Urolithiasis is a diagnosis that frightens many. After all, not everyone understands what can be expected from such a pathology. Doctors divide stones in the kidneys and urinary system according to different criteria: type, shape, size and type of formation. Anton Prityko, a urologist at City Clinical Hospital No. 17, Ph.D., member of the European and Russian Society of Urologists, told AiF.ru about what kind of stones a person can encounter and what rules can be used to eliminate them painlessly .
Division of stones
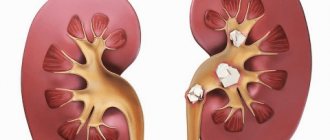
Urolithiasis is a chronic disease in which urinary stones form and are present in the urinary tract, says a urologist. “The site of primary stone formation is often the kidneys. In this case, the outflow of urine is rarely disrupted, and a person may not feel the presence of stones,” explains Anton Prityko.
The stones, the doctor emphasizes, vary in their shape, size and composition:
- there are single small stones of 2-3 mm;
- there are large stones from 2-3 cm;
- Coral-shaped stones are also found, which fill the entire pelvicalyceal system of the kidney and thereby take on the shape of a coral.
Question answer
Is it possible to remove a kidney stone if you drink a lot? According to their chemical composition, stones are also divided into:
- oxalate;
- phosphate;
- urate;
- carbonates;
- stones containing magnesium salts.
“As a rule, oxalate stones are formed in urine in an acidic environment, have a lumpy surface with spikes, dark brown or black color, and a dense consistency. Phosphate stones are composed of calcium phosphate and usually form in alkaline urine with a pH above 7.0. They are of various shapes, white or gray. Urate stones are derivatives of uric acid, formed in sharply acidic urine at a pH of 5.0-5.8, and are more common with age. These stones are round in shape with a smooth surface, often flattened, without processes, bright yellow, orange, sometimes brownish in color, with a dense consistency,” says Anton Prityko.
There are also carbonates, which are white in color and form in alkaline urine. Stones containing magnesium salts are found in 5-10% of cases and are often combined with a urinary infection.
“However, stones are found in their “pure” composition in less than half of the cases. Often the stones have a mixed composition. To accurately understand the composition of the stone, you need to conduct a spectral analysis of it, and depending on the results of this study, you can select a specific diet,” says Prityko.
Don't lose a kidney. Is it possible to cure urolithiasis? More details
Stones in the kidneys
The mechanism of formation of kidney stone disease
Many experts argue that the basis for the formation of kidney stones is a violation of the protective colloids of urine and changes in the renal chlorenchyma.
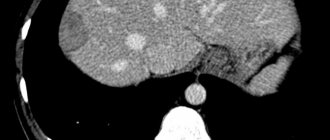
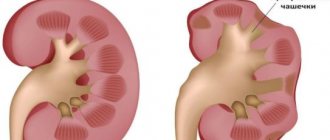
Stones are formed from crystals of salts and minerals that accumulate in the kidneys over time. When abnormalities occur in the body system and the renal canals, the balance of the concentration of water and other elements of urine is disrupted, then substances dissolved in them can precipitate and accumulate in the urinary tract. Over time, this sediment turns into stones. It is due to negative conditions and from insoluble particles that a micelle develops. This is the name of the cell that directly forms the core of the calculus. Also, stones form in the kidneys due to excessive salt content, amorphous sediments, fibrins, bacteria, foreign bodies in the urine, as well as inflammation. The intensity and direction of this process directly depends on the acid-base state of the internal environment of the body, which is assessed by the pH value. If the urine pH is normal (from 5 to 6), then the salts dissolve in it. During a sharp violation of this indicator, the colloidal state of urine and the conditions for the dissolution of salts in it change, which entails their precipitation. Disruption of the normal outflow of urine leads to the formation of single and multiple large stones. With a high concentration or a shift in the pH of urine in the kidneys, the process of crystallization of microlites occurs, which are retained in the channels. After which the stone can increase in size, localize in the kidneys, and descend into the urinary system.
There are several types of stone formation, differing in their composition and size, namely:
- Oxalates are stones consisting of black-gray salts that have a spiky surface and a dense structure. They are formed due to the high concentration of uric acid;
- phosphates. These smooth, whitish-gray stones form as a result of infections in the genitourinary system;
- urates - light yellow, smooth salt crystals formed from uric acid salts;
- carbonates - smooth, light-colored stones that appear when calcium settles in the urine;
- cystines are yellowish-white, smooth stones formed due to the deposition of cystine. They have a hereditary component;
- protein stones are flat, soft white stone formations that contain infectious microorganisms;
- cholesterol - soft, black stones formed by cholesterol;
- xanthine stones are stones that fall out with apatite in acidic urine.
In addition, stones of not only homogeneous, but also mixed types can form in the kidneys. One of the most complex variants of this disease are coral kidney stones growing in the pelvis. They have a bizarre shape with branched processes.
Necessary methods of prevention and prognosis of the disease
In most cases, the prognosis for treatment and further recovery is favorable. The disease may not recur if all specialist recommendations are followed. Otherwise, kidney stone disease can lead to the formation of calculous pyelonephritis, symptomatic hypertension, chronic renal failure and hydropyonephrosis. When stones are passed in the urine, they must be sent for laboratory tests, where the composition will be determined. This allows you to prescribe the correct dietary course of treatment, which will help avoid the formation of new stones. In addition to diets, experts recommend that their patients follow the following rules:
- constantly move, lead a healthy lifestyle;
- try to spend less time on long trips by transport;
- if your work activity takes place at the computer, then you need to take breaks more often, getting up and warming up;
- carefully monitor the level of acid and alkali in the urine using litmus paper;
- consume foods containing vitamin C in moderation;
- do not abuse alcoholic beverages;
- adhere to the regime of drinking a large volume of water so that about three liters of urine are excreted per day;
- if you are overweight, try to get rid of it;
- pay attention to the regularity of bowel movements;
- Do not use diuretics without doctor's advice. This can lead to dehydration;
- do not drink chilled beer or kvass. These drinks affect the smooth functioning of the kidneys;
- do not swim in cold water;
- avoid drafts;
- reduce portions of foods containing proteins, since protein in the body increases acidity. It resists the absorption of calcium, which leads to the precipitation of calcium salts.
Considering that the symptoms of kidney stones are very similar to various types of diseases, the patient is recommended to seek help from a doctor at the first sign. If kidney stones are removed, the patient must strictly follow the prescribed diet and eliminate associated risk factors.
Symptoms of the problem
There are some clear signs that stones have formed:
- pain in the lumbar region, as well as in the side or lower abdomen, which can radiate to the groin area - they can intensify with physical activity, movement and when drinking large amounts of liquid, and can occur either periodically or constantly;
- blood in the urine (color may vary from light to rich);
- urinary retention;
- sand in urine;
- nausea or vomiting;
- cloudy urine;
- pain during urination;
- an increase in parameters such as blood pressure and body temperature.
At the same time, symptoms often appear already at an advanced stage; in the early stages of stone development, they may not manifest themselves at all.
Article on the topic
For the heart and kidneys. Nutritionist - about who benefits from eating radishes
Nutrition correction
It is no secret, doctors note, that some foods can negatively affect the development of stones.
There are general principles of diet therapy for urolithiasis, says the urologist:
- limiting excessive total food intake;
- consumption of varied foods; limiting foods rich in substances that promote stone formation;
- intake of liquid in a volume that maintains the daily amount of urine from 1.5 to 2.5 liters (part of the liquid can be taken in the form of cranberry or lingonberry fruit drinks, mineral water.)
“With oxalate stones, patients should limit their diet to coffee and cocoa products, chocolate, strong tea, sorrel, spinach, black currants, strawberries, nuts, cheese, cottage cheese, and milk.
For urate stones, it is necessary to limit the intake of meat, chocolate, strong tea and coffee, alcohol, fried and spicy foods, and legumes (beans, peas, peanuts). Recommended are boiled poultry, boiled fish, milk, cucumbers, cabbage.
If you have phosphorus-calcium stones, smoked meats, alkaline mineral waters, whole milk, fermented milk products, spices are excluded; you should limit yourself to eating potatoes, pumpkin, berries, green vegetables, cottage cheese, cheese, feta cheese. Bread, poultry, green apples, pears, lard, vegetable fats, sauerkraut, lingonberries, red currants, rose hip decoction are recommended,” advises the urologist.
The filter is faulty. How do the kidneys signal that they are unhealthy? More details
Urolithiasis disease
General principles of therapy
Both surgical treatment methods and conservative therapy are used.
Treatment tactics are determined by the urologist depending on the age and general condition of the patient, the location and size of the stone, the clinical course of urolithiasis, the presence of anatomical or physiological changes and the stage of renal failure. As a rule, surgical treatment is necessary to remove stones from urolithiasis. The exception is stones formed by uric acid derivatives. Such stones can often be dissolved by conservative treatment of urolithiasis with citrate mixtures for 2-3 months. Stones of other compositions cannot be dissolved.
The passage of stones from the urinary tract or surgical removal of stones from the bladder or kidney does not exclude the possibility of recurrence of urolithiasis, therefore it is necessary to implement preventive measures aimed at preventing relapses. Patients with urolithiasis are recommended for complex regulation of metabolic disorders, including care for maintaining water balance, diet therapy, herbal medicine, drug therapy, physical therapy, balneological and physiotherapeutic procedures, and sanatorium-resort treatment.
Diet therapy
The choice of diet depends on the composition of the stones found and removed. General principles of diet therapy for urolithiasis:
- A varied diet with a limited amount of food;
- Restriction in the diet of foods containing large amounts of stone-forming substances;
- Take a sufficient amount of fluid (daily diuresis of 1.5-2.5 liters should be ensured).
For urolithiasis with calcium oxalate stones, it is necessary to reduce the consumption of strong tea, coffee, milk, chocolate, cottage cheese, cheese, citrus fruits, legumes, nuts, strawberries, black currants, lettuce, spinach and sorrel. In case of ICD with urate stones, you should limit the intake of protein foods, alcohol, coffee, chocolate, spicy and fatty foods, and exclude meat foods and offal (liver sausages, pates) in the evening.
If you have phosphorus-calcium stones, avoid milk, spicy foods, spices, alkaline mineral waters, and limit the consumption of feta cheese, cheese, cottage cheese, green vegetables, berries, pumpkin, beans and potatoes. Sour cream, kefir, red currants, lingonberries, sauerkraut, vegetable fats, flour products, lard, pears, green apples, grapes, and meat products are recommended.
Stone formation in urolithiasis largely depends on the pH of the urine (normally 5.8-6.2). Eating certain types of food changes the concentration of hydrogen ions in the urine, which allows you to independently regulate the pH of the urine. Plant and dairy foods alkalize urine, and animal products acidify. You can control the acidity level of urine using special paper indicator strips, freely sold in pharmacies.
If there are no stones on ultrasound (the presence of small crystals - microlites is allowed), “water shocks” can be used to flush the kidney cavity. The patient takes 0.5-1 liter of liquid on an empty stomach (low-mineralized mineral water, tea with milk, dried fruit decoction, fresh beer). If there are no contraindications, the procedure is repeated every 7-10 days. In cases where there are contraindications, “water shocks” can be replaced by taking a potassium-sparing diuretic drug or a decoction of diuretic herbs.
Phytotherapy
During the treatment of urolithiasis, a number of herbal medicines are used. Medicinal herbs are used to accelerate the passage of sand and stone fragments after extracorporeal lithotripsy, and also as a prophylactic agent to improve the condition of the urinary system and normalize metabolic processes. Some herbal preparations help increase the concentration of protective colloids in the urine, which prevent the process of salt crystallization and help prevent relapse of urolithiasis.
Treatment of infectious complications
With concomitant pyelonephritis, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. It should be remembered that complete elimination of urinary infection in urolithiasis is possible only after eliminating the root cause of this infection - a stone in the kidney or urinary tract. There is a good effect when prescribing norfloxacin. When prescribing drugs to a patient with urolithiasis, it is necessary to take into account the functional state of the kidneys and the severity of renal failure.
Normalization of metabolic processes
Metabolic disorders are the most important factor causing relapses of urolithiasis. Benzbromarone and allopurinol are used to reduce uric acid levels. If the acidity of urine cannot be normalized by diet, the listed drugs are used in combination with citrate mixtures. When preventing oxalate stones, vitamins B1 and B6 are used to normalize oxalate metabolism, and magnesium oxide is used to prevent crystallization of calcium oxalate.
Antioxidants that stabilize the function of cell membranes - vitamins A and E - are widely used. If the level of calcium in the urine increases, hypothiazide is prescribed in combination with drugs containing potassium (potassium orotate). For disorders of phosphorus and calcium metabolism, long-term use of bisphosphonates is indicated. The dose and duration of taking all drugs is determined individually.
Treatment of urolithiasis in the presence of kidney stones
If there is a tendency to spontaneous passage of stones, patients with urolithiasis are prescribed medications from the group of terpenes (extract of the fruit of ammi dentifrice, etc.), which have a bacteriostatic, sedative and antispasmodic effect.
Relief of renal colic is carried out with antispasmodics (drotaverine, metamizole sodium) in combination with thermal procedures (heating pad, bath). If ineffective, antispasmodics are prescribed in combination with painkillers.
Potential Risks
“The most common complication of kidney stones is their movement, movement beyond the pelvis into the ureter and obstruction of the outflow of urine from the renal collecting system, which can lead to inhibition of the function of the kidney itself and the development of an inflammatory process in it. In such cases, drug (antibacterial and anti-inflammatory) therapy is ineffective. Failure to see a doctor promptly can lead to serious consequences. After examining and communicating with the patient, the doctor will prescribe an examination or recommend hospitalization in a hospital for treatment,” says Anton Prityko.