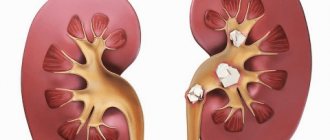
Types of kidney stones depending on composition
Oxalate stones (oxalic acid salts)
Oxalate - have a black-gray color and a dense consistency. They are formed from salts of oxaloacetic acid. Their surface is spinous, which leads to trauma to the mucous membranes when oxalate stones move through the ureter. The urine in such a situation will have a reddish tint due to blood.
Oxalates are formed in the kidneys quite often. They pose serious problems for nephrologists and surgeons because they are quite hard and therefore difficult to destroy. In liquid media, oxalate stones are practically insoluble. The solid structure and high content of calcium salts in oxalates allows this type of stones to be clearly visible on x-rays obtained during survey urography. Stones made from oxalic acid salts are very sharp, so they can cause severe pain to a person and cause bleeding from the urinary tract.
As a result, the only way to get rid of them is surgical removal if it is impossible to remove them through natural means.
Oxalate stones are formed with prolonged and frequent consumption of parsley, baked goods, and sweet foods. Practical observations of doctors show that oxalates are more often observed in people who adhere to a healthy lifestyle.
Phosphate stones
Phosphate - have a smooth surface, light gray color. Easily crushed under mechanical or ultrasonic influence. Formed in an alkaline environment. When urine pH shifts above 6.3, people with a tendency to form phosphate stones will have white, loose flakes in their urine. They are the initial sign of the formation of this type of stones. If at this moment the acid-base balance of urine is not “shifted” to the acidic side, the formation of large stones is likely. To get rid of phosphates in the urine, you should drink mineral waters such as “Sairme”, “Truskavets”, as well as cranberry and lingonberry juices. These stones often contain salts of oxalic and uric acid.
Urate stones (uric acid salts)
Urates are smooth and round with a loose structure. They have a yellow-brown color. Formed from uric acid. From all types of stones in urolithiasis, urate occurs in 15% of cases. Most often they occur with gout (a disorder of uric acid metabolism). In hot countries, the likelihood of dehydration increases, so the frequency of detection of urate stones is higher. When performing survey urography using X-rays, these types of stones are not detected. In most cases, it is possible to get rid of uric acid salts by alkalizing the urine. During treatment, it is important that urates are identified before they damage the kidneys and ureters.
Cystine stones (amino acid cystine)
Cystine stones are characterized by their round shape, yellowish-white color, smooth surface and soft consistency. They are formed from the amino acid cystine. Cystinuria occurs in 2-3% of urolithiasis. When the level of cystine in the urine is constantly elevated (with some inborn errors of metabolism), hexagonal crystals can be seen in the urine upon microscopic examination. These are cystine stones. They are poorly soluble in water, so treatment of cystine stones is possible using surgical lithotripsy.
The diagnosis of cystine metabolism disorder can be established only after a thorough examination of the patient. If these stones are detected in a person’s urine, anamnesis should be collected to determine the presence of pathology in relatives. To treat cystinuria, it is sometimes sufficient to use urine alkalization agents, and in some cases, surgical lithotripsy. The choice of therapy depends on the composition of the stones, their number and size.
Protein, cholesterol and xanthine stones
Protein - various in shape. They are small in size, white in color, soft in texture and have a flat surface. They are a collection of bacteria and fibrin. Protein (struvite, infection) stones arise as a result of the decomposition of urea by bacteria. As a result, it precipitates, from which stones gradually form. Protein stones are more common in women, which is associated with the anatomical structure of the genital organs. Due to the short urethra and the close location of the anus, there is a possibility of microorganisms from the rectum entering the vagina if personal hygiene is not observed. Infectious stones also contain uric acid salts, phosphates, and leukocytes.
Cholesterol - consist of cholesterol, so they are rarely found in the kidneys. Their specific feature is their black color and soft consistency. They are dangerously brittle. Even when passing through the kidneys, they can break down into parts that impede the functionality of the kidneys.
Xanthine stones are formed when the metabolism of the enzyme xanthine oxidase is disrupted. As a result, the mechanism for converting xanthine into uric acid is disrupted. Due to the fact that this substance is poorly soluble in water, it is excreted from the body unchanged. Xanthine stones are not detected by x-rays, since they contain virtually no calcium, but are clearly visible by ultrasound due to their soft structure.
Carbonate - have a white color, soft consistency, smooth surface. Formed from carbonic acid. The shape of carbonate stones is varied.
In conclusion, some advice for people with urolithiasis:
- If you find stones in your urine, you should not panic. Small stones that get into the urine usually do not cause serious problems. However, they are a harbinger of the body's tendency to form stones.
- By the appearance of small stones in urine, try to determine their type. Get your urine tested to check its acid-base status and the presence of salts.
- If there are acidic stones in your urine, drink alkaline mineral waters. With alkaline stones, it is enough to change the nature of the diet to dissolve them. Phosphates are quickly neutralized when switching to protein foods.
- Cramping pain in the lower back may indicate the presence of a large stone in the kidneys or ureter. The likelihood of pathology increases if at the same time there is an increase in the urge to urinate with a decrease in the volume of daily urine. In such a situation, you should immediately contact a nephrologist and perform a survey urography. After the examination, the specialist may prescribe intravenous urography to identify the level of blockage of urination, as well as determine the functionality of the urinary system. The study involves obtaining a series of panoramic images of the kidneys 7, 15 and 30 minutes after intravenous administration of a contrast agent.
Nephrolithiasis is a kidney disease in which salts accumulate in the bean-shaped organs. The more mixture of organic and mineral substances collected in natural filters, the more problems with urine excretion.
It is important to know not only the size of the stones, but also the types of kidney stones. The prescription of treatment, selection of diet and medications depend on this indicator. To actively dissolve and remove stones of different chemical compositions, a certain approach is required. How to remove kidney stones? How to deal with phosphates, urates and oxalates? How to prevent the accumulation of harmful salts? The answers are in the article.
How to treat kidney stones?
The general treatment regimen includes stone removal and prevention of recurrent stone formation.
- Conservative therapy helps relieve inflammation and remove stones naturally.
- Lithotripsy is a procedure for crushing stones using a shock wave or laser.
- And surgical intervention helps to remove stones of any type and size.
In each case, an individual and comprehensive approach is required so that even the smallest stone does not cause trouble. Don't take care of your stones - take care of your kidneys!
Reasons for education
Kidney stones do not develop overnight. Salts are deposited gradually, stones in most cases grow slowly. If a person does not know about the problem, maintains his usual lifestyle, and does not adjust his diet, then the disease progresses, the stones increase in size, become heavier, and negative symptoms appear.
On a note:
- The main reason for the appearance of stones is a violation of colloid balance, pathological processes in the renal parenchyma. The elementary cell - the basis of the future stone - is formed during complex physico-chemical transformations. Fibrin threads, foreign particles, and amorphous sediments gradually attach to the core;
- The more disturbances in metabolic processes, the higher the volume of purines, calcium salts, phosphorus, the more actively the kidney stones enlarge. Violation of the acidity level of urine, incorrect ratio of salts in urine, changes in the composition of urinary colloids provoke crystallization of microlites;
- Initially, stones appear in the renal papillae, then microliths are retained in the tubules, harden, and microscopic stones are formed. Under favorable conditions, the formations grow, develop in the bean-shaped organs or descend lower - into the urinary tract;
- The higher the concentration of salt crystals in the urine, the more actively the particles settle on the core (matrix).
Disorders of mineral metabolism in some cases occur due to a hereditary predisposition, but more often patients suffering from signs of nephrolithiasis themselves accelerate the development of pathological processes. It is important to know the reasons that cause the accumulation of salts in the kidney tissue.
Find out about the causes of a horseshoe kidney in a child and about treatment options for the pathology.
Read about the causes and treatment of frequent urge to go to the toilet in men at this address.
Causes of kidney stones and provoking factors:
- poor nutrition. Excess of any food harms the body. With frequent consumption of red meat, strong coffee, spinach, offal, mackerel, cod, beer, black tea, purines accumulate. The result is that uric acid salts are deposited in the bean-shaped organs, bladder, and joints;
- Excess milk, cheese, meat, and other types of protein foods provoke the accumulation of calcifications.
Other negative factors:
- “hard” water;
- sharp alkalization or increase in acidity of urine;
- stagnation of urine;
- congenital renal pathologies;
- urinary tract infections;
- dehydration in the heat;
- lack of fluid for a long period;
- postoperative period after treatment of fractures;
- high acidity of urine;
- increased levels of calcium and vitamin D in the body.
Types of kidney stones
In stones, doctors identify no more than three main stone-forming minerals; other elements are present as impurities. The formations differ not only in chemical composition, but also in shape and density. Some types of stones are easily dissolved under the influence of herbal and synthetic preparations, while others have to be crushed with ultrasound or removed openly.
General information:
- phosphates. Slightly rough or smooth stones are formed by calcium salts of phosphoric acid. Quite soft stones have different shapes and colors - from white to light gray. Stones appear when urine becomes alkalized. Phosphates grow quite quickly, but the use of herbal preparations, herbal decoctions, and diet loosens the body of the deposits, then it is easy to crush the kidney stones with ultrasound;
- oxalates. A dangerous type of stones: the surface is uneven, the protrusions resemble thorns, the color is dark gray, almost black, high density. The formations negatively affect the mucous membranes, injure the surface, and accumulate blood pigment. Oxalate kidney stones cause pain in the lower back, abdomen, genitals, thighs, and groin area. Oxalates often affect the condition and color of urine: blood clots appear, urine turns yellow or becomes reddish. Stones are easy to detect on a kidney ultrasound due to their high density, but stones are difficult to crush, herbal formulations are ineffective in dissolving oxalates;
- urates. Uric acid salts quickly accumulate in various parts of the body when there is an excess supply of purines or when mineral metabolism is disrupted. Urate kidney stones are smooth, hard in consistency, and yellowish-brown in color. Urates are quite difficult to see on an x-ray, but the formations are easy to dissolve with the help of a specially designed diet, the use of natural remedies and synthetic compounds.
Other types of stones are less common:
How to determine the presence of urate stones
Diagnosis of urate stones is often difficult due to their composition. The low density of the formations prevents them from appearing on x-rays. Therefore, they are determined using ultrasound or after a urine test.
Gout may be an indirect sign of the development of urate stones. Both diseases are caused by the same factors, so when one is detected, they immediately check for the second.
The patient cannot feel how urate stones form in the kidneys, but will notice the following symptoms:
- sudden severe lower back pain that is not affected by body position or movement;
- nausea, vomiting along with pain;
- increased urge to go to the restroom;
- other typical signs of ICD.
Treatment of urate kidney stones must begin immediately, then they can be eliminated without surgery.
Characteristic signs and symptoms
While the stones are small, the patient does not suspect the presence of salt formations in the kidneys or urinary tract. Discomfort appears as stones grow and move through ducts and tubules. The sharp edges of hard formations scratch delicate tissues; urine analysis shows an increased level of red blood cells.
In severe cases of nephrolithiasis, blood is noticeable in the urine. Blockage of the ducts interferes with the excretion of urine, pain and stinging appear during urination.
Other signs of kidney stones:
- pain in the lumbar region when bending over, after training, lifting weights, active movements;
- cloudy urine;
- the movement of stones provokes painful lumbago in nearby areas;
- swelling appears on the lower extremities and eyelids;
- the process of urination is disrupted, the volume of urine decreases;
- weakness and excessive fatigue appear for no particular reason;
- blood pressure increases;
- often feel thirsty.
General rules and methods of treatment
Goals of therapy:
- dissolve (break up) and remove salt formations;
- stop injury to mucous membranes;
- prevent relapses;
- normalize mineral metabolism;
- restore the outflow of urine;
- relieve the patient from painful symptoms.
General rules for treating kidney stones:
- diet taking into account the chemical composition of stones;
- more movement, but without heavy physical activity;
- taking herbal and synthetic drugs that dissolve stones. Many formulations with natural oils and plant extracts effectively crush stones;
- a correct drinking regimen is required: the urologist prescribes the optimal amount of fluid taking into account the severity of the pathology, usually 2 or more liters;
- drinking warm purified water to reduce hardness, improve the composition of the liquid, and get rid of harmful impurities;
- endoscopic operations, crushing of formations with ultrasound, lithotripsy. In advanced cases, with large formations, open abdominal surgery is performed.
Treatment of kidney stones with stone breaking tablets:
- oxalates. Cyston, Cholestyramine;
- urates. Allopurinol, Potassium Citrate;
- phosphates. Madder extract, spilled capsules;
- universal compositions. Uralit U, Tiopronin, Blemaren.
Look at the location of the human kidneys and learn about the functions of the paired organ.
What does Nitroxoline help with and how to take the drug for urogenital infections? The answer is in this article.
Follow the link https://vseopochkah.com/mochevoj/mocheispuskanie/nespetsificheskij-uretrit.html and read about the rules and features of the treatment of nonspecific urethritis in men.
How to get rid of phosphates
Elements of therapy:
- treatment table No. 14 is effective;
- the patient should give up dairy products, fruits and vegetables, increase the consumption of vegetable oils, fish, meat, and baked goods;
- with phosphaturia, you can eat cereals, legumes, spices, drink tea and coffee;
- decoctions of barberry and grape roots are useful;
- It is important to increase the acidity of urine so that the stones soften and are easily crushed by ultrasound.
How to dissolve urates
Helpful Tips:
- It is necessary to follow a diet for kidney stones: reduce the consumption of offal, veal, sardines, mackerel, cod, strong coffee and black tea, chocolate;
- give up beer and other alcoholic drinks;
- exclude acidic foods and items with oxalic acid. You should not eat citrus fruits, beets, spinach, cocoa, sorrel, or lettuce.
How to remove oxalates
Recommendations:
- stones are difficult to dissolve, diet reduces the risk of the formation of new stones, but removal of existing formations often requires kidney lithotripsy or open surgery if there is a noticeable increase in the size of oxalates;
- do not consume millet, tomato, orange juices, citrus fruits, red grapes, dark plums, persimmons;
- just as when fighting urates, you should not eat spinach, sorrel, sour foods, drink beer, coffee, black tea;
- It is important to give up vegetables from the nightshade family: tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, sweet peppers.
The following video contains a video animation on the problem “Kidney stones: types of kidney stones, causes and stages of their formation, risk factors and preventive measures:”
Currently, the incidence of urolithiasis (urolithiasis) among the population of our country, according to medical statistics, reaches 20-30%, which experts associate with the deterioration of the quality of drinking water and the unfavorable environmental situation in general. One of the significant exogenous factors is an excess of heavy metal compounds (in particular lead), the accumulation of which in the body inevitably leads to various metabolic disorders.
What foods cause kidney stones?
The development of urolithiasis is 57% dependent on nutrition. Drinking sweetened water (the sweetener is fructose) increases the risk of stone formation, but acidic lemon water may reduce the risk of stone formation.
Excessive consumption of coffee and tea should be discouraged. And mineral water in adequate volume can act as a factor in the prevention of urolithiasis. The best nutrition is balanced: not a single newfangled diet can be physiological. Teach yourself and your children to drink plain water: this is not liters of green tea or compote, but regular drinking water. And its amount should depend on both climate and physical activity.
Changes in the composition of the intestinal microflora affect the formation of stones. The microorganism O. formigenes consumes oxalates to maintain vital functions. It reduces their concentration in the body, therefore reducing the risk of oxalate stones. If the number of O. formigenes colonies decreases, the concentration of oxalates will not decrease and they will be deposited in the kidneys.
Taking antibacterial drugs for more than two months shifts the urine pH to the alkaline side and reduces the concentration of citrates in the urine. This becomes a factor predisposing to the development of ICD.
Causes of kidney stones
With urolithiasis, urate kidney stones often form. In terms of frequency of occurrence, stones of this composition occupy the next place after the most common oxalate formations. They are most often diagnosed in young and mature patients (from 20 to 50 years). In older people and pediatric patients, deposits are more likely to occur in the bladder. In many cases, the first signs of the development of the disease are renal colic - intense pain.
Urate stones are formed from uric acid salts against the background of their increased concentration. The direct causes of the formation of stones include low pH (acidic reaction) of urine and a slowdown in its formation.
Please note: it is now possible to promptly detect an increased likelihood of developing pathology by regularly determining the urine reaction an hour before meals using test strips.
Uric acid compounds (urates) are derivatives of the normal metabolism of protein compounds, so they are always present in a certain amount in the body, and it is not possible to completely get rid of them. You can prevent the formation of urate stones and sand in the kidneys by eating foods that shift the urine pH to the alkaline side.
Important: normally urine is alkaline (6.0-7.0). At pH levels above 5.5 (neutral), the likelihood of urate formation is low.
If urine formation does not occur at sufficient speed, then its concentration and the percentage of urate content in it increase. As a result, the salts precipitate, gradually forming a dense formation. In such situations, the degree of acidification of urine can be reduced by consuming a large amount of liquid (at least one and a half liters per day, and in hot weather - at least two).
Factors predisposing to the formation of urate deposits include:
- physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle);
- starvation;
- the use of certain analgesics in dosages exceeding the recommended ones;
- lack of B vitamins;
- poor nutrition (in particular, consumption of animal protein in large quantities).
Please note: physical inactivity leads to disruption of various metabolic processes, in particular the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium.
How are kidney stones formed?
To start the process of stone formation, certain conditions are necessary. All stones differ in composition: urates, oxalates, phosphates, struvites, etc. A prerequisite for stone formation is oversaturation of urine with substances such as:
- calcium
- oxalate (oxalic acid salt)
- uric acid
- sodium
- phosphorus
Stone formation is accelerated if there is a low concentration of magnesium and citrates (citric acid salts) in the urine. They neutralize oxalates and calcium salts, preventing them from turning into stones.
Urine pH is an important factor in stone formation. The solubility of salts from which stones are formed depends on the acidity index. This is why stones from different salts are formed at different pH values.
Clinical picture
Urate stones may not make themselves felt for a long time. Symptoms in most cases develop unexpectedly.
The patient develops renal colic with characteristic symptoms:
- intense pain in the lumbar region (usually one-sided, from the side of the affected organ, but “girdling” is not excluded);
- pain “radiates” to the abdominal region (stomach), bladder and genitals;
- the pain syndrome is almost impossible to relieve;
- the patient develops chills;
- changing posture does not bring relief;
- in some cases, dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting) occur.
Important: hyperthermia (increase in general body temperature) against the background of colic is highly likely to indicate the development of an acute inflammatory process in the kidney tissues.
The cause of renal colic is obstruction (blockage) of the urinary tract with a stone, which prevents the passage of urine.
One of the possible symptoms may be gross hematuria, i.e. the presence of blood in the urine.
How to find out about the existence of stones in the body?
Very often a person does not even realize that a malfunction has occurred in his body and the process of stone formation has started. For a long time, urate stones in the kidneys do not manifest themselves in any way, and the disease proceeds latently, that is, secretly.
If the stone reaches a fairly large size and stretches the kidney capsule or begins to move through the urethra, then the patient experiences pain.
The severity of pain may vary. The patient may only have unpleasant stretching in the lumbar region or unbearable renal colic.
The manifestations of renal colic are characterized by:
- sudden onset of an attack of intense pain radiating to the groin, scrotum, and pelvic organs in women;
- the pain is so severe that it forces the patient to take a forced position;
- a possible increase in temperature, accompanied by chills or heavy sweating (indicates the addition of an infectious agent and the onset of the inflammatory process);
- there is a feeling of nausea, up to an attack of vomiting;
- When urinating, the pain intensifies, and the urine may darken due to blood.
Diagnostics
Urate stones are more often found in male patients. This is due to the fact that many men prefer meat products and consume relatively little fruit, vegetables and dairy products.
Excess uric acid not only leads to the formation of urate, but also causes gout (develops when uric acid salts are deposited in the joint area). The incidence of gout is also higher among men.
Please note: in women, severe forms of urate nephrolithiasis are more common - large coral-shaped formations.
To identify the nature of the pathology, anamnesis data is usually not enough.
Diagnosis of urate stones includes:
- general blood analysis;
- in-depth laboratory examination of the patient’s urine;
- conducting survey and excretory urography;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- spiral CT (computed tomography);
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- contrast fluoroscopy.
Please note: conventional x-ray examination in most cases is not very informative.
When making a diagnosis and subsequent choice of treatment tactics, it is necessary to take into account the presence of concomitant diseases, such as:
Treatment for kidney stones
Therapy for urate deposits differs from the treatment process for other types of stones.
General principles of conservative treatment
One of the specific features of urates is their relatively easy dissolution, so in most cases conservative measures can achieve a positive effect.
Dissolving urate stones in the kidneys involves consuming large volumes of fluid in order to shift its pH to the alkaline side. In addition, the patient is shown a diet in which the diet should include a large amount of dairy and plant foods (such products contribute to the alkalinization of urine). Alkaline mineral waters are shown.
Traditional treatment for kidney stones
Traditional medicine recommends herbal remedies with a diuretic effect and infusions of medicinal herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect.
Diuretic herbs include, in particular, horsetail and bearberry. A decoction of lingonberry leaves is also an effective diuretic.
Diet for kidney stones
Following a special diet is considered one of the main ways to dissolve urate stones in the kidneys and ureter.
Foods and drinks that should be excluded from the diet:
- fatty pork and beef;
- animal products rich in purine bases (liver, kidneys, veal);
- fish and meat broths;
- offal;
- canned food;
- red wine;
- beer.
Products whose consumption is advisable to reduce:
- legumes (beans, peas, lentils);
- bakery products (especially from higher varieties of wheat);
- spinach;
- sorrel;
- onion;
- oat groats;
- Fish and seafood;
- spices;
- chocolate and cocoa;
- coffee;
- strong tea.
Important: patients are also recommended to reduce their salt intake.
Foods that must be included in the diet to remove urate stones from the kidneys:
- eggs;
- milk and fermented milk drinks;
- cottage cheese;
- cheese;
- pasta;
- nuts;
- any fruit;
- seeds;
- wheat and buckwheat;
- foods rich in ascorbic acid (lemon, rose hips, etc.);
- watermelons.
Please note: for treatment and prevention, fractional nutrition is indicated, which involves eating small portions 5-6 times a day.
Treatment of urate kidney stones with tablets
Acute symptoms can be reduced by antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Antispasmodic drugs relax the smooth muscles of the urinary tract, helping to reduce obstruction of the duct and accelerate the removal of stones and sand naturally.
If disorders of purine metabolism are detected, drugs from the group of uricostatics (Allopurinol) are prescribed. The presence of high concentrations of urates and oxalates in the urine is an indication for the use of magnesium oxide, and if there is a high content of calcium salts, then Hypothiazide is prescribed (standard dosages).
Patients are advised to take the so-called. “citrate mixtures” to alkalize urine and maintain its pH in the range from 6.2 to 6.8.
Surgery
To remove kidney stones, surgery may be a necessary measure, which is resorted to in 3-5% of cases. Surgery is necessary if large coral-like formations occur. Crushing kidney stones with ultrasound and laser (lithotripsy) is also used relatively rarely.
For urate kidney stones whose size does not exceed 2.5 cm, minimally invasive extracorporeal lithotripsy is successfully used to destroy the stone.
Why do kidney stones form?
Urolithiasis is a disease of organs and systems associated with:
- diabetes mellitus
- hypertension
- metabolic syndrome
- myocardial infarction
- stroke
Among the causes of metabolic disorders, a certain contribution is made by:
- hereditary factor
- poor nutrition
- sedentary lifestyle
- insufficient fluid intake
- diseases of the endocrine, digestive and genitourinary systems
Therefore, to combat the disease, an integrated and interdisciplinary approach is required, including the knowledge of endocrinologists, nutritionists and nephrologists.
“Discovering” and “defusing” a stone is not the only goal. One of the important tasks remains to identify the cause in each specific case in order to prevent relapse. So, what affects stone formation and what risk factors can be identified? This includes diet, climate, water hardness, occupational risks, aging, testosterone deficiency, cardiovascular diseases, etc.
Cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes and obesity are closely associated with an increased risk of urinary stone formation. Obesity is associated with “internal” hypoxia and the production of reactive oxygen species that can cause “harm”; in addition, daily excretion of calcium, uric acid and oxalates in the urine increases.