Possible complications
Despite the fact that night blindness has been declared an independent disease, most often it is a manifestation of completely different serious pathological disorders.
Sometimes it takes a lot of time to identify the cause and treat the underlying disease. You need to understand that the disease is not always easy to treat; for example, with functional or essential hemeralopia, vision restoration can be almost completely restored. To do this, you must follow all the doctor’s advice and not violate the rules of treatment.
As a rule, the outcome of recovery from the acquired form of the disease depends on the illness to which it is due. Here everything depends on a quick diagnosis of the main disease and its degree, the correct prescription of treatment and the individual characteristics of the body.
To diagnose hemeralopia, you should consult an ophthalmologist; it is this doctor who is able to see all the changes and abnormal abnormalities in the retina. Using a special device, using electroretinography, a specialist will determine the stage of the disease and see all those deviations that do not allow a person to fully see.
Questions and answers on the topic “Night blindness”
Question:
Hello, at dusk, black, non-transparent circles appear in the center of my field of vision, and disappear in daylight. What is this? Answer:
Hello. A dark spot in the center of the visual field appears during a pathological process in the area of the macula of the retina. Another reason for the appearance of a dark spot in the center of the visual field may be damage to the choroid. Damage to the choroid leads to impaired nutrition of the retina, and therefore to impaired light perception function. If a dark spot appears in the center of your field of vision, you should first consult an ophthalmologist.
Question:
Hello, at dusk I begin to see poorly, especially when I look into the distance, everything blurs for me, as if it is covered with a veil and I have to strain my eyes, and it also happens when I look close and then into the distance everything is blurry for several seconds. Maybe I don't have enough vitamins or my vision is getting worse? What to do? Answer:
Hello. Your question can only be answered after a complete diagnostic vision examination.
Where does the name “night blindness” come from?
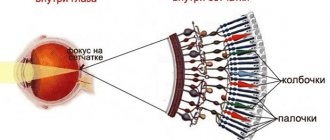
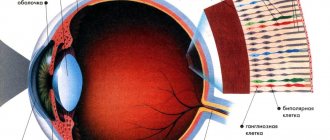
All people have a retina in the internal structure of the eye. It is penetrated by blood vessels and nerve fibers. The nerve endings are called rods and cones. The name comes from their shape. The rods are elongated, and the cones have a bulge in the middle, like a flask. These formations perceive black and white or color images.
The pigment rhodopsin is located on the rods. If the patient is in daylight, rhodopsin is present in the rods. With the onset of darkness, the substance disintegrates and returns to its structure only when daylight comes. In patients suffering from night blindness, this process is slowed down or completely absent. Vitamin A is required for normal synthesis of rhodopsin. If its amount decreases, the substance cannot recover after destruction.
The disease is called night blindness due to the fact that only rods are located on the retina of chickens. Therefore, their vision is black and white. When twilight sets in, they completely lose their vision function and see nothing. This is why chickens fall asleep as soon as there is less light.
Night blindness - treatment with folk remedies
2
- Mix 2 parts each of blueberry leaves, linden flowers and dandelion (leaves, roots and flowers), add 1 part each of buckwheat and sea buckthorn leaves. Pour a tablespoon of the prepared herbal mixture into a glass of boiling water and heat in a water bath for 15 minutes. Then leave in a warm place for half an hour, strain and take the prepared decoction one glass three times a day after meals;
- Pour a teaspoon of wildflower flowers into a glass of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes. Take the finished infusion one tablespoon three times a day after meals;
- Pour a teaspoon of blue cornflower flowers into a glass of boiling water and leave for one hour. Strain the infusion and take 1/4 cup three times a day half an hour before meals;
- Pour one tablespoon of blueberries into a glass of boiling water and leave for four hours. Strain the finished infusion and take half a glass three times a day, regardless of meals;
- Eat sea buckthorn berries fresh or frozen, two glasses a day;
- Pour three tablespoons of sea buckthorn berries into a glass of boiling water and leave for half an hour, then strain. Drink the prepared infusion twice a day an hour after meals. You can add honey or sugar to the infusion to improve the taste;
- Pour two tablespoons of nettle leaves and stem tips with a glass of boiling water, leave for an hour, then strain. Take the finished infusion 1/3 cup three times a day half an hour before meals;
- Take half or a whole glass of fresh carrot juice 2-3 times a day, half an hour before meals. The juice should be prepared immediately before use and stored for no more than 30 minutes;
- Take blueberry juice diluted three times a day before meals. For each dose, you need to dilute a tablespoon of juice in half a glass of water;
- Take half a glass of grape juice three times a day, half an hour before meals;
- Sprout the wheat grains, then grind them in a meat grinder. Pour a tablespoon of sprouted wheat grains into a glass of boiling water and heat in a water bath for half an hour. Then leave for 15 minutes, then strain. Take the finished decoction 1/3 cup three times a day, regardless of meals;
- Fish oil take 30–40 ml three times a day;
- Every day, eat a small piece of lightly fried beef liver;
- Take a teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil three times a day before meals.
How to treat night blindness?
How to treat and how to cure night blindness is determined by the ophthalmologist depending on the causative factor:
- the congenital form is incurable;
- Essential blindness is difficult to treat, the effect is not always observed;
- in the symptomatic form, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease.
Medicinal and non-medicinal methods are applicable in treatment. When myopia develops, a person is given appropriate glasses or lenses.
Nutrition
For any type of disease, vitamins - retinol, riboflavin - have a positive effect. They are contained in the following products:
- all types of greens;
- Cod liver;
- dairy products;
- eggs;
- vegetables;
- fruits;
- berries;
- millet.
The daily menu must contain at least two products from this list.
Medicines
For night blindness, drug treatment consists of taking vitamins:
- A (retinol acetate) – 50–100 thousand IU per day;
- B2 (riboflavin) – 20 mg per day.
Other drugs are prescribed according to the underlying disease. If necessary, vitamins are prescribed in the form of Taufon eye drops.
Folk recipes
Treatment with traditional methods also aims to saturate the body with vitamins. For this purpose, decoctions and infusions are used, prepared from medicinal plants, which contain vitamins A, B, PP.
- Take equal quantities of blueberry, buckwheat and sea buckthorn leaves, dandelion and linden flowers. Mix, take 20 grams of the mixture and pour a glass of boiling water over it. Keep in a water bath for 15 minutes, without bringing to a boil. Strain and take a glass of decoction after meals.
- Grind blue cornflower flowers, take them in the amount of a teaspoon. Brew a glass of boiling water and let stand for 60 minutes. Drink 50 ml before meals.
- Take 10 grams of washed blueberries. Add 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for at least 4 hours. Drink 100 ml 3 times a day.
- Take 60 grams of washed sea buckthorn berries. Add 200 ml of hot boiled water, let stand for 60 minutes. Drink fresh brewed infusion before meals. Eat the berries from the infusion.
- Grind the leaves and tops of the nettles. Take 20 grams of raw materials, add a glass of boiling water. Let stand for 30 minutes, remove leaves. Drink 50 ml before meals.
- Grate fresh carrots on a fine grater. Squeeze the juice and drink 50 ml before meals. Prepare fresh juice for each use.
- It is recommended to eat carrots, blueberries and sea buckthorn daily. It is best to eat these foods fresh and raw.
It is permissible to use any folk remedies after consultation with a doctor, in the absence of allergies to the constituent components.
And a few more secrets for improving night vision from Lyudmila Lazareva:
If a driver has difficulty seeing while driving in the dark at night, he is most likely overexerted. In this case, a short rest is recommended to avoid getting into an accident.
Operation
Indicated if the patient has glaucoma or cataracts, retinal detachment:
- laser coagulation of the retina;
- expansion of the chambers of the eye;
- cataract extraction;
- placement of an artificial lens;
- operations on the cornea.
Surgical treatment is carried out according to strict indications. It does not guarantee a complete cure for night blindness.
Diet
If the disease is caused by a violation of the supply of nutrients to the human body, it is recommended to consume the following foods:
- greens, vegetables, fruits, berries;
- fish;
- various types of grain products;
- dairy products.
If this is not enough, it is recommended to use multivitamin complexes. If the absorption of substances is reduced due to various diseases, the doctor may prescribe intravenous administration of vitamins using a dropper. Such courses must be taken periodically to keep your body in good shape.
Medicines
It is recommended to use different groups of medications, depending on the cause that caused the disease:
- For glaucoma, medications are taken that reduce intraocular pressure. These include Trusopt, Azopt, Dorzopt. You must be careful when using these products. They have many contraindications and possible side effects.
- Drops that reduce lens clouding due to cataracts. These include Taurine, Oftan-katachrome, Quinax. Their action is carried out by reducing the secretion of protein inside the lens, which increases opacification. Additional agents enhance metabolic processes, increased tissue regeneration (renewal, healing) occurs.
- Oral multivitamins. The use of droppers that deliver beneficial substances directly into the blood. Use vitamins A, B2, PP.
Surgery
Currently, surgical methods for treating the eye tissue area have advanced. There are many ways that can cure various diseases that cause vision defects:
- laser surgery to eliminate retinal defects;
- correction of narrowed chambers of the eyes;
- replacement of your own lens with an artificial model;
- changes in the shape of the cornea.
The operation requires a complete eye examination. The referral is given by an ophthalmologist. After surgery, the following outcomes are possible:
- complete restoration of vision function with reduced light intake;
- partial restoration of vision function at dusk;
- lack of effect from the operation;
- relapse of the disease over time due to the fact that the underlying cause has not been eliminated.
Traditional methods
Some categories of patients decide to completely abandon medications that can be used to restore vision function. Doctors recommend complex treatment, which is based on medications and folk remedies.
There are recipes that help restore the deficiency of vitamins in the eye area:
- Take blueberries, sea buckthorn, chamomile, and calendula in equal quantities. Take 30g of the resulting mixture and pour boiling water over it. Leave for 30 minutes. Do not bring to a boil. Decant the liquid, let it cool, drink every day before meals.
- Blueberry infusion. The berries are poured with boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes, drain the liquid, and drink the resulting decoction throughout the day instead of water.
- Carrots are processed using a juicer. The result is a concentrated juice, which you drink 100 ml of water before each meal.
Treatment
Treatment of night blindness depends on the causes and consists of treating the underlying disease. Let us dwell in more detail on how to treat night blindness. There is no specific treatment for hemeralopia yet. If it is acquired and not congenital, the intensity of the manifestations of night blindness can be reduced by treating the underlying disease.
If the cause is cataracts, you may need surgery to replace the lens. For cataract patients, night blindness is a real problem in the true sense of the word.
Night blindness caused by myopia is corrected with lenses. Lenses cannot provide normal twilight vision, but they can improve visual perception to some extent.
Treatment of congenital hemeralopia is an impossible task. No therapy gives any tangible results.
Essential hemeralopia is reversible and preventable. This type of night blindness can be treated by correcting eating habits.
Eating vegetables and fruits rich in carotene will compensate for the deficiency of this very important element.
Fat-soluble vitamin A, contained in carrots, spinach, sea buckthorn, and rose hips, once in the body, is converted into retinol and embedded inside the photoreceptor neurons that regulate daytime and twilight vision. As a result, all symptoms of night blindness disappear.
Night blindness is a vitamin disease. Vitamin A deficiency (“night blindness”)
Vitamin A deficiency (“night blindness”) is a visual disorder expressed in the inability to see in dim (twilight and night) lighting, photophobia, decreased color perception to blue and yellow colors, which occurs when there is a deficiency in the body, usually in early spring.
Night blindness, also called night blindness, is a disease associated with a disorder of human twilight vision. The origin of congenital night blindness is not yet fully understood.
Sometimes the disease is associated with anemia, exhaustion, pregnancy, and certain eye diseases (for example, glaucoma).
The occurrence of the disease is caused by a long-term lack of food or its provitamin - carotene; impaired absorption of carotene in the gastrointestinal tract; disorders of the liver's formation of carotene. The main manifestation of the disease, in addition to growth retardation, should be considered night blindness, as well as some changes in the eyes: dryness, inflammation of the eyelids, keratinization of the conjunctiva, etc. Pigment spots, rashes, etc. appear on the skin. The mucous membranes harden and dry out, which leads to the appearance of bronchitis, otitis media and other diseases. Patients lose their appetite, lose weight, and the acidity of gastric juice drops. The body becomes very sensitive to infections.
Symptoms and course:
In patients, the ability to navigate in space at dusk or in a dark room sharply decreases; in good lighting, the patient sees normally.
The main manifestation of the disease, in addition to growth retardation, should be considered night blindness, as well as some changes in the eyes: dryness, inflammation of the eyelids, keratinization of the conjunctiva, etc.
Pigment spots, rashes, etc. appear on the skin. The mucous membranes harden and dry out, which leads to the appearance of bronchitis, otitis media and other diseases.
Patients lose their appetite, lose weight, and the acidity of gastric juice drops.
The body becomes very sensitive to infections.
In this state, a person’s visual acuity and associated orientation in space during the twilight period noticeably decrease. Characteristic is:
- decreased light sensitivity;
- worse adaptation in the dark;
- a noticeable change in the electroretinogram;
- narrowing of the field of view;
- predominantly;
- for various colors.
The seriousness of this disease is also confirmed by the fact that a medical certificate for the right to drive a car with night blindness found in the driver is not issued.
When making diagnoses, doctors, in addition to the patient’s complaints, are also guided by the results of a study of human dark adaptation.
Recognition:
Based on clinical findings and contrastometry.
Treatment:
If the cause of the disease is poor nutrition, then “night blindness” goes away quickly with intake or by eating food rich in it (animal and cod liver, fresh fruits, vegetables, especially carrots). Since it belongs to the group of fat-soluble substances, sour cream and butter are recommended.
When a decrease in twilight vision is caused by other reasons - damage to the retina or eye (high myopia, retinal degeneration, etc.), then the underlying disease is treated
Congenital (night blindness) cannot be treated. Moreover, with this disease, vision gradually deteriorates.
With essential night blindness, a diet that includes foods containing the contents found in butter, cod liver, cheese, milk, egg yolk, provitamin A, which is rich in spinach, carrots, lettuce, green peas, tomatoes, blackberries, black currants, helps. gooseberries, peach, cherry, apricots, fish. Additionally, you should take riboflamin in a daily dose of approximately 0.02 grams per day. By the way, even with symptomatic night blindness, these products will not be superfluous at all, and can have a beneficial effect.
At the beginning of treatment for this disease, doctors try to find the cause of the disease, to somehow determine what the body lacks. An examination is carried out to determine the level of carotene in the blood. If the concentration of these vitamins is low, appropriate treatment is prescribed. You may also need examinations from other specialists.
It is known for sure that self-treatment of night blindness is absolutely pointless, with the possible exception of the diet suggested above. By the way, millet is useful here.
Night blindness disease
The disease night blindness develops in humans against the background of a deficiency of vitamin A (retinol), “responsible” for vision. It is found in visual purple, a light-sensitive substance in the human retina. When there is enough vitamin A, then a person sees well. If night blindness develops, vitamin A is in short supply, and it urgently needs to be replenished in order to avoid complete loss of vision. Acquired night blindness in humans is called functional. Functional hemelaropia can develop in the following conditions:
- a person suffers from diseases of the retina (for example, retinal detachment, discoloration or inflammatory processes),
- macular degenerative processes develop,
- a person suffers from myopia, cataracts, glaucoma, traumatic brain injuries and other head injuries.
In addition, an improperly lit workplace, working at a computer, reading under a table lamp, as well as a lack of eye protection from ultraviolet radiation (bright sun at sea or in the mountains) negatively affect vision. People over 40 years of age can also become potential victims of night blindness, since, starting from this age, the metabolic rate in the body decreases, which impairs the nutrition of the retina. This leads to a deterioration in the ability to see in semi-darkness and darkness. Functional hemelaropia is not dangerous, and in most cases it can be successfully treated.
But there is another type of this disease, which is quite dangerous because it develops at the genetic level and cannot be treated. The development of this type of night blindness is determined by the structure of the retina of the human eye. Normally, the human retina contains special light-sensitive cells - rods and cones. They are present in the retina in a ratio of 18:1. With a decrease in the number of rods in the retina, a person begins to see worse in twilight and darkness, i.e. night blindness develops. And this disease is called so because the retina of a chicken contains only cones, so chickens can distinguish colors well, but see practically nothing in the dark.
Symptoms of night blindness
Symptoms of night blindness do not appear in humans in normal lighting conditions. He can fully perform all tasks: read, write, work on a computer, etc. The disease night blindness makes itself felt only at dusk. A person sees objects blurry, the image loses clarity, sometimes the perception of colors is disrupted, this is especially noticeable on blue objects. The behavior of a person suffering from night blindness changes dramatically in conditions of lack of light: coordination of movements is impaired, he becomes more careful.
Night blindness, the symptoms of which we have just described, appears in conditions of vitamin A deficiency in the human body. Night blindness is often accompanied by conjunctivitis, dry skin and mucous membranes. Another symptom of night blindness is keratinization of skin areas on the abdomen and buttocks, as well as brittleness and hair loss, and the appearance of ulcers on the cornea of the eyes. This is especially true for children.
If you notice one or more symptoms of night blindness, contact an ophthalmologist who, using special tests, will determine your field of vision, the reaction of the pupils of your eyes to light, as well as the condition of the eye muscles and the retinal layer. Based on these studies, the doctor will conclude whether the person suffers from hemelaropia or not and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Treatment of night blindness
Treatment of night blindness, if it is congenital, is, unfortunately, impossible. Therefore, further we will talk about how to recover from functional hemelaropia, i.e. acquired night blindness. If you have been diagnosed with night blindness, treatment will depend on the cause. In order to get rid of night blindness, you need to cure the disease that caused it.
Most often, night blindness is caused by a lack of retinol; accordingly, vitamins for night blindness will be prescribed A and B2, which promote its best absorption. In severe cases, when a severe lack of vitamins is detected, it is replenished with the help of vitamin complexes. If the situation is not critical, then the patient should follow a diet rich in foods that are a source of vitamin A. These are carrots, cabbage, citrus fruits, vegetable and fruit juices, cheese, milk and dairy products, eggs, cod liver, as well as turkey and beef liver.
It should be noted that night blindness is not a harmless disease. It is fraught with general deterioration of vision or its complete loss. Please note that if you notice a deterioration in vision in only one eye, while the other sees normally in the dark, then this is not night blindness, but some other disease of the visual organs. In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor in order to diagnose and treat the disease in a timely manner.
In addition to a balanced diet, the prevention of night blindness includes protecting your eyes from the bright sun at sea and in the mountains by wearing sunglasses and special mountain glasses, proper lighting of the workplace, as well as taking good care of your health in general.
Deviations and diseases
Impaired twilight vision is a disease that in ophthalmology is referred to as hemeralopia. The disease is not differentiated by degree of complexity or intensity. Hemeralopia, colloquially referred to as “night blindness,” is a vision disorder with the following symptoms:
- Weakened vision in conditions of significantly reduced lighting brightness.
- Poor spatial orientation in the dark or twilight.
- Changes occurring in the mechanism of light adaptation.
- Narrowing of visual fields.
- Problems associated with the perception of yellow and blue colors (quite rare).
An additional sign of night blindness is dryness and keratinization of the epidermis around the eye. In addition, the patient may also experience hair fragility. Hemeralopia is caused by damage to the retina and optic nerve due to various reasons. Twilight vision problems can be:
- Symptomatic. This type of pathology is caused by damage to photoreceptors, which is caused by glaucoma, neuritis, pigmentary degenerations and other organic diseases of the retina, optic nerve or choroid. In this case, the examination also reveals changes in the fundus and visual field.
- Functional. The disease occurs due to the development of hypovitaminosis A in the body. The patient also experiences the formation of xerotic plaques. Plaques appear on the conjunctiva, which is accompanied by exfoliation of the epithelium and hyperkeratosis.
- Congenital. The features of the development of this type of disease are still unclear. The disease is not accompanied by changes in the fundus.
The reasons for the development of acquired may be:
- Lack of vitamin A, B2, nicotinic acid in the body.
- Liver diseases.
- Physical exhaustion.
- Anemia.
- Eye diseases: glaucoma, retinal dystrophy, high degrees of myopia, retinal pigment pathologies, optic nerve atrophy, congestive disc.
- Childhood diseases (measles, chickenpox).
- Toxic poisoning.
- Alcohol abuse, drug addiction.
- Sunburn of the conjunctiva, exposure to excessively bright light on the organs of vision.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the visual part of the brain caused by head trauma.
Hemeralopia
Signs
During the day, in good lighting, hemeralopia sufferers do not have any complaints.
Well, except that sometimes in very bright light they may develop photophobia. However, with the onset of dusk or when the room darkens, they notice that the outlines of objects become unclear and their fields of vision narrow. Color perception is impaired, especially blue and yellow colors. Children with hemeralopia are often frightened by the deterioration of their vision in the dark.
Description
The retina of the eye contains two types of light-sensitive cells - rods and cones. Rods are responsible for black-and-white vision and enable a person to see in low light conditions, while cones are responsible for color perception. Normally, there are approximately 18 times more rods than cones, and if their number decreases or their work is disrupted, a person begins to see worse in the dark and develops night blindness.
Hemeralopia is called night blindness because those suffering from this disease, like chickens, see poorly in the twilight: that the retina of a chicken's eye consists of only cones, so birds distinguish colors very well, but see almost nothing in the dark.
Hemeralopia can be congenital or acquired. Congenital hemeralopia is caused by genetic diseases such as hereditary retinitis pigmentosa or Usher syndrome. In this case, hemeralopia manifests itself quite early in childhood or adolescence.
Acquired hemeralopia can be either essential or symptomatic. Essential hemeralopia develops with functional disorders of the retina. This usually occurs due to a lack of vitamins, PP,. The cause of such vitamin deficiencies can be liver disease, poor and insufficient nutrition, alcoholism, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, rubella, and poisoning with certain chemicals. This hemeralopia worsens in the spring.
Symptomatic hemeralopia usually develops with ophthalmic diseases that damage the retina. This may be glaucoma, chorioretinitis, optic nerve atrophy, complicated high myopia, retinal detachment, cataracts. Symptomatic hemeralopia can develop with traumatic brain injury, with improper desk lighting, or in those who do not wear sunglasses.
A risk factor for the development of hemeralopia is age after 40 years. It is at this time that metabolic processes in the body slow down and the nutrition of the retina deteriorates.
Diagnostics
To diagnose this disease, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. The diagnosis is made based on patient complaints and research:
- perimetry (determining the field of view);
- ophthalmoscopy (detection of degenerative lesions on the retina);
- adaptometry (light perception test);
- electroretinography (study of the functional state of the retina);
- electrooculography (checking the surface layer of the retina).
In the case of essential hemeralopia, a consultation with a gastroenterologist will be required to determine the cause of the vitamin deficiency.
Treatment
Congenital hemeralopia cannot be treated.
In the case of symptomatic hemeralopia, treatment consists of eliminating the underlying disease that caused night blindness. In this case, the outcome of treatment is determined by the severity of the underlying disease. Both complete recovery and permanent loss of twilight vision are possible.
Essential hemeralopia responds well to treatment. To do this, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of vitamin deficiency, and often it is enough to simply change the diet and quality of nutrition. Doctors recommend eating more liver, carrots, spinach, lettuce, green onions, milk, cheese and egg yolks. Apricots, gooseberries, black currants and blueberries are also useful.
Prevention
Prevention of hemeralopia consists of proper nutrition and prevention of eye diseases. Ophthalmologists remind that the workplace should be well lit, and that, if necessary, in bright sunshine, when welding or in white snow, you need to wear safety glasses. You should try to protect your eyes and head from injury.
© Dr. Peter
Classification
The international classifier distinguishes four types of hemeralopia:
- Congenital.
- Symptomatic.
- Essential.
- False.
Congenital
Pathology occurs in childhood or early adolescence. Its appearance is due to genetic factors. Congenital night blindness can occur due to the following diseases:
- hereditary pigmentary rhinitis;
- Usher syndrome.
Children experience progressive deterioration of vision in the dark and poor spatial orientation at dusk. Visual dysfunction is persistent.
Symptomatic
It develops under the influence of external factors or pathologies present in the body. Most often, the causes of the disease are associated with ophthalmological disorders that cause damage to the retina.
Symptomatic hemeralopia is the most unpredictable. As a result, a person may develop an adaptation to low light levels, or he may permanently lose his vision.
Essential
It develops against the background of retinol deficiency or when its metabolism is disrupted. Night blindness can be caused by chronic dieting, starvation, poor diet, chronic alcoholism or malaria. The reason also sometimes lies in liver disease, anemia or severe exhaustion of the body. This type of hemeralopia is temporary and is the easiest to treat.
False
And it is also worth noting such a phenomenon as false night blindness. What does it mean? A person experiences slight deviations in vision at dusk due to eye fatigue, for example, when working at a computer for a long time or constantly watching TV. This type of hemeralopia cannot be treated and goes away on its own after rest.
False night blindness can occur due to visual fatigue
The term "night blindness", types
In ophthalmology, the disease in question has two medical names: hemeralopia and nyctalopia. In Russian terminology, the first option is used.
The term “hemerolopia” is derived from the Greek words “hemer”, “ala” and “op”, which translated into “day”, “blind”, “sight”, is used in the countries of the post-Soviet space. The term “nyctalopia” also comes from three Greek words “nyct”, “ala” and “op”, translated as “night”, “blind” and “sight”, used in England and Great Britain.
There are different types of hemeralopia: congenital, essential and symptomatic.
Congenital
It is hereditary and begins to appear in childhood and adolescence. During this period, children experience a progressive decrease in visibility at dusk and a lack of adaptation in the dark.
Essential
This form of night blindness is explained by insufficient intake of vitamin A into the body or impaired metabolism. The cause of this condition may be malnutrition during fasting, liver disease, alcohol abuse, or malaria. In such cases, the essential type of night blindness is temporary.
Symptomatic
Appears when:
- retinal dystrophy;
- inflammatory processes of the retina, as well as the membrane of the blood vessels of the eye,
- glaucoma;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- complicated myopia and other visual abnormalities.
In addition to night blindness, in these cases other symptoms of a specific disease appear.
There is also the concept of false night blindness, which is characterized by a slight deviation in vision in low light against the background of banal eye fatigue. This type of hemeralopia is not subject to therapeutic intervention and goes away in the patient after proper rest.
Prevention
It is impossible to cure hemeralopia on your own, but prevention must be carried out. Eye health largely depends on nutrition, so first of all you need to balance your diet.
To prevent disorders, it is necessary to include in the diet foods that are rich in vitamin A: carrots, tomatoes, blackberries, spinach, black currants, blueberries, apricots, dairy, seafood, egg yolk, millet.
In addition, you need to eat foods with vitamin B2. Considering that vitamin A is fat-soluble, it is better to combine it with fats.
If you have problems with twilight vision, you should not work at a computer or look at a bright TV, tablet, or phone screen in the dark. There should be additional light that softens the contrast between darkness and brightness. This rule also applies to healthy people.
You should rest your eyes every 40 minutes when working with small parts. It is unacceptable to read from electronic devices in the dark, as well as in bright lamplight. To prevent your eyes from being overloaded, the light should fall evenly.
When in the mountains, you should wear glasses with an ultraviolet filter. This will prevent you from being blinded by reflected rays.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics includes the following activities:
- Visometry - this procedure is familiar to everyone who has ever been examined by an ophthalmologist for visual acuity using Sivtsev’s letter table.
- Perimetry - determination of visual fields using a special device.
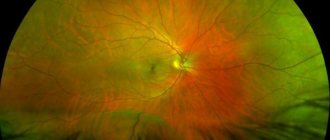
- Examination of the fundus with an ophthalmoscope. In this case, you can see the condition of the blood vessels, the retina and the condition of the optic nerve head. The fact is that the picture of the fundus differs in different forms. With essential hemeralopia there are no changes; with the congenital form, small foci of degeneration are visualized in the fundus.
- Tonometry is the measurement of intraocular pressure.
- Biomicroscopy of the eyes - using a Goldmann lens.
- Refractometry is a more detailed diagnosis prescribed for symptomatic hemeralopia. This is a test of the refractive power of the eye to detect ametropia.
- Electroretinography is a method for diagnosing the functional state of the retina.
- Ultrasound of the fundus of the eye - shows pathologies of the optic nerve head, visual impairment, clouding of the lens, retinal detachment, the presence of a tumor.
Which doctor should I contact if I have difficulty seeing in the dark?
If a person is concerned about the deterioration of dark vision and impaired adaptation to darkness, they should contact an ophthalmologist.
Clinical picture
The main complaint of patients suffering from Hemeralopia is poor vision in low light, at dusk, when moving from a brightly lit room to a dark one, whereas in conditions of sufficient lighting they can see well. The fundus is either changed (in congenital and symptomatic G.) or appears normal (in essential G.). The field of vision is often concentrically narrowed, and sometimes central vision may also suffer. With G., the so-called Purkinje phenomenon, characterized by the fact that, in low light conditions, objects colored green or blue appear lighter than objects colored red or orange. This phenomenon is observed only during normal functioning of the rod apparatus of the retina. The presence or absence of the Purkinje phenomenon can be established using special devices - adaptometers (see Visual adaptation, devices).
Treatment of night blindness
The hereditary form of the disease is incurable. A person's visual acuity at dusk will be reduced, regardless of the activities carried out.
When the disease was acquired during life, it is necessary to establish the factor that provoked night blindness. Only after this will it be possible to select the optimal treatment regimen.
If night blindness is a consequence of myopia, then the patient will need to wear glasses. They are selected depending on the visual characteristics of a particular person. Glasses can be replaced with contact lenses. According to indications, laser vision correction, scleroplasty, lens replacement surgery, etc. can be performed.
In case of night blindness caused by cataracts or glaucoma, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention. This could be phacoemulsification of cataracts, antiglaucomatous surgery, or cataract extraction.
Laser coagulation is prescribed to patients with retinal detachment.
The essential form of the disease responds well to treatment. The patient must be given an individual nutrition plan. The menu will have to include foods rich in carotene and retinol.
Such products include:
- Butter.
- Cod liver.
- Cheeses and milk.
- Chicken eggs.
- Tomatoes and spinach.
- Carrot.
The patient is given installations with eye drops enriched with a vitamin component. Be sure to take additional vitamin A, riboflavin, and nicotinic acid.
Patients with diabetes need to receive sugar-burning medications or insulin injections to control blood glucose levels. Patients with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract are prescribed appropriate treatment.
As for the prognosis for recovery, it completely depends on what kind of pathology led to the deterioration of twilight vision. Both complete recovery and complete blindness are possible. In most cases, it is still possible to get rid of night blindness.
Complications of the disease include the formation of phobias and fear of the dark. In the future, this can provoke a mental disorder.
Treatment of night blindness
Treatment depends on the cause. Prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist. If there is a deficiency of vitamin A, a diet rich in vitamin A and vitamin supplements are indicated. Retinalamin is used in courses.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- Retinalamine (a drug that improves the regeneration of retinal tissue, for systemic use in ophthalmology). Dosage regimen: parabulbar or intramuscular 5-10 mg (dissolving in 1-2 ml of 0.5% procaine solution, water for injection or 0.9% sodium chloride solution) 1 time per day. Course of treatment - 5-10 days; if necessary, repeat after 3-6 months.
- Retinol acetate (vitamin A) - is involved in the formation of visual purple rhodopsin, necessary for twilight vision. Dosage regimen: tablets are prescribed orally (3-5 tablets 3 times a day) or an oil solution of vitamin A (10-20 drops 3 times a day after meals on a piece of black bread, or 2 times a day 5 drops each, increasing the dose by 5 drops per day to 30 drops twice a day for 2–3 months, then the dose is gradually reduced). If necessary, after 4 months the course of treatment is repeated.
- Intramuscular oil solutions of vitamin A are administered daily or every other day in a two-step manner: adults - 10,000-100,000 IU (therapeutic doses vary depending on the nature of the disease), children - 5,000-10,000 IU. A total of 20-30 injections per course of treatment. The highest dose of vitamin A: single dose - 50,000 IU, daily - 100,000 IU.
Diagnosis of the disease
If twilight vision is impaired, you cannot delay a visit to an ophthalmologist and wait until it “goes away on its own,” since night blindness can be a symptom of other serious eye diseases. For example, this is how retinal dystrophy begins; the photo on the Internet shows changes in the pattern of its vessels. Neglecting your health can lead to vision loss. After a conversation with the patient, to clarify the diagnosis of night blindness and its cause, the ophthalmologist conducts a series of studies.
Previously, to determine changes in visual fields in night blindness, perimetry was prescribed. Light perception testing was carried out using adaptometry: a flash of light was directed at the eye and the time during which visual function was fully restored was recorded. A more accurate method for diagnosing night blindness is electroretinography. It is carried out similarly to the previous one, but it is not the time that is recorded, but the change in the electrical potential of the tissues caused by the flash of light. Electrooculography is also performed - a study of the retina and muscles of the eye and their movement.
To determine the adaptation of the organs of vision to darkness in night blindness, an adaptometer with special tables is used. They are a black cardboard base on which 3x3 cm squares of various colors are glued: blue, yellow, red and green. The ophthalmologist turns off the light and shows the table to the patient from a distance of about 50 cm. The test is considered positive, and adaptation is normal, if a person distinguishes yellow color after 30-40 seconds, blue - 40-50 seconds. The conclusion about visual impairment in night blindness is made when the perception of blue is delayed by more than a minute.
Diet and vitamins to prevent night blindness
When twilight blindness occurs in both adults and children, special attention should be paid to the patient’s nutrition. Food should contain foods rich, as already noted, in vitamins A and B2
And also RR. These include many vegetables:
- carrot;
- salad;
- green leeks;
- spinach.
It is important to combine their use with fats of animal origin: butter, sour cream. It must be remembered that they are learned only together
Berries and fruits you should eat:
- apricots;
- peaches;
- cherries;
- gooseberry;
- red and black currants;
- blueberries and blackberries.
As already mentioned, it is necessary to increase the consumption of butter, milk, cheese, egg yolks and millet porridge are also useful.
In addition, the ophthalmologist may prescribe vitamin complexes or preparations of ryboflavin and vitamin A.
Important! If night blindness occurs, do not use fluorescent lamps. Children with mild hemeralopia are prescribed to wear glasses in the evening. The result of treatment for night blindness will depend to a very large extent on the causes that caused the disease
Here, it is possible either complete elimination of symptoms and recovery, or a persistent disorder that cannot be treated
The result of treatment for night blindness will depend to a very large extent on the causes that caused the disease. Here, it is possible either complete elimination of symptoms and recovery, or a persistent disorder that cannot be treated.
Another important point in the treatment of hemeralopia will be the age of the patient. The older the patient, the lower the chances of recovery.
What to do with night blindness
Many people note that their vision noticeably worsens in the evening. Moreover, similar symptoms can be observed even in those who have never had visual impairments. What causes the decrease in visual acuity in the evening, is it possible to cope with this phenomenon? Let’s look at this in this article.
How does night blindness, or blurred vision in the evening, manifest itself?
A condition in which twilight vision deteriorates is called night blindness, or hemeralopia. It is characterized by a decrease in visual acuity and loss of spatial orientation at dusk or in poor lighting. The main symptoms of hemeralopia are decreased sensitivity to light, impaired vision adaptation to darkness, and narrowing of the visual fields. At the same time, in the daytime and in good lighting, a person can see normally.
Ophthalmologists note that it is not an independent disease. More often it indicates the presence of an ophthalmological disease, a lack of vitamins or eye fatigue. In any case, hemeralopia seriously affects the quality of life of people, especially in winter, when daylight hours are greatly reduced.
Why vision deteriorates in the evening: the main causes of hemeralopia
Experts identify several reasons that cause twilight and night vision disorders.
Heredity.
In some cases, hemeralopia is present in a person from birth and persists throughout life.
Vitamin A deficiency.
Retinol is one of the most important vitamins for vision. It is part of rhodopsin (visual pigment) and plays a critical role in the process of light perception. The daily intake of vitamin A for adults ranges from 800 to 1000 mcg. If, for one reason or another, not enough retinol enters the body, a person’s night vision deteriorates and “night blindness” develops.
Eye diseases.
Hemeralopia may be a symptom of some ophthalmological diseases. Poor vision in the dark and at twilight may indicate degenerative changes in the retina, inflammatory diseases of the choroid and retina, optic nerve atrophy, glaucoma and other eye diseases. As a rule, in such cases, “night blindness” is not the only symptom and is accompanied by other clinical manifestations of the disease.
Eye fatigue.
Another common reason why vision decreases in the evening is eye fatigue. If you spend all day in the office at the computer, watch a lot of TV, do sewing or other work that requires good near vision, then in the evening excessive muscle tone occurs. This leads to the fact that distant vision in the evening deteriorates noticeably. The danger of frequent eye fatigue is that regular overstrain of the accommodative muscles can sooner or later lead to myopia, and then appropriate correction will be required.
Main types of night blindness
Depending on the cause that caused hemeralopia, there are several types of night blindness.
Congenital.
In this case, the disorder of twilight and night vision is hereditary and permanent. Congenital hemeralopia manifests itself already in childhood or adolescence and is characterized by a persistent decrease in vision in the dark and a disrupted process of adaptation to changes in illumination. This type of night blindness cannot be cured.
Essential.
This type of hemeralopia occurs when vitamin A is insufficiently supplied to the body or its absorption is impaired. Most often, essential hemeralopia develops in people who adhere to unbalanced diets, eat poorly, suffer from alcoholism, liver disease, and neurasthenia. Impaired absorption of retinol is typical for patients with endocrine diseases, reduced immunity, hepatitis, chronic diseases of the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract. This type of “night blindness” responds well to treatment: it is enough to normalize the intake of retinol in the body or restore metabolic processes.
Symptomatic.
This is a twilight vision disorder that is a symptom of other eye diseases. Therapy in this case consists of treating the underlying disease.
"False night blindness."
If evening vision deteriorates at times due to daytime eye fatigue, then this type of hemeralopia is called “false night blindness.”
Risk groups: who experiences vision loss in the evening?
Night blindness can develop in people of any gender. However, during menopause, serious hormonal changes occur in the female body, due to which the risk of developing hemeralopia becomes several times higher than among representatives of the stronger sex of the same age.
Several other categories of people are also at risk:
• socially vulnerable segments of the population whose diet is depleted in vitamins, including retinol; • adherents of unbalanced strict diets; • patients with chronic diseases that affect the absorption of vitamins; • people over 40 years old, because retinal nutrition deteriorates with age; • patients with certain ophthalmological diseases; • people who work a lot on the computer.
Why is poor vision in the dark dangerous?
Hemeralopia not only reduces the quality of life of patients, it can be truly dangerous.
Firstly, if you don’t pay attention in time to the fact that your vision is diminishing and adaptation to darkness is impaired, you can miss a dangerous ophthalmological disease that will lead to irreversible changes.
Secondly, according to European doctors, night blindness causes road accidents no less often than drunk driving. People who have impaired light perception may not notice dangers on the road, which leads to accidents. For this reason, commissions that determine the professional suitability of drivers and other specialists often conduct a night blindness test.
Deterioration of vision in the evening: diagnosis, treatment and prevention
In most cases, night blindness is treatable, so if your vision in the dark has worsened, you should see an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Diagnosis usually includes analysis of patient complaints, study of clinical symptoms and electroretinography, which allows us to determine the presence of retinal abnormalities.
Also, for diagnostic purposes, the doctor may conduct the following studies:
• perimetry - determination of visual fields; • electrooculography - assessment of the state of the eye muscles and the surface of the retina during movements of the eyeball; • adaptometry - testing for light perception.
Based on the diagnostic results, the specialist determines the type of hemeralopia and prescribes appropriate treatment.
If “night blindness” is associated solely with overwork, then the doctor will recommend changing your work schedule: resting your eyes, taking frequent breaks, maintaining a distance between your eyes and the computer monitor, and performing special exercises. Correct lighting, which should be moderately bright and comfortable, helps to avoid visual fatigue. It is not recommended to work at a monitor or watch TV in the dark.
With essential hemeralopia, it is important to increase the intake of vitamin A into the body or eliminate the causes that interfere with its absorption. With this form of the disorder, diet therapy is often prescribed, which involves a balanced diet and consumption of foods with large amounts of retinol and other vitamins. With “night blindness” you need to eat a lot of fresh berries and fruits (blueberries, black currants, gooseberries, apricots, peaches), herbs and vegetables (carrots, spinach, tomatoes, green peas), as well as cod liver, butter, cheese, eggs , milk. If necessary, the doctor will prescribe a complex of vitamin preparations that compensate for the lack of retinol in the body.
The success of treating symptomatic hemeralopia directly depends on the severity of the underlying disease. If it can be treated or corrected, then the night vision disorder will also be reversible. For example, surgical treatment of myopia or glaucoma in most cases helps to restore clear vision to the patient and restore the light sensitivity of the retina, thereby relieving him of night blindness.
The only form of hemeralopia that cannot be treated is congenital. However, to reduce the severity of symptoms, a specialist may prescribe vitamins and diet therapy.
For people who are at risk for developing hemeralopia, but do not yet have symptoms of this disorder, doctors recommend taking preventive measures:
• eat a balanced diet, eating plenty of foods with vitamin A; • protect your eyes from bright light (dazzled headlights, flashlights, reflected light rays); • regularly visit an ophthalmologist for timely diagnosis of myopia or ophthalmological diseases; • undergo an annual medical examination to identify chronic diseases and conditions that can trigger the development of hemeralopia.
Paying close attention to eye health will help prevent the development of night blindness and maintain good vision in the dark.
Come for a diagnosis at the Kazakh Research Institute of Eye Diseases at the address: Almaty, Tole bi street, 95a (corner of Baitursynov street). Telephone; +7 (727) 279 54 36
More news in the Telegram channel “zakon.kz”. Subscribe!
What causes night blindness? Night blindness
Night blindness is a human disease in which there is no ability to fully see at dusk or in poor lighting. The eyes become less sensitive to light, the field of vision narrows, and primary colors are poorly distinguished.
Causes
The disease develops due to a lack of vitamin A in the human body or lack of adequate nutrition. The disease can also be caused by improper liver function, anemia and severe exhaustion of the entire body.
Congenital disease manifests itself at a very early age and is genetic in nature.
The disease can also develop against the background of existing vision defects, namely: glaucoma, cataracts, myopia, and so on.
However, the root cause of this disease, regardless of its form, is a lack of rhodopsin pigment and its insufficient production in the retina
Signs
With a lack of vitamin A and night blindness, a person experiences a constant deterioration in the ability to see clearly at dusk or in poor lighting; the retina of the eyes becomes extremely sensitive to bright daylight or artificial light. The patient has an inability to distinguish colors, mainly in all shades of blue. A common indicator of vitamin A deficiency is the presence of dark spots in a person's field of vision when he suddenly moves from a dark place into a brightly lit room. The ability to navigate in space at night is lost.
Night blindness, if its cause is not vitamin A deficiency, very often occurs with persistent conjunctivitis, dry skin and mucous membranes. Also a sign of the disease are keratinized areas of skin that appear on the abdomen and buttocks, brittleness and hair loss, and the appearance of ulcers on the cornea of the eyes, especially in children.
Disease detection
The diagnosis of night blindness is made by an ophthalmologist based on an examination of the patient and examination of his complaints. Research is also carried out using special equipment that establishes the fact of abnormal processes occurring in the retina and cornea of the human eye. Vitamin A deficiency is determined using a complete blood test.
Treatment
If the disease is caused by a lack of vitamin A or poor nutrition, then diet therapy is prescribed to treat it. This method is based on eating foods high in calories. These include:
- eggs;
- cheese;
- milk and dairy products;
- Cod liver;
- a wide variety of vegetables and fruits;
- other foods rich in vitamin A.
Congenital night blindness is also treated with a balanced diet, but this rarely gives a positive result. This method may somewhat improve the child’s ability to see at dusk or in poor lighting, but full vision will never be achieved.
Treatment of night blindness, which appears against the background of another eye disease, takes into account the severity of the underlying vision pathology. For example, getting rid of glaucoma through surgery can completely restore the ability to see and navigate equally well in any lighting.
Danger of disease
The lack of comprehensive treatment is fraught with serious consequences. Children experience deterioration of peripheral vision or its complete loss. Adults with night blindness very often get into accidents, since they have practically no visual acuity and the ability to fully navigate the road.
It is worth noting that decreased vision in one eye is not a sign of the disease, since it always affects both eyes.
Prevention of night blindness
Night blindness is a disease that can be prevented, if it is not hereditary, by performing a number of the following preventive measures:
- adhere to proper nutrition, consuming foods with vitamins, especially A and B2;
- avoid the glare of oncoming headlights;
- use the welding machine only with a special mask;
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight;
- the workplace should be well lit;
- do not look at the bright snow;
- avoid visiting the solarium;
- wear sunglasses as needed;
- undergo regular preventive examinations and promptly treat concomitant diseases.
To summarize the above, it should be noted that night blindness is an eye disease that can be completely cured if the patient behaves correctly.
March 30, 2018
Essential hemeralopia (night blindness) is a twilight vision disorder resulting from diseases of the retina and optic nerve. The main cause of the disease is considered to be vitamin deficiency or hypovitaminosis A, B2, PP. Hemeralopia can be congenital, which cannot be treated, or acquired. It can also develop after measles or chickenpox in childhood. Common causes of the disease are malnutrition and anemia, liver disease, exposure to alcohol, and bright light. Treatment is symptomatic.
How to Simply Recommend
Instructions
If difficulties arise in spatial orientation, impaired adaptation to darkness, narrowing of the field
vision
consult an ophthalmologist. As a rule, preparations of animal origin containing vitamins A, B2, and PP are prescribed.
To treat hemeralopia, use a diet based on eating foods that contain essential vitamins. Eating beef is especially beneficial.
liver
, carrots with
oil
, cream or sour cream. It is useful to include two or three of the following products in your daily diet. These are tomatoes, spinach, green onions, black currants, apricots, gooseberries, cod liver, dairy products, egg yolk, caviar, millet.
Take advantage of traditional medicine recipes that help improve visual health.
nerve
and retina
eyes
. Prepare the following herbal collection. Take 2 parts each of leaves and roots of dandelion, cordate linden flowers, blueberry leaves, one part each of leaves
sea buckthorn
and buckwheat
sowing
After chopping, mix the ingredients.
Brew 3 tablespoons of the collection with 750 ml of boiling water. After soaking in a water bath for 15 minutes, leave for half an hour. Strain and drink 200 ml three times a day after meals.
Use stinging nettle for treatment. It is recommended to consume soup daily in the spring.
tops
young plants. During the rest of the year, take nettle infusion. Brew 2 tablespoons of crushed nettle leaves with a glass of boiling water.
After leaving for an hour, strain. Take 1/3 cup three times a day half an hour before meals.
Also use grass - wildflower (chicken
blindness
). Brew 5 grams of dry herb with 200 ml of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes, strain. Drink 15 ml three times a day after meals.
Take fish oil 2 tablespoons three times a day. Course – 3-4
weeks
.
note
Essential hemeralopia is treatable and must be treated. According to statistics, the number of accidents involving drivers suffering from this disease is almost the same as those involving drunken motorists.
Helpful advice
Also include freshly prepared grape juice, carrot juice, blueberry juice, sea buckthorn juice, and sea buckthorn oil in your diet.
How to treat night blindness
The congenital type of hemeralopia is practically untreatable, but the others can be successfully combated. For example, if night blindness is the result of some other eye disease, then the main treatment method here will be therapy for the underlying disease. Sometimes surgical intervention (laser vision correction) may be necessary.
The essential type of disease is treated mainly with a special diet. The patient should add foods high in vitamin A to their diet and also maintain a healthy daily routine.
Diet for night blindness plays a very important role in the treatment of this disease. Be sure to include the following foods in your diet:
- Carrot.
- Egg yolk.
- Tomatoes.
- Cheese.
- Millet.
- Berries.
- Butter.
- Spinach.
- Beef liver or cod liver.
Also, do not forget about vegetables and fruits: peaches, pumpkin juice, green peas, apricots, parsley. To improve the absorption of vitamin A, you need to add foods with vitamin E to your diet: nuts, seeds, broccoli, potatoes.
Eye drops for night blindness
Riboflavin. This is a multicomponent vitamin preparation that contains riboflavin (that is, vitamin B2). This remedy is considered only preventive; it helps to enrich the tissues with the necessary amount of oxygen and facilitate the conduction of nerve impulses, especially in the retina. Indicated for night blindness, keratitis, conjunctivitis, iriditis.
Typically, the dosage of riboflavin is as follows: twice a day, the patient instills one drop of the drug into each eye. The duration of therapy can only be prescribed by a doctor.
The product is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to its components. Side effects include: short-term loss of visual acuity, allergies.
Vitamins
Typically, the treatment of night blindness is based on increasing the intake of vitamin A into the human body. Usually, drugs with this vitamin are prescribed in the following dosage: adults - up to 100 thousand IU of the vitamin per day, children - up to 5 thousand IU of the vitamin per day. You should also simultaneously prescribe medications with vitamins B2 and PP.
Traditional treatment
- Try to drink at least a little fish oil three times a day.
- Try to add the following foods to your daily diet: carrots, peas, green onions, spinach, black currants, beans, parsley, gooseberries, sea buckthorn.
- Drink one mustard seed daily with plenty of water. Gradually increase the dose of grains (up to 20 pieces), and then start decreasing again.
Please note that before using traditional methods of treating night blindness, you must consult your doctor.
Herbal treatment
- Infusion of stinking cornflower herb. Take 10 g of raw material, pour one glass of water, leave for 15 minutes, then strain. Take one tablespoon per day (3-4 times) before meals.
- Decoction of seed millet. Take one cup of millet, pour two liters of water into an enamel pan, cook until the grain is completely boiled. Use until vision improves.
- A decoction of medicinal herbs. Take equal shares of primrose leaves, lingonberries, blackberries, viburnum, forest raspberries, lemon balm and snake knotweed rhizomes (one teaspoon each). Brew the resulting mixture in 0.35 liters of boiling water. Leave for one hour. Take half a glass three times a day.
Surgical treatment
If hemeralopia was caused by myopia, glaucoma, cataracts, then, in some cases, it is difficult to do without surgical treatment. Sometimes refractive surgery is necessary, which is based on the correction of corneal and retinal defects. If night blindness is caused by pigmentary dystrophy, then a transplantation is necessary. Glaucoma or cataracts are treated with lens replacement (laser eye surgery), which, of course, also helps with night blindness.
Night blindness or hemelaropia is a disease with impaired vision in twilight and twilight. Therefore, this disease is also called twilight and night blindness. Is this disease dangerous? What causes it to appear? How does it manifest and how to treat it? Read about this in our article.
Prognosis and prevention
As already indicated, congenital night blindness is practically untreatable. Essential and symptomatic hemeralopia has a more favorable prognosis. However, they can also lead to vision loss. To judge an accurate prognosis, the doctor must carefully examine the patient and assess all the risks.
Many people with night blindness develop a persistent fear of the dark. This is especially true for children. Sometimes this is in the nature of a phobia, and sometimes it can develop into obsessive mental disorders.
Prevention of night blindness includes the following measures:
- Make sure you have vitamin A in your daily diet;
- Protect your eyes from ultraviolet radiation;
- Avoid visiting a solarium;
- Do not overexert the visual analyzer;
- People who have had previous episodes of night blindness are strongly advised to protect their eyes from bright lights (fluorescent lights, welding, car headlights);
- Visit your eye doctor's office annually.