Consultation with a urologist – 1,750 rubles.
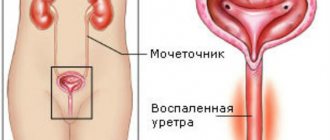
Pyelonephritis
- inflammatory kidney disease of predominantly bacterial etiology, characterized by damage to the renal pelvis, calyces and renal parenchyma.
The inflammatory process is initially localized in its internal part, where the pyelocaliceal structure of the kidney is located and where urine concentration occurs.
In the absence of treatment, or if it is carried out inadequately, the inflammation slowly spreads to the renal cortex. At the same time, sclerosis and shrinkage of the kidney develop Source: Nekrasova A.A. Be careful - pyelonephritis! / A.A. Nekrasova // Atmosphere. Cardiology. - 2004. - No. 2. - P. 40-41. . The disease can occur in acute
or
chronic
form. Among patients of all ages, the majority are women, the ratio between them and men ranges from 1:3 to 1:30. Among men, the incidence of pyelonephritis increases after 40 years of age, which in most cases is associated with the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia Source: Rumyantsev A.Sh. Etiology and pathogenesis of pyelonephritis / A.Sh. Rumyantsev, N.S. Goncharova // Nephrology. - 2000. - T. 4. - No. 3. - P. 40-52. .
What becomes the root cause of the disease?
Currently, pyelonephritis is considered to be an exclusively ascending urinogenic infection, in which bacteria from the bladder enter the renal parenchyma Source: Bergeron MG Treatment of pyelonephritis in adults / MG Bergeron // Med. Clin. North Amer. Antimicrobial Therapy. - 1995. - Vol. 79. - No. 3. - P. 619-649. .
Among the pathogens, gram-negative flora predominates, which is sown on average in 80% of cases. In general, among the causative agents of pyelonephritis, E. coli is the leader, which is found in approximately 80% of patients. In second place, according to various authors, is Proteus mirabilis - 14-16%, Enterecocci - 21%, Klebsiella pneumoniae - 12-15% Source: Rumyantsev A.Sh. Etiology and pathogenesis of pyelonephritis / A.Sh. Rumyantsev, N.S. Goncharova // Nephrology. - 2000. - T. 4. - No. 3. - P. 40-52. .
Urinary tract infections caused by Candida are mainly observed in patients with diabetes mellitus, seriously ill patients receiving long-term broad-spectrum antibiotics, when treated with corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, cytostatics and any other patients with immunodeficiency of other origins and a long-standing catheter.
Viral pyelonephritis occurs mainly in children during an epidemic of group A influenza. At the beginning of the disease, it is characterized by an abacterial course, but after 4-5 days opportunistic flora joins Source: Rumyantsev A.Sh. Etiology and pathogenesis of pyelonephritis / A.Sh. Rumyantsev, N.S. Goncharova // Nephrology. - 2000. - T. 4. - No. 3. - P. 40-52. .
The reservoir of uropathogenic bacteria is the rectum, perineum and urethra. In addition, in men the source of pathogenic E.coli is the prostate gland, and in women it is the vagina Source: Rumyantsev A.Sh. Etiology and pathogenesis of pyelonephritis / A.Sh. Rumyantsev, N.S. Goncharova // Nephrology. - 2000. - T. 4. - No. 3. - P. 40-52. .
The most important factors predisposing to the penetration of uropathogenic bacteria into the urethra and bladder include:
- Anatomical features of the female urinary tract: short, wide urethra and proximity to the anorectal zone.
- Intense sexual activity, which can cause tissue irritation and increase susceptibility to infection, as well as increase the mechanical transfer of bacteria from the anal-vaginal area to the urethra.
- Use of a diaphragm and spermicides for contraceptive purposes, which contribute to the colonization of the vagina by E. coli.
- Delayed postcoital voiding.
- Homosexual contacts.
- Menopause period.
- Irregular toileting of the male genital organs.
- Insufficiency of local immunity.
- Any anatomical or functional disorders leading to disruption of urine outflow, as well as instrumental manipulations.
Forecasts and preventive recommendations
With immediate qualified treatment, the prognosis will be favorable. There are also a few simple rules that will help you avoid serious complications. If there are congenital pathologies, they require monitoring and timely correction. And also do not forget about a healthy lifestyle; during the off-season, the body needs an abundant supply of vitamins. People prone to frequent relapses of urinary system diseases require regular monitoring by a specialist, at least twice a year.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
As the disease progresses, the symptoms of pyelonephritis are quite vivid. This may be an elevated temperature, swelling of the face, general malaise of the body, pain, discomfort in the lower back, and trembling may begin. Nausea and vomiting may also occur.
Not everyone, however, approximately every third patient experiences problems with urination, experiences pain during this process, and also upon visual analysis, the urine has an unnatural color, perhaps even blood.
However, it is also worth noting that such symptoms may not be caused by kidney inflammation, and self-medication in such cases is simply contraindicated. It is necessary to contact professional doctors.
How long does it take to treat pyelonephritis?
The most common question patients ask: “How long does it take to treat pyelonephritis?” It all depends on how timely the patient presented, what type of pyelonephritis was diagnosed and how accurately the patient follows all the instructions and procedures.
Often, this disease is asymptomatic or with mild symptoms, so many patients do not pay special attention to the first signs and the disease progresses, which leads to more serious problems with the functioning of the organ. As a result, people turn to a doctor when their health condition no longer allows them to lead their usual rhythm of life and serious complications arise.
There are two main types of pyelonephritis - acute and chronic. Depending on what type the patient has, the duration of therapy in the hospital takes so long.
If the patient came for the first time with this diagnosis and the disease is in an acute form, then treatment of this type is more successful and the treatment time is much shorter.
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis:
- High temperature, but without chills and aching joints;
- The pain in the lower back is not severe, it can radiate to the right hypochondrium;
- Nausea, vomiting;
- Frequent or, conversely, rare urination;
- Change in the color and odor of urine.
The treatment of acute pyelonephritis includes several mandatory points:
- Strict bed rest;
- Strict adherence to the diet (restriction of salt and protein);
- Antibiotics selected by the attending physician for 10 days;
- Compliance with the water regime, the volume of liquid is at least 2 liters in fractional portions.
For the chronic type of this disease, treatment will take a longer time, at least one year. If the diet is violated or the doctor’s instructions are not followed, treatment can drag on for years. Typically, chronic pyelonephritis occurs as a result of untreated acute pyelonephritis, non-compliance with diet, refusal to take medications and herbal remedies, and hypothermia.
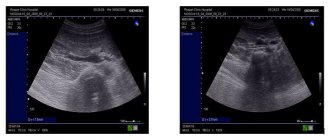
Symptoms of the chronic type are not so obvious; all patients may have different symptoms. A urine test does not always show changes or abnormalities in the organs of the urinary system. The diagnosis can only be confirmed using ultrasound.
Symptoms of chronic disease:
- High blood pressure
- Fatigue and decreased performance
- Possibly shortness of breath
- Stool disorders
- Dull, mild pain in the lumbar region
Basic methods of complex treatment of chronic form:
- Antibacterial therapy from 1 to 5 weeks. However, the course of therapy will need to be carried out systematically as prescribed by the doctor monitoring you;
- Treatment with mineral water for 4 to 6 weeks. The course will need to be repeated after the break. During the year you need to conduct 2-3 courses;
- Physiotherapy in consultation with a doctor;
- Phytotherapy;
- A course of vitamins.
All chronic treatment tactics are designed for duration and repetition of the course of treatment. Your kidneys will hurt constantly if you do not repeat several courses of therapy within a year, depending on the condition, in a clinic or hospital. Monitoring of treatment only by ultrasound every six months.
There are many cases when patients take pills in large quantities and complain that recovery does not occur, but you need to be treated not only with medications. Treatment of chronic pyelonephritis should be comprehensive. There are examples when a patient cured it with Nephrodilin in 3 weeks. Or using herbal decoctions in addition to the main treatment, patients got rid of the diagnosis in 3 years. Depending on the stage of the disease, the effectiveness of treatment, and individual characteristics, the recovery time of patients may vary.
With advanced pyelonephritis, complications will certainly begin.
Possible complications and pathologies:
- The inflammatory process will lead to the formation of ulcers;
- Formation of a carbuncle. In this case, only surgical intervention will help;
- Kidney abscess;
- Acute renal failure;
- Sepsis.
Treatment of infection
Treatment of pyelonephritis should be comprehensive and include, in addition to medication, diet. In case of kidney disease of this kind, it is necessary to eat low-fat foods, avoid fried, spicy, and excessively salty foods. It is also prohibited to consume any foods that are bright red in color.
When treating kidneys, antibiotics are mainly prescribed, and the patient must undergo a full course of treatment in order to completely destroy the bacteria inside his body. Painkillers are also prescribed for severe pain.
However, unfortunately, such a disease can return and become chronic . Therefore, it is necessary to undergo regular diagnostics to identify this disease. “SM-Clinic” makes it possible to start treatment in a timely manner under the supervision of experienced specialists.
Sources:
- Bergeron MG Treatment of pyelonephritis in adults / MG Bergeron // Med. Clin. North Amer. Antimicrobial Therapy. - 1995. - Vol. 79. - No. 3. - P. 619-649.
- Nekrasova A.A. Be careful - pyelonephritis! / A.A. Nekrasova // Atmosphere. Cardiology. - 2004. - No. 2. - P. 40-41.
- Rumyantsev A.Sh. Etiology and pathogenesis of pyelonephritis / A.Sh. Rumyantsev, N.S. Goncharova // Nephrology. - 2000. - T. 4. - No. 3. - P. 40-52.
- Styazhkina S.N. Structure of incidence of pyelonephritis / S.N. Styazhkina [and others] // Problems of modern science and education. — 2016.
Use of Fitolysin® paste in complex therapy of urinary tract infections
For cystitis, urethritis, exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis, treatment should be comprehensive. Together with the antibiotic, Fitolysin® paste can be prescribed to prepare an oral suspension (hereinafter referred to as Fitolysin®), which, according to the instructions, is used for the complex treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the urinary system.6
The drug has a natural composition, which includes a condensed extract of a mixture of plant raw materials (9 components), 4 essential oils and auxiliary components6.
Fitolysin® paste is intended for the preparation of an oral suspension. In this form, the active components are better absorbed into the blood and delivered directly to the site of inflammation.2,6 The convenient release form significantly simplifies the dosage and use of the drug.
The herbal preparation has antispasmodic, diuretic, and anti-inflammatory effects. According to the instructions, Fitolysin® paste should be taken 3-4 times a day, dissolving 1 teaspoon of the composition in half a glass of sweet warm water. The course of treatment lasts from 2 weeks to 1.5 months (can be extended if necessary).6
Postoperative period in children
Features of postoperative management of children after kidney surgery vary greatly and are determined not only by the general condition of the child, but also by the condition of the postoperative wound.
If the general condition is severe due to severe intoxication or the development of a septic condition, the child is left in the intensive care ward under the supervision of resuscitators. Resuscitators continue antibacterial therapy, but at the same time they also use techniques to maintain cardiac and respiratory functions.
If the condition is not regarded as serious, the baby is quickly transferred first to the surgical room and then to the general ward. There he continues to be under the supervision of doctors. Gradually, drainage is removed from the wound, and a decision is made about the possibility of removing the nephrostomy, which previously drained urine from the affected organ.
The nephrostomy must be removed gradually, clamping the tube for an increasingly longer period of time, ranging from an hour to a day. At the same time, the patient’s condition is carefully monitored in order to promptly notice the development of unfavorable symptoms.
Healing is considered complete when there is no discharge from a small fistula for at least 2-3 days. While the wound is healing, therapy with previously selected drugs is constantly continued, the diet and regimen recommended by the doctor are followed.
Forecast. Prevention
The prognosis for pyelonephritis is favorable. Most acute pyelonephritis is successfully treated on an outpatient basis, and only a small proportion of cases require hospitalization. Nevertheless, a certain percentage of deaths remains. The reasons for the unfavorable course of the disease are age over 65 years, the addition of acute renal failure, untimely detection of purulent complications requiring surgical intervention, and severe concomitant diseases such as decompensated diabetes mellitus. [5]
Drawing up an individual prevention plan begins with studying the history of a specific disease. In particular, it is necessary to answer the question of how the bacteria entered the kidney: through blood or urine? With the hematogenous route of infection, it is necessary to sanitize the foci of chronic infection existing in the body, eliminate hypothermia and carry out the prevention of seasonal colds. In the case of urinogenic infection, it is necessary to prevent inflammatory diseases of the bladder.
In the case of a secondary form of acute pyelonephritis, it is advisable to restore the normal outflow of urine from the affected kidney.
Regardless of the route of microbes entering the kidney, all patients are recommended to consume a sufficient amount of fluid and a variety of urological herbal preparations. [4]
Diagnostics
Diagnostics begins in the doctor’s office, who collects all the information about the patient, palpates the abdominal cavity, determining the surface condition of the organ, its size, and pain. Next, the patient needs to undergo general blood and urine tests, which, in case of inflammation, will show significant deviations from the norm in the indicators of leukocytes, red blood cells, and if acute purulent pyelonephritis has formed, there are impurities of pus, blood and cloudy sediment in the urine. Bacterial culture will help identify the pathogen. This is important when choosing an antibiotic and prescribing a course of treatment.
Instrumental
Acute pyelonephritis is diagnosed using ultrasound, which is used to confirm the diagnosis and during treatment to determine the effectiveness of therapy. An ultrasound can show the condition of the tissues of the organ, its size, the presence of foci of inflammation and their location. If there is insufficient data from this type of study and the doctor cannot make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is advised to undergo a urographic examination, MRI or CT scan of the kidneys.
Urography is performed using contrast, which is concentrated in the kidneys, which makes it possible to assess the condition of the organ, their size, the presence of inflammation and erosion. With an MRI or CT scan, the doctor receives the most accurate images of the kidneys, and all changes in them, foci of inflammation and other pathologies are visible. Differential diagnosis is needed in order to exclude other diseases that have symptoms similar to those of acute pyelonephritis. This is appendicitis if the pain is localized on the right, cholecystitis, cholangitis and andexitis.
Treatment of purulent pyelonephritis in children
If a small patient develops purulent kidney damage, his hospitalization in a hospital becomes mandatory, and the baby’s life depends on it. Indeed, with purulent pyelonephritis, the risk of mortality is 20%, which is considered a high figure.
Treatment begins immediately intensively, with antibiotic therapy, diuretics, antipyretics and anti-inflammatory drugs. The baby may also be prescribed medications that prevent blood clotting and antioxidants that help the body cope with the infection faster.
Kidney drainage surgery may be performed to remove pus from the affected organ. The need for drainage is considered in each case individually.
The intervention can be performed by two methods: open and laparoscopic, depending on the severity of the organ damage by the pathological process. If the focus of pus is small, preference is given to the laparoscopic technique, and if the entire organ is affected, you will have to resort to the open method. During drainage, a tube is inserted into the source of pus, through which pathological secretions are drained out.
Drainage helps speed up the healing process and increase the likelihood of saving the patient’s organ.
How does the disease manifest?
The first manifestation of the disease is often pain in the lumbar region, often on one side. The pain may radiate towards the spine or to the buttock. This is characterized by an increase in body temperature to high numbers. As a rule, when we talk about acute pyelonephritis, the temperature rises sharply, often with chills. In this case, there is general weakness and malaise. Dysuric phenomena may also occur, namely: pain and cramping during urination, as well as its frequency.
Chronic pyelonephritis during an exacerbation manifests itself with the same symptoms, only they are, as a rule, already familiar to the patient, since the manifestations of the disease do not actually change from exacerbation to exacerbation. In addition, in the chronic form, the symptoms may be less pronounced than in the acute course of the infectious-inflammatory process in the pyelocaliceal system.
Complications
Damage to the kidneys by an inflammatory process, that is, pyelonephritis, is a dangerous disease that can not only cause a lot of difficulties for the patient, but also lead to death if timely and comprehensive assistance is not provided. Most often, complications of the disease are associated with the spread of pathological processes to surrounding tissues. Conditions such as paranephritis, urosepsis, bacteremic shock, etc. can develop.
The doctor’s task is to stop the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms as quickly as possible precisely in order to prevent the spread of pathological processes both throughout the organ itself and into nearby tissues.
Another dangerous complication of the disease is the development of renal failure. The pathology can be either acute, requiring immediate medical attention, or it can become chronic, which will progress with age due to the fact that the urinary organs have already been damaged once.
We must not forget that the disease can be very aggressive and severe, and then the affected organ cannot be saved. In this case, a removal operation is performed, which has an adverse effect on the body as a whole, but allows saving the life of the patient.