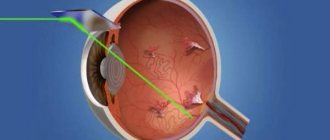
More than 20 million vision restoration operations have been performed worldwide. However, there are complaints of visual impairment after laser correction. Nevertheless, the procedure is in demand as it helps restore clarity and eliminate the manifestations of myopia and hypermetropia. This effect is achieved by modeling a new shape of the cornea. As a result, light refraction changes and image sharpness increases.
Advantages and disadvantages of the operation
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Applicable to all types of visual impairments | Age restriction: not available under 18 years of age |
| Safety and non-traumatic | Does not prevent senile farsightedness |
| Quick tangible results | Not applicable for glaucoma, retinal abnormalities, cataracts |
| No pain | There are risks during pregnancy and breastfeeding |
| Performed under local anesthesia | Re-correction may be necessary |
| The duration of the procedure is no more than 20 minutes | Expensive |
| Possibility of correction on one or two eyes at once | Complete stabilization of vision - more than six months |
| No need for postoperative hospitalization | Any injury to the visual organ is subsequently suffered in a more severe form |
| Fast post-operative recovery | There is a small chance of pathology regression |
| A quick return to normal life |
Pros and cons of laser correction
A contraindication to correction is the presence of eye diseases such as cataracts, glaucoma, various retinal pathologies, as well as tuberculosis, diabetes, inflammatory diseases, infections and oncology. This method is not recommended for pregnant and lactating women.
The optimal age of patients is from 18 to 45 years old due to the fact that before the age of 18 the human body is in a period of growth, and after 45 years the period of hormonal changes and age-related changes begins.
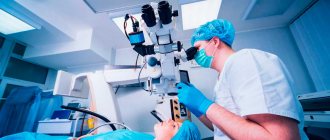
The positive aspects are speed, painlessness, quick recovery - the surgical intervention lasts 15-20 minutes, under local anesthesia, after which the patient is in the clinic for only 1.5-2 hours. The rehabilitation period takes 1-1.5 weeks. Full recovery in most cases occurs within a month.
Quick and tangible results, the opportunity to live without glasses and contacts – all this attracts patients. Before the operation, the doctor performs the necessary examinations, and if the diagnostic results allow, surgery is prescribed. After the correction, you must follow all the doctor’s instructions so that the rehabilitation period goes smoothly.
Possible complications after laser correction
Why are there?
According to statistics, complications after laser correction occur in 1-2% of cases. However, unpleasant postoperative symptoms are more common.
A defect in the equipment or the inexperience of the surgeon may cause visual impairment after the procedure.
It is important to understand that surgery to restore vision may have undesirable consequences. Some of them go away in a couple of hours, others last longer. However, there are more serious complications that appear long after surgery. The fact that vision decreases can be caused by various reasons, for example, visiting a dubious clinic or an inexperienced surgeon, as well as inadequate technical facilities of the institution. One of the consequences provoked by this factor is the loss of vacuum at the moment of cutting the outer cover of the cornea. The reasons for this are as follows:
- depressurization of the structure of the visual organ due to shifting or compression of tissues;
- factory defect of blades or other structural elements of equipment;
- failure to create the proper vacuum level before making the cut.
Frequent manifestations
After eye surgery, small accumulations of blood around the cornea may be visible. This is a temporary phenomenon that does not last longer than a month. Photophobia is also noted during the recovery period. In the first six months after surgery, vision decreases, patients see poorly in the dark, and glare is noticed around the light source. Sometimes the visual organs become inflamed, which requires additional consultation with the attending physician. At first, vision may decrease, there is pain in the eyes and a feeling of discomfort.
During the rehabilitation period, an ophthalmic solution is used to relieve eye inflammation.
In the postoperative period, anti-inflammatory drops are prescribed. Individual sensitivity to the drug can lead to an increase in intraocular fluid pressure. The first month after correction, the near image is cloudy, while the patient’s distance vision is twice as good. In 10-15% of cases, there is a feeling of dryness in the eyes. This symptom usually disappears after 6 months, during which time moisturizing drops must be used. During the rehabilitation period, you may also experience:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- increased lacrimation;
- a veil before the eyes;
- permanent dilation of the pupils;
- conjunctivitis.
What to do if your vision has deteriorated?
Myopia
You begin to have difficulty seeing objects located far away.
At the same time, objects nearby are still clearly visible. In young people, myopia most often manifests itself in early childhood and is associated with myopia (congenital weakness of the eye muscles), in adults - with less pronounced myopia, which appears a little later, and much less often - with age-related reasons: changes in the shape of the cornea, sclerosis of the lens, etc. Therefore, the main cause of myopia is hereditary. The biophysics of myopia is simple - the beam is focused not on the retina, but a little closer. What to do. An examination by an ophthalmologist is sufficient to diagnose myopia, determine its degree and select a correction method (wearing glasses and/or contact lenses, LASIK laser correction, etc.).
Take the test Is it time to get your eyes checked? Believe in tears Pseudomyopia
Many people have to look at a computer, tablet or phone monitor for a long time. Prolonged tension can lead to overstrain of the eye muscles and the appearance of a symptom of pseudomyopia, when the eye has difficulty reorienting itself to objects at a distance. In this case, objects in the distance may appear blurry for some time.
What to do. After every hour of working at the computer, take a 10-minute break, do eye exercises, and use computer glasses.
Farsightedness
The ability to see objects located in the distance remains the same, and even improves somewhat, while objects located close become blurry. Unlike myopia, it is not hereditary, but an age-related disease. Farsightedness occurs mainly in middle and old age and is called presbyopia. Its reason is a decrease in the ability of the lens to change curvature, as a result the beam is focused not on the retina, but behind it. Diagnosis of farsightedness is simple - just visit an ophthalmologist and choose a correction method. But even such a simple disease has its pitfalls. With incipient presbyopia, the eye is able to focus the beam on the retina due to constant overstrain of the eye muscles. As a result, vision in a normal situation remains normal, but about an hour after starting to read or work at the computer, a headache and lacrimation appear. Don't miss this symptom and make an appointment with your doctor on time.
What to do. To slow down the development of presbyopia, choose glasses in time, LASIK laser correction is possible.
Astigmatism
This is an impairment of the eye's ability to see clearly. The cause may be abnormalities in the shape of the cornea, lens or vitreous body of the eye, most often congenital. As a result, the image is formed on the retina as if in two places, the clarity of the image decreases, progressive deterioration of vision, rapid fatigue during work, headache, and possible vision of objects as curved and double vision. Astigmatism can be easily detected using a special test, looking at a piece of paper with black parallel lines with one eye. When the sheet is rotated in front of an astigmatic eye, the lines become blurred.
What to do. Astigmatism is treated with glasses, special contact lenses, and LASIK laser correction provides good results.
Vegetovascular dystonia (vascular spasm)
Dysfunction of the nervous regulation of blood vessels is more common in adolescents and young women, but can occur at any age. In addition to causeless anxiety and constantly wet palms, the disease can manifest itself as so-called vascular crises, accompanied by headache, nausea and various visual disturbances, including the appearance of dark spots and spots before the eyes and even loss of visual fields. Fortunately, such a crisis passes quickly.
What to do. You may need to consult a neurologist, take an electroencephalogram (EEG) and select a course of sedative and vasodilating pills.
Glaucoma
The disease has many causes and one consequence – increased intraocular pressure. This causes dangerous changes in the structures of the eye and optic nerve, which can lead a person to complete blindness, and has characteristic symptoms. Among them are the appearance of “fog” or “mesh” before the eyes, “rainbow circles” when looking at a light source, a feeling of heaviness, tension and periodic pain in the eye, deterioration of vision at dusk. More often, glaucoma develops gradually, there is time to worry about the growing symptoms and make an appointment with a doctor, but sometimes an acute attack of glaucoma occurs suddenly. In this case, the patient is bothered by severe pain in the eye and headache, nausea, vomiting, and general weakness are possible. It is interesting that of the indicated symptoms, one, the main one, may be missing - pain in the eye, then an attack of glaucoma is mistaken for a migraine, flu, toothache, meningitis and even food poisoning.
What to do. In case of an acute attack, the main thing is to call an ambulance in time, and if other diseases are excluded, be sure to get an examination by an ophthalmologist. In case of a chronic course, be constantly under the supervision of an ophthalmologist conducting treatment.
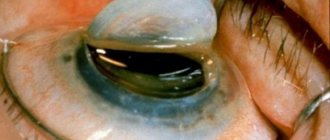
Cataract
This is a disease of the lens – the main “lens” of our eye. Remember when a small speck quietly appears on the camera lens and then tediously accompanies all your vacation photos? Likewise, darkening the lens spoils the perception of the world. The first symptoms of cataracts include the flickering of “flies” and “stripes” before the eyes, increased sensitivity to bright light, blurred vision, distortion of the objects in question, and weakened perception of colors and shades. A common first symptom is difficulty in choosing glasses to correct farsightedness. This is no coincidence, because both diseases are age-related.
What to do. Do not delay surgical treatment; today, lens replacement is very quick and with minimal risk of complications.
Brain neoplasms
The appearance of any neoplasm in the cranial cavity necessarily leads to an increase in intracranial pressure. This causes swelling of the optic nerves and transient blurred vision. It is transient. Those who are ill describe it as “a veil suddenly falling over the eyes.” It comes suddenly and goes away slowly, up to 30 minutes. Another symptom is the so-called “morning blindness,” when a person wakes up almost blind, and after a while “sees clearly.” Another important symptom is a progressive deterioration of vision against the background of the listed symptoms. As well as headaches radiating to the bridge of the nose and the back of the head, and occasional double vision.
What to do. An MRI is the most effective way to detect brain tumors. It is not necessary that it will be a tumor; more than half of brain tumors do not have malignant potential and do not recur.
Age-related farsightedness is a natural human condition. The process begins at age 25, but only by age 40–50 do letters become blurry when read. By the age of 65, the eye almost completely loses the ability to correctly focus the beam on the retina.
Hemeralopia
Previously, this disease, popularly called night blindness, was very common. Nowadays, there are few new cases, but it occurs among residents of the North, as well as among those suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with poor absorption of vitamins. The main reason is a lack of vitamin A, which is found in butter, milk, cheese, eggs, blackberries, black currants, peaches, tomatoes, spinach, lettuce, and some other vegetables and fruits. The main symptoms are significant deterioration of vision in the dark, impaired perception of colors, especially blue, and the appearance of “spots” in the field of vision when moving from a darkened room to a lighter one.
What to do. Contact your therapist and ophthalmologist and take a blood test to check your vitamin A level.
Stroke
Sudden blurred vision may be one of the first symptoms of a stroke. A sudden decrease or complete disappearance of vision in both eyes, the appearance of fog in front of the eyes, double vision, loss of half the field of vision (a person stops seeing on one side) will make you think about a neurological cause. This is accompanied by weakness of the limbs on one side, speech impairment, and loss of consciousness.
What to do. If you experience any sudden visual disturbances, call an ambulance immediately.
Multiple sclerosis
Visual impairment is one of the common symptoms of the first onset of multiple sclerosis. In this case, vision in one eye suddenly decreases, up to complete blindness, which is restored within a few days, black spots appear in the field of vision, fog and a veil before the eyes, double vision. Multiple sclerosis most often affects women 20–40 years old, but recently the disease has become more common in both adolescents and men. After the “debut”, the disease may not manifest itself in any way for 10 or even 20 years, so a sudden visual impairment will subsequently become an important diagnostic episode.
What to do. Consult a neurologist and perform an MRI.
Author: Alexey Fedorov Published: September 23, 2020
Postoperative visual impairment: consequences
In some cases, it is noted that after correction, vision decreases. This can happen even long after surgery. This decline in vision is called regression of the operating effect. Most often this occurs with severe myopia or farsightedness. Patients with large pupils sometimes see distorted images in the dark. In addition, some report poor vision in dim lighting. This phenomenon explains the decrease in contrast sensitivity. There is a possibility of corneal opacification, retinal detachment, bulging of thin areas of the cornea, flap slippage and corneal failure. The following possible symptoms negatively affect visual function, causing severe discomfort:
In some cases, a regression of the surgical effect occurs, which is accompanied by pain and burning in the organs of vision.
- pain;
- adhesion of the eyelid and mucous membrane;
- sensation of a foreign object;
- burning sensation;
- fog in the eyes.
After operation
The restrictions associated with scleroplasty are usually minimal. So, after 10-14 days, the child can already resume sports and other types of physical activity; the forced pause in schooling does not exceed one and a half weeks; swimming in the pool is allowed after one postoperative month in the absence of any complications.
However, two restrictions must still be observed strictly and for quite a long time (up to one and a half to two years after the operation): intense visual loads are contraindicated, as well as physical strain (in particular, lifting even heavy weights that are quite feasible for a child). If scleroplasty is performed on a girl, questions are often asked about the possible impact of the surgery on the ability to perform reproductive functions - for example, there are concerns that natural childbirth will be contraindicated. In this regard, the prognosis is favorable: scleroplasty does not increase, but, on the contrary, reduces the likelihood that myopia will become a mandatory indication for cesarean section. Speaking about scleroplasty, it would be deontologically and ethically incorrect to omit the fact that this ophthalmic surgical technique is practiced only in the CIS countries; Experts from European countries do not consider its effectiveness to be sufficiently justified.
What to do if symptoms occur?
Severe prolonged eye pain, permanent fluctuations in vision, flashes of light are reasons to seek advice from an ophthalmologist. The same applies to inflammation of the cornea, a feeling of dryness in the eyes and slight clouding. In most cases, these symptoms are eliminated with complex therapy. However, in some cases it is necessary to re-correct. Such manifestations include sudden loss of vision, severe clouding of the cornea, and displacement of the pupils. In this situation, immediate contact with your doctor is required.
Long-term complications
Long-term consequences of the procedure may appear in the coming months or years following the operation. The incidence of such complications on average does not exceed 3%.
The most common long-term consequences of laser vision correction include:
- defective metabolic processes, causing insufficient tissue nutrition, development of dry eye syndrome;
- frequent inflammatory processes in the visual system;
- the occurrence of astigmatism, leading to blurred vision at various distances;
- progressive clouding of the ocular cornea;
- deterioration of visual function in farsighted or nearsighted patients;
- deformation of the cornea, complemented by impaired light transmission and the occurrence of keratectasia (bulging of thinned corneal areas);
- increase in intraocular pressure indicators;
- thinning of the corneal tissue, formation of keratoconus.
When such problems arise, there is a need for detailed ophthalmological diagnostics and appropriate treatment.
Benefits of laser correction of farsightedness
This method of treating hypermetropia has a number of undeniable advantages. Laser correction is a painless and bloodless procedure performed on an outpatient basis. Vision is restored quite quickly, side effects disappear within a few days, and there are almost no complications. However, there are also “disadvantages” to this method of correcting refractive errors. There are many contraindications to laser surgery - age-related and medical. Laser correction is not suitable for treatment for anyone under 18 years of age. Another drawback is the fairly high cost. But 95% of patients stop wearing glasses and contacts. The effect of the operation lasts for many years.