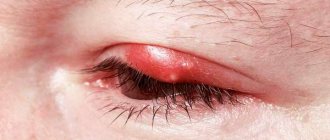
Main symptoms of cataracts
As the pathology progresses, the pupil loses its natural dark pigment and becomes cloudy, visually creating the feeling that it has been covered with a dense whitish film.
However, at this stage it is already obvious that a disease is developing that requires treatment. But for therapy to bring results, the disease must be identified at the initial stage. Before visual symptoms appear, the patient’s subjective sensations will help recognize cataracts:
- When working with small elements, the main part of them cannot be seen;
- Visual acuity decreases despite wearing corrective optical products;
- Periodically, spots and stripes appear before the eyes;
- A shining halo appears around objects.
| Cataracts almost never go away without symptoms. In extreme cases, they will appear in the second stage, when it is not too late to start therapy. |
PROGRESS OF THE OPERATION
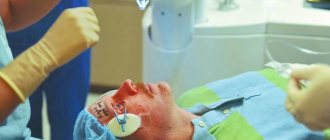
Ultrasound phacoemulsification of cataracts is performed on an outpatient basis. This means that there is no need to stay in the hospital. Previously, a person undergoes the necessary examination and takes an analysis, which makes it possible to identify possible diseases and contraindications. On the appointed day, the patient comes to the clinic an hour before the required time, and after 3-4 hours returns home. Everything happens quite quickly and consistently:
- Preparation, which consists of a preliminary conversation, changing clothes, taking the necessary medications (sedatives, dilating the pupil, etc.)
- Anesthesia is performed locally using special drops.
- The patient is placed on the table, the healthy eye is covered with a special napkin, and the surgical area is treated with antiseptics.
- Viscoelastic is injected into the anterior chamber of the eye - a substance that softens the lens and protects other structures of the eye from destruction.
- An instrument called a phacoemulsifier is inserted through a puncture in the cornea.
- The affected lens is converted into an emulsion using ultrasound.
- The formed substance is removed.
- A pre-selected IOL is installed in place of the lens.
- The protective solution is removed.
- The incision is sealed without the use of sutures.
The patient is under the supervision of a doctor for some time, after which he can freely go home.
Contraindications for laser cataract treatment
The procedure has limitations:
- If the patient has had a heart attack in the last six months, then the operation cannot be performed;
- Oncology;
- Violation of the blood clotting process;
- Exacerbation of chronic ailments;
- Increased intracranial or intraocular pressure;
- Inflammatory pathologies of the organ of vision;
- Ischemia;
- Thinning cornea;
- Use of a pacemaker;
- Increased blood sugar.
| Vision correction using laser is prohibited for pregnant women. Since during this period her hormonal levels are unstable, this can provoke the development of unpleasant consequences after surgery. |
Indications and contraindications
Laser cataract surgery has certain indications and contraindications. Indications for laser treatment:
- clouding of the lens with decreased visual function;
- people with altered corneas (dystrophic changes, small thickness);
- swollen, overripe forms of cataract;
- cataract in combination with secondary glaucoma;
- secondary turbidity.
Contraindications to laser treatment of cataracts:
- infectious diseases of the eyes or other organs;
- period of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- disorders of the blood coagulation system;
- uncorrected cardiovascular pathologies;
- presence of a pacemaker;
- diabetes mellitus with unstable glucose levels;
- increased ICP;
- oncological neoplasms.
Laser treatment is not recommended for pregnant women due to changes in hormonal status. The decision to undergo laser treatment for children under 18 years of age is made on an individual basis.
Treatment and surgery for cataracts
There are several modern techniques that help get rid of a clouded lens and restore vision:
- Extracapsular method;
- Use of ultrasound;
- Application of laser.
The essence of the first technique is that the posterior capsule of the lens is preserved, leaving a small space between it and the anterior part of the eye. Only the nucleus of the affected element and cell masses are removed. The main disadvantage is the use of sutures, since a large incision is made to carry out all the manipulations. We will consider the other two methods in more detail below.
Cataract surgery with femtosecond laser
The device automatically performs all the complex stages of surgery to remove the lens and install the implant:
- Corneal incision;
- Performing an anterior capsulorhexis;
- Phacofragmentation.
The femtosecond laser makes the ideal cut according to individually specified parameters for each patient. Jewelry precision allows the hole to remain sealed after the operation is completed and speed up the recovery process.
The opening of the capsule is also calculated down to the millimeter; this parameter is especially important when implanting premium intraocular lenses. Laser crushing of the lens reduces the amount of ultrasound used, which significantly reduces the level of stress on the cornea and minimizes the risk of complications.
Benefits of cataract removal with a femtosecond laser
The procedure has several undeniable advantages over its “competitors”:
- No incisions are required; all manipulations to crush and extract the lens are carried out remotely;
- 100% safety. During the operation, the doctor sees the eye in 3D format, he can examine its smallest elements. Thanks to this, it is possible to control the progress of the intervention and maintain the integrity of all structures;
- High accuracy. The main part of the procedure takes place automatically, manipulations are performed with an accuracy of one micron. Instead of a knife puncture, the laser gently pushes the eye tissue apart and creates an ideally shaped incision. It heals in a short time because it self-seals and remains stable;
- Fast regeneration. During the operation, no surgical instruments are used; almost all actions are performed remotely. This avoids the risk of complications and speeds up the recovery process;
- Modern implants can 100% replace the human lens. It’s not for nothing that they are called “smart lenses”. The main thing is to distribute them perfectly in the capsule. And only a laser can do this with filigree precision. The IOL must be strictly in the center and maintain a stable position; even the slightest displacement will negatively affect visual acuity.
Return to contents
Ultrasound phacoemulsification
The principle of the procedure is that special equipment is inserted through a small incision on the cornea, emitting ultrasound waves. They crush the affected lens until it reaches the dispersed phase. The resulting emulsion is removed from the eye using a system of tubes.
The main disadvantage of the technique is that a large number of ultrasonic waves negatively affects the condition of nearby tissues and structures. The level of harm caused depends on the power of the vibrations.
How does phacoemulsification occur?
At the beginning of the operation, the doctor manually or using a laser makes a microscopic incision measuring about two and a half millimeters. All further manipulations are carried out through it. A universal substance is injected into the anterior chamber of the visual apparatus, designed to protect the internal structures of the eye from damage.
Then, under the influence of ultrasound, the cloudy mass is destroyed and removed from the cavity through a vacuum syringe. An implant is installed in the cleaned capsule in place of the removed lens, which will subsequently perform all the functions of its “predecessor”.
| The final stage of the operation is washing out the protective substance; an irrigation solution is used for this. |
Cataract surgery with a scalpel (phacoemulsification)
This is the surgical removal of the lens and its replacement with an artificial lens. Through very small incisions at the edge of the cornea, a special instrument is inserted into the eye, which, once opened through a small puncture in the lens capsule, uses ultrasound to crush the hardened and cloudy lens into tiny particles and wash out the resulting liquid.
Then a foldable (multifocal) soft artificial lens is implanted into the eye. It also lasts a lifetime and no longer needs to be replaced.
The advantages of this approach include an individual approach to each patient, thanks to which the risk of complications, despite the frightening description of the technology, tends to zero.
Difference between ultrasound and laser cataract removal
All operations aimed at eliminating the “film” are reduced to crushing and removing the affected lens, followed by the installation of implants, which are intraocular lenses. The use of a laser in this area has made it possible to increase the effectiveness of the operation and minimize the risk of complications.
The incision made in the cornea closes itself, so no stitches are required. The patient can return home several hours after surgery.
Corneal incision
Manipulation is carried out using a diamond knife; it ensures maximum precision and accuracy of the cut. The femtosecond device creates a “notch” of an ideal shape. The cut must be straight, stretched or crooked will not maintain tightness and stability. In this case, the risk of complications increases.
Formation of capsulorhexis
The lens is housed in a special capsule, which is supported by numerous ligaments. To get the contents you need to cut the “packaging”. Using a surgical instrument, the doctor makes a small round hole in the capsule. The laser carries out a similar procedure several times faster and more accurately, which allows you to achieve perfect alignment.
The cut should be circular so that the tension force is distributed evenly over the entire surface and the capsule does not tear. It is almost impossible to carry out such filigree work manually; the hole turns out torn, so the tension force in the meridians is not uniform.
| This threatens in the future rupture of the capsule and, accordingly, further problems with vision. The laser helps to make an even cut, which eliminates the risk of complications. |
Lens destruction
During phacoemulsification, the doctor inserts the tip of an instrument into the damaged eye and crushes the lens using ultrasound. The laser creates flashes of energy in the thickness of the clouded mass, cutting the structure into microscopic cubes. They are sucked out of the cavity using a tip. In advanced situations, the doctor can simultaneously use laser and ultrasound, but sets a lower power so as not to harm other structures of the eye.
Reducing the force of the devices will help keep the corneal endothelial cells intact and avoid eye burns. Return to contents
What is the difference between laser cataract treatment and traditional surgery?
“Femtocataract” is not a special type of disease. This term (perhaps not very successful) refers to one of the methods of treating cataracts, which is based on the use of ultrashort pulse (femtosecond) lasers. Reducing the duration of photon exposure is of fundamental importance: the shorter the light “injection”, the less traumatic, the more limited the surgical field and the lower the risk of undesirable consequences. Therefore, in the technological evolution of pulsed lasers, the count has long been on such small time intervals that it’s not even easy to imagine them - it’s even difficult to write them down in numbers. Thus, a femtosecond is 0.000000000000001 fraction of a normal second.
However, femtosecond lasers today are no longer a technological limit: the release of the first laboratory samples of generators with an attosecond pulse (“femto” = 10 15, “atto” = 10 18) is reported. When replacing a cataract lens, a femtosecond laser is used at the most dangerous stage and area in terms of consequences: to depressurize the eyeball and create access to the lens capsule. Compared to contact microsurgical instruments, the laser scalpel shows such obvious advantages that, apparently, in the near future this technique will be included in standard IOL implantation protocols.
Consequences of cataract removal
After surgery, patients may encounter some problems:
- Increased lacrimation. This symptom indicates that an infection has occurred. During the operation, the entry of pathogenic microorganisms is excluded, since the procedure is carried out under sterile conditions. But if the doctor’s recommendations are not followed (rubbing the eyes, getting water into the organ of vision, etc.), the “pest” could easily penetrate;
- Redness of the eye. Is a sign of developing infection or hemorrhage;
- Swelling of the cornea. Some swelling is normal for three hours after surgery. They usually resolve without outside help;
- Painful sensations. Sometimes intraocular pressure increases after cataract removal. Most often, the reason is in the solution that is used during the intervention. If it cannot pass freely through the drainage system, side effects are observed;
- Retinal detachment. The risk group includes patients suffering from myopia;
- Implant displacement. This happens very rarely. Most often, this complication causes capsule rupture;
- Endophthalmitis. An extensive abscess of the eyeball is one of the most dangerous consequences of cataract surgery. May cause blindness;
- Cloudiness of the capsule. The reason lies in the growth of epithelial cells on the posterior wall. Reduces visual acuity, occurs very often (approximately 25% of cases).
| Complications after cataract removal can be caused by a doctor’s error, concomitant pathologies, or non-compliance with the rehabilitation regime. |
When is surgery scheduled?
It is usually carried out at the second or third stage of the disease if the following symptoms are present:
- decreased vision up to 50%;
- the appearance before the eyes of various optical effects (spots, dots) that prevent the patient from leading a normal lifestyle;
- When looking at a light source, halos and glare appear before the eyes.
These signs indicate that lens replacement is necessary, otherwise the consequences may be irreversible.
Recovery after surgery
Vision returns to normal approximately a month after surgery. During this time, the brain gets used to the updates that have occurred in the visual apparatus. Some patients experience dry eyes, in which case the doctor prescribes moisturizing drops.
Thirty days later, the doctor prescribes new corrective optics. Try to do more work that requires active participation of the eyes. This will be a kind of training for the visual apparatus.
After surgery, the patient must adhere to the following medical recommendations for three months:
- Go outside only with sunglasses, even if the weather is cloudy;
- Avoid getting soapy water in your eyes;
- Do not sleep on the operated side;
- Always keep your head upright if possible;
- Do not lift anything weighing more than five kilograms.
Following simple rules and restrictions will help avoid the risk of complications.
Surgical treatment of traumatic cataracts
The timing of opacification removal will depend on the severity of the inflammatory process, the need to restore vision (this applies to children with an increased risk of amblyopia), future operations and the general condition of the patient. The treatment method and timing should be determined by the doctor, taking into account the vision prognosis and the presence of concomitant pathologies. The surgical plan will be based on the severity and location of the cataract.
The most common method of cataract removal is phacoemulsification, but surgery is contraindicated for brown cataracts. The lens is removed using ultrasound through a small puncture. The entire procedure takes up to 20 minutes. The doctor breaks up the cloudy masses and sucks them out of the capsule in order to insert a special lens into the vacant space. Modern implants are no different in functionality from a natural lens. The rehabilitation period does not take much time, and postoperative recommendations do not complicate the patient’s life. In the vast majority of cases, surgery provides a complete cure for cataracts.
Sometimes they resort to extracapsular extraction. This method is used less and less, although it remains acceptable if the ligaments of Zinn are weak and there is no vitreous hernia. Technologies that make it possible to implant intracapsular rings and capsular hooks are used when removing traumatic cataracts using an anterior approach. In the presence of severe phacodonesis, lens subluxation and capsule damage, another method of removing the opacities should be considered.
Primary extraction of traumatic cataracts is advantageous in that it eliminates the cause of inflammation, normalizes the level of intraocular pressure and carries out visual rehabilitation. Disadvantages of the procedure include a long rehabilitation period and an increased risk of inflammation. It may also be that the cataract did not affect your visual function and surgery will not help restore it.
Implantation of an intraocular lens
Implantation of an intraocular lens can be carried out after cataract removal by any method (provided that there is no inflammation and the risk of infection is low). The lens can be installed in the capsular bag, anterior chamber, ciliary groove, and fixed near the sclera or iris.
In children, clouding of the lens greatly increases the chances of developing amblyopia (lazy eye syndrome). Since rapid opacification of the posterior capsule often occurs after extraction, capsulotomy and vitrectomy (anterior) must be performed along with it. When operating on a child, the doctor must minimize the impact on the developing eye.
Opacities do not always progress, so the doctor must determine the advisability of surgery. If other structures of the eye have not been damaged, unnecessary intervention can only cause harm. When cataracts do not impair vision or provoke inflammation, infection or glaucoma, dynamic monitoring of the condition of the lens is recommended.
Traumatic cataracts are not always treated surgically. In cases where the clouding is not localized in the center of the lens and is not very dense, optical correction can be done. This is due to the fact that such cataracts do not interfere with normal vision.
Cataract laser treatment price
The price for laser cataract removal depends on the clinic, region, service, and type of implant. It can vary from forty to seventy thousand rubles.
Before surgery, it is mandatory to conduct a thorough examination of the patient and a second consultation with an ophthalmologist. Such a service will cost an additional seven or ten thousand rubles.
Remember that most often clinics announce the cost of surgery per eye. Thus, if surgical intervention is necessary for two eyes, then it will cost from eighty to one hundred and forty thousand rubles.
Cost of the operation
The estimated cost of laser surgery for cataracts starts from 40,000 per eye. Pre-collection of tests not included in this amount is required. Laser treatment is carried out on the basis of specialized budget and private clinics.
Laser treatment creates conditions for rapid recovery of the eyeball, which shortens the rehabilitation period. High precision of the laser beam minimizes the risks of complications. Vision begins to recover in the first days after surgery and reaches maximum quality within six months.
Are you familiar with laser treatment for cataracts? Tell us about your impressions in the comments. Share the article on social networks. Protect your eyesight. All the best.
Indications for surgery
Cataracts spread very quickly and can lead to complications such as complete blindness.
Previously, the operation was performed only when the disease was fully mature, but now, with the introduction of new surgical technologies, the procedure can be performed at any stage of the disease.
This eliminates the possibility of complications.
Indications for the operation are:
- Overripe cataract.
- A swelling form of cataract, which is dangerous due to its consequences in the form of glaucoma.
- Change of position of the lens, its dislocation.
- Secondary glaucoma.
- Examination of the fundus (in case of retinal detachment or changes in the fundus due to disease).
It is advisable to start treatment at the first symptoms of the disease; in this case, you can choose a more gentle method.
In some cases, the indication for surgery is the need to preserve 100% vision for professional activities. In this case, for example, for a vehicle driver, visual acuity at the time of the operation should be 0.5. When such high clarity of vision is not required, values of 0.1 are acceptable.
With bilateral cataracts, surgery begins on the eye where visual acuity is lower.
What surgical methods exist?