Home / Pyelonephritis - symptoms, prevention and treatment
Pyelonephritis is a bacterial inflammation of the kidneys, or rather its pelvis and parenchyma. This pathology can be secondary, i.e., occur due to other kidney diseases (for example, urolithiasis, glamerulonephritis), or it can be primary (for example, due to hypothermia). Most often, the causative agents of this disease are staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, Proteus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella.
The main provoking factors for the occurrence of pyelonephritis. Knowing the main provoking factors for the onset of the disease, you can prevent the occurrence of a chronic form of inflammation and the development of complications:
- Hypothermia.
- Pyelonephritis appeared earlier.
- Diseases of the genitourinary system (glamerulonephritis, urethritis, cystitis, kidney stones.).
- Inflammatory diseases (tonsillitis, sinusitis, etc.).
- Untreated pyelonephritis.
- Frequent stress, overexertion.
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Diabetes.
- Pregnancy.
- Injuries to the kidneys and bladder.
- Prolonged stagnation of urine in the bladder.
- Anomalies of the genitourinary system.
- The presence of hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamins).
- HIV infection (provokes the occurrence of other diseases, including pyelonephritis). Women are more predisposed to pyelonephritis than men due to the anatomical structure of the female genitourinary system. They have a wider and shorter urethra, so infection can easily “reach” the kidneys.
Signs of acute pyelonephritis . This disease usually makes itself felt with high fever, vomiting, lethargy, discomfort in the muscles, and chills. After two or three days you may experience lower back pain. In such cases, urination usually becomes painful and the urine becomes cloudy. Before lower back pain occurs, you may have discomfort in the groin.
Where should chronic pyelonephritis be treated?
The disease occurs in waves, when it is difficult to separate the period of exacerbation of the process from remission based on clinical signs, and the manifestations are very atypical and sluggish.
The goal of therapy is to reduce the activity of inflammation, ideally to rid the urinary tract of pathological microflora.
- In case of exacerbation of the disease, which occurs against the background of normal urine excretion, treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis.
- Inpatient treatment is indicated for patients with complications - impaired excretion or passage of urine, which creates favorable conditions for the growth and reproduction of bacterial flora.
- In all cases of purulent process or septic condition, symptoms of renal failure, microflora resistance to antibiotics, hospitalization is necessary.
What can a patient do for himself with pyelonephritis?
Regardless of the activity of the process, drinking plenty of fluids is necessary to remove microbes and their toxins, so a person suffering from chronic pyelonephritis should drink a lot, at least 2.5 liters. Limitations on fluid volumes are imposed when “renal” hypertension develops; in this case, consultation with a cardiologist is necessary.
- Drink “soft”, plain water is better, the good therapeutic effect of cranberry and lingonberry fruit drinks has been proven.
- You can use diuretic herbal mixtures; hypertensive patients need to coordinate their actions with a doctor, since diuretics are prescribed to reduce blood pressure; harmless herbal tea can become a “fly in the ointment.”
- You can take herbal preparations cystone and canephron, which “clean” the urine.
- Salty and spicy foods are limited, the dietary regime is gentle, that is, nothing irritating and no spices.
Prevention of pyelonephritis
Disease prevention aims to prevent infectious agents from entering the kidneys and controlling risk factors. Here are the main points of prevention.
- To prevent and treat pyelonephritis, you should drink enough
- Avoiding hypothermia
- Treatment of foci of infection in the body.
- Treatment of diseases that provoke pyelonephritis.
- It is recommended to go to the toilet immediately after the urge appears, without delay.
- Women are advised to empty their bladder after sexual intercourse to prevent bacteria from entering it.
- You need to drink enough. - Do not use spermicides or condoms with them.
- Clinicians should take precautions when using urinary catheters.
How is chronic pyelonephritis treated?
In the latent phase, in the absence of clinical symptoms, antibacterial therapy is usually not carried out. The need for antibiotics arises when the process worsens. For mild or moderate severity, antibiotics are prescribed in tablets for two weeks; for severe cases, injectable drugs in high doses are prescribed.
Before prescribing antibiotics, the type of infectious agent and its sensitivity to the drug must be determined, and in this case it is important how quickly this analysis can be performed in the laboratory of a medical institution.
In some severe and rapidly progressing cases, antibiotics are prescribed empirically, but after receiving the test result, treatment is adjusted.
Surgery for pyelonephritis
As a rule, chronic pyelonephritis develops against the background of disturbances in the outflow of urine, therefore, during an exacerbation, it is immediately determined whether there are any obstacles to the flow of urine from the kidney; if there is compression or narrowing of the ureter, then they resort to prompt restoration of normal passage.
If a carbuncle or purulent inflammation develops, an emergency operation is also performed, during which a locally located source of inflammation is removed and a temporary outflow of urine is established directly from the kidney - a nephrostomy.
In case of pyonephrosis - purulent melting of the kidney, when it is a bag of pus, it is necessary to remove it for health reasons.
The non-functioning kidney, which is a constant source of infection and a stimulator of increased blood pressure, is also removed.
Adequate treatment will help avoid surgery and prolong remission; for this, the Medicine 24/7 clinic applies an individual approach to each patient based on clinical recommendations from the world's leading medical centers. Administrators are always ready to take your call
We will call you back
Leave your phone number
Chronic pyelonephritis arises from acute. In some cases, the first inflammation of the kidney remains undiagnosed, since it occurs under the guise of another disease, most often a protracted acute respiratory viral infection. If after the first attack of pyelonephritis the symptoms of the disease persist for more than six months or after recovery there are at least two exacerbations over the same period, then we can talk about a chronic form of the infection.
Why does pyelonephritis “prey” on women?
The cause of the inflammatory process in the kidneys is pathogenic microorganisms. In 90 cases out of 100, the causative agent of the infection is Escherichia coli; much less frequently, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, enterococci and staphylococci become the cause of the disease.
The infection enters the kidneys through the urethra. In women it is quite wide and short (approximately 3 cm). Since the urethra is located in close proximity to the entrance to the vagina and anus, pathogenic microorganisms enter from there first into the urethra, and from there into the bladder.
The entry of infection into the kidneys from the bladder is referred to as the “ascending route.” How does this happen? Urine is expelled upward from the bladder. This process is called reflux. Bacteria can also enter the kidney via an ascending route without the presence of reflux, although this significantly increases the likelihood of developing pyelonephritis.
It occurs in cases where the natural outflow of urine is obstructed:
- the presence of stones;
- structural defects of the bladder;
- inability to release urine due to an unforeseen situation (being in a public place without access to a toilet).
Once in the kidneys, the infection initiates an inflammatory process.
In addition to the ascending route of infection into the kidneys, a descending route is also noted. Pathogenic microorganisms can be delivered by blood flow to the kidneys from any source of infection: from a diseased tooth, from the intestines, from the respiratory tract, etc.
Why does chronic pyelonephritis develop?
Everything in the body is individual, severe acute pyelonephritis may never remind itself again, and an unnoticed and very easily passed infection will remain in the body forever.
Chronicity of kidney inflammation is promoted by:
- Inadequate treatment of acute infection, which implies the wrong choice of drug, insufficient dose or irregular use, as well as refusal to continue taking medication when subjective improvement occurs.
- An unrecognized violation of the outflow of urine, which contributes to stagnation and proliferation of microflora.
- Long-term residence of inactive forms of bacteria in the interstitial tissue of the kidney, their activation under favorable immune conditions.
- Concomitant diseases that weaken the defenses.
- Immune deficiency.
Symptoms of acute pyelonephritis
Clinical manifestations of AP usually develop within several hours to one day. Classic symptoms include:
- persistent or relieving fever. The symptom is present in most cases, and the temperature often exceeds 39.4 degrees;
- pain in the costovertebral angle. The intensity of pain varies: from mild to severe. Most often, pain is felt on the side of the affected kidney, but bilateral pain syndrome is also possible;
- nausea and/or vomiting. The symptom varies in frequency and intensity. As a rule, with AP, anorexia is pronounced;
- macrohematuria (blood in the urine, which can be determined visually. It is registered in 30-40% of young women. It is not very typical for men.
Men, children and elderly patients who have symptoms of acute kidney pyelonephritis for more than six days are diagnosed with complicated AP until proven otherwise.
In geriatric patients, along with the characteristic signs of AP, there may be a deterioration in general condition, decompensation of concomitant diseases and changes in mental status.
Symptoms of chronic kidney inflammation
Acute pyelonephritis has characteristic symptoms, chronic pyelonephritis has nothing typical, everything is determined by the amount of tissue involvement and the type of inflammation at the moment. However, the initially focal local process covers the entire kidney over the years, replacing normal tissue with connective tissue scar tissue, disabling the functions of the organ and developing renal failure.
Chronic infection can occur without any obvious manifestations - a latent phase, in waves with alternating activity and subsidence of the process. It is often difficult to understand that there is an exacerbation, but when the activation of the infection is quite clearly separated from remission by an increase in the intensity of symptoms, then a recurrent version of the infection is assumed. Symptoms during an exacerbation are the same as for any sluggish infection:
- temperature reaction of varying severity,
- painful discomfort in the lumbar region,
- weakness and fatigue.
If the temperature rises for no apparent reason and weakness and fatigue persist for a long time, then a serious problem should be suspected; the Medicine 24/7 clinic will conduct an examination as soon as possible and determine the root cause of the symptoms of malaise.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis has clear manifestations; it is usually diagnosed after a medical interview and examination, supported by a urine test. On the other hand, chronic pyelonephritis increasingly occurs latently and is diagnosed during random examinations.
The most important laboratory test is a urine test. It may include:
- leukocyte esterase test strip (to quickly detect pus in the urine);
- nitrite production test (confirms the presence of bacteria);
- test for blood in urine:
- gross hematuria is visible when examining urine;
- microhematuria is determined microscopically;
- determination of protein in urine.
- bacteriological culture of urine (done in case the pathogen turns out to be resistant to standard antibiotics).
Medical imaging may be needed to determine the extent of kidney damage, identify causes of obstructed urine flow, diagnose kidney abnormalities, and make differential diagnoses. Applicable:
- computed tomography (CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- ultrasonography;
- scintigraphy;
- CT and MRI urography.
Signs of disease activity
The diversity of clinical symptoms and the frequent secretive course led to the determination of the activity of the process according to objective criteria of the state of urine and blood. The more pronounced the urinary findings, the more active the inflammation in the kidneys.
In the urinary sediment after centrifugation of urine, the number of “dead” leukocytes and the proportion of active forms - “live” and increased in size leukocytes - Sternheimer-Malbin cells, and the number of bacteria are determined. The titer of antibodies produced against bacteria, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and protein toxins are determined in the blood.
For each phase of the disease, certain quantitative criteria have been established; during exacerbation their level is maximum, during remission it is close to normal. If it is impossible to determine the stage of the process, they resort to provocation when inflammation occurs in response to the use of a certain medicine.
Classification of pathology
Pyelonephritis is classified according to various criteria.
| Name of the sign of the disease | Classification of pyelonephritis according to the specified criteria |
| Number of affected kidneys |
|
| Patency of the urinary tract |
|
| Path of infection |
|
The clinical description of the pathology is most often based on the nature of the course of pyelonephritis (acute, chronic).
Also, the clinical description takes into account the condition of occurrence (primary, secondary).
Indications for diagnosing “complicated pyelonephritis” in women are:
- the appearance of infection in the urinary system after diagnostic or therapeutic procedures using instrumental methods (catheterization, cystoscopy, ureteral stenting, etc.);
- dysfunction of the urinary tract;
- anatomical deviations in the development, structure or position of the organs of the urinary system, congenital or acquired.
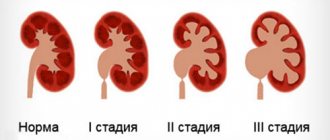
In chronic pyelonephritis, there are 4 stages described in the table.
| Stage designation | Damage to the kidney | Brief explanations |
| I | When the glomeruli are preserved, the collecting ducts atrophy. | The collecting ducts play a leading role in the formation of final urine. |
| II | Individual glomeruli become hyalinized (protein is introduced into the structure of the glomeruli). The tubules atrophy to a greater extent. There is a proliferation of connective tissue. | The kidney glomeruli (in a healthy woman their number is about 1.5 million) are the main filter of the body; they filter about 150 liters of liquid per day. The tubules are responsible for ion exchange. The proliferation of connective tissue depresses the internal structure of the kidney |
| III | Most of the glomeruli are destroyed. The tubules are dilated and filled with colloidal mass. | The colloidal mass in the tubules is a suspension of proteins. |
| IV | Characterized by the death of most tubules and glomeruli. The size of the kidney is significantly reduced. | Normal kidney sizes in women are (in mm):
Visualization of the size of the organ is carried out using CT and ultrasound |
Is it possible to cure chronic pyelonephritis?
Why is kidney inflammation dangerous? First of all, the possibility of activating a dormant purulent infection and spreading it in the body - sepsis. Secondly, by the development of a wrinkled kidney with its complete exclusion from the vital functions of the body. If, with unilateral nephritis, the second kidney is healthy, then it can take over the work “for that guy,” and when both kidneys are sick and have little functionality, then this is renal failure with the prospect of dialysis and transplantation.
Any chronic process is incurable; adequate therapy can not only reduce the manifestations of the disease, but also increase the period of life free from symptoms - remission.
Specialists at the Medicine 24/7 clinic develop an individual program of treatment and observation of the patient in order to put the pathological process into remission and prolong it as long as possible. If you are not healthy, contact the Center for Urology and Andrology by phone +7 (495) 230-00-01
What is the danger of the disease?
Pathology leads to impaired kidney function.
Among the most significant functions of the paired organ, we note:
- Excretory (the kidneys form urine and are released from it. Along with urine, products of protein metabolism, drugs, hormones, etc. are excreted from the body).
- Secretory (through a complex mechanism, the kidneys regulate blood pressure).
- Metabolic (participation in metabolism). In addition, the kidneys maintain a stable environment in the body - homeostasis.
Malfunctions of the kidneys caused by pyelonephritis provoke:
- intoxication (poisoning) of the body;
- impaired blood pressure, which negatively affects the entire cardiovascular system;
- metabolic disorders, which can lead to pathology of many organs and systems of the body.
If the disease is not treated, it will involve the entire body in the pathological process.