Home>Useful>Effects of alcohol on the kidneys
quick menu (hide)
- Damage caused by alcoholic drinks
- Safe amount of alcohol for the kidneys
- Consequences of drinking alcohol
- How to restore and reduce damage to the kidneys?
Alcohol with harmful breakdown products leaves the kidneys in urine. Let's determine how alcohol affects the kidneys. It contributes to increased stress and poisoning of the renal system, which, along with negative components, removes beneficial substances necessary for the body. We will talk below about how to restore kidneys after alcohol.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Cyston
Pharmacodynamics. The effect of the drug is due to the properties of the components included in its composition. Didymocarpus stem contains isopedicin, pedicin, essential oil, pedicillin. Has pronounced diuretic properties. Saxifraga reed is a diuretic, has an astringent effect, reduces irritation of the mucous membrane of the urinary tract, promotes the dissolution and destruction of stones in the kidneys and bladder by influencing the crystal-colloid balance; has an antimicrobial effect. Madder heart contains anthraquine glycosides and ruberythric acid, which help dissolve oxalate stones in the urinary tract and thereby promote their excretion. Madder has an astringent and diuretic effect. The rhizomes of the membranous plant have an antimicrobial effect at the level of the genitourinary system. Rough strawflower has an antispasmodic and diuretic effect. Onosma multifolia exhibits antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, diuretic, antimicrobial effects, and reduces irritation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. Used in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Vernonia ashy is used for bladder spasms and difficulty urinating. Silicon lime acts as a diuretic and promotes the dissolution of stones in the urinary tract. Purified mineral resin is a balanced, tonic composition of useful mineral and organic components. In addition to correcting urinary excretion, it affects the digestive processes, absorption and assimilation of food. Helps improve digestion and metabolism. Taking the drug Cyston causes an increase in blood flow to the kidneys and urinary tract, has a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect. Cystone prevents the process of stone formation, reduces the concentration in the urine of elements that contribute to the formation of stones (oxalic acid, calcium, hydroxyproline). Cyston promotes the removal of stones through micro-crushing. By acting on the mucin, which connects the individual parts together, stones and crystals are destroyed. The drug promotes the disintegration of stones and leads to their demineralization. Cystone has antimicrobial activity, especially affecting Escherichia coli , Klebsiella spp. and other gram-negative bacteria. It also has an antispasmodic effect, relieving painful urination. Pharmacokinetics. We haven't studied it.
Cystitis
Among lower urinary tract infections, the leading place is occupied by inflammation of the bladder - cystitis.
Cystitis is the most common urological disease in women. The incidence of uncomplicated urinary tract infections varies between age groups depending on gender and increases with age. It is quite high for women aged 20-40 years and amounts to 25 - 35% and is extremely low at this age for men (less than 1%). There is an opinion that, to one degree or another, signs of cystitis are observed at least once in every second woman’s life. Urologists believe that every 4th woman in Russia suffers from cystitis, and 10% of them suffer from recurrent cystitis.
Cause
Cystitis is a polyetiological (multi-cause) disease, that is, a consequence of a number of causes. But the leading cause is infection; cystitis of other origins are rare. The causative agents of cystitis can be bacteria, viruses, mycoplasmas, chlamydia, fungi of the genus Candida, trichomonas, anaerobic microorganisms, mycobacterium tuberculosis, treponema pallidum and others. It was revealed that acute cystitis was caused by Escherichia coli in 85.9% of cases.
Symptoms
Cystitis is easy to identify. It begins suddenly and immediately - acutely. Pain in the lower abdomen, frequent urge to urinate, constant runs to the toilet with minimal results. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by chills caused by a vascular response to bladder spasm. Acute cystitis is characterized by a rapid increase in symptoms of urinary disorders during the first few days.
The earliest sign of cystitis is pollakiuria (frequent urination). The intervals between urination are reduced to 5 – 15 minutes. The volume of individual portions of urine is small, since urine does not have time to accumulate in the bladder. I am concerned about the frequent urge to urinate, which does not stop day or night.
Treatment
At the first suspicion, you should consult a doctor. Depending on the situation, the doctor will prescribe the necessary comprehensive treatment. It must be etiological and pathogenetic. Depending on the clinical form of cystitis, treatment should be comprehensive and individual.
Treatment of acute cystitis consists mainly of antimicrobial therapy, plenty of fluid intake (up to 2 liters of fluid), and avoidance of sexual intercourse for 5 to 7 days. The earlier treatment is started, the easier the course and faster the recovery. Many medicinal plants (bearberry, knotweed, horsetail, celandine, cranberries and lingonberries, etc.) have bacteriostatic, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory effects, reduce mucus formation, and affect urine pH. The original herbal medicine Cyston has proven itself well.
Prevention
It is necessary to pay special attention to intimate hygiene, avoid hypothermia and do not forget about preventive measures. In the prevention of cystitis, regular bowel movements and bladder emptying are important. It is very useful to perform various physical exercises and move more. This helps eliminate congestion in the pelvic organs and enhance the peristalsis of the large intestine. If you are prone to constipation, you should include a lot of fruits and vegetables in your diet; it is recommended to take laxatives and cleansing enemas. Do not indulge in spicy and fatty foods, do not drink boiled milk. Foods and drinks that irritate the urinary tract are prohibited: pickles, smoked foods, seasonings, canned food, hot sauces, horseradish, vinegar, alcoholic beverages.
A dairy-vegetable diet enriched with vitamins, jelly, buckwheat porridge, wholemeal black bread, meat, fish, cottage cheese is recommended. Salt intake should be limited. Errors in diet can increase dysuria. Foods and liquids that increase dysuria should be excluded from food.
You need to know that a number of foods can irritate the bladder mucosa, increase dysuria and pelvic discomfort. These include:
- orange juice, - alcohol, - coffee, tea, Coca-Cola, - carbonated drinks, - black and red pepper, - chocolate, - spiced foods, - grapes, peaches, apples, apple juice, cranberries, avocados, bananas, - sour cream, yogurt, mayonnaise, - nuts, - vinegar, - cheeses, - raisins, - tomatoes, tomato juice and pastes, - onions (onions and leeks).
To prevent urinary tract infections (cystitis, pyelonephritis) in women, it is recommended to carry out vaginal sanitation along with other treatment methods.
Cyston ® for cystitis
Cystone is an original medicinal herbal preparation that is indicated for the complex treatment of urinary tract infections. The complex of biologically active substances that make up the drug Cyston has a diuretic, antispasmodic, litholytic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect.
Must remember! The first episode of cystitis indicates that it must be taken seriously. Many patients, feeling better after starting therapy, do not complete it. For which you then have to pay – cystitis is an insidious disease. Be attentive to yourself.
Use of the drug Cyston
Cystone is taken orally. Litolysis of oxalate, phosphate stones and stones formed by uric acid and urates: adults and children over 14 years of age - 2 tablets; children 6–14 years old - 1 tablet; children 2–6 years old - tablets 3 times a day for 3–4 months; in the future, adults and children over 14 years old - 1 tablet, children 6-14 years old - a tablet, 2-6 - ¼ tablet 2 times a day or until stones pass. For urinary tract infections: adults and children over 14 years of age - 2 tablets; children 6–14 years old - 1 tablet; children 2–6 years old - 1/2 tablet 3 times a day for 4–6 weeks. For recurrent urinary tract infection: adults and children over 14 years of age - 1 tablet; children 6–14 years old - 1/2 tablet; 2-6 years - 1/4 tablet 2 times a day for 6-12 weeks. For acute renal colic: adults and children over 14 years of age - 2 tablets; children 6–14 years old - 1 tablet; children 2–6 years old - 1/2 tablet 2 times a day until symptoms disappear. To prevent kidney stones: adults and children over 14 years of age - 1 tablet; children 6–14 years old - 1/2 tablet; children 2–6 years old - 1/4 3 times a day for 4–5 months.
Non-infectious stones
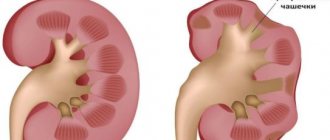
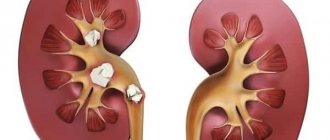
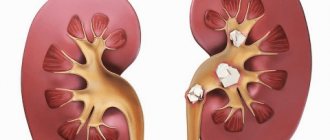
How to remove kidney stones depending on the composition and structural features:
- Oxalate stones. They are formed from calcium salts of oxalic acid if the urine is too acidic or alkaline. They have a dense structure and a surface with spikes, so they do not dissolve and are not excreted from the body. For removal, they resort to remote or contact lithotripsy. Some medications help to reduce the size, which also help to remove stones on their own.
- Phosphate stones. Consist of calcium salts of phosphate acid. The structure is soft, with a smooth surface, so they can be removed through a properly selected diet and drug therapy, but if they are large, they require surgical intervention.
- Cystine. Formed from the amino acid cystine as a result of a violation of cysteine metabolism. They are treated by taking medications that stop the conversion of cysteine to cystine. For large stones, surgical intervention is recommended.
- Cholesterol. Rarely encountered types of stones that form when there is high cholesterol in the blood. They crumble a lot, so they are especially dangerous. They are removed surgically because medications are often ineffective.
- Xanthine. They are formed when the metabolism of the enzyme xanthine oxidase is disrupted, which results in the formation of excess xanthine. It is poorly soluble in water and is excreted unchanged from the body. Due to their soft structure, stones can be treated with medication, but if they are large, surgical removal is prescribed.
Harm from alcohol
The liver is responsible for processing and neutralizing alcohol that enters the human body. In the future, everything is excreted through the kidneys. But due to the increased harmfulness of the breakdown products of alcohol, after a feast the load on them increases, since in addition to their main functions they must also remove toxic substances from the body.
The renal system regularly receives water with various substances that will be excreted. Similar to the system of purification channels, water with organic and mineral components moves through the vessels. They pass through various filters and substances that are not required for the body, reach the end and are eliminated. And the elements that are still required return to the blood with water (this is a reabsorption process). As a result, water returns to the blood in almost the same volume and a large volume of elements.
After processing alcohol, acetaldehyde appears in our body, which is dangerous for the kidney system (nephrotoxic). It reduces the reabsorption of the organ's tubules, as a result of which useful elements are filtered and excreted along with unnecessary components. That is, a person loses useful organic and mineral elements, due to the lack of which the hangover syndrome intensifies the next morning. During the elimination of alcohol from the body, significant damage is caused to the kidneys.
Stones of infectious nature
Separately, it is worth noting stones of an infectious nature. In addition to urates, these include:
- Struvite. Formed as a result of infection in an infected alkaline environment, they occur in 15% of cases. Consist of ammonium and magnesium phosphate. They are difficult to treat with medications and can only be eliminated by shock wave lithotripsy or open surgery if the stones are large. Due to the infectious nature, antibiotics are additionally prescribed.
- Carbonate. They are formed in alkaline urine, contain magnesium salts, are often combined with a urinary infection and occur in 5-10% of cases. The structure is smooth, the consistency is soft, and can be of different shapes. They can be dissolved with medication, but if they are large, they can be removed surgically.
If the diameter is large (more than 2 cm), regardless of the chosen method of crushing kidney stones, after surgical treatment, medications, plenty of fluids and diet are prescribed to help remove the remaining small fragments in the urine.