Causes of cloudy urine
Normal urine is clear.
It becomes cloudy only when pathological impurities appear.
It may be pus or salt.
If the urine is cloudy and white, it is most often pus.
It appears in inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
Different organs can become inflamed:
- urethra;
- prostate;
- kidneys;
- testicles;
- bladder.
Where exactly the source of inflammation is located can often be determined by additional symptoms.
If they are not there, laboratory tests and instrumental studies will help to understand the situation.
Normal urine color is light yellow.
It can change when you eat certain foods or drink too much or not enough.
The less water a person drinks, the lighter the urine.
The less he drinks, the more substances are dissolved in the urine.
Accordingly, it becomes darker.
In most cases, pathology cannot be judged by color.
Although sometimes he gives the doctor additional information for diagnosis.
Among the reasons why cloudy urine occurs in men, it is also worth highlighting kidney stones.
This condition is characterized by the formation of stones in the urinary system.
It is preceded by metabolic disorders and increased excretion of crystals in the urine.
When there are a lot of them, salts begin to precipitate.
As a result, stones are formed, which cause renal colic and pyelonephritis.
As you can see, there can be quite a few reasons why urine is cloudy.
Let's look at the main ones.
Reasons for color change
Cloudy urine should not cause panic. At times, the phenomenon occurs in healthy people. You should take a closer look at your lifestyle and diet. When cloudy urine becomes a constant phenomenon, an examination of the urinary system is required. A single visual examination of urine will not be able to detect pathology, so there is a need for microscopic examination of urine sediment and laboratory diagnosis.
Urine may become cloudy for several reasons
The causes of cloudy urine are the following factors:
- physical activity that causes dehydration, i.e. being under constant exposure to high temperatures;
- kidney diseases;
- oversaturation with oxygen provokes crystallization of urine and turbidity of discharge;
- taking medications;
- features of the daily diet - the presence of cottage cheese, jelly, jellied meat;
- development of urolithiasis;
- course of male pathologies (prostatitis, prostate adenoma);
- eating foods with calcium;
- mycoplasmosis.
The presence of flakes, blood impurities, and a strong odor in cloudy urine indicates a serious pathology of the kidneys and urea.
Cloudy urine due to urethritis
The urethra is the tube through which urine is discharged to the external environment.
It comes out of the bladder.
In men, the urethra is also connected to the prostate and testicles, as sperm exits through it into the external environment.
When the urethra becomes inflamed, pus appears in the urine.
This indicates the bacterial origin of the inflammation.
With a small amount of urethral discharge, pus dissolves in the urine and becomes invisible.
For it to be detected by the patient, there must be a lot of purulent discharge.
Accordingly, in addition to impurities in the urine, other symptoms are also observed.
These include:
- soreness of the urethra, especially when urinating;
- redness of its distal part;
- compaction determined by palpation;
- copious purulent discharge.
The last symptom is especially important.
If pus forms in the urethra, it must be released into the external environment.
If this does not happen, most likely, impurities enter the urine from other organs.
Probable causes of purulent urethritis:
- nonspecific bacterial inflammation;
- candidiasis;
- gonorrhea, less often - other sexually transmitted infections.
Pathology requires treatment.
It should be started as quickly as possible.
Because from the urethra, inflammation can spread to other organs.
Possible pathologies
Cloudy urine is a high probability of the appearance of any pathologies, for example, such as:
- Cystitis
This is an infectious disease characterized by inflammation of the bladder. With cystitis, not only cloudy urine is detected, but also other symptoms. Increased temperature, pain in the urethra, and sometimes blood are added to the process. Cystitis in men is often accompanied by prostatitis, which can cause pain. They are localized in the groin area, scrotum or extend to the lower back.
The first symptoms of cystitis are a reason to contact a urologist. During the examination, a urine test is considered mandatory. The presence of cystitis is determined by its cloudiness, protein content, increased ESR and an increase in the number of leukocytes.
- Pyelonephritis
If cystitis is in an advanced state, the infection can spread to important nearby organs through the urethra. Bacteria develop rapidly and infect the renal pelvis and other elements of the organ. Kidney inflammation can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly. Chronic infection over many years leads to gradual breakdown of tissue in the kidneys.
Pyelonephritis develops not only from cystitis. Often relapses occur with hypothermia, prolonged exposure to dampness on the lower extremities, or decreased immunity from ARVI.
- Urethritis
When the urinary canal becomes inflamed, men experience discharge and pain. The urine becomes cloudy and changes color. There are many factors for the development of pathology. It can be associated with sexually transmitted diseases, congestive processes in the pelvis, allergies and injuries. If symptoms persist for a long time, it causes serious discomfort in daily life.
- Liver disorder
Dark urine with a cloudy admixture is the main symptom of a change in its functionality or structure. Changes in the composition and color of urine occur with hepatitis, pigmentary and fatty hepatosis, and cirrhosis. Liver diseases carry many complications, some of them dangerous, even fatal.
Prostatitis and cloudy urine
The prostate gland can also become inflamed.
It is connected to the urethra, since the organ forms about 30% of the volume of ejaculate.
Inflammation of the prostate can be a consequence of urethritis.
The infection initially affects the urethra.
It then spreads upward to the prostate gland.
In other cases, prostatitis develops without previous urethritis.
This most often occurs if the disease is caused by a nonspecific bacterial flora.
The infection gets there from other purulent foci through the blood or lymph.
Prostatitis can be acute and chronic.
With chronic sluggish flow, urine rarely becomes cloudy.
If pus is released, it is very small.
It is not enough for the urine to become very dilute and the patient to notice cloudiness.
Although in a laboratory test, leukocytes can be detected in the analysis, which indicates an inflammatory process.
In acute prostatitis, there is a lot of pus.
But this form of the disease:
- is relatively rare;
- manifests itself with many other symptoms.
Acute prostatitis is characterized by a sudden onset.
A person experiences severe pelvic pain.
They radiate to the perineum and rectum.
The flow of urine may stop.
Or urination becomes very difficult.
This is the result of swelling of the prostate and compression of the proximal urethra.
General symptoms appear: body temperature increases, headaches, general weakness and malaise occur.
The urine becomes cloudy white because pus formed in the prostate leaks into the urethra.
From there it is washed out during urination.
Acute prostate is a serious disease, which is often complicated by abscess formation.
It requires treatment in a hospital setting.
Cystitis and cloudy urine
The bladder is another potential source of pus that may end up in the urine.
As a result, it becomes cloudy and may contain flakes and sediment.
Threads are often identified visually.
With severe cystitis, blood impurities also appear.
The disease is more common in women.
In them, cystitis often becomes a complication of urethritis.
This is due to the fact that the female urethra is short and wide.
E. coli and other bacteria easily penetrate through it in an ascending manner, causing acute cystitis.
Pus accumulates inside the bladder.
It is evenly distributed in the urine, so it becomes cloudy.
In men, this condition also sometimes occurs, but approximately 3 times less often.
It develops much more often as a complication of other diseases, such as:
- prostatitis;
- urethritis;
- cancer;
- chronic urinary retention;
- urethral strictures.
The causative agent in 90% of cases is E. coli.
It multiplies quickly and releases ammonia, which disrupts the function of the smooth muscle structures of the bladder.
Associated symptoms:
- painful urination;
- frequent and strong urges;
- pain in the pubic area;
- discharge of a drop of blood at the end of urination.
Urine completely loses transparency.
It is cloudy and smells unpleasant.
It contains a lot of bacteria and leukocytes.
Urine also contains epithelial cells.
In this case, general symptoms are usually absent.
There is no high body temperature or weakness.
This is due to the fact that the lining of the bladder does not absorb toxins that accumulate in the urine.
They do not enter the bloodstream and do not cause intoxication of the body.
Associated symptoms
Cloudy urine is usually not the only sign of the disease; taking into account the accompanying symptoms, a preliminary diagnosis can be made. After carrying out diagnostic manipulations, it is refuted or confirmed, and the necessary course of therapy is prescribed.
Cloudy urine may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- red tint of urine. It is formed as a result of damage to the excretory canals against the background of the passage of sand and stones through them. Cloudy urine mixed with blood clots indicates disease or traumatic injury to the kidneys, bladder or ureter;
- cloudy urine with admixtures of leucorrhoea indicates a fatty change in the renal tissue, its decay, and the course of lymphostasis;
- urine with turbid impurities and the presence of salts does not pose a threat to the patient’s life, but can cause the formation of urolithiasis;
- discharge with flakes indicates inflammatory processes such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis;
- cloudy dark urine indicates pathologies of the liver, pancreas, and kidneys. This situation is often observed with tumor formations in the urinary system.
Cloudy urine due to pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is called inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system and renal parenchyma.
This is a dangerous disease that can lead to the destruction of functional organ tissue.
During reproductive childhood, men get sick 7-8 times less often than women.
Only after 60 years does this ratio level out.
The increase in the incidence of the disease among men at this age is due to the fact that their pyelonephritis develops as a complication of prostate diseases:
- cancer;
- benign hyperplasia.
As the prostate increases in size, the urethra is compressed.
And with cancer, the ureters are often compressed.
This provokes hemodynamic disturbances, stagnation of urine and the development of bacterial inflammatory processes.
The most common pathogens:
- E. coli – in 75% of cases;
- Proteus – another 15%;
- the remaining microorganisms account for 10% (klebsiella, staphylococcus, candida, mycoplasma and others).
Pyelonephritis can occur in acute or chronic form.
In the second case, the urine becomes cloudy during exacerbations of the disease.
General manifestations of the disease:
- fever;
- headache;
- malaise;
- pain in muscles and joints.
When tapping the lower back with the edge of the palm, pain is noted.
Blood or red blood cells appear in the urine.
As the disease progresses, life-threatening complications are possible.
They are associated with both a purulent process and impaired renal function.
Cloudy urine in a man with urolithiasis
This is a common cause of cloudy urine.
According to rough estimates, urolithiasis affects about 5% of the population.
In the structure of urological diseases, urolithiasis reaches 40%.
This is the most common reason for visiting a urologist.
Two thirds of patients become ill between the ages of 30 and 50 years.
In 20% of cases, the pathology leads to disability.
Therefore, the disease must be detected and treated promptly.
Even with an asymptomatic form of the pathology, the patient should be constantly monitored.
The urine becomes cloudy due to excess salt formation.
Crystals form from them.
Often cloudy urine remains the only symptom of the disease for a long time.
When large stones appear, a dull aching pain appears in the lower back.
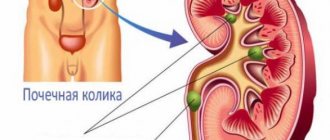
Sometimes a man experiences an attack of renal colic.
Severe pain occurs that is not relieved by medications and does not depend on body position.
Colic is associated with the movement of stones along the ureter.
The stone gets stuck in it and blocks the flow of urine.
It accumulates in the kidney, stretching the capsule.
The capsule contains many nerve endings, so the process is very painful.
Sometimes the stone comes out on its own or after taking antispasmodics.
The drugs relax the smooth muscle structures of the ureter, increasing its lumen.
If the stone does not come out, it must be crushed or removed surgically.
Associated symptoms of renal colic:
- muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall;
- vomit;
- chills;
- decreased heart rate;
- decrease in urine volume.
The disease is characterized by complications.
This is pyelonephritis, acute or chronic renal failure.
Treatment
Treatment methods depend on diagnostic results. For infectious lesions, antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Cystitis is eliminated with a single dose of Monural, nitrofurantoin preparations, and a course of cephalosporins.
For glomerulonephritis, antibiotic therapy is supplemented with hormonal, antihypertensive, and diuretic drugs. Patients with the acute form are treated in a hospital. They require bed rest and diet.
Treatment for prostatitis includes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, alpha-blockers to facilitate urination, and immunomodulatory agents.
Diet correction is also necessary for urolithiasis. The diet is prescribed depending on the composition of the stones. If necessary, they are removed surgically.
Urologist Alexander Nikolaevich Zakutsky gives advice on proper nutrition for urolithiasis
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are used as adjuvant therapy. Decoctions and infusions help speed up the excretion of urine and the washing out of pathogens, as well as relieve inflammation of the mucous membranes:
- Infusion of bearberry leaves against infections. Pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of water, carefully bring to a boil, and hold in a water bath for half an hour. Strain the broth, add boiled water to the boiled volume. Drink a tablespoon 5 times a day half an hour after meals.
- A decoction of cherry stems to increase urination. Pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of water and boil for 10 minutes. Drink a tablespoon before meals.
- Infusion of lingonberry leaf to enhance the diuretic and antiseptic effect. Pour two tablespoons of leaf with a glass of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Drink 100 ml three times a day. Another recipe: pour a tablespoon of boiling water over a tablespoon and simmer over low heat for half an hour. Drink 70 ml three times a day half an hour after meals.
At the pharmacy you can buy special kidney tea: “Brusniver”, “Fitonefrol”, monocomponent mixtures. The latter includes orthosiphon stamen, horsetail, St. John's wort, lingonberry leaf, chamomile, and half-pol.
Brusniver kidney tea has antimicrobial activity against staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus and some other microorganisms. Has anti-inflammatory and diuretic effects. Price from 110 rubles
Cloudy urine in a man after sex
Some patients notice that their urine begins to become cloudy a few days or weeks after changing partners.
Sometimes the cause of cloudiness is sexually transmitted infections.
They cause inflammatory processes:
- urethra;
- prostate;
- much less often - kidneys or bladder.
The formation of large amounts of pus is not typical for most STDs.
Therefore, a sexually transmitted disease is the last thing a doctor will think about when he sees purulent urine.
STDs can cause this symptom only if:
- gonorrhea;
- severe course of other sexually transmitted infections due to immunodeficiency or concomitant diseases of the genitourinary organs;
- addition of bacterial superinfection.
If it is gonorrhea, then signs of the disease appear 3-4 days after sex.
A large amount of pus accumulates in the urethra.
It has a yellow color and an unpleasant odor.
Pus gets into the urine, causing it to become cloudy.
Associated symptoms:
- soreness of the urethra;
- swelling and redness;
- nocturnal involuntary ejaculation;
- frequent daytime spontaneous erections.
The disease can be dangerous.
It leads to the formation of abscesses.
It often spreads to the testicles and prostate, causing infertility.
It provokes urethral strictures, which have to be treated surgically.
The pathology can become chronic.
Therefore, if signs of gonorrhea appear, treatment should be done immediately.
Only the acute form is easily cured.
Chronic and complicated cases are treated with difficulty, for a long time, sometimes in a hospital setting.
Causes of pathological symptoms
Why is my urine cloudy? Cloudiness of the color of urine in representatives of the stronger sex is not an independent ailment, but a symptom of another disease or pathological process not only in the excretory system, but also in other organs. Cloudy or foamy urine in men may appear due to mild dehydration. If there are no accompanying symptoms, diagnosis is not required; as soon as water metabolism normalizes, the symptom disappears on its own.
Natural negative factors:
- strong physical exertion, overheating of the genitourinary system (long stay in a sauna, on the beach, work in enterprises with elevated air temperatures). Regular exposure to high temperatures or a single overheat leads to cloudy urine; in most cases, limiting contact with a negative factor relieves the unpleasant symptom;
- oversaturation with oxygen leads to crystallization of urine and further clouding of discharge;
- taking medicinal products. The instructions for the medication may describe a side symptom - cloudy urine; take this fact into account when you see your doctor.
Learn about the causes of kidney hemangioma and treatment options for the disease.
What polyuria is in women and how to treat the disease is written on this page.
Causes of cloudy urine and pathological negative factors:
- pathogenic microorganisms and their metabolic products lead to cloudy urine. An unpleasant symptom is observed during the course of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. Additionally, there are other symptoms (fever, painful emptying of the bladder, pain in the genitourinary area);
- course of urolithiasis. If there is sand in the kidneys, stones in the patient’s excretory system, urine changes not only the color and smell, but salt impurities appear, making the urine cloudy;
- often cloudy urine indicates the course of male diseases (prostatitis, prostate adenoma). The inflammatory process, pathogenic microorganisms, unprotected sexual intercourse with different partners cause the formation of ailments, against the background of which a man’s urine becomes noticeably cloudy;
- mycoplasmosis. It is transmitted sexually and leads to the development of urethritis and epididymitis. Cloudiness in this case is accompanied by itching during urination, unpleasant sensations in the genital area;
- cloudy urine mixed with white flakes indicates cystitis. Lack of therapy leads to an inflammatory process in the kidneys; urine not only changes its consistency, but also acquires a foul odor.
Cloudy urine with admixtures of leucorrhoea (phosphoric acid salts, protein) often indicates the following pathologies in men:
- physical overload, emotional stress;
- pathologies of the urinary system;
- hypothermia or overheating;
- excessive consumption of phosphates, calcium or medications containing these substances;
- inflammatory processes of the genital organs.
Cloudiness of urine in the stronger sex often occurs against the background of the negative factors described above.
Note! If cloudy urine does not go away after a few days, you should think about the causes of the pathology and immediately consult a urologist. Negative factors for urine turbidity are divided into two groups: natural and pathological. A physician will help identify the root cause and eliminate it in time.
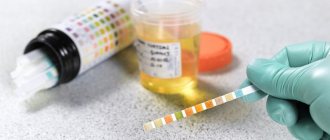
Cloudy urine: what tests are needed?
To understand why your urine is cloudy, your doctor will need to take tests from you.
He also conducts instrumental research.
As we have already said, in most cases the cause is pus or salt crystals in the urine.
To identify them, a general urine test is used.
During the study, the following may be discovered:
- salts, and which ones are indicated (oxalates, phosphates, urates and others);
- bacteria;
- leukocytes;
- red blood cells.
This analysis alone is enough to immediately understand in most cases why the urine becomes cloudy.
Either this is due to urolithiasis, or a purulent inflammatory process.
If kidney stones are suspected, they should be visualized.
For this, an ultrasound or x-ray is performed.
An even more informative study is computed tomography.
If stones are detected, an in-depth examination of the patient is carried out.
It is aimed at:
- determining the type of stones (what they are made of);
- identifying possible complications;
- finding out the reasons for the formation of stones (for example, gout, dietary habits, hypervitaminosis, inflammatory kidney diseases, etc.).
If the cause is an inflammatory process, then the doctor’s first priority is to find out:
- which organs are inflamed;
- what microorganisms provoked the inflammation.
To determine the topic of the lesion, a three-glass urine sample is used.
A man urinates alternately into three vessels.
The first and last time he releases a little urine.
The main volume goes into the middle portion.
Decoding the results:
- a high level of leukocytes in 1 serving speaks in favor of urethritis;
- if there is a high content of inflammatory cells in only 3 servings, it is highly likely that we are talking about prostatitis;
- if pus and cloudiness are observed in all three portions, this is cystitis or pyelonephritis;
- signs of inflammation in portions 1 and 3 with a normal result in portion 2 indicates a combination of urethritis and prostatitis.
Additionally, ultrasound is used; according to indications, X-rays or endoscopic examinations (urethro- and cystoscopy) can be performed.
It is important for the doctor to find out the type of microorganism that caused the inflammatory process.
If nonspecific inflammation is suspected, the doctor tests urine or a smear from the urethra on a nutrient medium.
Colonies of bacteria grow on it.
Identification is carried out based on their appearance, antigenic or enzymatic properties.
Antibiotic sensitivity is also assessed.
As a result, after conducting this study, the doctor knows not only the pathogen, but also how best to treat the disease.
A bacterioscopic examination of smears from the urogenital tract is also carried out.
If indicated, PCR testing for sexually transmitted infections is performed.
Diagnostics
The basis for diagnosing possible diseases that cause cloudy urine in men is laboratory research methods:
- general blood analysis. Necessary for determining the level of leukocytes, erythrocytes, hemoglobin in the blood;
- blood chemistry. Helps evaluate the functioning of internal organs, as well as determine the body’s need for microelements;
- general urine analysis. During the study, indicators such as transparency, color, smell, level of leukocytes and red blood cells are assessed;
- bacteriological examination of urine. Necessary for inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system. Thanks to the analysis, it is possible to determine the type of causative agent of the disease. The test is also indispensable for selecting the right antibiotic: when examining biological material, the susceptibility of pathogenic microorganisms to certain medications is determined;
- Amburger's method. Makes it possible to assess the severity of hematuria. The analysis shows how many formed elements are excreted in the urine in one minute;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko. Shows how many red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders are in 1 ml of biological material;
- urethral smear to check for sexually transmitted infections;
Laboratory research methods will help determine the cause of cloudy urine
Instrumental research methods also provide important information about the condition of the patient’s body:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, ureters, bladder. Detects kidney stones, cysts, malignant formations;
- excretory urography. It is carried out to assess the condition of the renal vessels;
- cystoscopy. Performed to examine the bladder. It is carried out using a cystoscope (a flexible tube equipped with a mini-camera), which is inserted through the urethra;
Cystoscopy allows you to evaluate the condition of the bladder - Computed tomography of the genitourinary system is one of the most accurate instrumental methods, which is based on obtaining layer-by-layer images of organs. It is carried out to clarify the results of an ultrasound examination.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis exists in order to make a single correct diagnosis. There are diseases that have similar symptoms. Based on the results of laboratory tests and instrumental research methods, the true disease is determined by exclusion.
In case of cloudy urine, the specialist will first of all differentiate between pathologies of the genitourinary system. If such diseases are not found, then other possible options will be considered:
- blood diseases;
- liver pathologies;
- arterial hypertension.